Презентация на 26-28.04.16 5..pptx
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Peter Spicka, Senior Adviser for Banking Supervision and Financial Stability The views expressed in this presentation are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official views of the Deutsche Bundesbank
Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Peter Spicka, Senior Adviser for Banking Supervision and Financial Stability The views expressed in this presentation are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official views of the Deutsche Bundesbank
 Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Overview § Introduction § Macro-prudential toolkit § Macro-prudential instruments in European banking regulation § Transmission mechanisms and channels § Review of initial experiences 27/04/2016 Slide 2
Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Overview § Introduction § Macro-prudential toolkit § Macro-prudential instruments in European banking regulation § Transmission mechanisms and channels § Review of initial experiences 27/04/2016 Slide 2
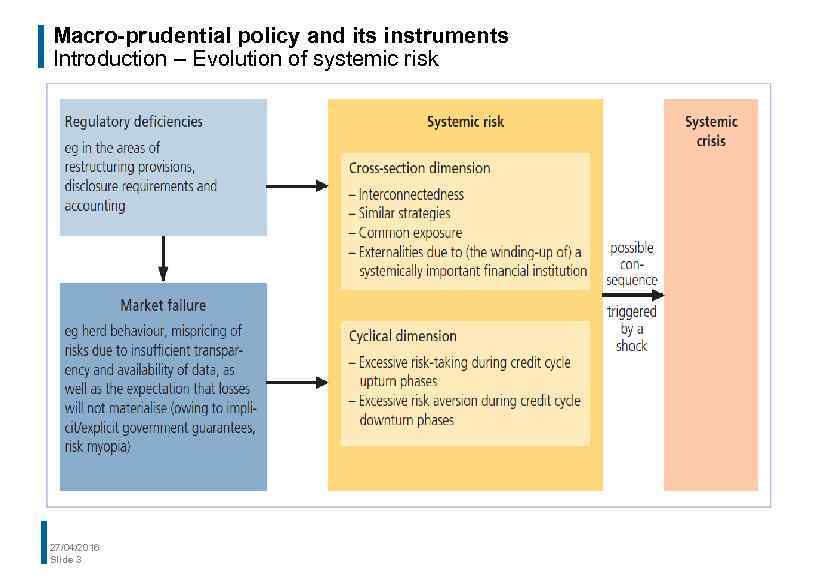 Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Introduction – Evolution of systemic risk 27/04/2016 Slide 3
Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Introduction – Evolution of systemic risk 27/04/2016 Slide 3
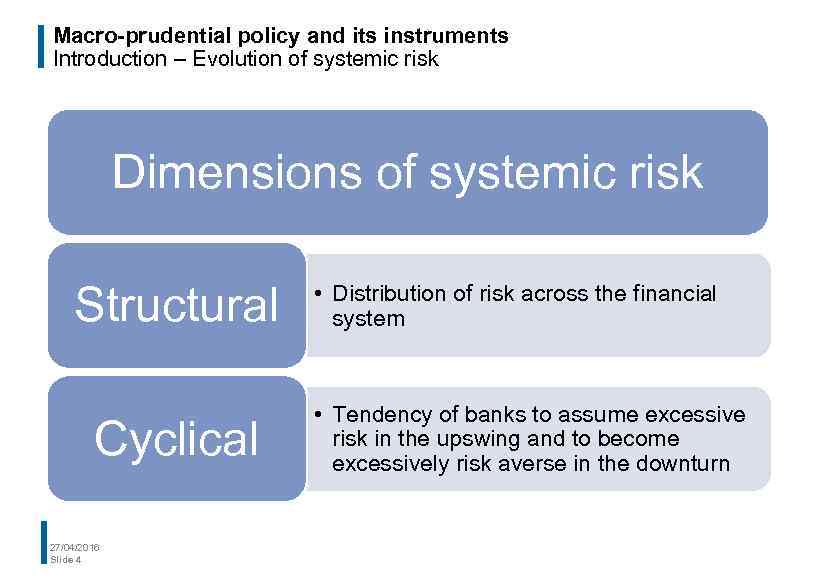 Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Introduction – Evolution of systemic risk Dimensions of systemic risk Structural Cyclical 27/04/2016 Slide 4 • Distribution of risk across the financial system • Tendency of banks to assume excessive risk in the upswing and to become excessively risk averse in the downturn
Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Introduction – Evolution of systemic risk Dimensions of systemic risk Structural Cyclical 27/04/2016 Slide 4 • Distribution of risk across the financial system • Tendency of banks to assume excessive risk in the upswing and to become excessively risk averse in the downturn
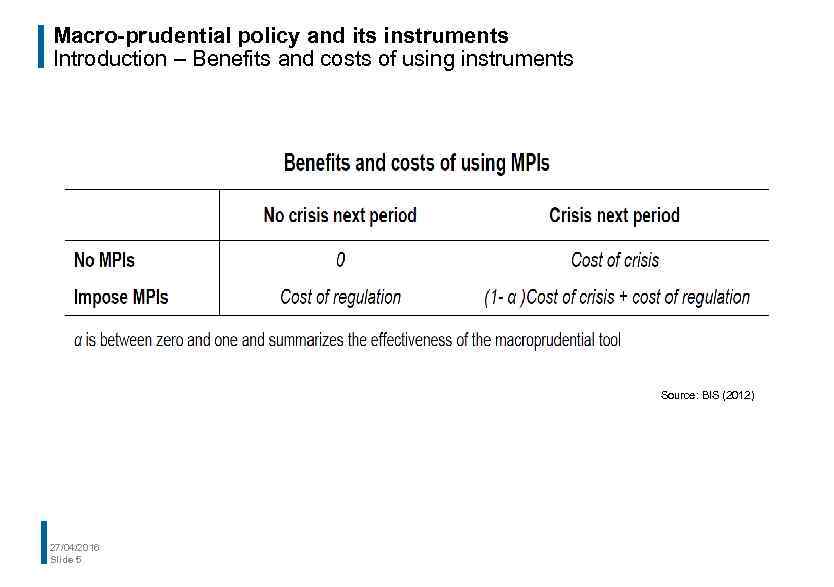 Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Introduction – Benefits and costs of using instruments Source: BIS (2012) 27/04/2016 Slide 5
Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Introduction – Benefits and costs of using instruments Source: BIS (2012) 27/04/2016 Slide 5
 Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Overview § Introduction § Macro-prudential toolkit § Macro-prudential instruments in European banking regulation § Transmission mechanisms and channels § Review of initial experiences 27/04/2016 Slide 6
Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Overview § Introduction § Macro-prudential toolkit § Macro-prudential instruments in European banking regulation § Transmission mechanisms and channels § Review of initial experiences 27/04/2016 Slide 6
 Macro-prudential toolkit General considerations Systemic perspective required for regulation • Regulatory arbitrage between banking, insurance and shadow banking sector to be avoided • Cumulative impact of reforms must be considered • Possible counteractive effects or conflicting incentives should be noted • Lack of consistency can reduce the intended effect of the new rules 27/04/2016 Slide 7
Macro-prudential toolkit General considerations Systemic perspective required for regulation • Regulatory arbitrage between banking, insurance and shadow banking sector to be avoided • Cumulative impact of reforms must be considered • Possible counteractive effects or conflicting incentives should be noted • Lack of consistency can reduce the intended effect of the new rules 27/04/2016 Slide 7
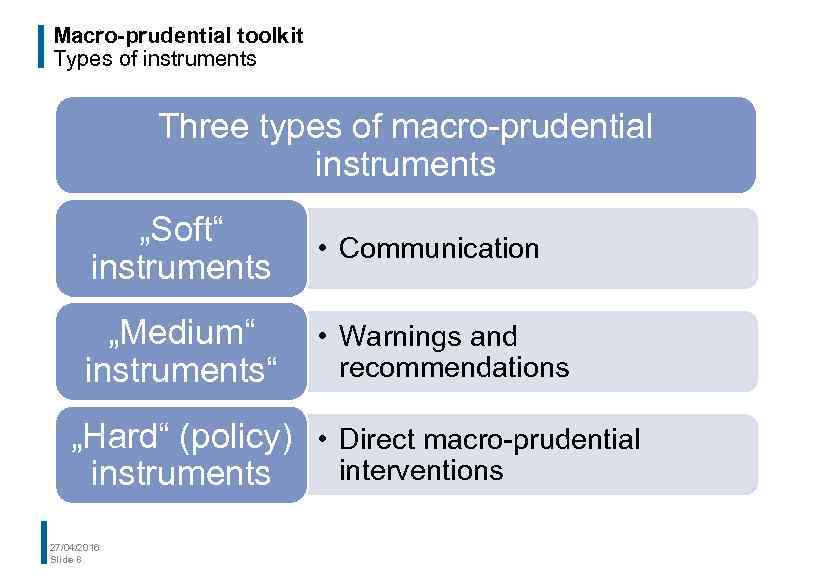 Macro-prudential toolkit Types of instruments Three types of macro-prudential instruments „Soft“ instruments • Communication „Medium“ instruments“ • Warnings and recommendations „Hard“ (policy) • Direct macro-prudential interventions instruments 27/04/2016 Slide 8
Macro-prudential toolkit Types of instruments Three types of macro-prudential instruments „Soft“ instruments • Communication „Medium“ instruments“ • Warnings and recommendations „Hard“ (policy) • Direct macro-prudential interventions instruments 27/04/2016 Slide 8
 Macro-prudential toolkit ”Soft” instruments Communication • • • 27/04/2016 Slide 9 Speeches Articles and interviews Financial Stability reports Discussion Papers Journal publications Conferences
Macro-prudential toolkit ”Soft” instruments Communication • • • 27/04/2016 Slide 9 Speeches Articles and interviews Financial Stability reports Discussion Papers Journal publications Conferences
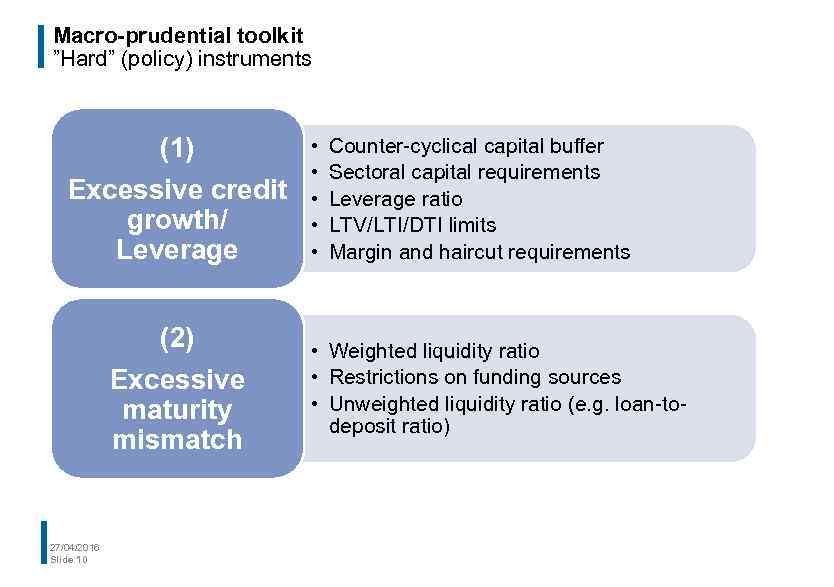 Macro-prudential toolkit ”Hard” (policy) instruments (1) Excessive credit growth/ Leverage (2) Excessive maturity mismatch 27/04/2016 Slide 10 • • • Counter-cyclical capital buffer Sectoral capital requirements Leverage ratio LTV/LTI/DTI limits Margin and haircut requirements • Weighted liquidity ratio • Restrictions on funding sources • Unweighted liquidity ratio (e. g. loan-todeposit ratio)
Macro-prudential toolkit ”Hard” (policy) instruments (1) Excessive credit growth/ Leverage (2) Excessive maturity mismatch 27/04/2016 Slide 10 • • • Counter-cyclical capital buffer Sectoral capital requirements Leverage ratio LTV/LTI/DTI limits Margin and haircut requirements • Weighted liquidity ratio • Restrictions on funding sources • Unweighted liquidity ratio (e. g. loan-todeposit ratio)
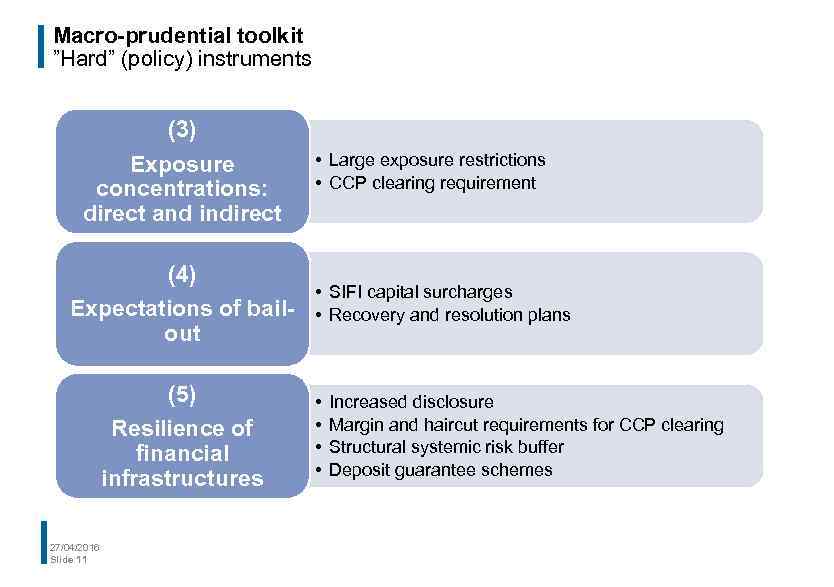 Macro-prudential toolkit ”Hard” (policy) instruments (3) Exposure concentrations: direct and indirect • Large exposure restrictions • CCP clearing requirement (4) • Expectations of bail- • out (5) Resilience of financial infrastructures 27/04/2016 Slide 11 • • SIFI capital surcharges Recovery and resolution plans Increased disclosure Margin and haircut requirements for CCP clearing Structural systemic risk buffer Deposit guarantee schemes
Macro-prudential toolkit ”Hard” (policy) instruments (3) Exposure concentrations: direct and indirect • Large exposure restrictions • CCP clearing requirement (4) • Expectations of bail- • out (5) Resilience of financial infrastructures 27/04/2016 Slide 11 • • SIFI capital surcharges Recovery and resolution plans Increased disclosure Margin and haircut requirements for CCP clearing Structural systemic risk buffer Deposit guarantee schemes
 Macro-prudential toolkit Conclusions Macro-prudential toolkit • Owing to complexity of markets and intermediaries, systemic risk can arise in a wide variety of highly unpredictable forms • Not possible to create a conclusive list of specific threats and suitable instruments • Important to constantly check and , if necessary, update the toolkit of instruments • To adequately and promptly counter stability dangers, the responsible macro-prudential supervisors require sufficient flexibility in the use of instruments 27/04/2016 Slide 12
Macro-prudential toolkit Conclusions Macro-prudential toolkit • Owing to complexity of markets and intermediaries, systemic risk can arise in a wide variety of highly unpredictable forms • Not possible to create a conclusive list of specific threats and suitable instruments • Important to constantly check and , if necessary, update the toolkit of instruments • To adequately and promptly counter stability dangers, the responsible macro-prudential supervisors require sufficient flexibility in the use of instruments 27/04/2016 Slide 12
 Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Overview § Introduction § Macro-prudential toolkit § Macro-prudential instruments in European banking regulation § Transmission mechanisms and channels § Review of initial experiences 27/04/2016 Slide 13
Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Overview § Introduction § Macro-prudential toolkit § Macro-prudential instruments in European banking regulation § Transmission mechanisms and channels § Review of initial experiences 27/04/2016 Slide 13
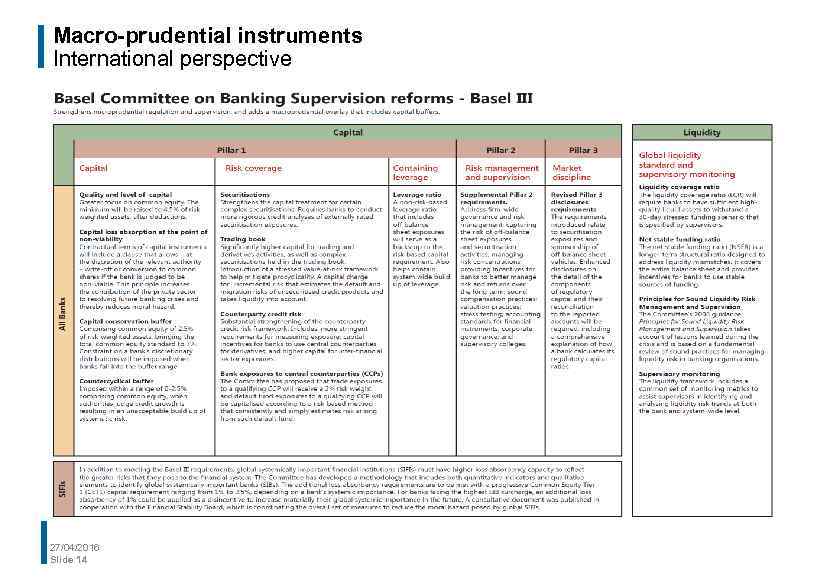 Macro-prudential instruments International perspective 27/04/2016 Slide 14
Macro-prudential instruments International perspective 27/04/2016 Slide 14
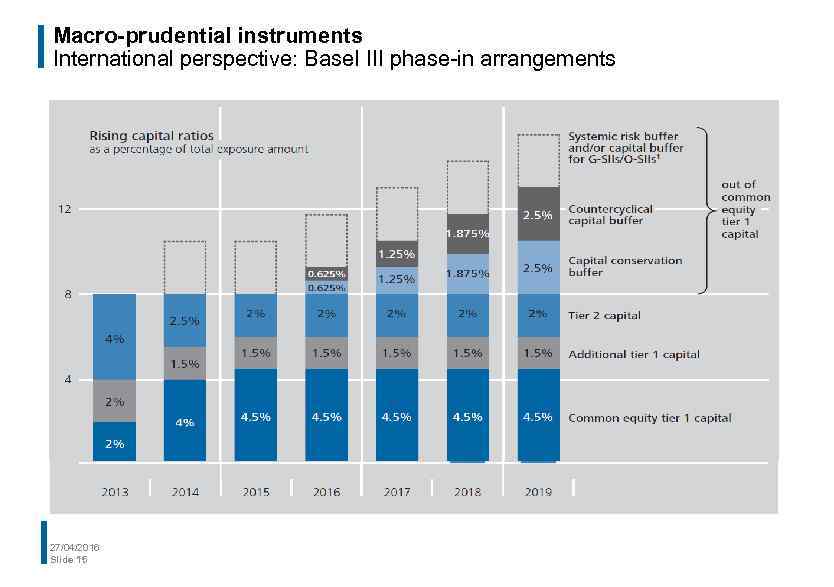 Macro-prudential instruments International perspective: Basel III phase-in arrangements 27/04/2016 Slide 15
Macro-prudential instruments International perspective: Basel III phase-in arrangements 27/04/2016 Slide 15
 Macro-prudential instruments European perspective Basel III is implemented in the EU through a directive and a regulation (CRD IV/CRR) • Temporary tightening of supervisory requirements at national level, including: • Capital requirements • Risk weights • Disclosure obligations • Liquidity requirements • Systemic risk buffer • Countercyclical buffer 27/04/2016 Slide 16
Macro-prudential instruments European perspective Basel III is implemented in the EU through a directive and a regulation (CRD IV/CRR) • Temporary tightening of supervisory requirements at national level, including: • Capital requirements • Risk weights • Disclosure obligations • Liquidity requirements • Systemic risk buffer • Countercyclical buffer 27/04/2016 Slide 16
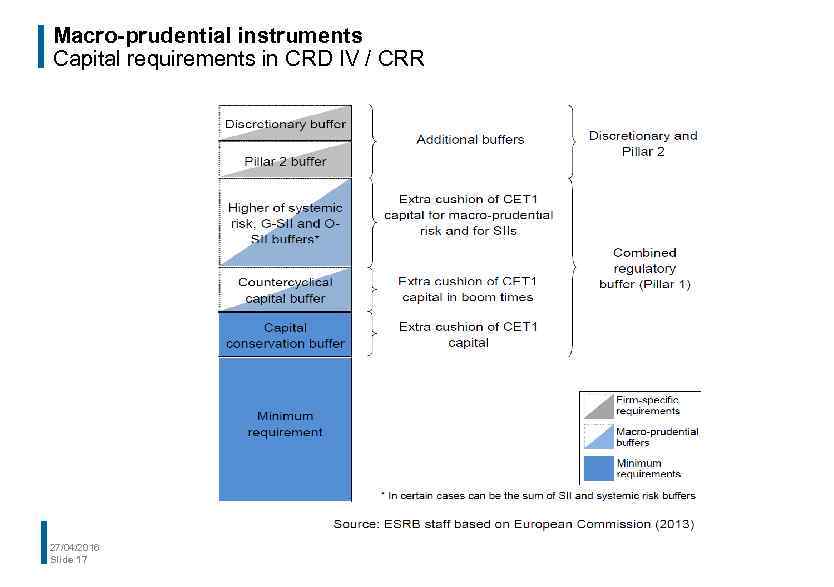 Macro-prudential instruments Capital requirements in CRD IV / CRR 27/04/2016 Slide 17
Macro-prudential instruments Capital requirements in CRD IV / CRR 27/04/2016 Slide 17
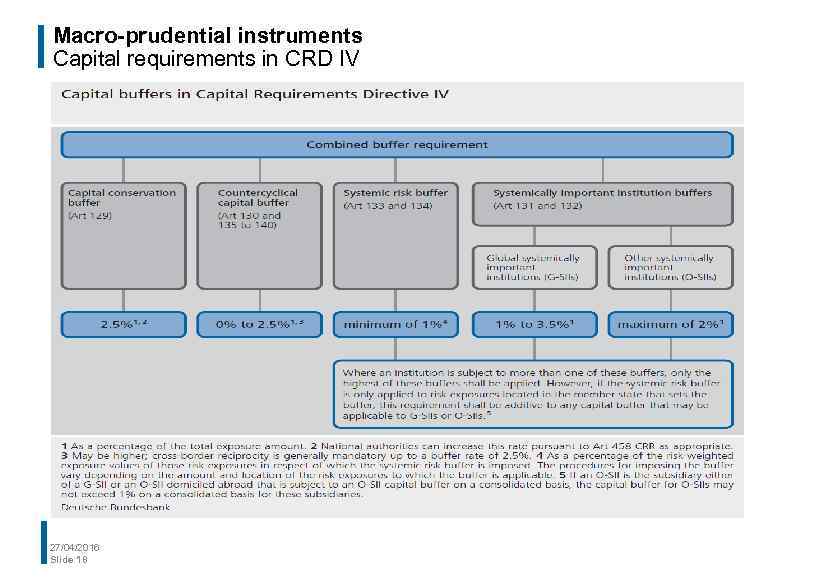 Macro-prudential instruments Capital requirements in CRD IV 27/04/2016 Slide 18
Macro-prudential instruments Capital requirements in CRD IV 27/04/2016 Slide 18
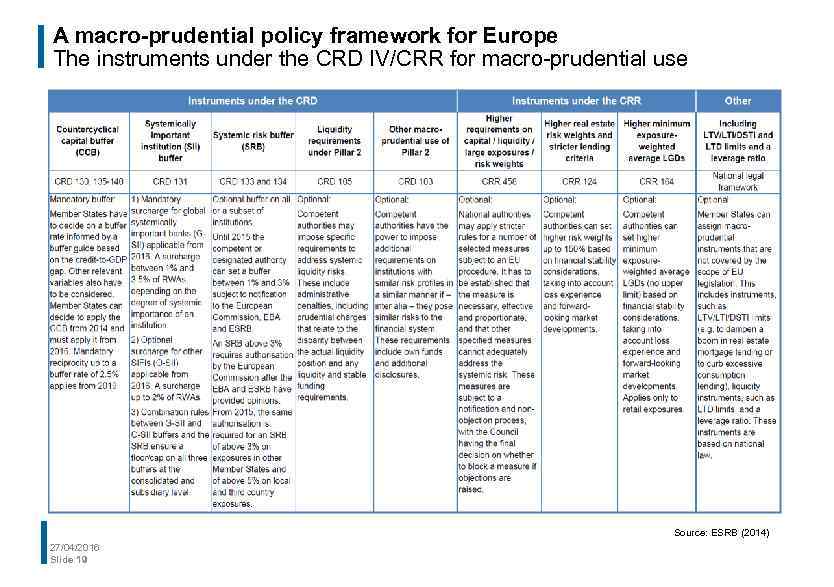 A macro-prudential policy framework for Europe The instruments under the CRD IV/CRR for macro-prudential use Source: ESRB (2014) 27/04/2016 Slide 19
A macro-prudential policy framework for Europe The instruments under the CRD IV/CRR for macro-prudential use Source: ESRB (2014) 27/04/2016 Slide 19
 Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Overview § Introduction § Macro-prudential toolkit § Macro-prudential instruments in European banking regulation § Transmission mechanisms and channels § Review of initial experiences 27/04/2016 Slide 20
Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Overview § Introduction § Macro-prudential toolkit § Macro-prudential instruments in European banking regulation § Transmission mechanisms and channels § Review of initial experiences 27/04/2016 Slide 20
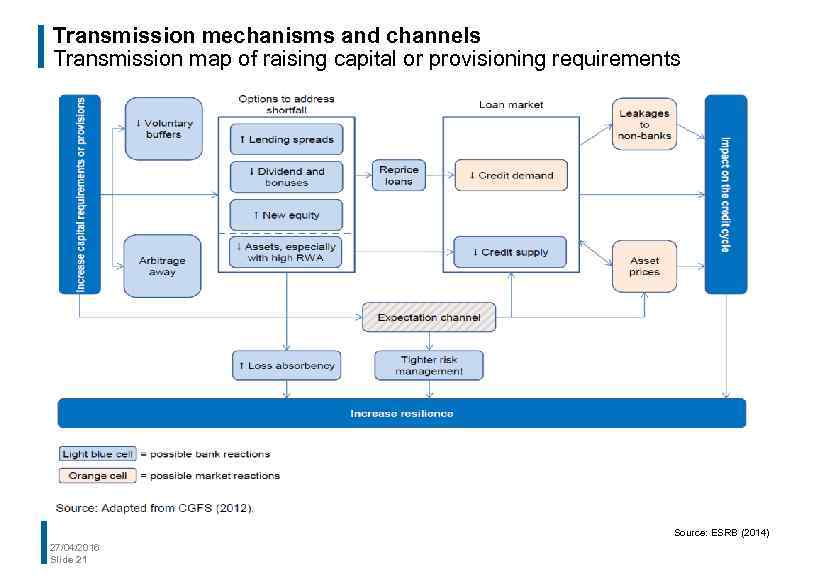 Transmission mechanisms and channels Transmission map of raising capital or provisioning requirements Source: ESRB (2014) 27/04/2016 Slide 21
Transmission mechanisms and channels Transmission map of raising capital or provisioning requirements Source: ESRB (2014) 27/04/2016 Slide 21
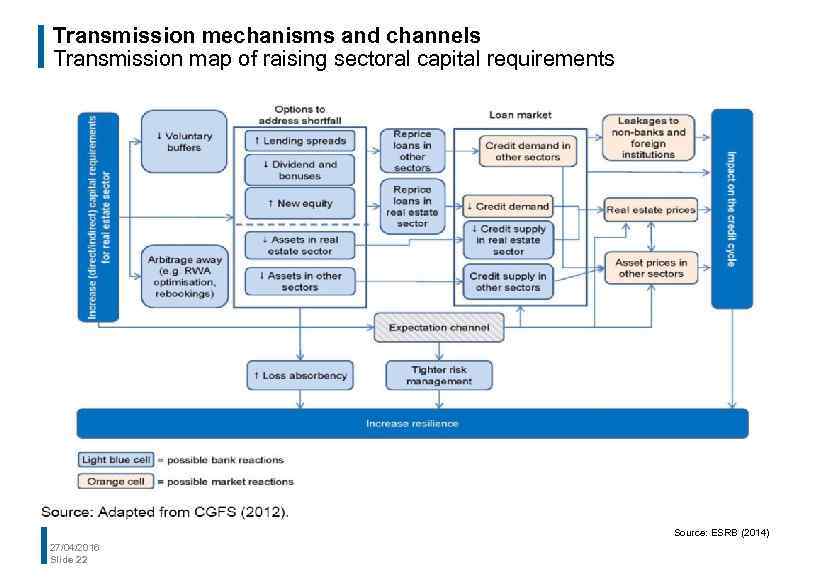 Transmission mechanisms and channels Transmission map of raising sectoral capital requirements Source: ESRB (2014) 27/04/2016 Slide 22
Transmission mechanisms and channels Transmission map of raising sectoral capital requirements Source: ESRB (2014) 27/04/2016 Slide 22
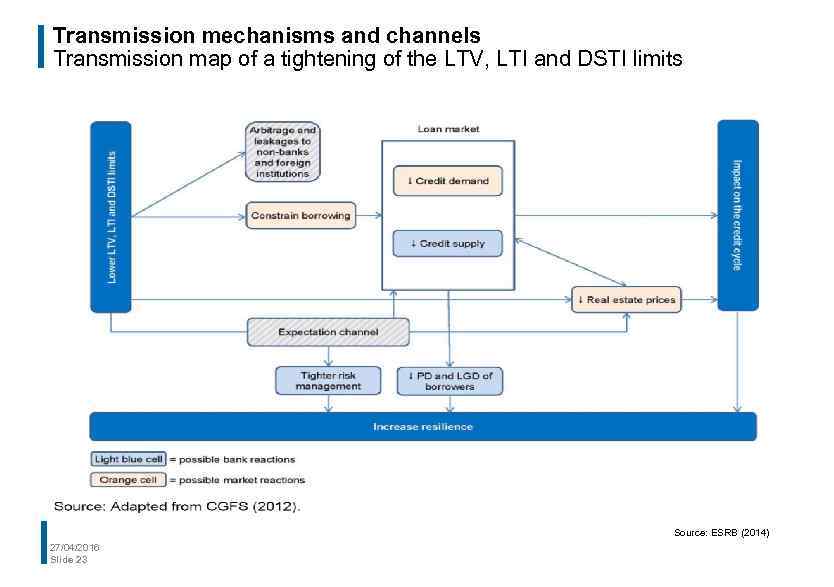 Transmission mechanisms and channels Transmission map of a tightening of the LTV, LTI and DSTI limits Source: ESRB (2014) 27/04/2016 Slide 23
Transmission mechanisms and channels Transmission map of a tightening of the LTV, LTI and DSTI limits Source: ESRB (2014) 27/04/2016 Slide 23
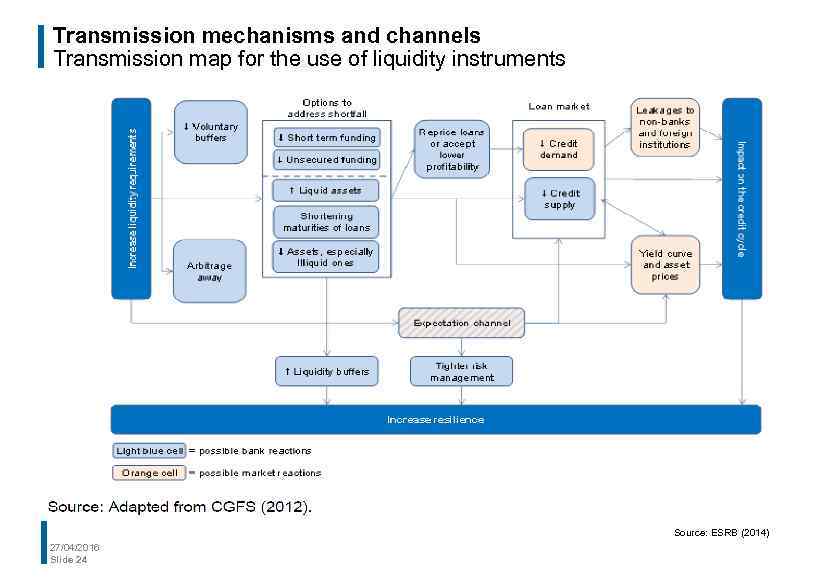 Transmission mechanisms and channels Transmission map for the use of liquidity instruments Source: ESRB (2014) 27/04/2016 Slide 24
Transmission mechanisms and channels Transmission map for the use of liquidity instruments Source: ESRB (2014) 27/04/2016 Slide 24
 Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Overview § Introduction § Macro-prudential toolkit § Macro-prudential instruments in European banking regulation § Transmission mechanisms and channels § Review of initial experiences 27/04/2016 Slide 25
Macro-prudential policy and its instruments Overview § Introduction § Macro-prudential toolkit § Macro-prudential instruments in European banking regulation § Transmission mechanisms and channels § Review of initial experiences 27/04/2016 Slide 25
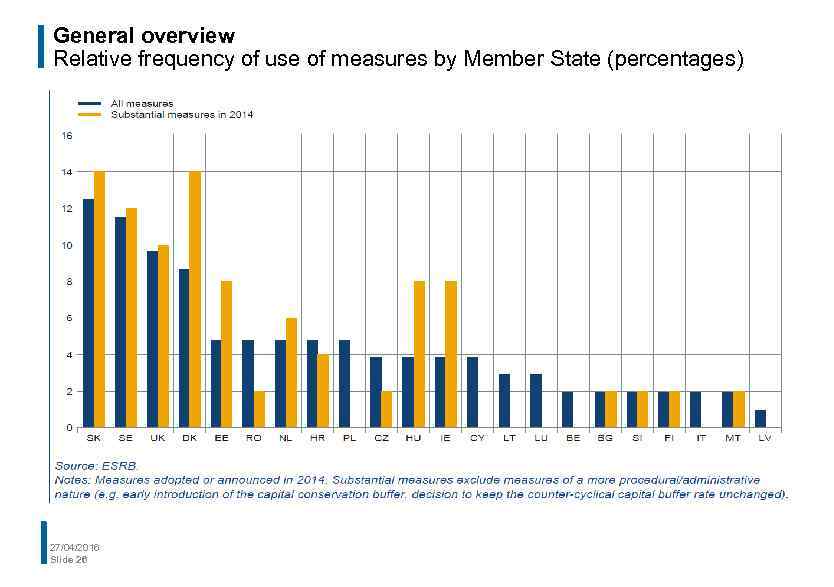 General overview Relative frequency of use of measures by Member State (percentages) 27/04/2016 Slide 26
General overview Relative frequency of use of measures by Member State (percentages) 27/04/2016 Slide 26
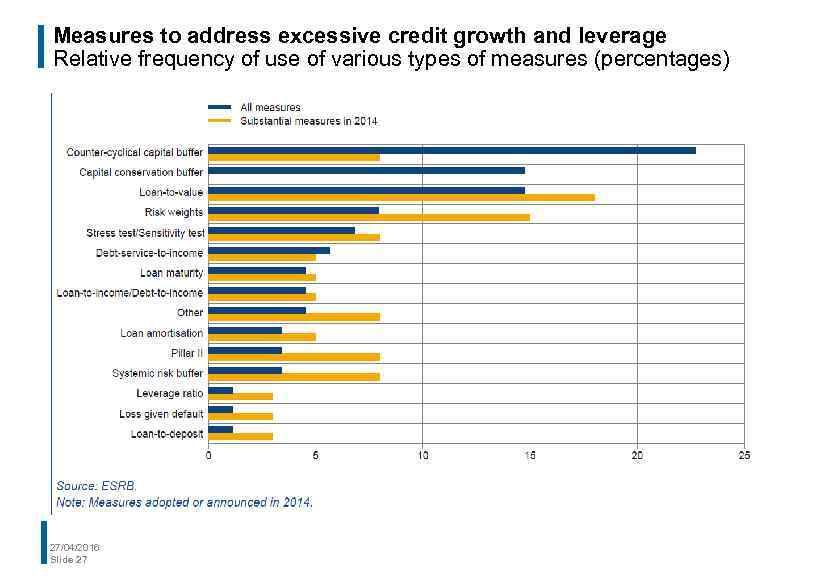 Measures to address excessive credit growth and leverage Relative frequency of use of various types of measures (percentages) 27/04/2016 Slide 27
Measures to address excessive credit growth and leverage Relative frequency of use of various types of measures (percentages) 27/04/2016 Slide 27
 Thank you very much for your attention! Contact: Peter. Spicka@bundesbank. de
Thank you very much for your attention! Contact: Peter. Spicka@bundesbank. de


