Lecture3 (MAC).ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
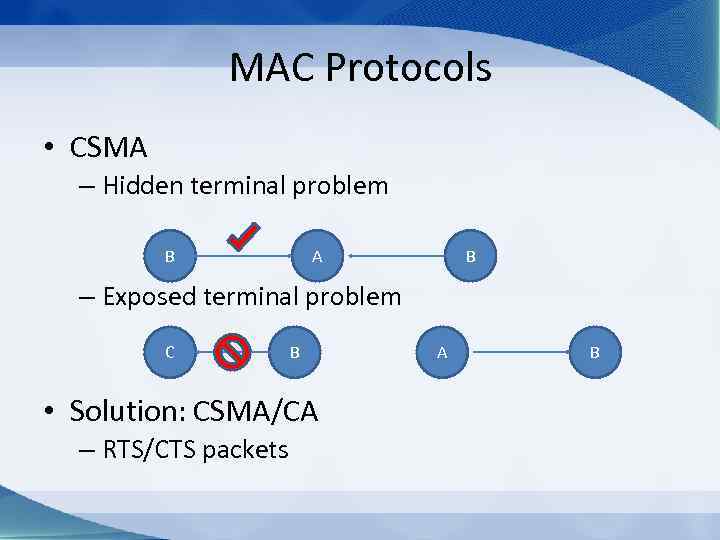
MAC Protocols • CSMA – Hidden terminal problem B A B – Exposed terminal problem C B • Solution: CSMA/CA – RTS/CTS packets A B
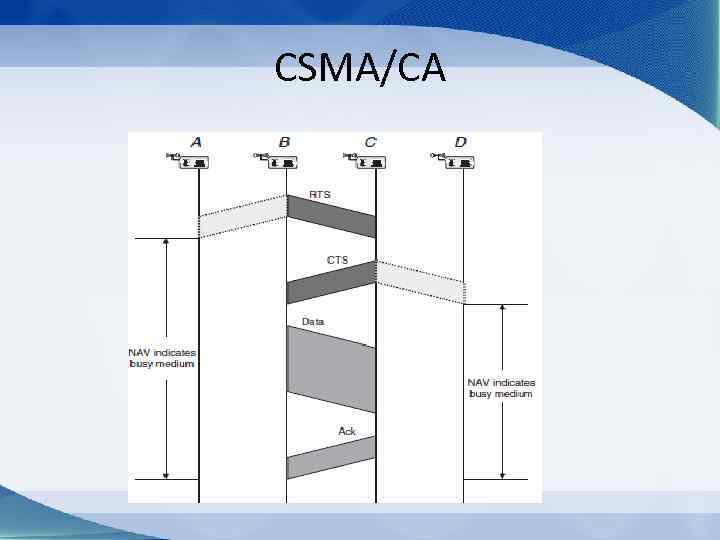
CSMA/CA
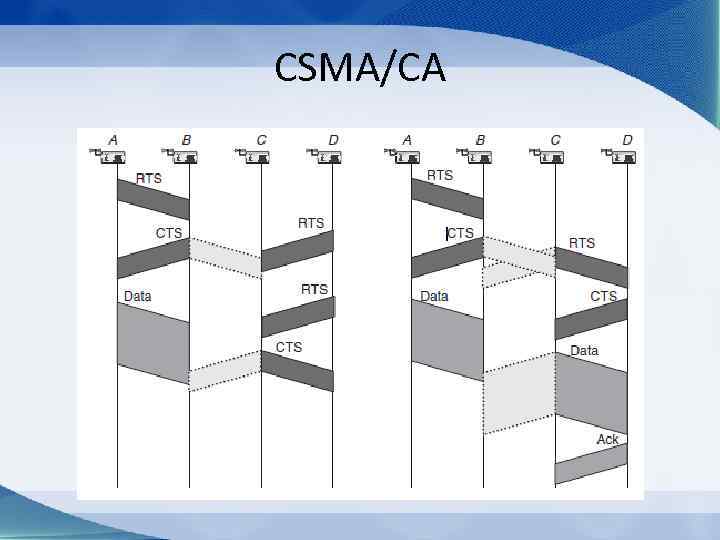
CSMA/CA

Energy problems • • Collision Overhearing Idle listening Protocol overhead

Contention based Protocols • S-MAC (Listen and Sleep intervals) • B-MAC (Preamble based) • Wise. MAC
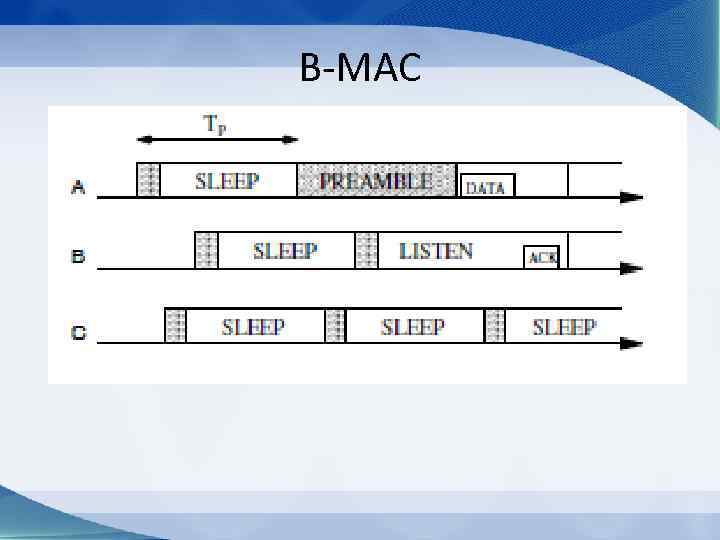
B-MAC
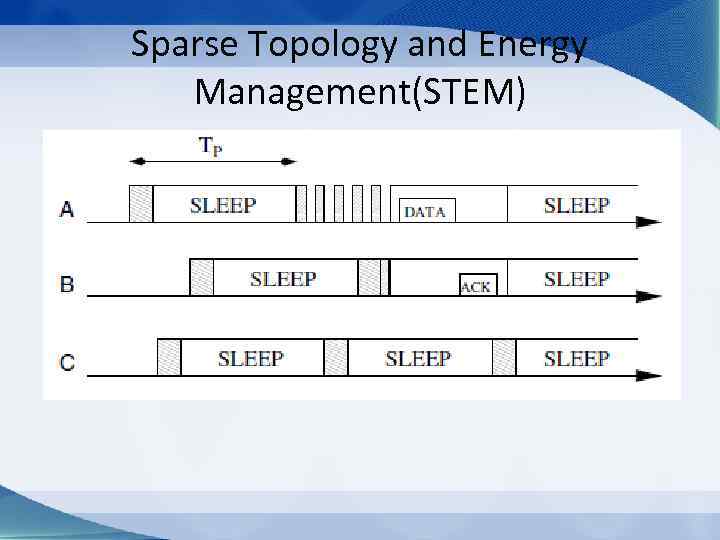
Sparse Topology and Energy Management(STEM)

Reservation based protocols • Avoids collision by assigning slots to nodes • A number of TDMA-based protocols have been developed • TRAMA

Traffic Adaptive MAC (TRAMA) • No collisions • Switches to sleep mode whenever nodes are not transmitting or receiving • Time is slotted • Depending on nodes information determines the nodes transmission slot • No data to transmit -> no slot assigned
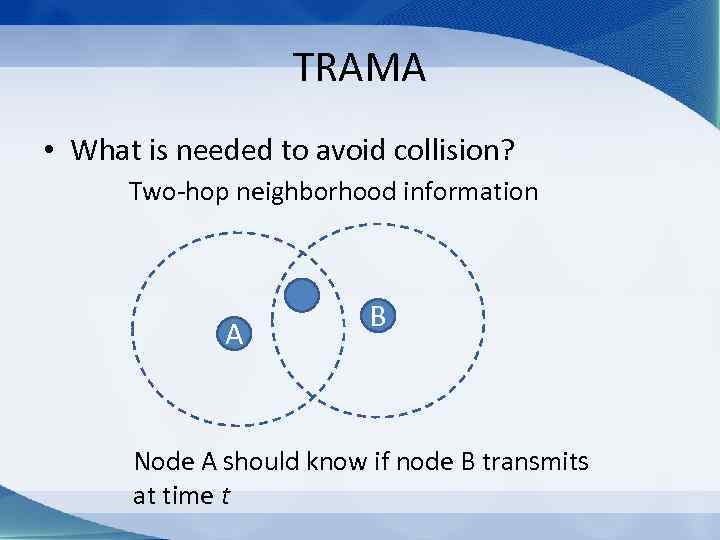
TRAMA • What is needed to avoid collision? Two-hop neighborhood information A B Node A should know if node B transmits at time t
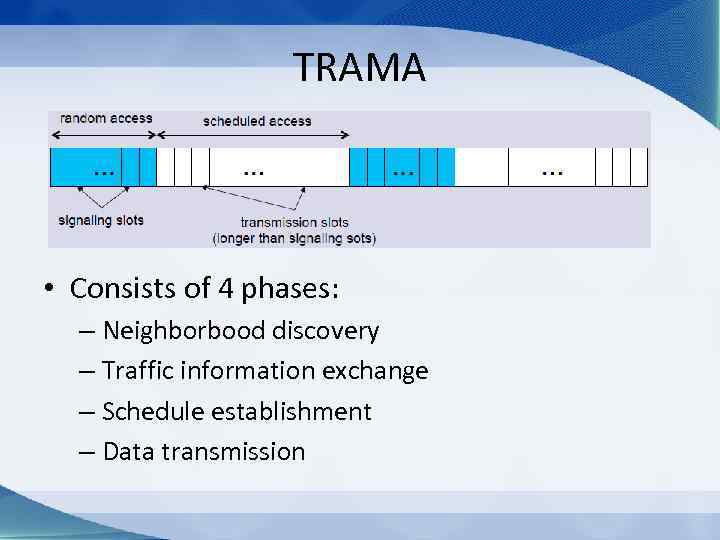
TRAMA • Consists of 4 phases: – Neighborbood discovery – Traffic information exchange – Schedule establishment – Data transmission

TRAMA • Neighbor protocol (NP) • Schedule exchange protocol (SEP) • Adaptive exchange algorithm (AEA)
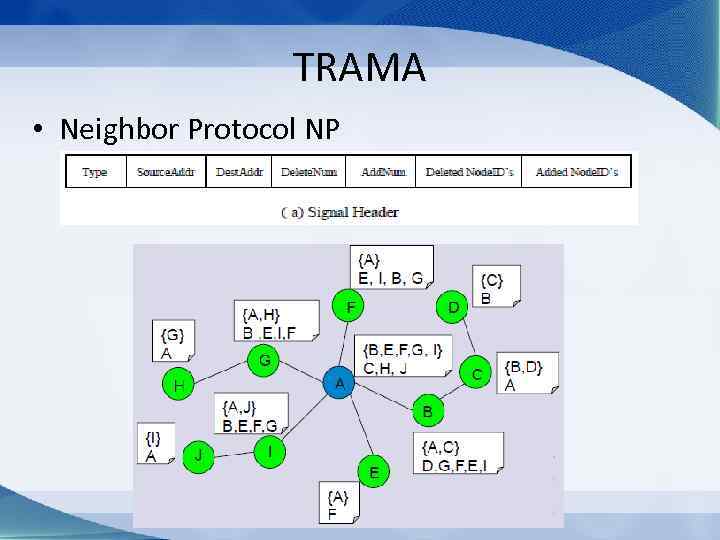
TRAMA • Neighbor Protocol NP

TRAMA • Schedule Exchange protocol (SEP) – Compute the packet rate X – Find winning slots in [t, t+X] – Create schedule – Announce schedule
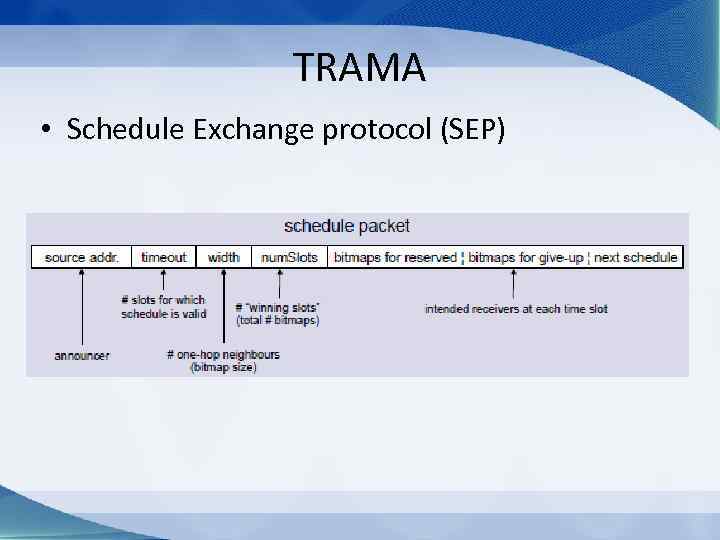
TRAMA • Schedule Exchange protocol (SEP)
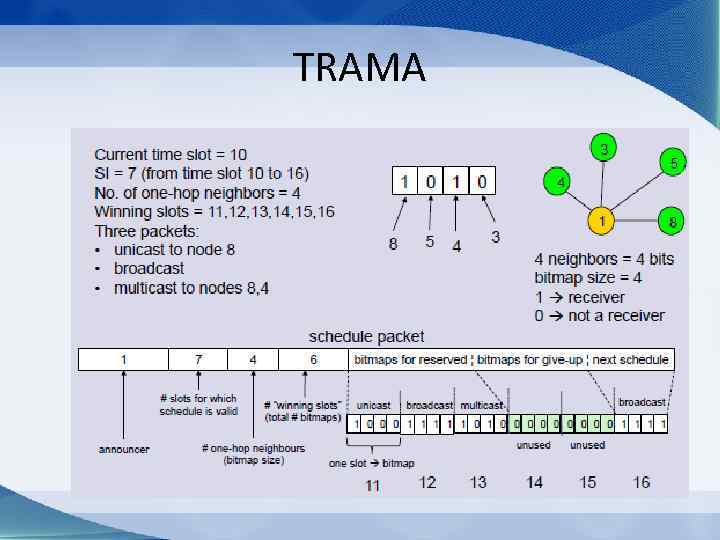
TRAMA
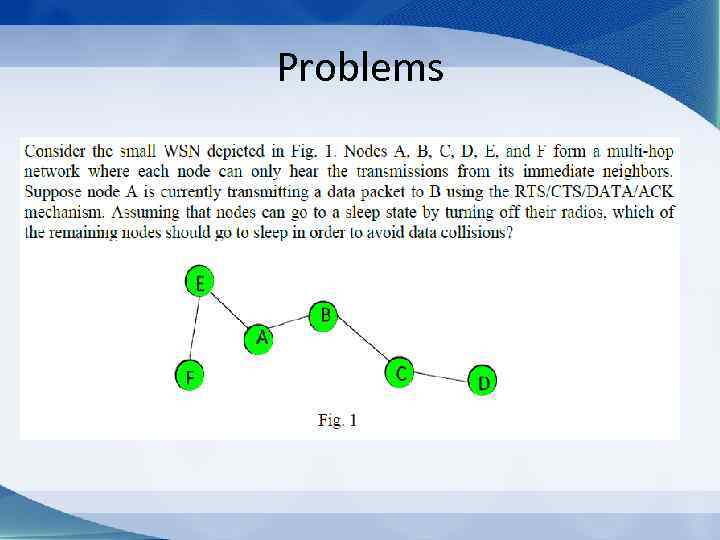
Problems
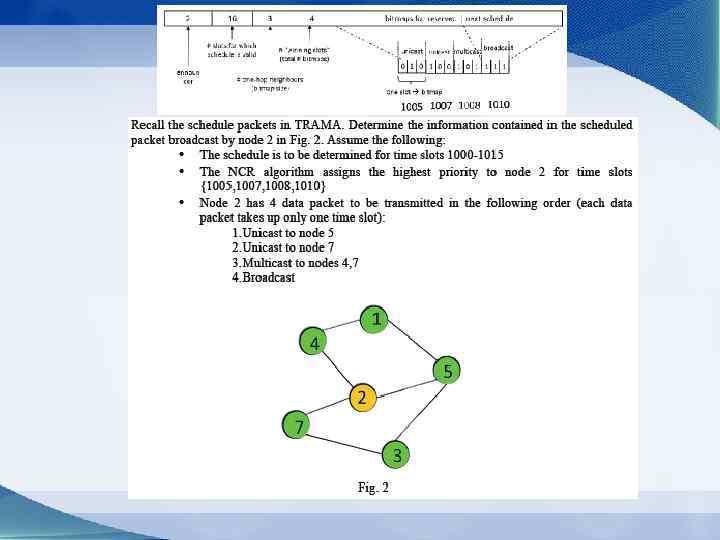
Problems
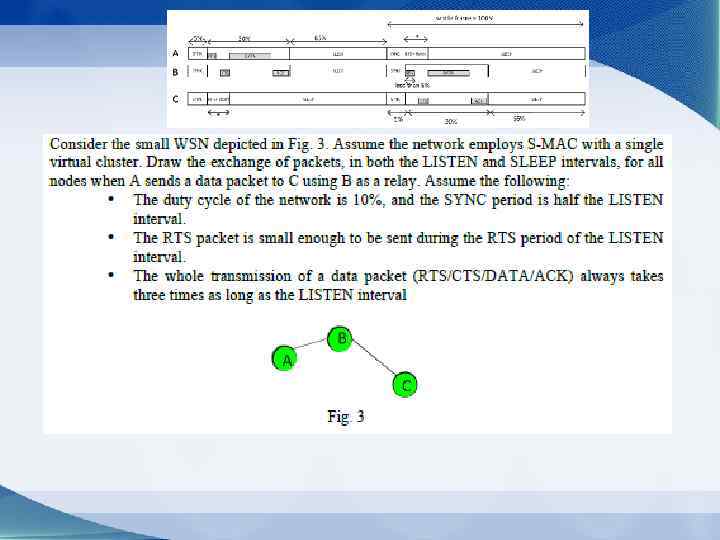
Problems
Network Layer • Responsible for delivering data to destination • Many Network layer (Routing) protocols have been proposed – Energy consumption – Scalable – Robustness -…

Routing protocols • • Data centric Hierarchical Geographical Qo. S-based
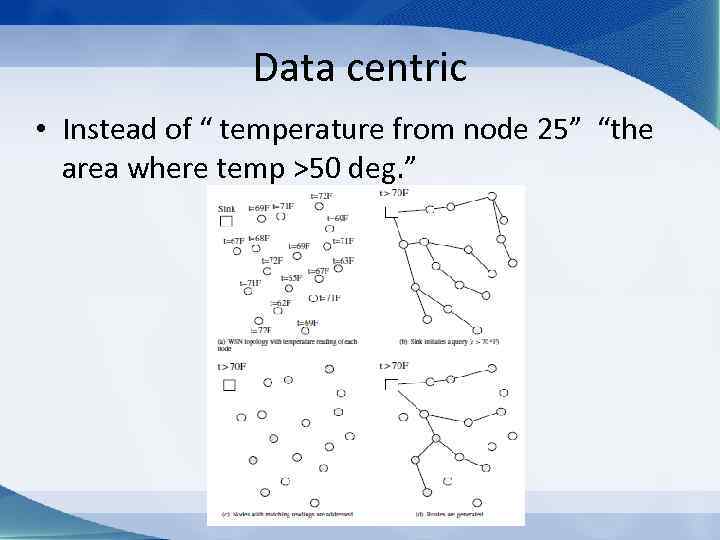
Data centric • Instead of “ temperature from node 25” “the area where temp >50 deg. ”
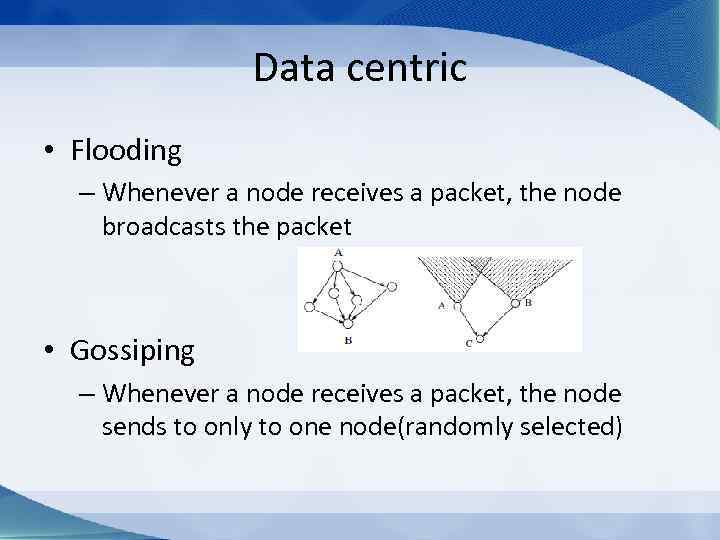
Data centric • Flooding – Whenever a node receives a packet, the node broadcasts the packet • Gossiping – Whenever a node receives a packet, the node sends to only to one node(randomly selected)
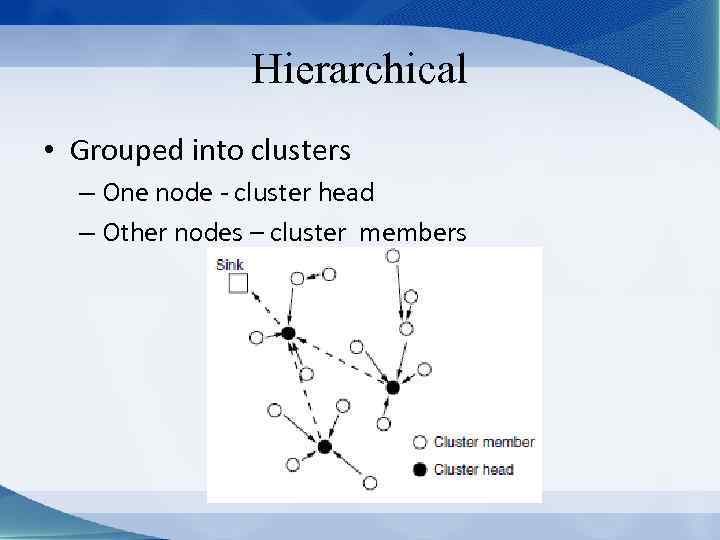
Hierarchical • Grouped into clusters – One node - cluster head – Other nodes – cluster members

Hierarchical 1. LEACH: Low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy 2. PEGASIS 3. PEDAP August, 2004
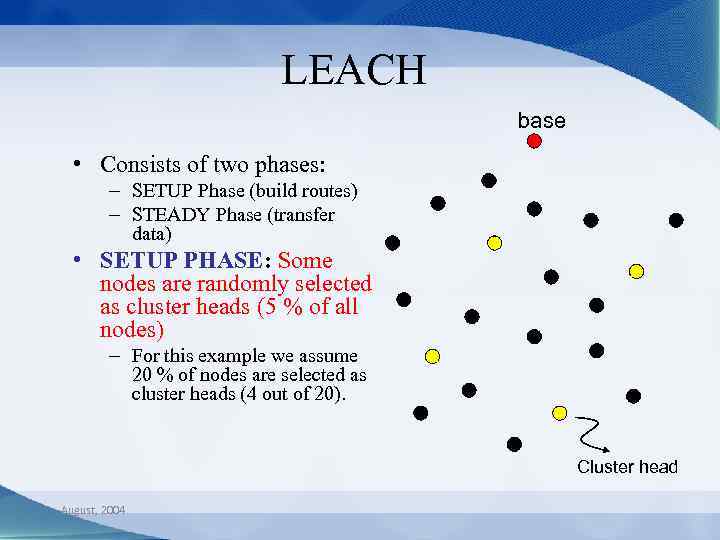
LEACH base • Consists of two phases: – SETUP Phase (build routes) – STEADY Phase (transfer data) • SETUP PHASE: Some nodes are randomly selected as cluster heads (5 % of all nodes) – For this example we assume 20 % of nodes are selected as cluster heads (4 out of 20). Cluster head August, 2004
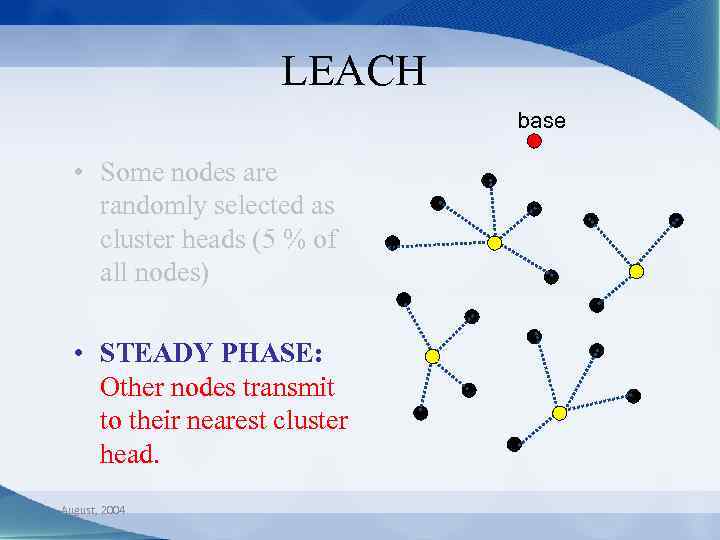
LEACH base • Some nodes are randomly selected as cluster heads (5 % of all nodes) • STEADY PHASE: Other nodes transmit to their nearest cluster head. August, 2004
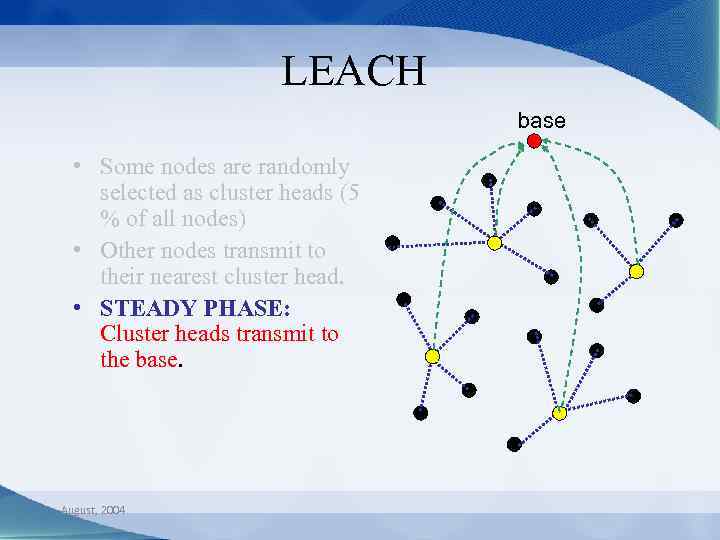
LEACH base • Some nodes are randomly selected as cluster heads (5 % of all nodes) • Other nodes transmit to their nearest cluster head. • STEADY PHASE: Cluster heads transmit to the base. August, 2004
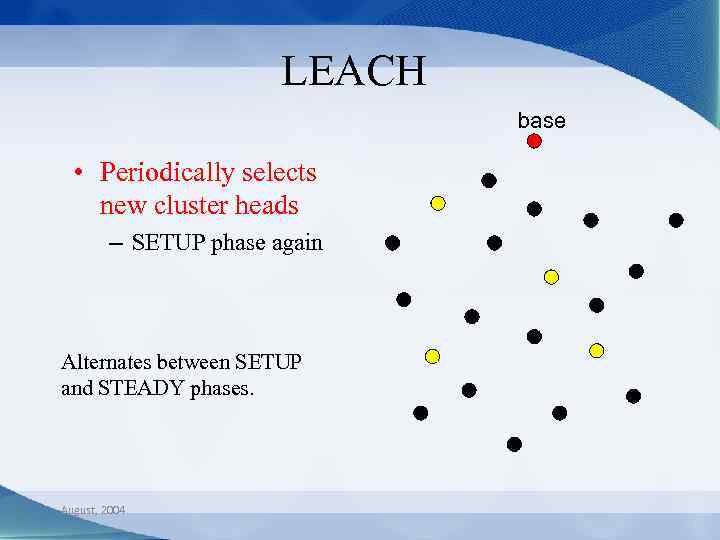
LEACH base • Periodically selects new cluster heads – SETUP phase again Alternates between SETUP and STEADY phases. August, 2004

Schemes 1. LEACH: Low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy 2. PEGASIS: 3. PEDAP August, 2004
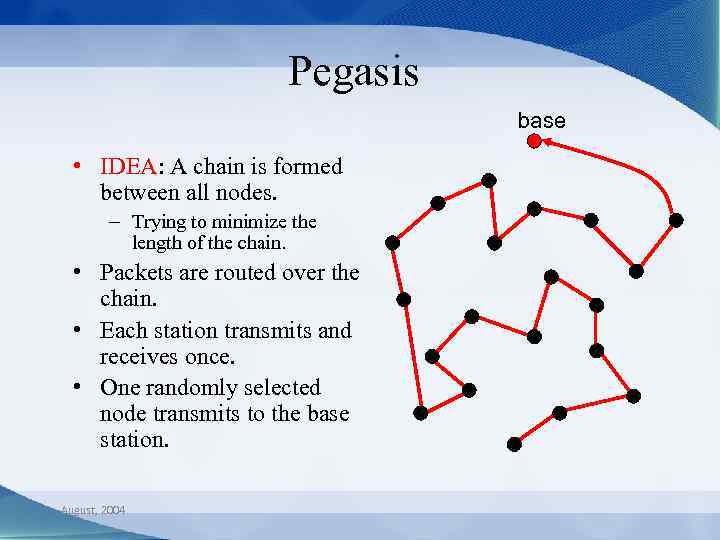
Pegasis base • IDEA: A chain is formed between all nodes. – Trying to minimize the length of the chain. • Packets are routed over the chain. • Each station transmits and receives once. • One randomly selected node transmits to the base station. August, 2004
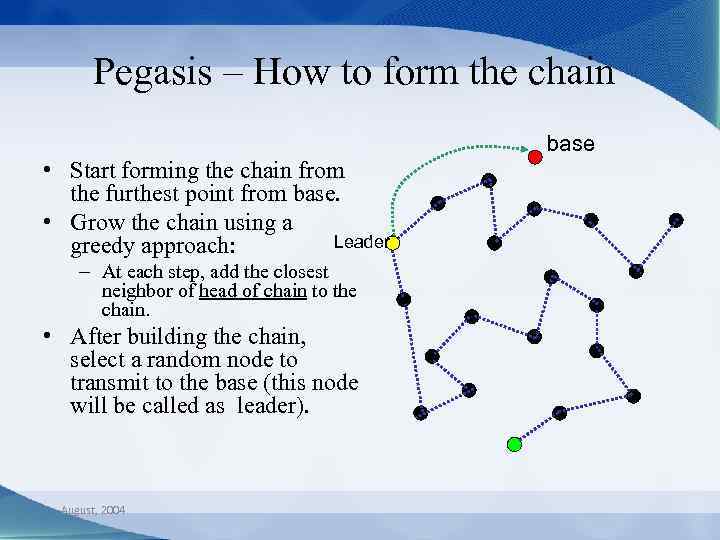
Pegasis – How to form the chain base • Start forming the chain from the furthest point from base. • Grow the chain using a Leader greedy approach: – At each step, add the closest neighbor of head of chain to the chain. • After building the chain, select a random node to transmit to the base (this node will be called as leader). August, 2004
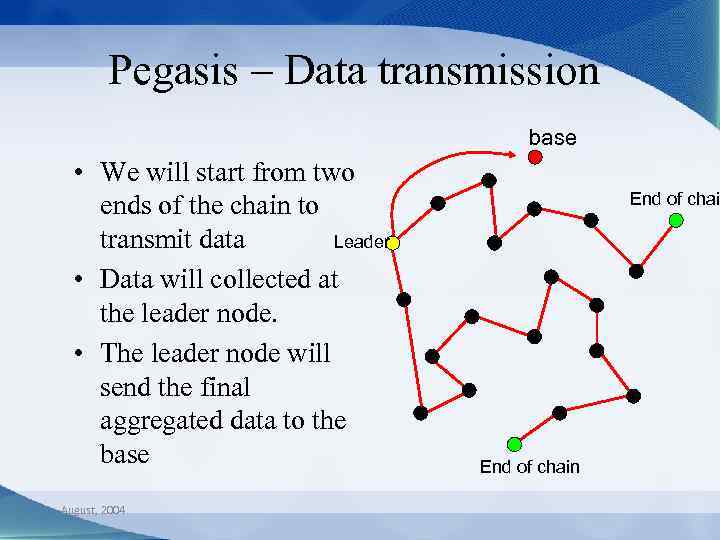
Pegasis – Data transmission base • We will start from two ends of the chain to Leader transmit data • Data will collected at the leader node. • The leader node will send the final aggregated data to the base August, 2004 End of chain

PEDAP • PEDAP: Power Efficient Data Gathering and Aggregation – Forward data from all sensors to the base over a minimum spanning tree. August, 2004
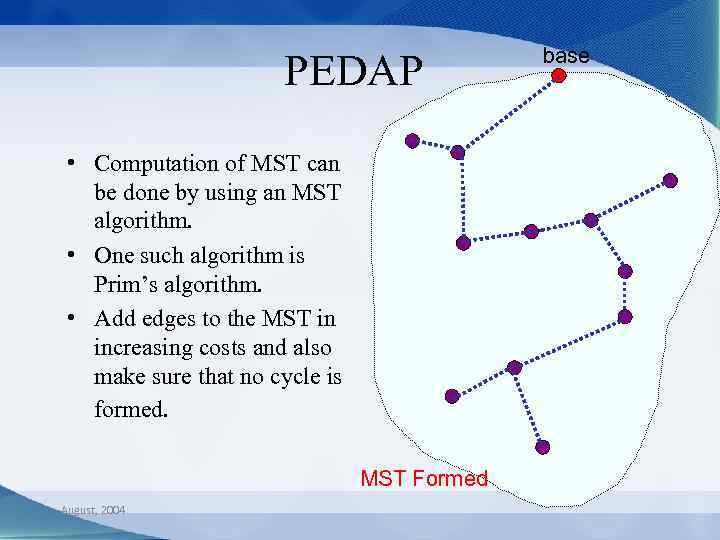
PEDAP • Computation of MST can be done by using an MST algorithm. • One such algorithm is Prim’s algorithm. • Add edges to the MST in increasing costs and also make sure that no cycle is formed. MST Formed August, 2004 base
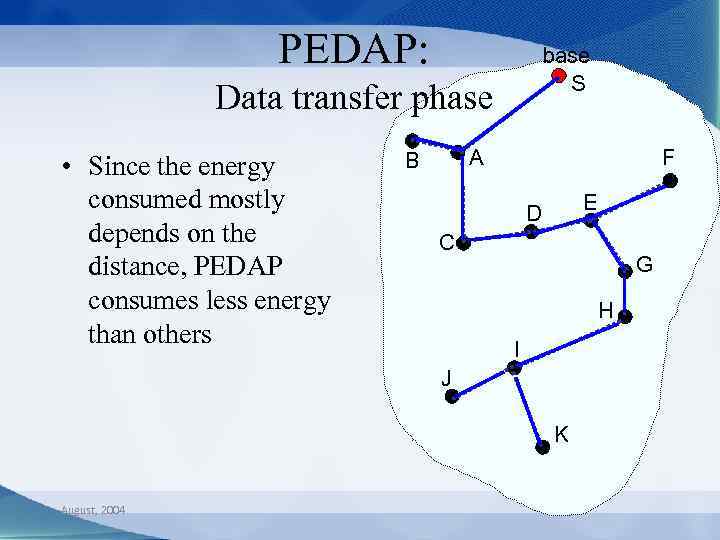
PEDAP: base S Data transfer phase • Since the energy consumed mostly depends on the distance, PEDAP consumes less energy than others A B F E D C G H I J K August, 2004
Lecture3 (MAC).ppt