9f5bd98b583b5157c877a30ff6b8e69e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Machine Learning for Stock Selection Robert J. Yan Charles X. Ling University of Western Ontario, Canada {jyan, cling}@csd. uwo. ca 1

Outline l Introduction l The stock selection task l The Prototype Ranking method l Experimental results l Conclusions 2

Introduction l Objective: – Use machine learning to select a small number of “good” stocks to form a portfolio l Research questions: – Learning in the noisy dataset – Learning in the imbalanced dataset l Our solution: Prototype Ranking – A specially designed machine learning method 3

Outline l Introduction l The stock selection task l The Prototype Ranking method l Experimental results l Conclusions 4
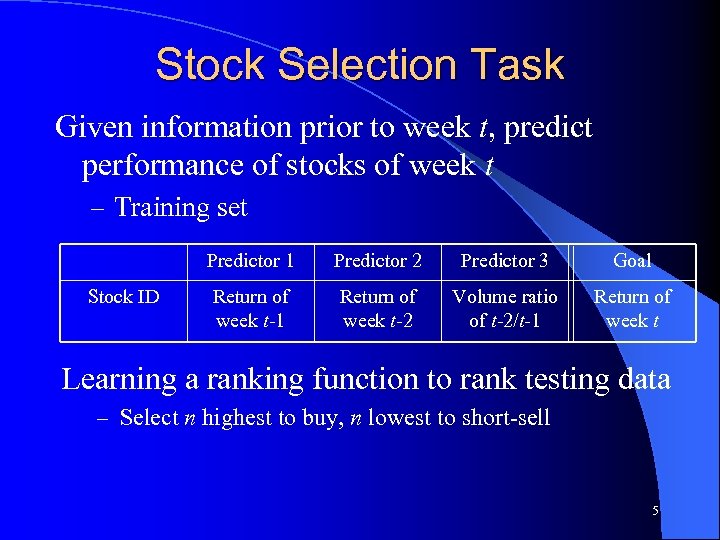
Stock Selection Task Given information prior to week t, predict performance of stocks of week t – Training set Predictor 1 Stock ID Predictor 2 Predictor 3 Goal Return of week t-1 Return of week t-2 Volume ratio of t-2/t-1 Return of week t Learning a ranking function to rank testing data – Select n highest to buy, n lowest to short-sell 5

Outline l Introduction l The stock selection task l The Prototype Ranking method l Experimental results l Conclusions 6

Prototype Ranking l Prototype Ranking (PR): special machine learning for noisy and imbalanced stock data l The PR System Step 1. Find good “prototypes” in training data Step 2. Use k-NN on prototypes to rank test data 7
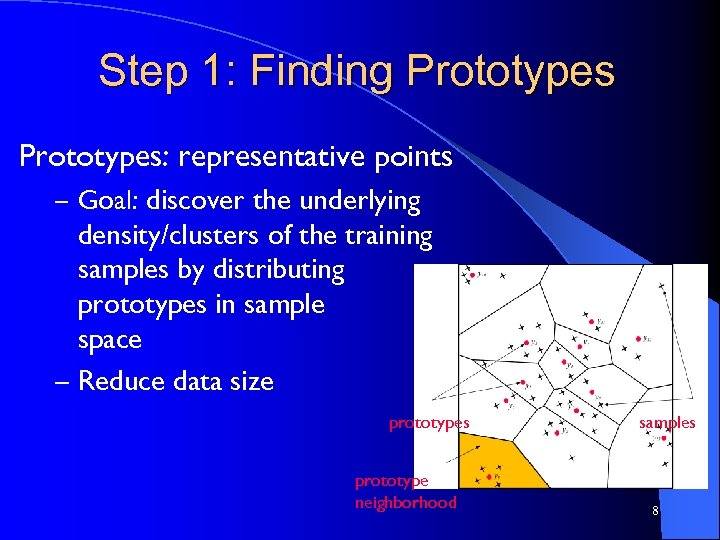
Step 1: Finding Prototypes: representative points – Goal: discover the underlying density/clusters of the training samples by distributing prototypes in sample space – Reduce data size prototypes prototype neighborhood samples 8

Finding prototypes using competitive learning General competitive learning Step 1: Randomly initialize a set of prototypes l Step 2: Search the nearest prototypes l Step 3: Adjust the prototypes l Step 4: Output the prototypes l Hidden density in training is reflected in prototypes 10

Modifications for Stock data l In step 1: Initial prototypes organized in a tree-structure – Fast nearest prototype searching l In step 2: Searching prototypes in the predictor space – Better learning effect for the prediction tasks l In step 3: Adjusting prototypes in the goal attribute space – Better learning effect in the imbalanced stock data l In step 4, prune the prototype tree – Prune children prototypes if they are similar to the parent – Combine leaf prototypes to form the final prototypes 11

Step 2: Predicting Test Data l The weighted average of k nearest prototypes l Online update the model with new data 12

Outline l Introduction l The stock selection task l The Prototype Ranking method l Experimental results l Conclusions 13

Data CRSP daily stock database – 300 NYSE and AMEX stocks, largest market cap – From 1962 to 2004 14

Testing PR l Experiment 1: Larger portfolio, lower average return, lower risk – diversification l Experiment 2: is PR better than Cooper’s method? 15
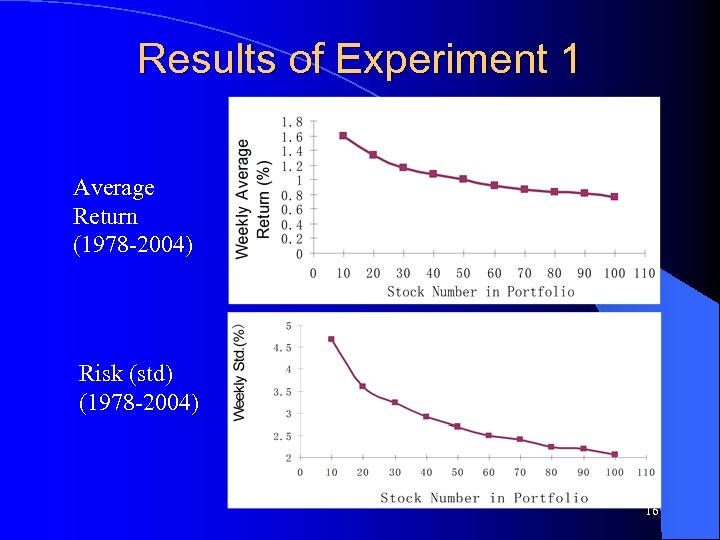
Results of Experiment 1 Average Return (1978 -2004) Risk (std) (1978 -2004) 16

Experiment 2: Comparison to Cooper’s method l Cooper’s method (CP): A traditional non. ML method for stock selection… l Compare PR and CP in 10 -stock portfolios 17
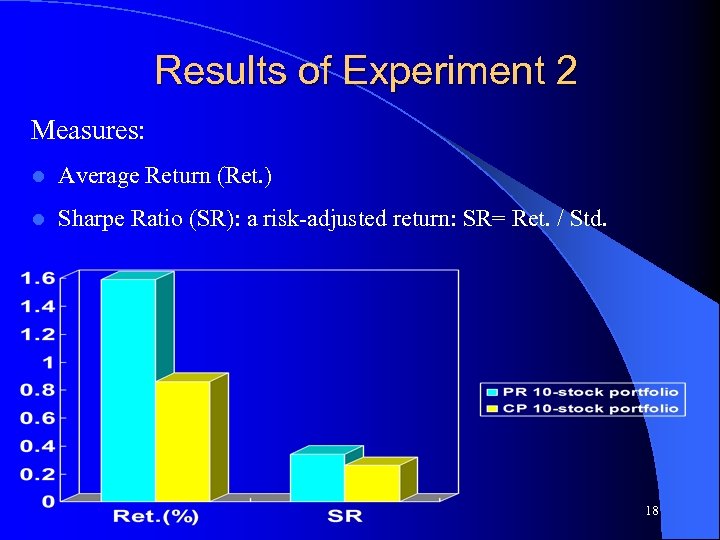
Results of Experiment 2 Measures: l Average Return (Ret. ) l Sharpe Ratio (SR): a risk-adjusted return: SR= Ret. / Std. 18

Outline l Introduction l The stock selection task l The Prototype Ranking method l Experimental results l Conclusions 20

Conclusions l PR: modified competitive learning and k-NN for noisy and imbalanced stock data l PR does well in stock selection – Larger portfolio, lower return, lower risk – PR outperforms the non-ML method CP l Future work: use it to invest and make money! 21
9f5bd98b583b5157c877a30ff6b8e69e.ppt