be737032ea2323f5383b990511a6eb65.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 MA 5242 Wavelets Lecture 2 Euclidean and Unitary Spaces Wayne M. Lawton Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore 2 Science Drive 2 Singapore 117543 Email matwml@nus. edu. sg Tel (65) 6874 -2749
MA 5242 Wavelets Lecture 2 Euclidean and Unitary Spaces Wayne M. Lawton Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore 2 Science Drive 2 Singapore 117543 Email matwml@nus. edu. sg Tel (65) 6874 -2749
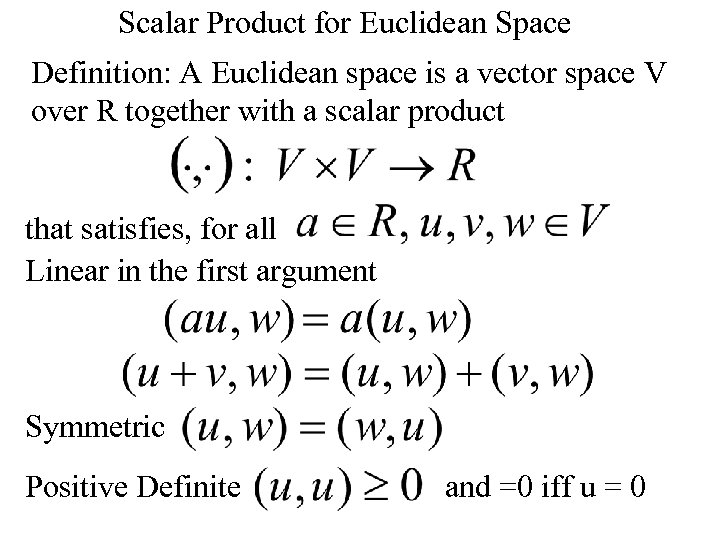 Scalar Product for Euclidean Space Definition: A Euclidean space is a vector space V over R together with a scalar product that satisfies, for all Linear in the first argument Symmetric Positive Definite and =0 iff u = 0
Scalar Product for Euclidean Space Definition: A Euclidean space is a vector space V over R together with a scalar product that satisfies, for all Linear in the first argument Symmetric Positive Definite and =0 iff u = 0
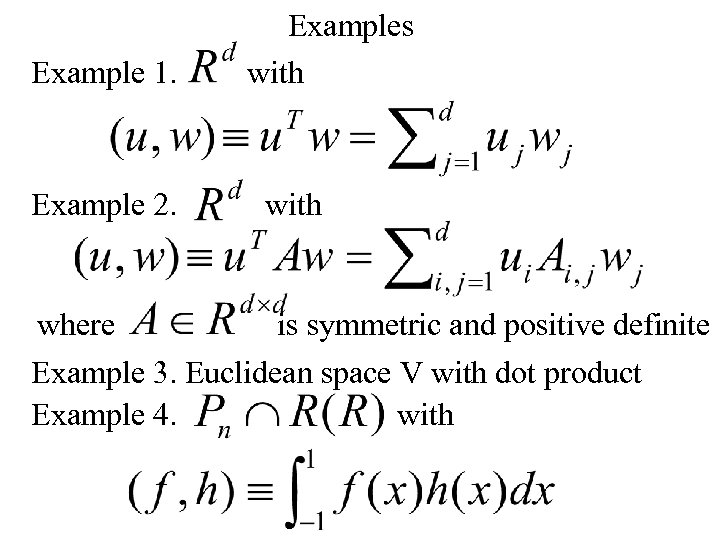 Example 1. Example 2. Examples with where is symmetric and positive definite Example 3. Euclidean space V with dot product Example 4. with
Example 1. Example 2. Examples with where is symmetric and positive definite Example 3. Euclidean space V with dot product Example 4. with
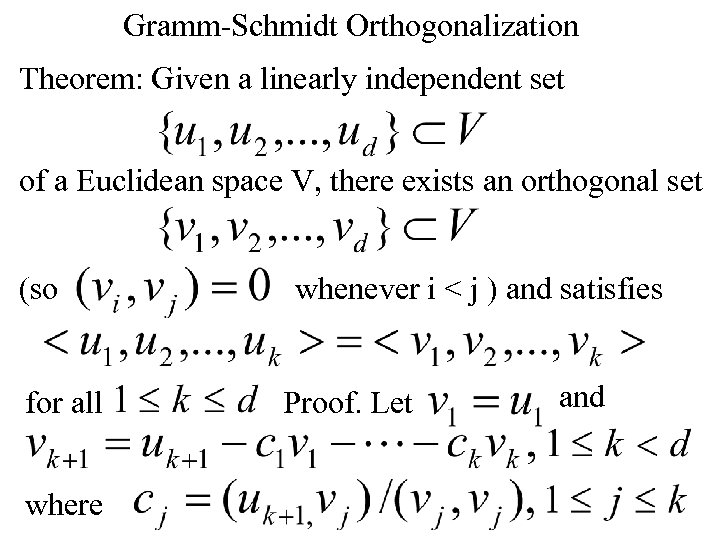 Gramm-Schmidt Orthogonalization Theorem: Given a linearly independent set of a Euclidean space V, there exists an orthogonal set (so for all where whenever i < j ) and satisfies Proof. Let and
Gramm-Schmidt Orthogonalization Theorem: Given a linearly independent set of a Euclidean space V, there exists an orthogonal set (so for all where whenever i < j ) and satisfies Proof. Let and
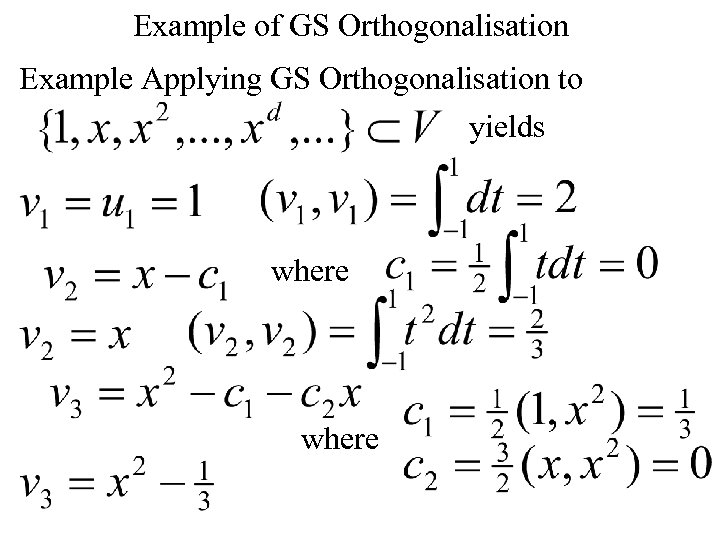 Example of GS Orthogonalisation Example Applying GS Orthogonalisation to yields where
Example of GS Orthogonalisation Example Applying GS Orthogonalisation to yields where
 Problem Set 1 1. Orthogonalize the following basis of 2. Continue the GS Orth. on previous page to obtain 3. Show that contains only even powers of x for k odd and odd powers of x for k even 4. Show that all zeros of are in [-1, 1]
Problem Set 1 1. Orthogonalize the following basis of 2. Continue the GS Orth. on previous page to obtain 3. Show that contains only even powers of x for k odd and odd powers of x for k even 4. Show that all zeros of are in [-1, 1]
 Gramm Matrices Definition: The Gramm matrix of a set is defined by its entries Example 1. The Gramm matrix for a basis of that consists of the columns of a matrix B is Example 2. The Gramm matrix for the monomial basis of with scalar product is the Hilbert matrix
Gramm Matrices Definition: The Gramm matrix of a set is defined by its entries Example 1. The Gramm matrix for a basis of that consists of the columns of a matrix B is Example 2. The Gramm matrix for the monomial basis of with scalar product is the Hilbert matrix
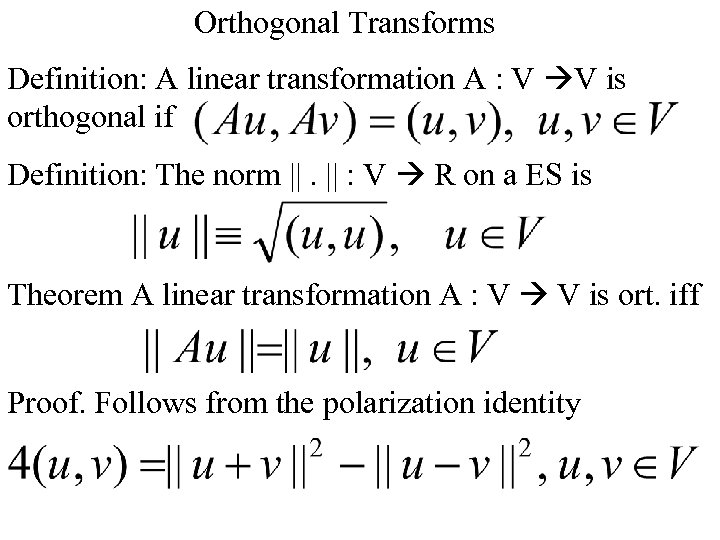 Orthogonal Transforms Definition: A linear transformation A : V V is orthogonal if Definition: The norm ||. || : V R on a ES is Theorem A linear transformation A : V V is ort. iff Proof. Follows from the polarization identity
Orthogonal Transforms Definition: A linear transformation A : V V is orthogonal if Definition: The norm ||. || : V R on a ES is Theorem A linear transformation A : V V is ort. iff Proof. Follows from the polarization identity
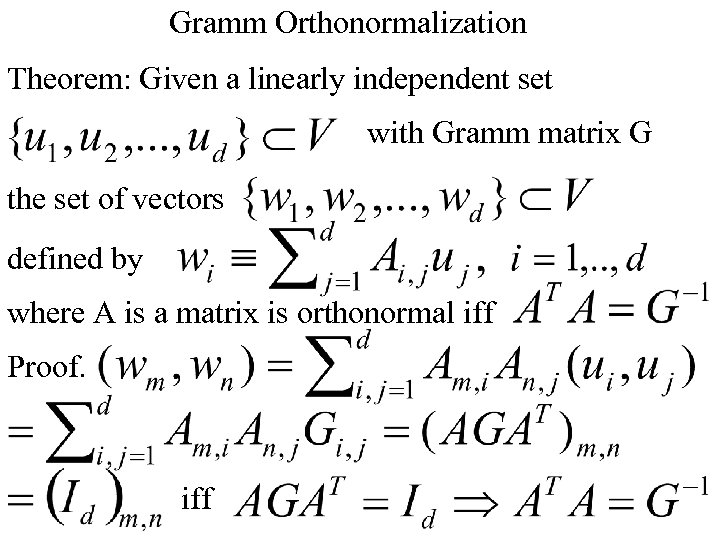 Gramm Orthonormalization Theorem: Given a linearly independent set with Gramm matrix G the set of vectors defined by where A is a matrix is orthonormal iff Proof. iff
Gramm Orthonormalization Theorem: Given a linearly independent set with Gramm matrix G the set of vectors defined by where A is a matrix is orthonormal iff Proof. iff
 Haar Transform (one stage) on given by matrix
Haar Transform (one stage) on given by matrix
 Discrete Wavelet Transform For suitable real entries this matrix is orthogonal.
Discrete Wavelet Transform For suitable real entries this matrix is orthogonal.
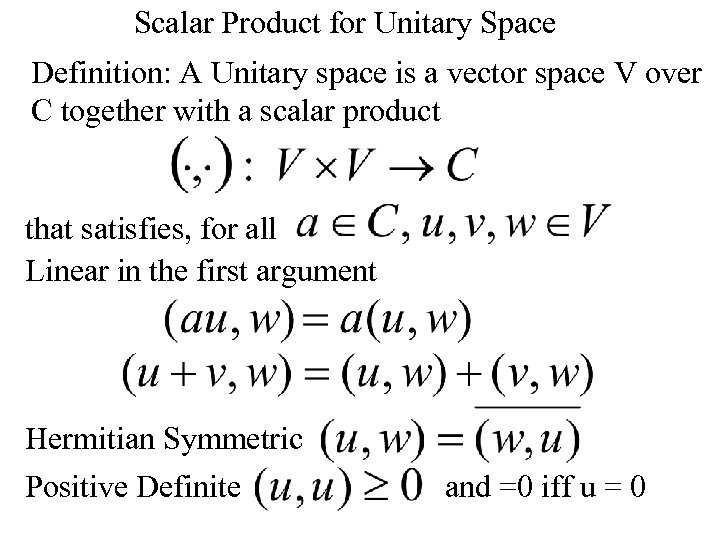 Scalar Product for Unitary Space Definition: A Unitary space is a vector space V over C together with a scalar product that satisfies, for all Linear in the first argument Hermitian Symmetric Positive Definite and =0 iff u = 0
Scalar Product for Unitary Space Definition: A Unitary space is a vector space V over C together with a scalar product that satisfies, for all Linear in the first argument Hermitian Symmetric Positive Definite and =0 iff u = 0
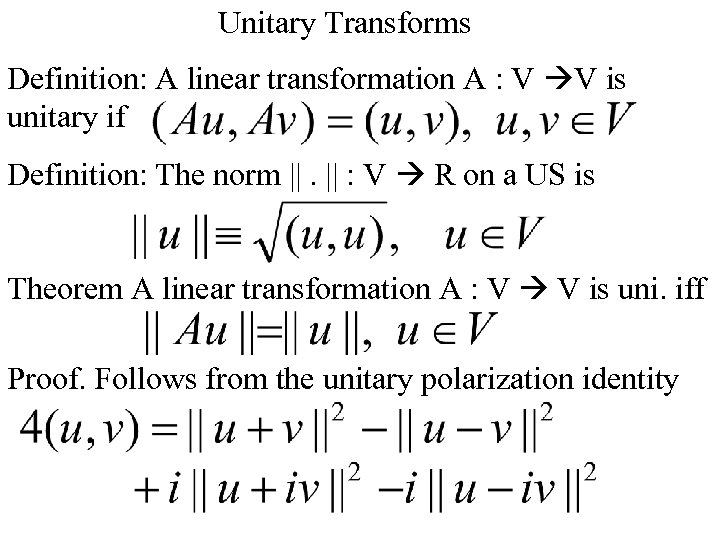 Unitary Transforms Definition: A linear transformation A : V V is unitary if Definition: The norm ||. || : V R on a US is Theorem A linear transformation A : V V is uni. iff Proof. Follows from the unitary polarization identity
Unitary Transforms Definition: A linear transformation A : V V is unitary if Definition: The norm ||. || : V R on a US is Theorem A linear transformation A : V V is uni. iff Proof. Follows from the unitary polarization identity
 Problem Set 2 1. Prove that a set of vectors in a Euclidean or Unitary space is linearly independent iff its Gramm matrix is positive definite 2. Derive the polarization identities and theorems 3. Show that the columns of a square matrix having complex entries are orthogonal iff its rows are. 4. State & derive the Schwarz inequality for ES & US 5. State & derive the triangle inequality for ES & US
Problem Set 2 1. Prove that a set of vectors in a Euclidean or Unitary space is linearly independent iff its Gramm matrix is positive definite 2. Derive the polarization identities and theorems 3. Show that the columns of a square matrix having complex entries are orthogonal iff its rows are. 4. State & derive the Schwarz inequality for ES & US 5. State & derive the triangle inequality for ES & US
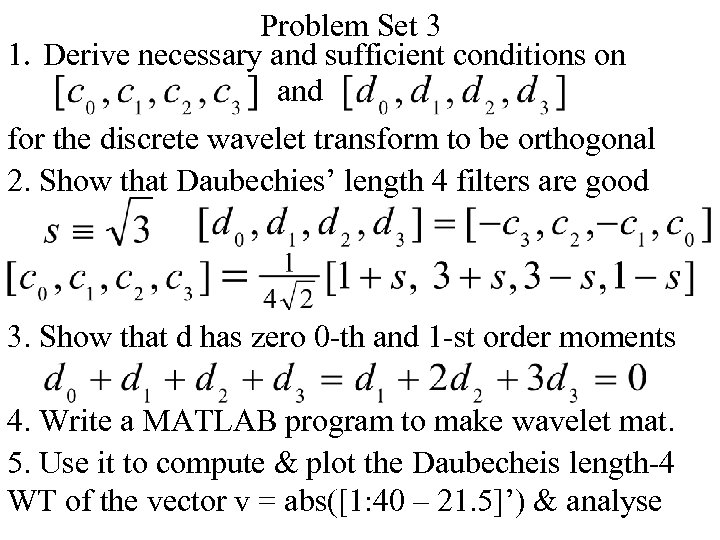 Problem Set 3 1. Derive necessary and sufficient conditions on and for the discrete wavelet transform to be orthogonal 2. Show that Daubechies’ length 4 filters are good 3. Show that d has zero 0 -th and 1 -st order moments 4. Write a MATLAB program to make wavelet mat. 5. Use it to compute & plot the Daubecheis length-4 WT of the vector v = abs([1: 40 – 21. 5]’) & analyse
Problem Set 3 1. Derive necessary and sufficient conditions on and for the discrete wavelet transform to be orthogonal 2. Show that Daubechies’ length 4 filters are good 3. Show that d has zero 0 -th and 1 -st order moments 4. Write a MATLAB program to make wavelet mat. 5. Use it to compute & plot the Daubecheis length-4 WT of the vector v = abs([1: 40 – 21. 5]’) & analyse


