dc105cfcf40f9726b80abcafc5bf0391.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Macroeconomic for Social Negotiators Open Economy: Exchange rates Gustavo Rinaldi - ITC-ILO Consultant University of Turin - ESCP – Europe Turin, November 2016
Macroeconomic for Social Negotiators Open Economy: Exchange rates Gustavo Rinaldi - ITC-ILO Consultant University of Turin - ESCP – Europe Turin, November 2016
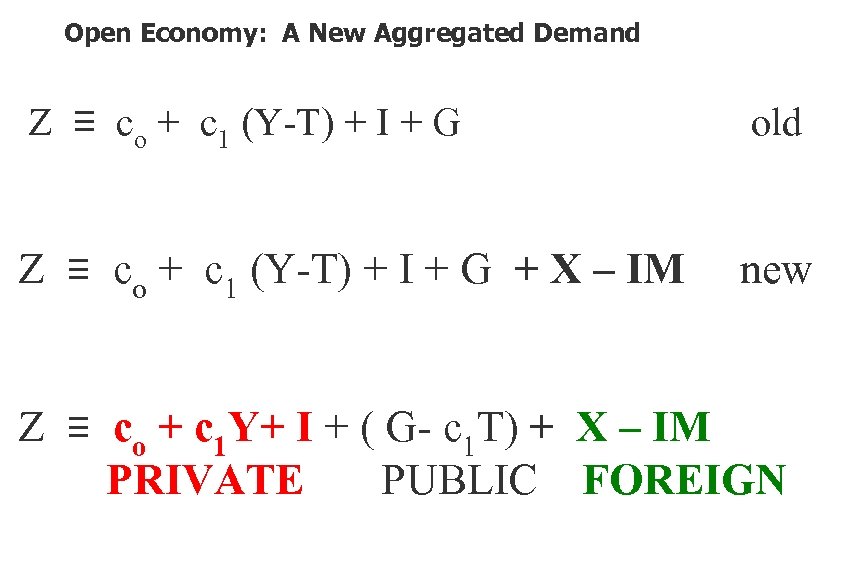 Open Economy: A New Aggregated Demand Z ≡ co + c 1 (Y-T) + I + G old Z ≡ co + c 1 (Y-T) + I + G + X – IM new Z ≡ co + c 1 Y+ I + ( G- c 1 T) + X – IM …. . . PRIVATE PUBLIC FOREIGN
Open Economy: A New Aggregated Demand Z ≡ co + c 1 (Y-T) + I + G old Z ≡ co + c 1 (Y-T) + I + G + X – IM new Z ≡ co + c 1 Y+ I + ( G- c 1 T) + X – IM …. . . PRIVATE PUBLIC FOREIGN
 + X – IM Trade Balance Trade Deficit, if < 0 Trade Surplus, if > 0
+ X – IM Trade Balance Trade Deficit, if < 0 Trade Surplus, if > 0
 What is the price in international business? Price matters Exchange rate matters
What is the price in international business? Price matters Exchange rate matters
 Open Economy: A New Aggregated Demand + X – IM Trade balance affects Balance Of Payments significantly, A rise in deficit could lead a country to suffer.
Open Economy: A New Aggregated Demand + X – IM Trade balance affects Balance Of Payments significantly, A rise in deficit could lead a country to suffer.
 If residents in foreign countries buy national goods The Aggregated Demand of domestic goods increases; X increases, hence: Z ≡ co + c 1 (Y-T) + I + G + X – IM
If residents in foreign countries buy national goods The Aggregated Demand of domestic goods increases; X increases, hence: Z ≡ co + c 1 (Y-T) + I + G + X – IM
 Open Economy: A new choice Shall I buy national or foreign goods? Given quality and taste, what might determine my demand?
Open Economy: A new choice Shall I buy national or foreign goods? Given quality and taste, what might determine my demand?
 Nominale exchange rate A) How much foreign currency should I give to obtain a unit of domestic currency? You paid $1, 48 (29 April 2011) to buy € 1 http: //markets. ft. com/markets/overview. asp B) You can also use the reverse, i. e. the price in national currency of a foreign currency (1/1, 48) $ 1 = € 0, 68 We just have to be consistent WE USE A
Nominale exchange rate A) How much foreign currency should I give to obtain a unit of domestic currency? You paid $1, 48 (29 April 2011) to buy € 1 http: //markets. ft. com/markets/overview. asp B) You can also use the reverse, i. e. the price in national currency of a foreign currency (1/1, 48) $ 1 = € 0, 68 We just have to be consistent WE USE A
 Nominale exchange rate A) How much foreign currency should I give to obtain a unit of domestic currency? You paid $1, 22 (30 Decemeber 2014) to buy € 1 http: //markets. ft. com/markets/overview. asp B) You can also use the reverse, i. e. the price in national currency of a foreign currency (1/1, 22) $ 1 = € 0, 82
Nominale exchange rate A) How much foreign currency should I give to obtain a unit of domestic currency? You paid $1, 22 (30 Decemeber 2014) to buy € 1 http: //markets. ft. com/markets/overview. asp B) You can also use the reverse, i. e. the price in national currency of a foreign currency (1/1, 22) $ 1 = € 0, 82
 (Nominal) Exchange rates regimes: Flexible: authorities (our government and central bank) leave it to fluctuate freely Fixed : Government and/or the central bank fix an exchange rate between national currency and a foreign currency or a basket of foreign currencies, and actively defend it. Mixes
(Nominal) Exchange rates regimes: Flexible: authorities (our government and central bank) leave it to fluctuate freely Fixed : Government and/or the central bank fix an exchange rate between national currency and a foreign currency or a basket of foreign currencies, and actively defend it. Mixes
 The Real Exchange Rate
The Real Exchange Rate
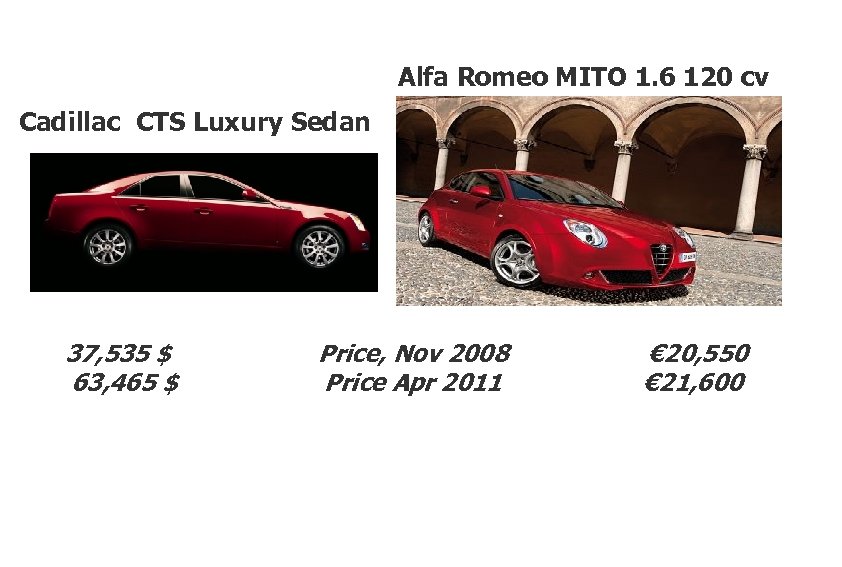 Alfa Romeo MITO 1. 6 120 cv Cadillac CTS Luxury Sedan 37, 535 $ 63, 465 $ Price, Nov 2008 Price Apr 2011 € 20, 550 € 21, 600
Alfa Romeo MITO 1. 6 120 cv Cadillac CTS Luxury Sedan 37, 535 $ 63, 465 $ Price, Nov 2008 Price Apr 2011 € 20, 550 € 21, 600
 How many Cadillac Sedan was I able to buy with one Alfa MITO in 2008 (at exchange rate of 1. 3$ = 1€? 1. 3233 * 20. 550 = 37, 535 26, 565 37, 535 = 0, 7
How many Cadillac Sedan was I able to buy with one Alfa MITO in 2008 (at exchange rate of 1. 3$ = 1€? 1. 3233 * 20. 550 = 37, 535 26, 565 37, 535 = 0, 7
 How many Cadillac Sedan could I have bought with one Alfa MITO in April 2011 at the exchange rate of $1, 48 =€ 1? 1. 48 * 21, 600 = 63, 465 31, 968 = 0, 50 63, 465 Is a rise of imports of Sedan likely relative to 2008, ceterus-paribus? Should we expect export of Mito to rise? What has happened to the euro (relative to dollar) in 2014 (relative to 2008)? But then, is the likely effects on imports of Sedan and exports of Mito consistent with the exchange rate movement? What other factor may explain the discripancy?
How many Cadillac Sedan could I have bought with one Alfa MITO in April 2011 at the exchange rate of $1, 48 =€ 1? 1. 48 * 21, 600 = 63, 465 31, 968 = 0, 50 63, 465 Is a rise of imports of Sedan likely relative to 2008, ceterus-paribus? Should we expect export of Mito to rise? What has happened to the euro (relative to dollar) in 2014 (relative to 2008)? But then, is the likely effects on imports of Sedan and exports of Mito consistent with the exchange rate movement? What other factor may explain the discripancy?
 How many Cadillac Sedan can I buy with one Alfa MITO? It Depends on: P price Alfa Mito P* price Cadillac Sedan E Nominale exchange rate (cost in $ of € 1)
How many Cadillac Sedan can I buy with one Alfa MITO? It Depends on: P price Alfa Mito P* price Cadillac Sedan E Nominale exchange rate (cost in $ of € 1)
 How many Cadillac Sedan can I buy with one Alfa MITO? It Depends on: = REAL P E P* EXCHANGE RATE
How many Cadillac Sedan can I buy with one Alfa MITO? It Depends on: = REAL P E P* EXCHANGE RATE
 We are not just interested in these cars, therefore we shall use the price indexes (GDP deflators). The value of GDP deflators depends on the bases that we use; its absolute value is not very important, but its variation is very important
We are not just interested in these cars, therefore we shall use the price indexes (GDP deflators). The value of GDP deflators depends on the bases that we use; its absolute value is not very important, but its variation is very important
 Real Exchange Rate Variations Real Appreciation: goods of this country become more expensive Real Depreciation
Real Exchange Rate Variations Real Appreciation: goods of this country become more expensive Real Depreciation
 Real Exchange Rate and Trade Balance (X – IM) = f ( Y, Y*) The trade balance is a negative function of the real exchange rate and of our GDP, Y, finally, is a positive function of the GDP of our trade partners, Y*)
Real Exchange Rate and Trade Balance (X – IM) = f ( Y, Y*) The trade balance is a negative function of the real exchange rate and of our GDP, Y, finally, is a positive function of the GDP of our trade partners, Y*)
 Reflection - Does exchange rate depreciation necessarily improve trade balance? - The Marshall-Learner condition, - Is the depreciation of currency necessrily good? - Problems of liquidity dollarization - Inflation (the poor and essential imports)
Reflection - Does exchange rate depreciation necessarily improve trade balance? - The Marshall-Learner condition, - Is the depreciation of currency necessrily good? - Problems of liquidity dollarization - Inflation (the poor and essential imports)
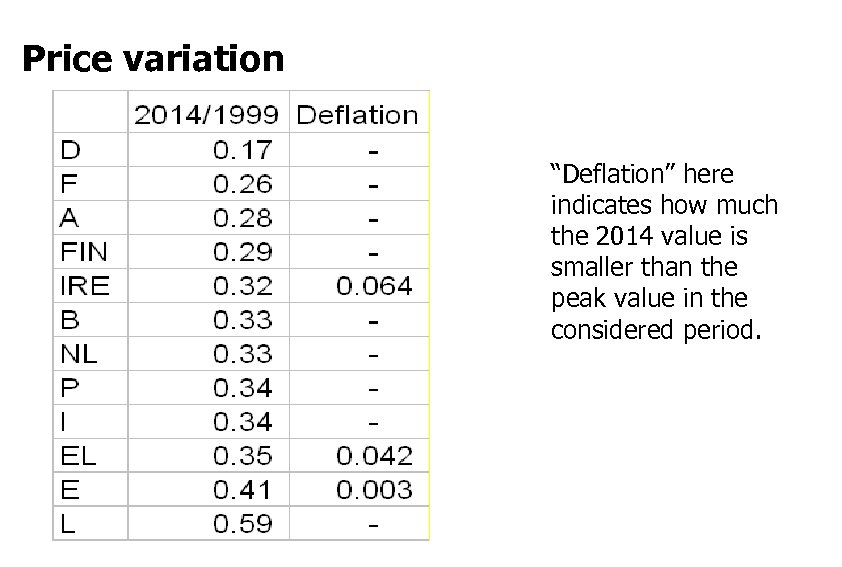 Price variation “Deflation” here indicates how much the 2014 value is smaller than the peak value in the considered period.
Price variation “Deflation” here indicates how much the 2014 value is smaller than the peak value in the considered period.
 Real Exchange rate with Germany
Real Exchange rate with Germany
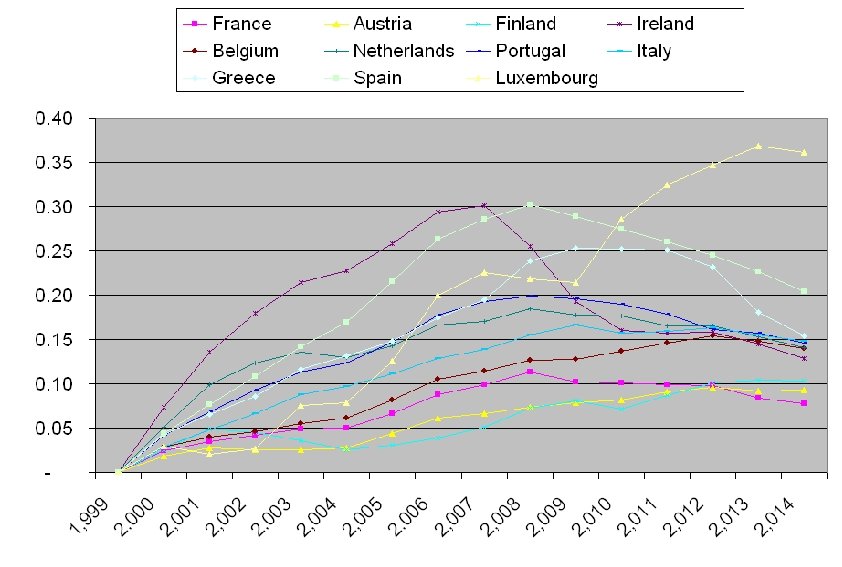
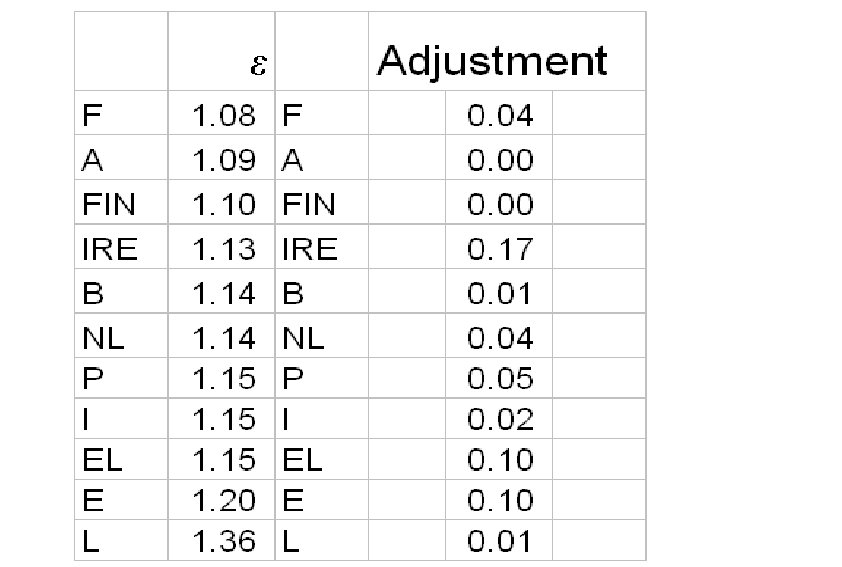
 Adjustment: the difference of real exchange rate between peak year and 2014
Adjustment: the difference of real exchange rate between peak year and 2014
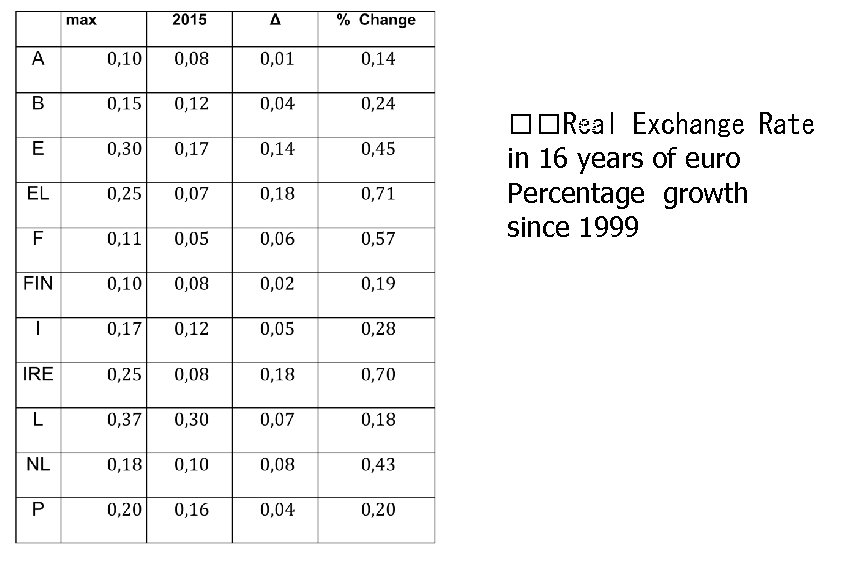 GGg Real Exchange Rate in 16 years of euro Percentage growth since 1999
GGg Real Exchange Rate in 16 years of euro Percentage growth since 1999
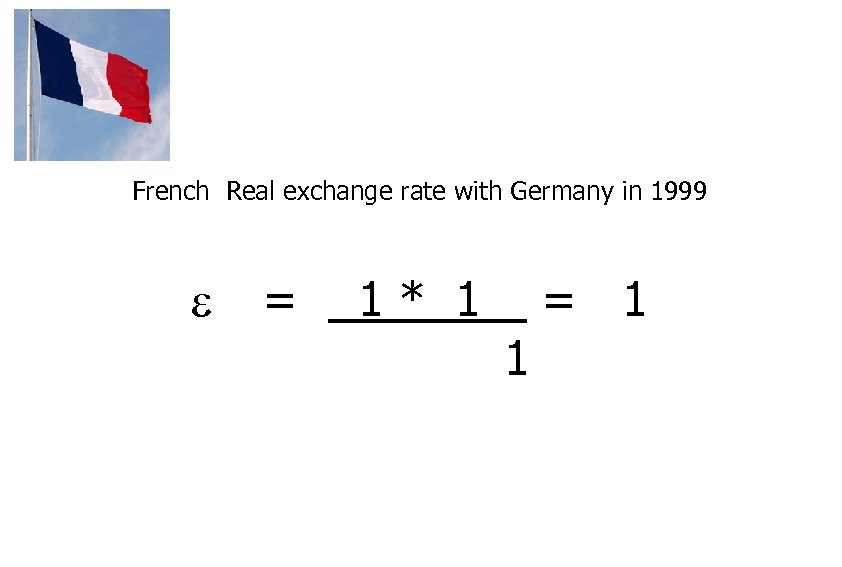 French Real exchange rate with Germany in 1999 = 1* 1 = 1 1
French Real exchange rate with Germany in 1999 = 1* 1 = 1 1
 French Real exchange rate with Germany in 2014 = 1 * 1. 26 1. 17 = 1. 08 On average French goods have worsened their relative position with German goods by 8 % in 15 years
French Real exchange rate with Germany in 2014 = 1 * 1. 26 1. 17 = 1. 08 On average French goods have worsened their relative position with German goods by 8 % in 15 years
 The End Thank You!
The End Thank You!


