 M A N A G E M E N T S I M U LA T I ON Management Simulation Week 3 Getting it together
M A N A G E M E N T S I M U LA T I ON Management Simulation Week 3 Getting it together
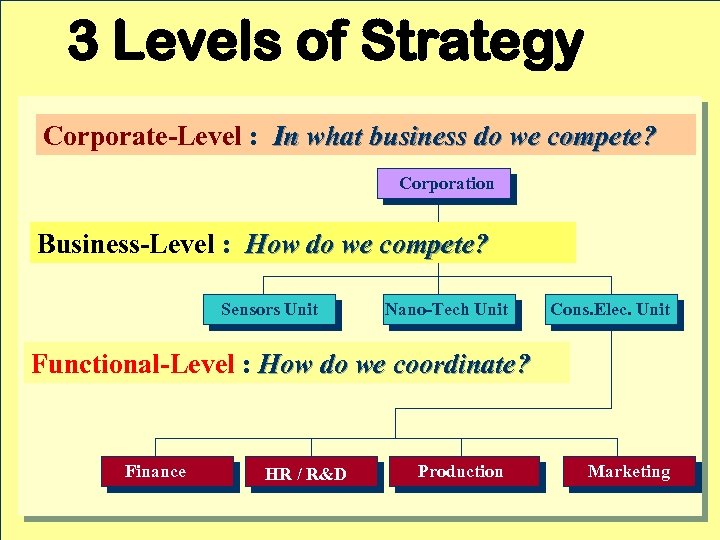 3 Levels of Strategy Corporate-Level : In what business do we compete? Corporation Business-Level : How do we compete? Sensors Unit Nano-Tech Unit Cons. Elec. Unit Functional-Level : How do we coordinate? Finance HR / R&D Production Marketing
3 Levels of Strategy Corporate-Level : In what business do we compete? Corporation Business-Level : How do we compete? Sensors Unit Nano-Tech Unit Cons. Elec. Unit Functional-Level : How do we coordinate? Finance HR / R&D Production Marketing
 Level 3 - Functional Strategy How do we coordinate?
Level 3 - Functional Strategy How do we coordinate?
 Marketing Coordinates w/: n n n R&D when products are launched or repositioned Production in its unit sales & margins forecast Finance w/ overall sales projections & the budget
Marketing Coordinates w/: n n n R&D when products are launched or repositioned Production in its unit sales & margins forecast Finance w/ overall sales projections & the budget
 D coordinates w/: n n n Marketing when products are repositioned or introduced Production when products are launched or material costs change Finance over budget.
D coordinates w/: n n n Marketing when products are repositioned or introduced Production when products are launched or material costs change Finance over budget.
 Production coordinates w/: n n n R&D about new product introduction & material costs Marketing about demand, scheduling, and inventory Finance about plant and equipment changes, inventory levels, & margins
Production coordinates w/: n n n R&D about new product introduction & material costs Marketing about demand, scheduling, and inventory Finance about plant and equipment changes, inventory levels, & margins
 Finance coordinates w/: n n n R&D over budgets & product introductions Marketing about sales projections, margins & budgets Production about margins, plant & equipment changes & inventory levels
Finance coordinates w/: n n n R&D over budgets & product introductions Marketing about sales projections, margins & budgets Production about margins, plant & equipment changes & inventory levels
 Management Simulation Week 3 Strategic Alignment & Functional Integration
Management Simulation Week 3 Strategic Alignment & Functional Integration
 What makes a decision strategic? ü Multi-functional in scope & consequences ü Requires choice & trade-offs, integration & alignment R&D Prdtn Mrktg
What makes a decision strategic? ü Multi-functional in scope & consequences ü Requires choice & trade-offs, integration & alignment R&D Prdtn Mrktg
 In order to execute & achieve selected growth & competitive strategies--Need to coordinate decisions across all Functional domains Production R&D Marketing Finance HR
In order to execute & achieve selected growth & competitive strategies--Need to coordinate decisions across all Functional domains Production R&D Marketing Finance HR
 Getting In-Sync w/ Functional Planning The goal of functional planning is to achieve a state of Internal Strategic Alignment FINANCE PRODUCTION MARKETING
Getting In-Sync w/ Functional Planning The goal of functional planning is to achieve a state of Internal Strategic Alignment FINANCE PRODUCTION MARKETING
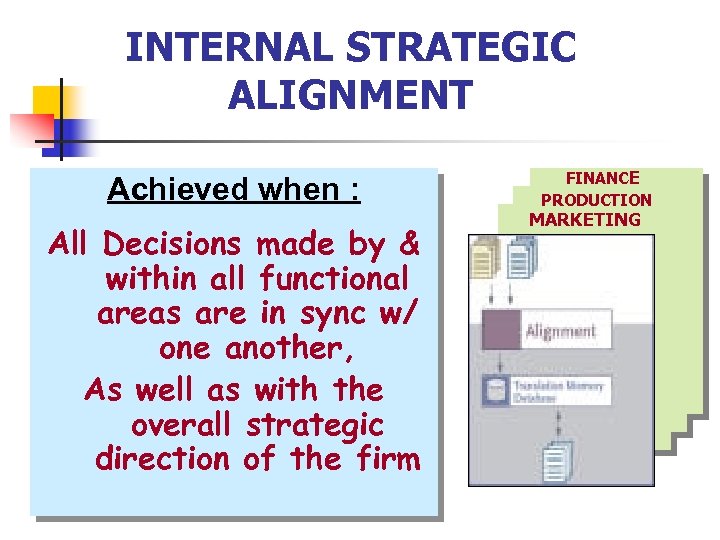 INTERNAL STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT Achieved when : All Decisions made by & within all functional areas are in sync w/ one another, As well as with the overall strategic direction of the firm FINANCE PRODUCTION MARKETING
INTERNAL STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT Achieved when : All Decisions made by & within all functional areas are in sync w/ one another, As well as with the overall strategic direction of the firm FINANCE PRODUCTION MARKETING
 Functional Planning Matrices Examples of: internal strategic alignment
Functional Planning Matrices Examples of: internal strategic alignment
 Functional Alignment: In Achieving Cost Efficiency
Functional Alignment: In Achieving Cost Efficiency
 Functional Alignment: Implementing Differentiation Strategy
Functional Alignment: Implementing Differentiation Strategy
 Functional Alignment: In Achieving Superior Innovation
Functional Alignment: In Achieving Superior Innovation
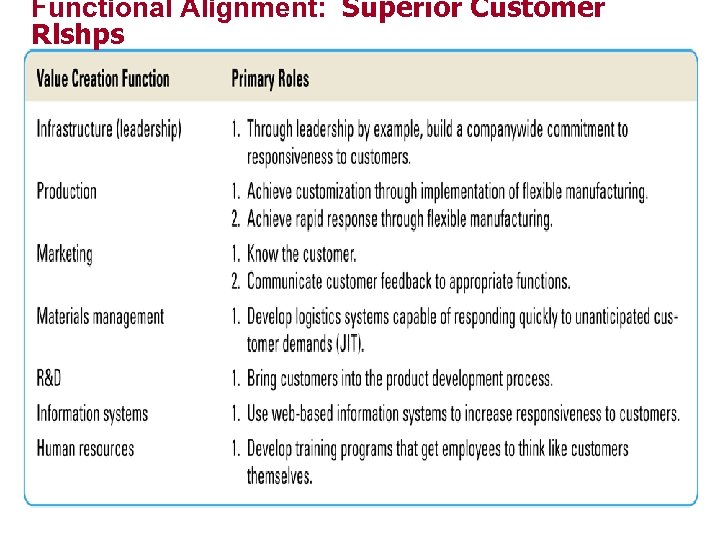 Functional Alignment: Superior Customer Rlshps
Functional Alignment: Superior Customer Rlshps
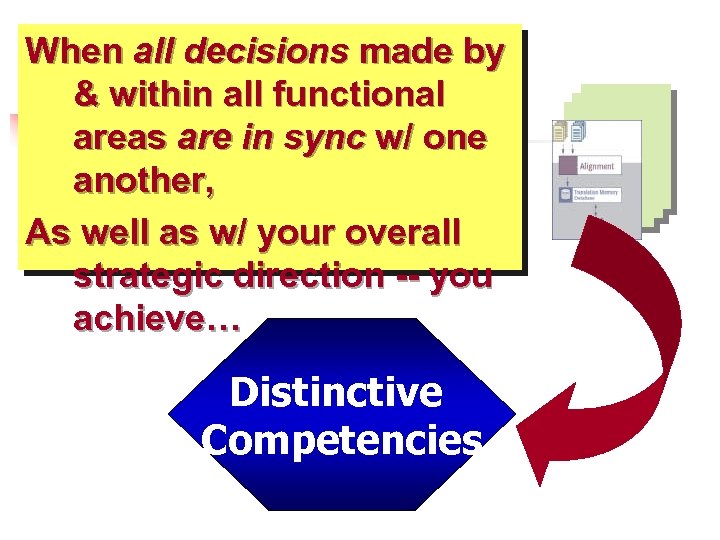 When all decisions made by & within all functional areas are in sync w/ one another, As well as w/ your overall strategic direction -- you achieve… Distinctive Competencies
When all decisions made by & within all functional areas are in sync w/ one another, As well as w/ your overall strategic direction -- you achieve… Distinctive Competencies
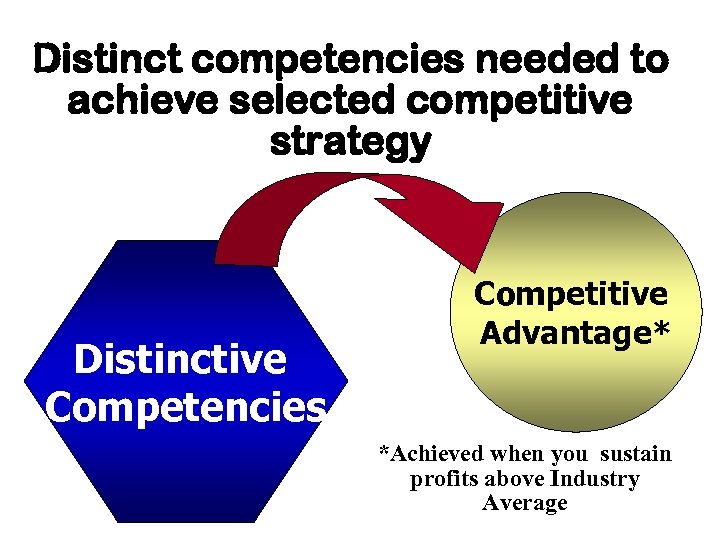 Distinct competencies needed to achieve selected competitive strategy Distinctive Competencies Competitive Advantage* *Achieved when you sustain profits above Industry Average
Distinct competencies needed to achieve selected competitive strategy Distinctive Competencies Competitive Advantage* *Achieved when you sustain profits above Industry Average
 Areas in which you can develop “Distinct Competencies” n n MARKETING: Awareness & Accessibility R&D: Product innovation & design PRODUCTION: Plant Automation & utilization Human Resources: Worker Expertise & Training
Areas in which you can develop “Distinct Competencies” n n MARKETING: Awareness & Accessibility R&D: Product innovation & design PRODUCTION: Plant Automation & utilization Human Resources: Worker Expertise & Training
 Distinct Competencies in automation & human resources could lead to a competitive advantage in cost leadership.
Distinct Competencies in automation & human resources could lead to a competitive advantage in cost leadership.
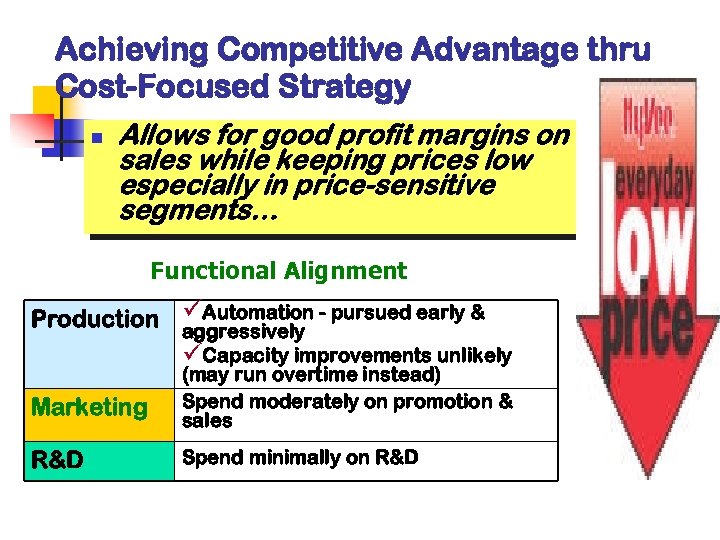 Achieving Competitive Advantage thru Cost-Focused Strategy n Allows for good profit margins on sales while keeping prices low especially in price-sensitive segments… Functional Alignment Production üAutomation - pursued early & aggressively üCapacity improvements unlikely Marketing (may run overtime instead) Spend moderately on promotion & sales R&D Spend minimally on R&D
Achieving Competitive Advantage thru Cost-Focused Strategy n Allows for good profit margins on sales while keeping prices low especially in price-sensitive segments… Functional Alignment Production üAutomation - pursued early & aggressively üCapacity improvements unlikely Marketing (may run overtime instead) Spend moderately on promotion & sales R&D Spend minimally on R&D
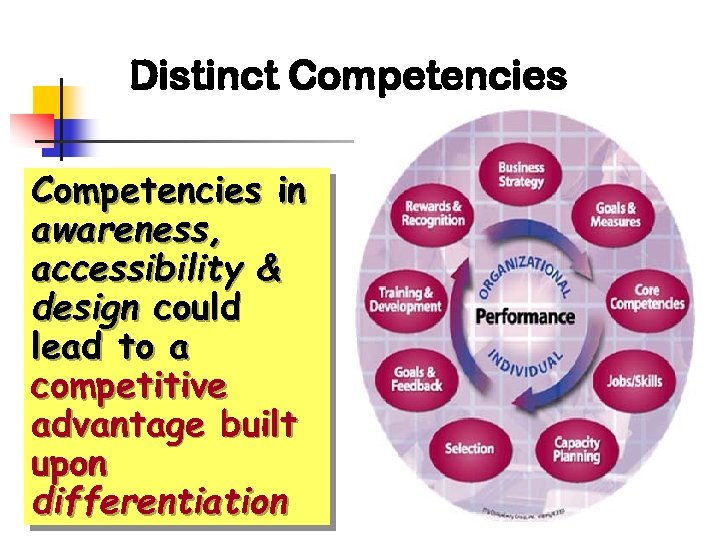 Distinct Competencies in awareness, accessibility & design could lead to a competitive advantage built upon differentiation
Distinct Competencies in awareness, accessibility & design could lead to a competitive advantage built upon differentiation
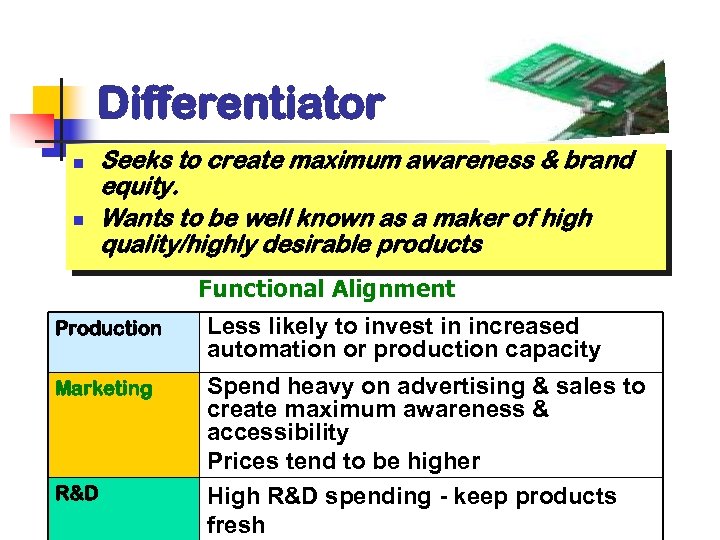 Differentiator n n Seeks to create maximum awareness & brand equity. Wants to be well known as a maker of high quality/highly desirable products Functional Alignment Production Less likely to invest in increased automation or production capacity Marketing Spend heavy on advertising & sales to create maximum awareness & accessibility Prices tend to be higher High R&D spending - keep products fresh R&D
Differentiator n n Seeks to create maximum awareness & brand equity. Wants to be well known as a maker of high quality/highly desirable products Functional Alignment Production Less likely to invest in increased automation or production capacity Marketing Spend heavy on advertising & sales to create maximum awareness & accessibility Prices tend to be higher High R&D spending - keep products fresh R&D
 Virtually all tactical mistakes that are made when implementing strategy are a consequence of the lack of synchronization of decisions made in at least two functional areas
Virtually all tactical mistakes that are made when implementing strategy are a consequence of the lack of synchronization of decisions made in at least two functional areas
 n You develop a new product but forget to buy plant & equipment for it…the year before it is to be launched… R&D and Production breakdown
n You develop a new product but forget to buy plant & equipment for it…the year before it is to be launched… R&D and Production breakdown
 n The company Marketing, takes an Production & emergency loan because Finance out of sync inventory levels increase…
n The company Marketing, takes an Production & emergency loan because Finance out of sync inventory levels increase…
 n You reposition a product from the High End to the Traditional segment, but do not address their material & labor costs… Marketing, R&D, and Production out of sync
n You reposition a product from the High End to the Traditional segment, but do not address their material & labor costs… Marketing, R&D, and Production out of sync
 n Financial decisions are made before knowing the budget demands of all R&D, Marketing and Production decisions… Everybody is out of sync!
n Financial decisions are made before knowing the budget demands of all R&D, Marketing and Production decisions… Everybody is out of sync!
 TODAY’S Begin drafting “functional alignment” strategic & tactical decisions matrices
TODAY’S Begin drafting “functional alignment” strategic & tactical decisions matrices
 Need to begin to determine the basic objectives & specific tactical decisions that need to be made within & across each management domain …in order to successfully implement your growth & competitive strategies
Need to begin to determine the basic objectives & specific tactical decisions that need to be made within & across each management domain …in order to successfully implement your growth & competitive strategies
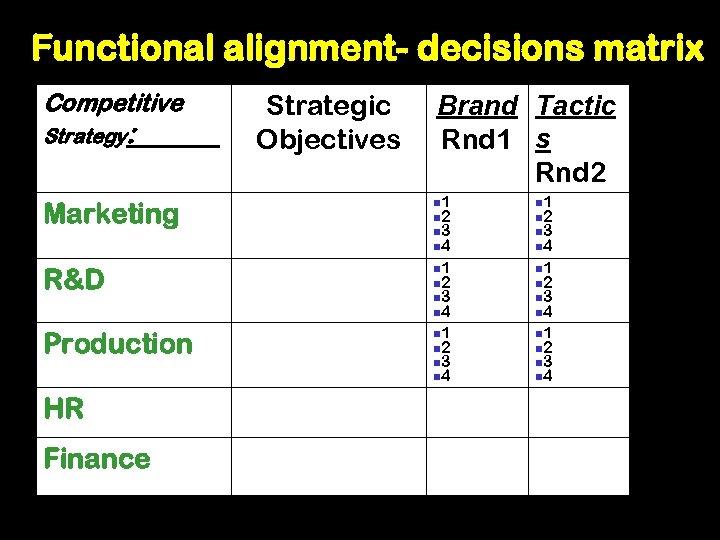 Functional alignment- decisions matrix Competitive Strategy: ______ Strategic Objectives Brand Tactic Rnd 1 s Rnd 2 Marketing n 1 n 2 n 3 n 4 R&D n 1 n 2 n 3 n 4 Production n 1 n 2 n 3 n 4 HR Finance
Functional alignment- decisions matrix Competitive Strategy: ______ Strategic Objectives Brand Tactic Rnd 1 s Rnd 2 Marketing n 1 n 2 n 3 n 4 R&D n 1 n 2 n 3 n 4 Production n 1 n 2 n 3 n 4 HR Finance
 EXAMPLE: Functional alignmentdecisions matrix BRAND: _new Competitive Strategy: Niche Differentiation Marketing R&D Production HR Finance Strategic Tactics Objectives Rnd 1 Rnd 2
EXAMPLE: Functional alignmentdecisions matrix BRAND: _new Competitive Strategy: Niche Differentiation Marketing R&D Production HR Finance Strategic Tactics Objectives Rnd 1 Rnd 2
 Competiti ve Strategy: ND Strategic Objectives Marketin Spend aggressively in promotion & sales in Hitech segments…. make our products easy for customers to find. . . price at a g premium. In the low tech segments we”ll exit gracefully, … as they exit the Low End R&D We will keep our existing Hi. Tech products (HI, PRF, & SIZE), phase out TRAD and LO, and introduce a new brand in the High End segment. Our goal is to offer technology oriented customers products that match their ideal criteria for positioning, age, and reliability Producti Grow capacity to meet demand … avoid overtime After products well positioned, investigate modest increases in automation on levels to improve margins, but keep ability to reposition products HR Finance Spend aggressively on recruitment, training; minimize labor T/O w/ +wage & benefit packages; Focus TQM & Process initiatives on reducing labor & material costs, R&D time and enhancing effectiveness of promo & sales budgets… We”ll finance investments primarily thru stock issues, retained earnings, supplement w/ bond offerings as needed. . When our
Competiti ve Strategy: ND Strategic Objectives Marketin Spend aggressively in promotion & sales in Hitech segments…. make our products easy for customers to find. . . price at a g premium. In the low tech segments we”ll exit gracefully, … as they exit the Low End R&D We will keep our existing Hi. Tech products (HI, PRF, & SIZE), phase out TRAD and LO, and introduce a new brand in the High End segment. Our goal is to offer technology oriented customers products that match their ideal criteria for positioning, age, and reliability Producti Grow capacity to meet demand … avoid overtime After products well positioned, investigate modest increases in automation on levels to improve margins, but keep ability to reposition products HR Finance Spend aggressively on recruitment, training; minimize labor T/O w/ +wage & benefit packages; Focus TQM & Process initiatives on reducing labor & material costs, R&D time and enhancing effectiveness of promo & sales budgets… We”ll finance investments primarily thru stock issues, retained earnings, supplement w/ bond offerings as needed. . When our
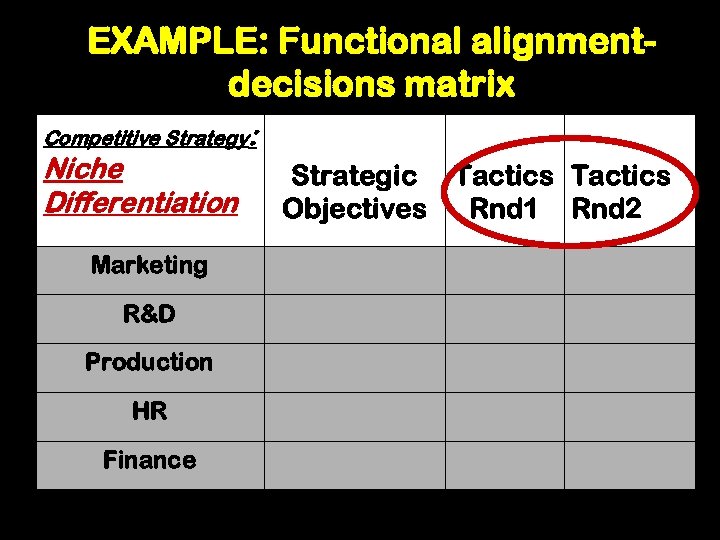 EXAMPLE: Functional alignmentdecisions matrix Competitive Strategy: Niche Differentiation Marketing R&D Production HR Finance Strategic Tactics Objectives Rnd 1 Rnd 2
EXAMPLE: Functional alignmentdecisions matrix Competitive Strategy: Niche Differentiation Marketing R&D Production HR Finance Strategic Tactics Objectives Rnd 1 Rnd 2
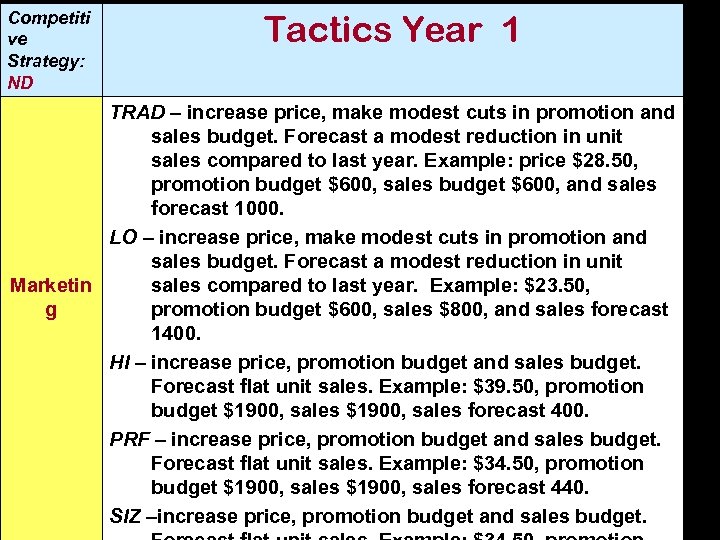 Competiti ve Strategy: ND Tactics Year 1 TRAD – increase price, make modest cuts in promotion and sales budget. Forecast a modest reduction in unit sales compared to last year. Example: price $28. 50, promotion budget $600, sales budget $600, and sales forecast 1000. LO – increase price, make modest cuts in promotion and sales budget. Forecast a modest reduction in unit sales compared to last year. Example: $23. 50, Marketin promotion budget $600, sales $800, and sales forecast g 1400. HI – increase price, promotion budget and sales budget. Forecast flat unit sales. Example: $39. 50, promotion budget $1900, sales forecast 400. PRF – increase price, promotion budget and sales budget. Forecast flat unit sales. Example: $34. 50, promotion budget $1900, sales forecast 440. SIZ –increase price, promotion budget and sales budget.
Competiti ve Strategy: ND Tactics Year 1 TRAD – increase price, make modest cuts in promotion and sales budget. Forecast a modest reduction in unit sales compared to last year. Example: price $28. 50, promotion budget $600, sales budget $600, and sales forecast 1000. LO – increase price, make modest cuts in promotion and sales budget. Forecast a modest reduction in unit sales compared to last year. Example: $23. 50, Marketin promotion budget $600, sales $800, and sales forecast g 1400. HI – increase price, promotion budget and sales budget. Forecast flat unit sales. Example: $39. 50, promotion budget $1900, sales forecast 400. PRF – increase price, promotion budget and sales budget. Forecast flat unit sales. Example: $34. 50, promotion budget $1900, sales forecast 440. SIZ –increase price, promotion budget and sales budget.
 Competitiv e Strategy: N D R&D Tactics Year 1 TRAD – tweak positioning to reduce age. Reduce reliability to reduce material cost. Example: Increase Performance by 0. 1 and reduce MTBF by 1000 hours. LO – leave positioning alone, allowing the product to age further. Reduce reliability to reduce material cost. Example: reduce MTBF by 1000 hours. . HI– improve positioning and reduce age. Hold reliability (MTBF) steady. Example: reduce Size by 1. 2, and increase Performance by 1. 2. PRF – improve positioning and reduce age. Improve reliability to enhance demand. Example: Increase Performance by 1. 4, reduce Size by 0. 5, and increase MTBF by 1000 hours. SIZE – improve positioning and reduce age. Hold reliability (MTBF) steady. Example: Reduce Size by 1. 4, and increase Performance by 0. 5. New HI – Launch a new High End product, with a project length of 20 to 23 months (no later than December of next
Competitiv e Strategy: N D R&D Tactics Year 1 TRAD – tweak positioning to reduce age. Reduce reliability to reduce material cost. Example: Increase Performance by 0. 1 and reduce MTBF by 1000 hours. LO – leave positioning alone, allowing the product to age further. Reduce reliability to reduce material cost. Example: reduce MTBF by 1000 hours. . HI– improve positioning and reduce age. Hold reliability (MTBF) steady. Example: reduce Size by 1. 2, and increase Performance by 1. 2. PRF – improve positioning and reduce age. Improve reliability to enhance demand. Example: Increase Performance by 1. 4, reduce Size by 0. 5, and increase MTBF by 1000 hours. SIZE – improve positioning and reduce age. Hold reliability (MTBF) steady. Example: Reduce Size by 1. 4, and increase Performance by 0. 5. New HI – Launch a new High End product, with a project length of 20 to 23 months (no later than December of next
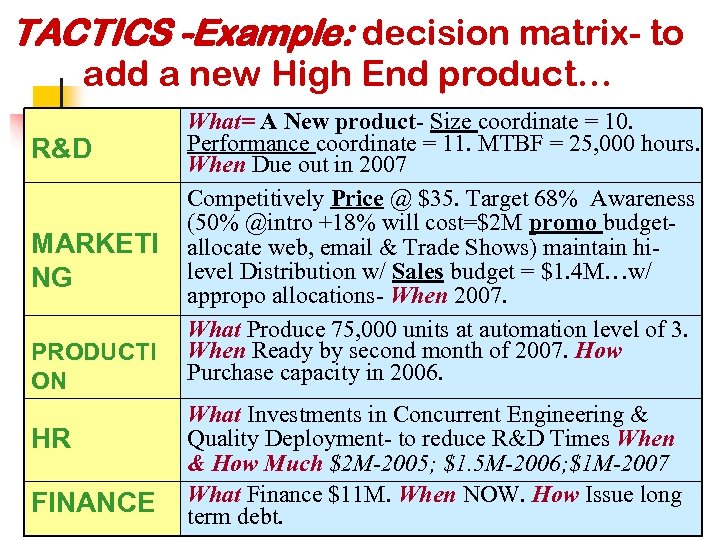 TACTICS -Example: decision matrix- to add a new High End product… R&D MARKETI NG PRODUCTI ON HR FINANCE What= A New product- Size coordinate = 10. Performance coordinate = 11. MTBF = 25, 000 hours. When Due out in 2007 Competitively Price @ $35. Target 68% Awareness (50% @intro +18% will cost=$2 M promo budgetallocate web, email & Trade Shows) maintain hilevel Distribution w/ Sales budget = $1. 4 M…w/ appropo allocations- When 2007. What Produce 75, 000 units at automation level of 3. When Ready by second month of 2007. How Purchase capacity in 2006. What Investments in Concurrent Engineering & Quality Deployment- to reduce R&D Times When & How Much $2 M-2005; $1. 5 M-2006; $1 M-2007 What Finance $11 M. When NOW. How Issue long term debt.
TACTICS -Example: decision matrix- to add a new High End product… R&D MARKETI NG PRODUCTI ON HR FINANCE What= A New product- Size coordinate = 10. Performance coordinate = 11. MTBF = 25, 000 hours. When Due out in 2007 Competitively Price @ $35. Target 68% Awareness (50% @intro +18% will cost=$2 M promo budgetallocate web, email & Trade Shows) maintain hilevel Distribution w/ Sales budget = $1. 4 M…w/ appropo allocations- When 2007. What Produce 75, 000 units at automation level of 3. When Ready by second month of 2007. How Purchase capacity in 2006. What Investments in Concurrent Engineering & Quality Deployment- to reduce R&D Times When & How Much $2 M-2005; $1. 5 M-2006; $1 M-2007 What Finance $11 M. When NOW. How Issue long term debt.
 Competitiv e Strategy: N D Productio n Tactics Year 1 For each product, schedule production w/ formula: (Unit. Sales. Forecast X 112%) – Inventory. On. Hand. – sell 100 to 300 units of capacity of Hi end prdt-, and given our new Hi end product it is unlikely we”ll need 900 units of capacity in the future. Make no other plant improvements to capacity or automation UNTIL YEAR 2 WHEN New High End product
Competitiv e Strategy: N D Productio n Tactics Year 1 For each product, schedule production w/ formula: (Unit. Sales. Forecast X 112%) – Inventory. On. Hand. – sell 100 to 300 units of capacity of Hi end prdt-, and given our new Hi end product it is unlikely we”ll need 900 units of capacity in the future. Make no other plant improvements to capacity or automation UNTIL YEAR 2 WHEN New High End product
 Competiti ve Strategy: ND Tactics Year 1 HR Invest $1. 5 million per selected – critical TQM (Quality Function Deployment; CCE ) & Process Initiatives (CPI, JIT, QIT, Channel Support & Concurrent Engineering) Financ e On proforma Balance Sheet-- add together Cash and Inventory accounts. -- Keep between 15% and 20% of balance sheet assets in Cash plus Inventory. Drive Cash position until it roughly equals your Inventory position. …. If you are cash poor, issue additional stock to cover the investment in new capacity. If
Competiti ve Strategy: ND Tactics Year 1 HR Invest $1. 5 million per selected – critical TQM (Quality Function Deployment; CCE ) & Process Initiatives (CPI, JIT, QIT, Channel Support & Concurrent Engineering) Financ e On proforma Balance Sheet-- add together Cash and Inventory accounts. -- Keep between 15% and 20% of balance sheet assets in Cash plus Inventory. Drive Cash position until it roughly equals your Inventory position. …. If you are cash poor, issue additional stock to cover the investment in new capacity. If
 Tonight’s Begin drafting “functionally aligned” strategic & tactical decisions matrices Competitiv Strategic e Strategy Objective s Brand Rnd 1 Tactic s Rnd 2 Marketing n 1 n 2 n 3 n 4 R&D n 1 n 2 n 3 n 4 Production n 1 n 2 n 3 n 4 HR Finance
Tonight’s Begin drafting “functionally aligned” strategic & tactical decisions matrices Competitiv Strategic e Strategy Objective s Brand Rnd 1 Tactic s Rnd 2 Marketing n 1 n 2 n 3 n 4 R&D n 1 n 2 n 3 n 4 Production n 1 n 2 n 3 n 4 HR Finance