58efdd3f7d8a891be664013825d4d7f4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 99
 Lymphoma
Lymphoma
 Haematological Neoplasia - Overview n Leukemias: Acute & Chronic, n Myeloid & Lymphoid n n Lymphomas: n n Hodgkins & Non-Hodgkins Premalignant: Myeloproliverative - MPS n Myelodysplastic - MDS n
Haematological Neoplasia - Overview n Leukemias: Acute & Chronic, n Myeloid & Lymphoid n n Lymphomas: n n Hodgkins & Non-Hodgkins Premalignant: Myeloproliverative - MPS n Myelodysplastic - MDS n
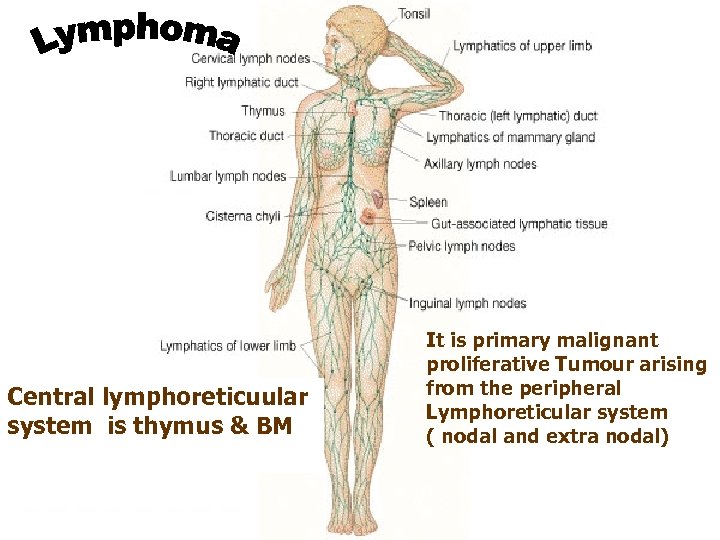 Central lymphoreticuular system is thymus & BM It is primary malignant proliferative Tumour arising from the peripheral Lymphoreticular system ( nodal and extra nodal)
Central lymphoreticuular system is thymus & BM It is primary malignant proliferative Tumour arising from the peripheral Lymphoreticular system ( nodal and extra nodal)
 Hodgkin lymphoma Thomas Hodgkin (1798 -1866)
Hodgkin lymphoma Thomas Hodgkin (1798 -1866)
 Epidemiology of lymphomas n n n 5 th most frequently diagnosed cancer overall for both males and females > females incidence NHL increasing over time n Hodgkin lymphoma stable n less frequent than non-Hodgkin lymphoma n overall M>F = 3 : 1 n peak incidence in 3 rd decade n
Epidemiology of lymphomas n n n 5 th most frequently diagnosed cancer overall for both males and females > females incidence NHL increasing over time n Hodgkin lymphoma stable n less frequent than non-Hodgkin lymphoma n overall M>F = 3 : 1 n peak incidence in 3 rd decade n
 Associated (etiological? ) factors n n n EBV infection smaller family size higher socio-economic status caucasian > non-caucasian possible genetic predisposition other: HIV? occupation? herbicides?
Associated (etiological? ) factors n n n EBV infection smaller family size higher socio-economic status caucasian > non-caucasian possible genetic predisposition other: HIV? occupation? herbicides?
 Hodgkin lymphoma n n n cell of origin: germinal centre B-cell Reed-Sternberg cells (or RS variants) in the affected tissues most cells in affected lymph node are polyclonal reactive lymphoid cells, not neoplastic cells
Hodgkin lymphoma n n n cell of origin: germinal centre B-cell Reed-Sternberg cells (or RS variants) in the affected tissues most cells in affected lymph node are polyclonal reactive lymphoid cells, not neoplastic cells
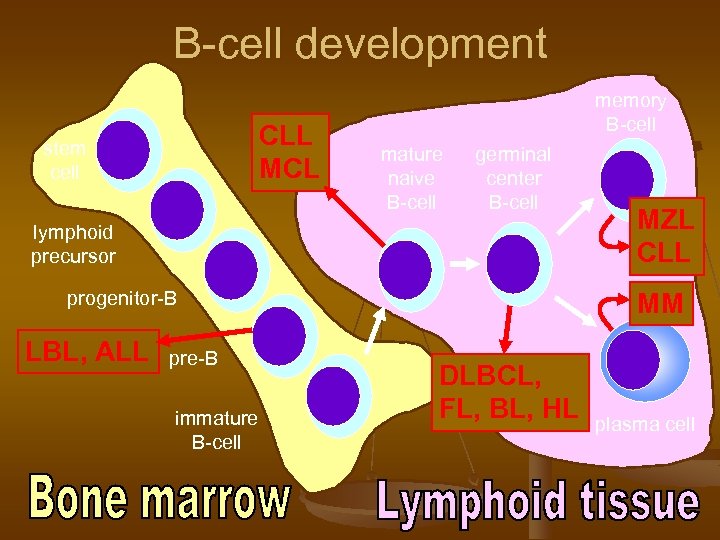 B-cell development CLL MCL stem cell memory B-cell mature naive B-cell germinal center B-cell lymphoid precursor progenitor-B LBL, ALL pre-B immature B-cell MZL CLL MM DLBCL, FL, BL, HL plasma cell
B-cell development CLL MCL stem cell memory B-cell mature naive B-cell germinal center B-cell lymphoid precursor progenitor-B LBL, ALL pre-B immature B-cell MZL CLL MM DLBCL, FL, BL, HL plasma cell
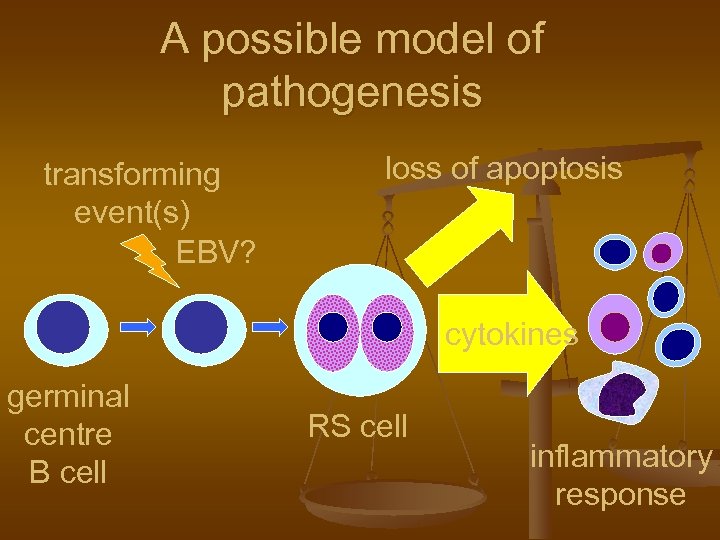 A possible model of pathogenesis transforming event(s) EBV? loss of apoptosis cytokines germinal centre B cell RS cell inflammatory response
A possible model of pathogenesis transforming event(s) EBV? loss of apoptosis cytokines germinal centre B cell RS cell inflammatory response
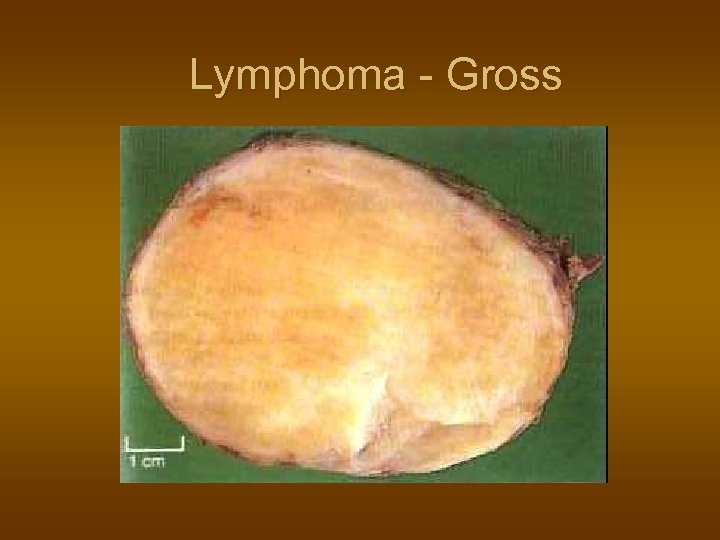 Lymphoma - Gross
Lymphoma - Gross
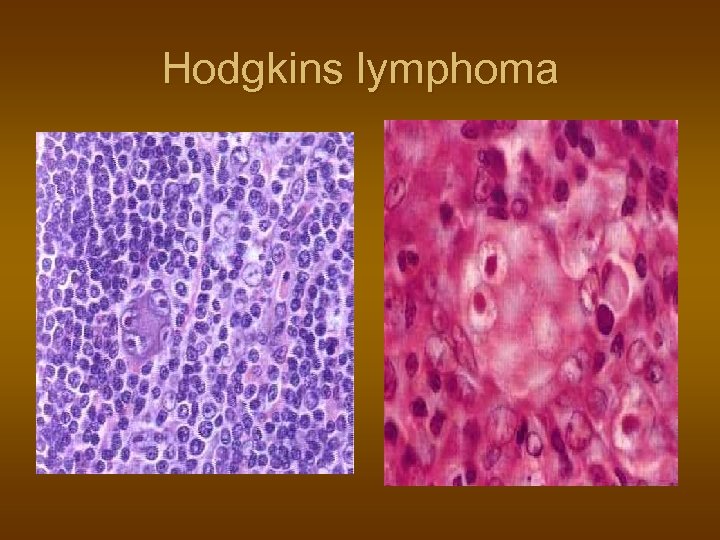 Hodgkins lymphoma
Hodgkins lymphoma
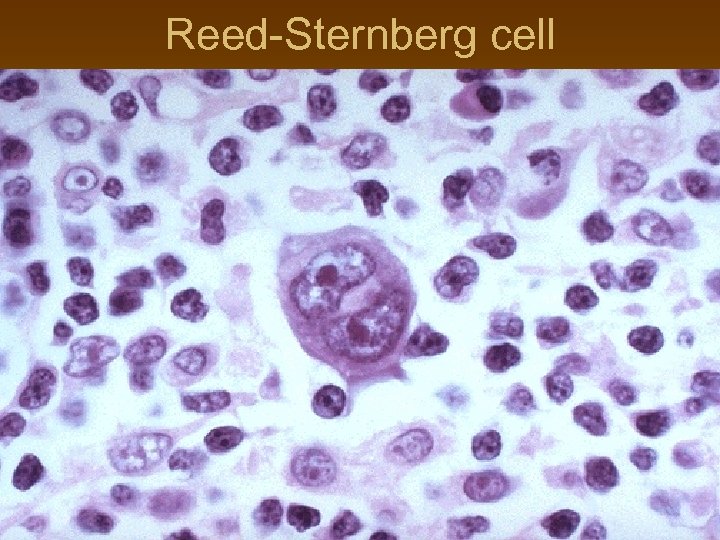 Reed-Sternberg cell
Reed-Sternberg cell
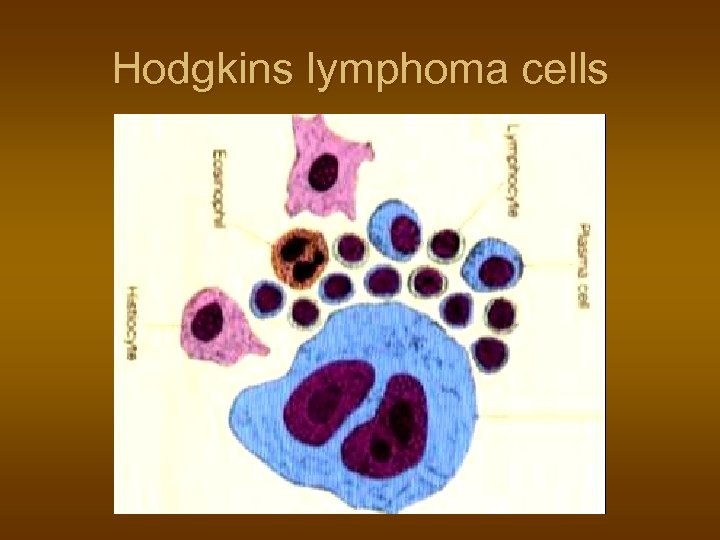 Hodgkins lymphoma cells
Hodgkins lymphoma cells
 Reed-Sternberg cell The Scream, 1893 Edvard Munch
Reed-Sternberg cell The Scream, 1893 Edvard Munch
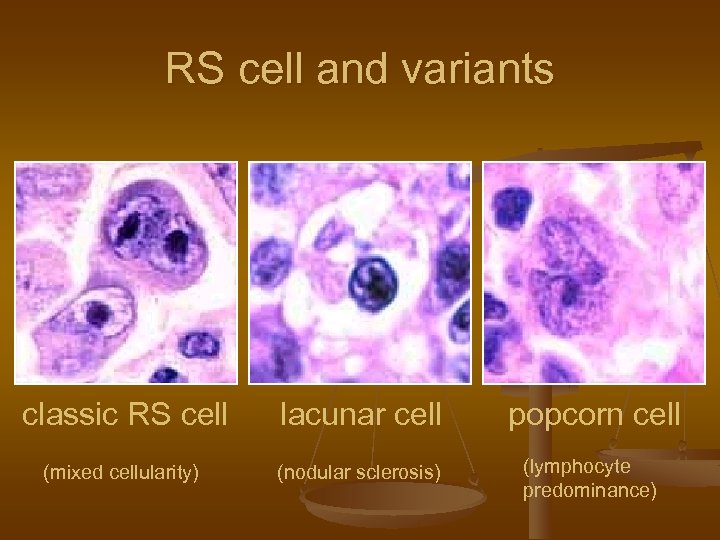 RS cell and variants classic RS cell lacunar cell popcorn cell (mixed cellularity) (nodular sclerosis) (lymphocyte predominance)
RS cell and variants classic RS cell lacunar cell popcorn cell (mixed cellularity) (nodular sclerosis) (lymphocyte predominance)
 Hodgkins Lymphoma: n n Painless, firm lymphadenopathy, Fever* Eosinophilia Only Reed-Sternberg cells malignant (B cell) Classification(WHO): Classic Hodgkins: n n n Lymphocyte predominant. Nodular Sclerosis. Mixed cellularity. Lymphocyte depleted. Nodular lymph. predominant (non-classic)
Hodgkins Lymphoma: n n Painless, firm lymphadenopathy, Fever* Eosinophilia Only Reed-Sternberg cells malignant (B cell) Classification(WHO): Classic Hodgkins: n n n Lymphocyte predominant. Nodular Sclerosis. Mixed cellularity. Lymphocyte depleted. Nodular lymph. predominant (non-classic)
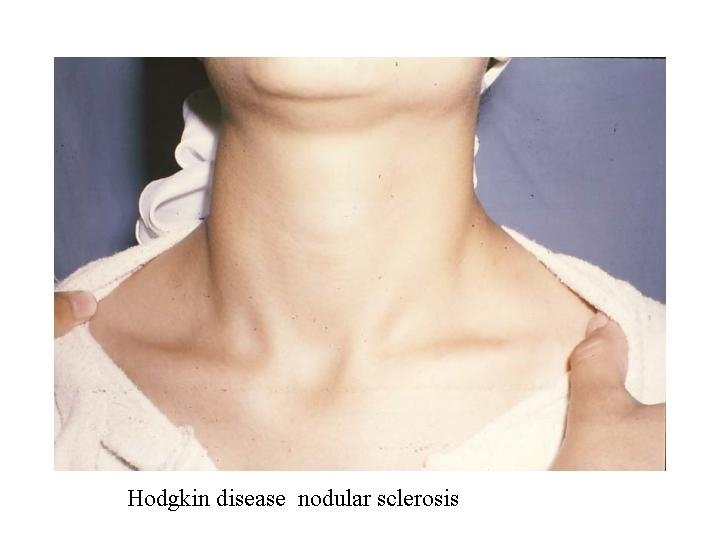
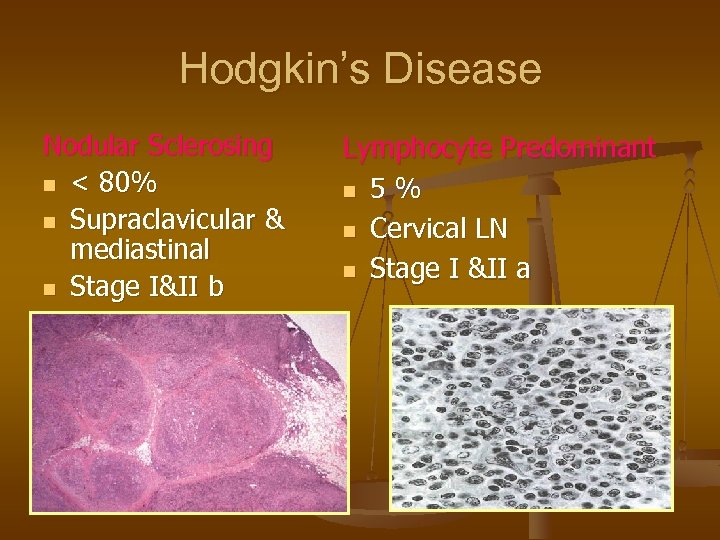 Hodgkin’s Disease Nodular Sclerosing n < 80% n Supraclavicular & mediastinal n Stage I&II b Lymphocyte Predominant n 5 % n Cervical LN n Stage I &II a
Hodgkin’s Disease Nodular Sclerosing n < 80% n Supraclavicular & mediastinal n Stage I&II b Lymphocyte Predominant n 5 % n Cervical LN n Stage I &II a
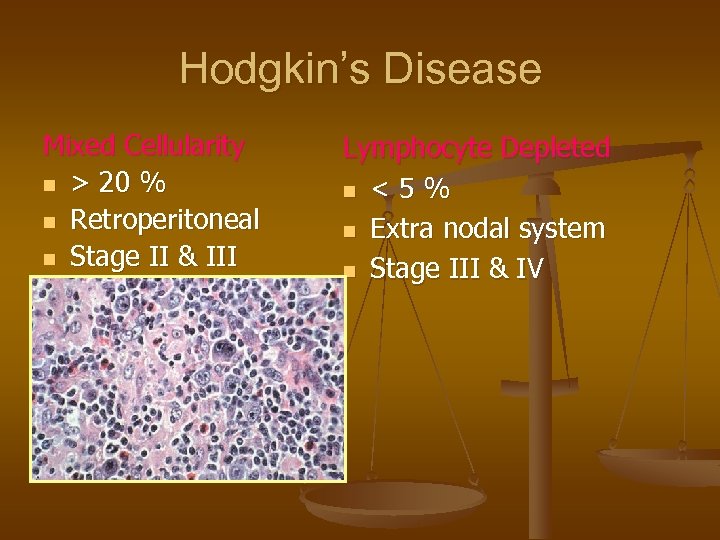 Hodgkin’s Disease Mixed Cellularity n > 20 % n Retroperitoneal n Stage II & III Lymphocyte Depleted n < 5 % n Extra nodal system n Stage III & IV
Hodgkin’s Disease Mixed Cellularity n > 20 % n Retroperitoneal n Stage II & III Lymphocyte Depleted n < 5 % n Extra nodal system n Stage III & IV
 Hodgkin’s Disease n Presentation n Asymmetric lymphadenopathy— 90% Firm, rubbery n Supraclavicular fossa n n n Spleen, liver (extranodal sites relatively uncommon except in advanced disease Constitutional symptoms— 1/3 of cases n Fever, night sweats, anorexia, weakness, weight loss
Hodgkin’s Disease n Presentation n Asymmetric lymphadenopathy— 90% Firm, rubbery n Supraclavicular fossa n n n Spleen, liver (extranodal sites relatively uncommon except in advanced disease Constitutional symptoms— 1/3 of cases n Fever, night sweats, anorexia, weakness, weight loss
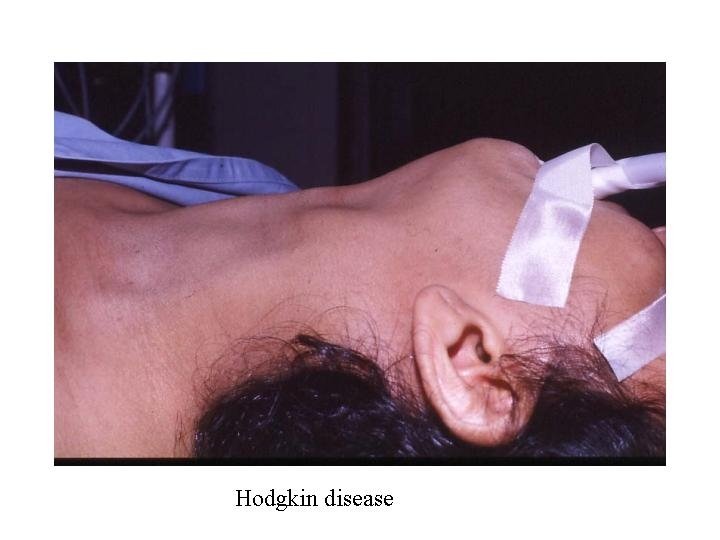
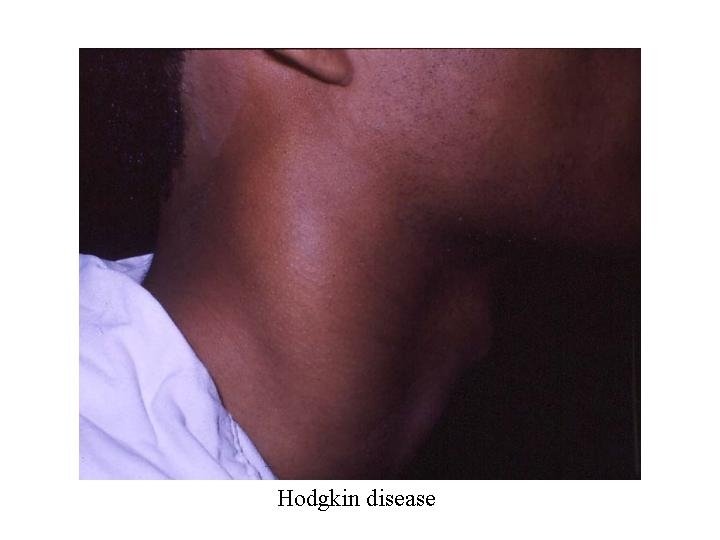
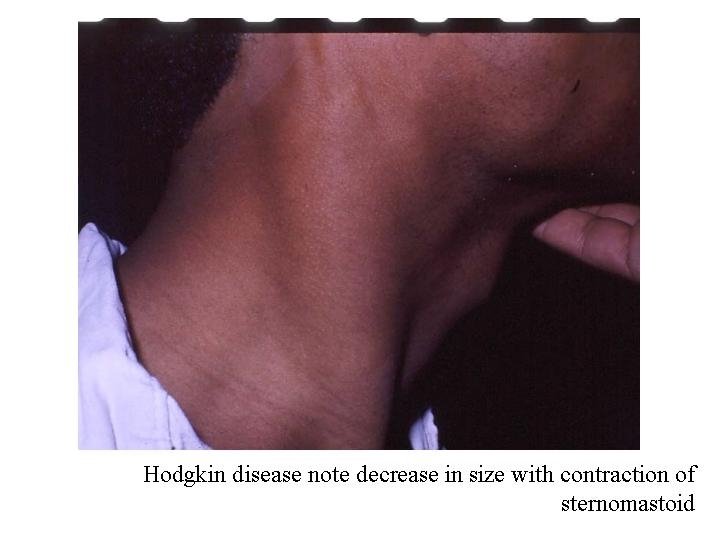
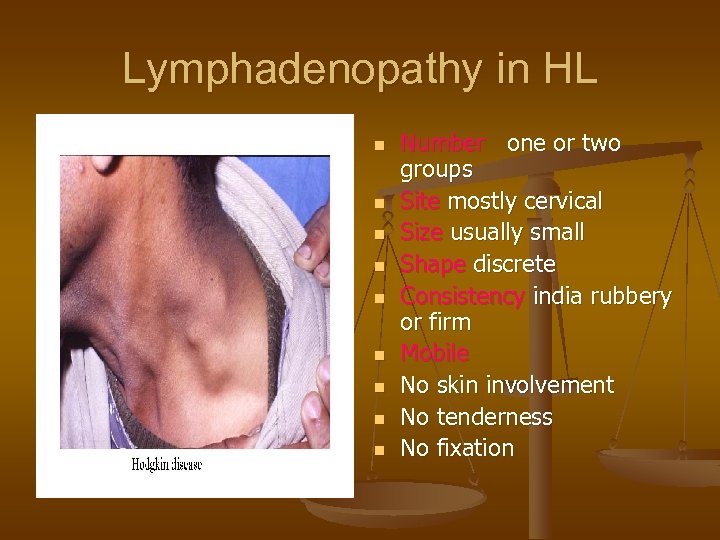 Lymphadenopathy in HL n n n n n Number one or two groups Site mostly cervical Size usually small Shape discrete Consistency india rubbery or firm Mobile No skin involvement No tenderness No fixation
Lymphadenopathy in HL n n n n n Number one or two groups Site mostly cervical Size usually small Shape discrete Consistency india rubbery or firm Mobile No skin involvement No tenderness No fixation
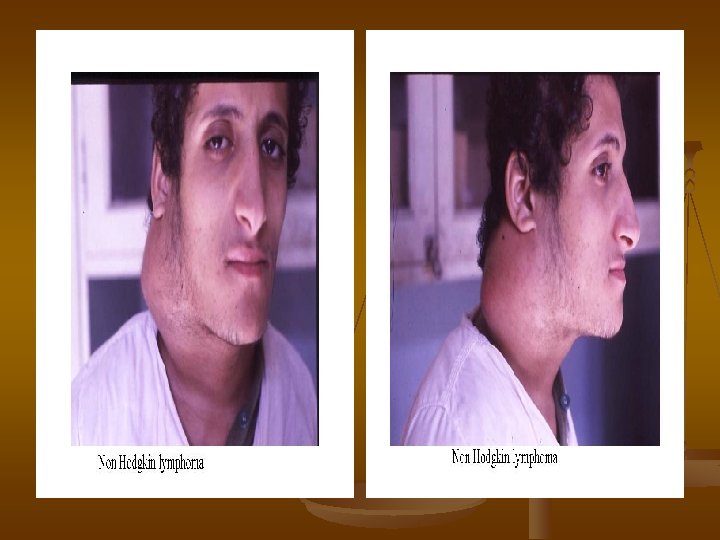
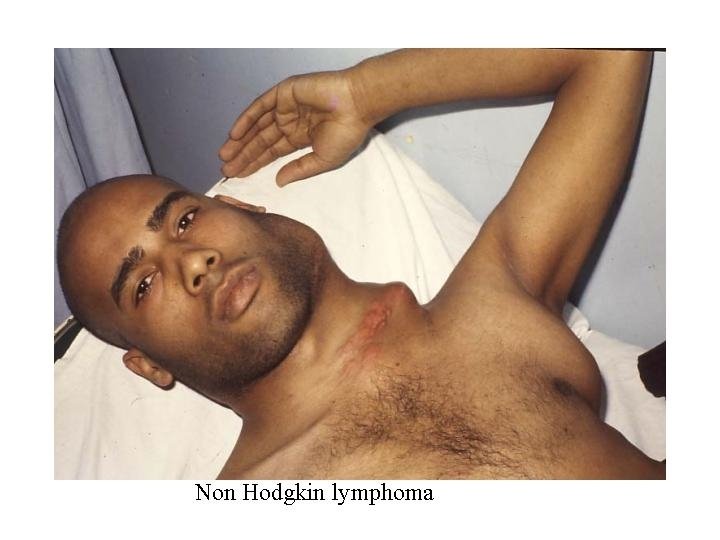
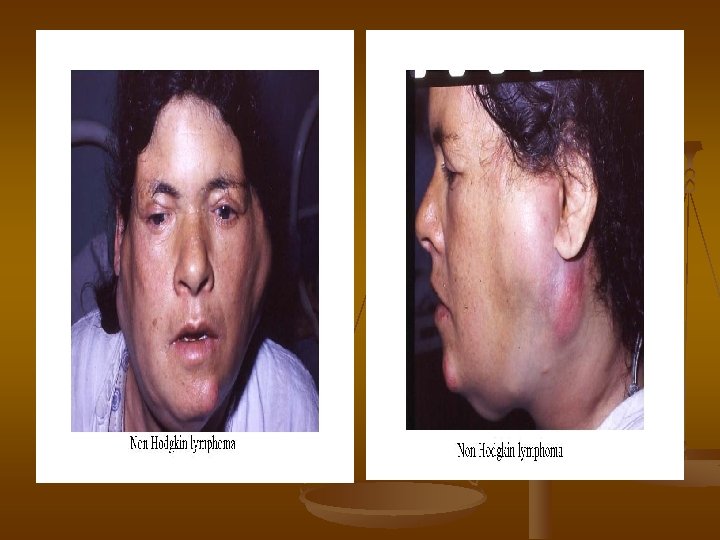
 Lymphadenopathy in NHL n n n n n Number multiple Site mostly extra nodal Size usually large Shape matted Consistency hard & cystic Fixed skin stretched & red tender fixation
Lymphadenopathy in NHL n n n n n Number multiple Site mostly extra nodal Size usually large Shape matted Consistency hard & cystic Fixed skin stretched & red tender fixation
 Lymphadenopathy in Lymphoma HL n n n n n Number one or two groups Site mostly cervical Size usually small Shape discrete Consistency india rubbery or firm Mobile No skin involvement No tenderness No fixation NHL n n n n n Number multiple Site mostly extra nodal Size usually large Shape matted Consistency hard & cystic Fixed skin stretched & red tender fixation
Lymphadenopathy in Lymphoma HL n n n n n Number one or two groups Site mostly cervical Size usually small Shape discrete Consistency india rubbery or firm Mobile No skin involvement No tenderness No fixation NHL n n n n n Number multiple Site mostly extra nodal Size usually large Shape matted Consistency hard & cystic Fixed skin stretched & red tender fixation
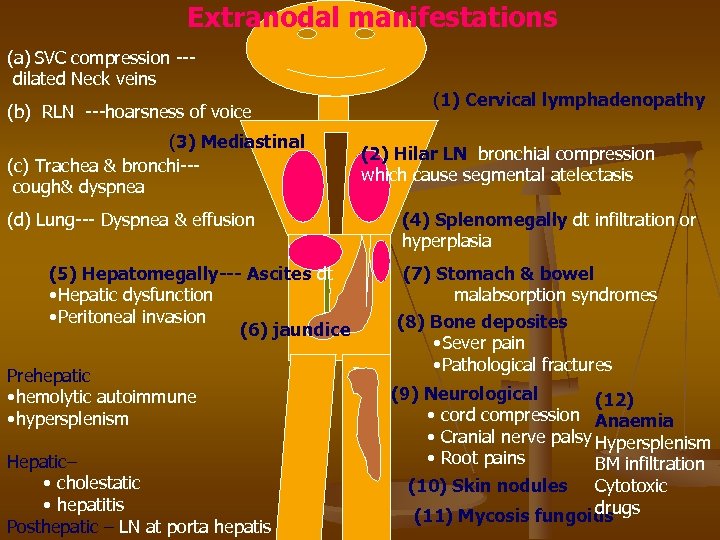
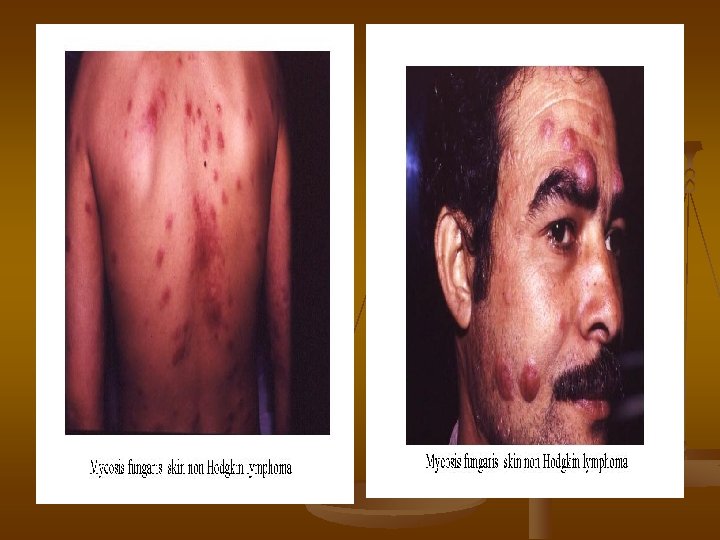
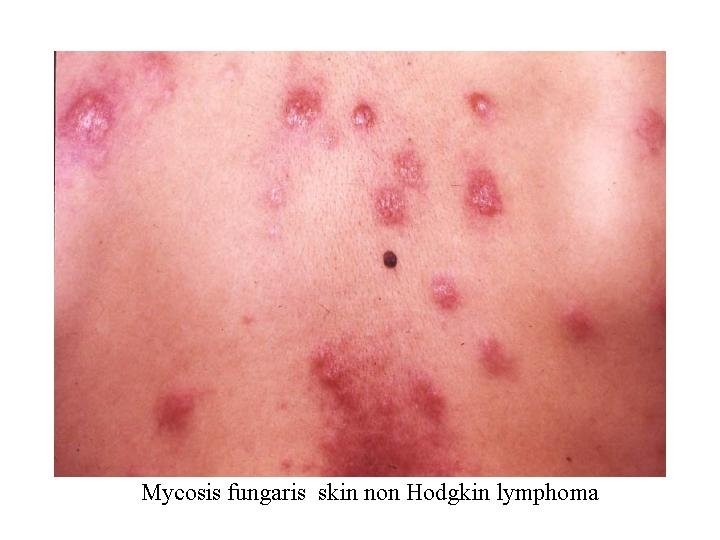
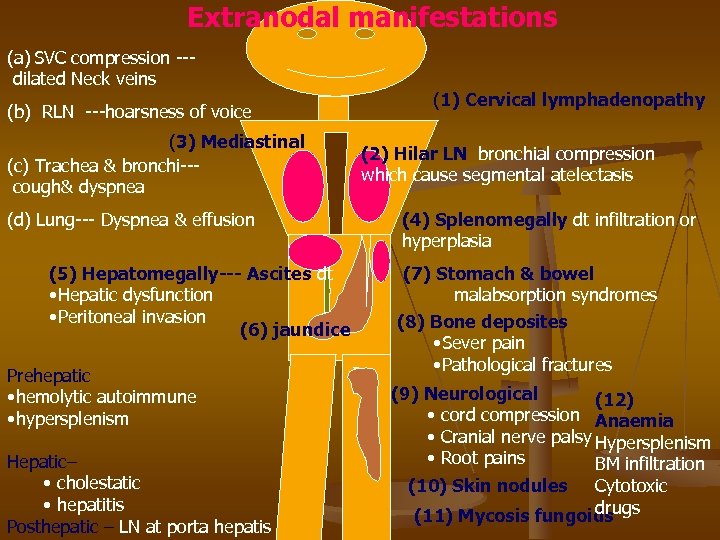 Extranodal manifestations (a) SVC compression --dilated Neck veins (b) RLN ---hoarsness of voice (3) Mediastinal (c) Trachea & bronchi--cough& dyspnea (d) Lung--- Dyspnea & effusion (5) Hepatomegally--- Ascites dt • Hepatic dysfunction • Peritoneal invasion (6) jaundice Prehepatic • hemolytic autoimmune • hypersplenism Hepatic– • cholestatic • hepatitis Posthepatic – LN at porta hepatis (1) Cervical lymphadenopathy (2) Hilar LN bronchial compression which cause segmental atelectasis (4) Splenomegally dt infiltration or hyperplasia (7) Stomach & bowel malabsorption syndromes (8) Bone deposites • Sever pain • Pathological fractures (9) Neurological (12) • cord compression Anaemia • Cranial nerve palsy Hypersplenism • Root pains BM infiltration Cytotoxic drugs (11) Mycosis fungoids (10) Skin nodules
Extranodal manifestations (a) SVC compression --dilated Neck veins (b) RLN ---hoarsness of voice (3) Mediastinal (c) Trachea & bronchi--cough& dyspnea (d) Lung--- Dyspnea & effusion (5) Hepatomegally--- Ascites dt • Hepatic dysfunction • Peritoneal invasion (6) jaundice Prehepatic • hemolytic autoimmune • hypersplenism Hepatic– • cholestatic • hepatitis Posthepatic – LN at porta hepatis (1) Cervical lymphadenopathy (2) Hilar LN bronchial compression which cause segmental atelectasis (4) Splenomegally dt infiltration or hyperplasia (7) Stomach & bowel malabsorption syndromes (8) Bone deposites • Sever pain • Pathological fractures (9) Neurological (12) • cord compression Anaemia • Cranial nerve palsy Hypersplenism • Root pains BM infiltration Cytotoxic drugs (11) Mycosis fungoids (10) Skin nodules
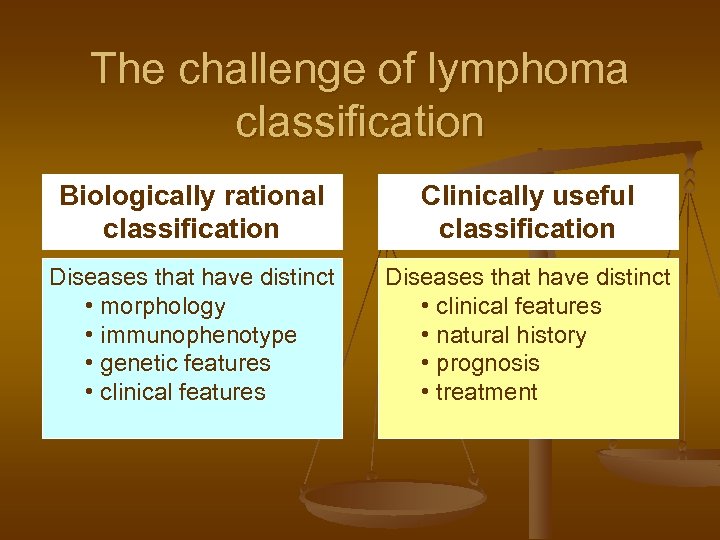 The challenge of lymphoma classification Biologically rational classification Clinically useful classification Diseases that have distinct • morphology • immunophenotype • genetic features • clinical features Diseases that have distinct • clinical features • natural history • prognosis • treatment
The challenge of lymphoma classification Biologically rational classification Clinically useful classification Diseases that have distinct • morphology • immunophenotype • genetic features • clinical features Diseases that have distinct • clinical features • natural history • prognosis • treatment
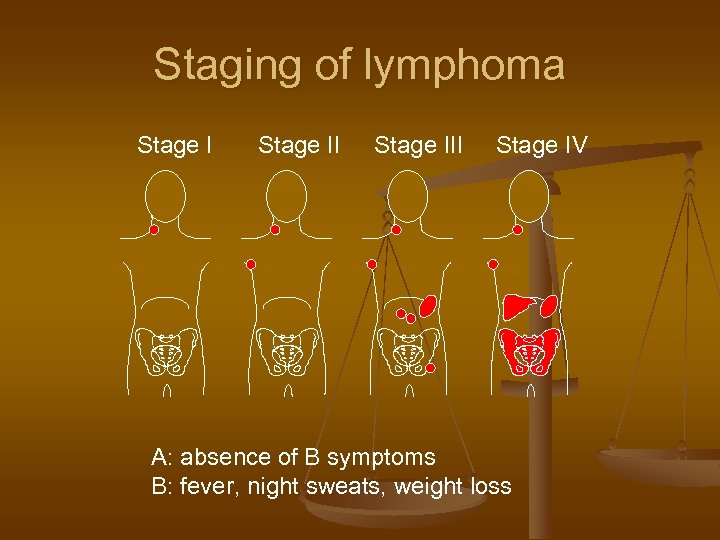 Staging of lymphoma Stage III Stage IV A: absence of B symptoms B: fever, night sweats, weight loss
Staging of lymphoma Stage III Stage IV A: absence of B symptoms B: fever, night sweats, weight loss
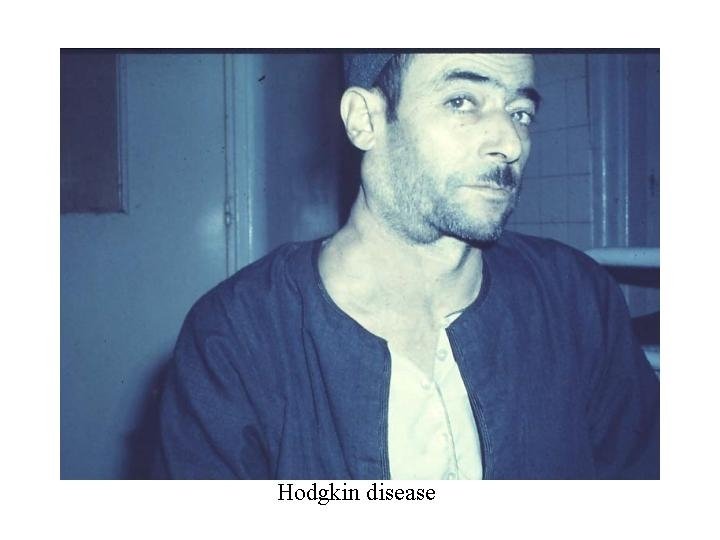
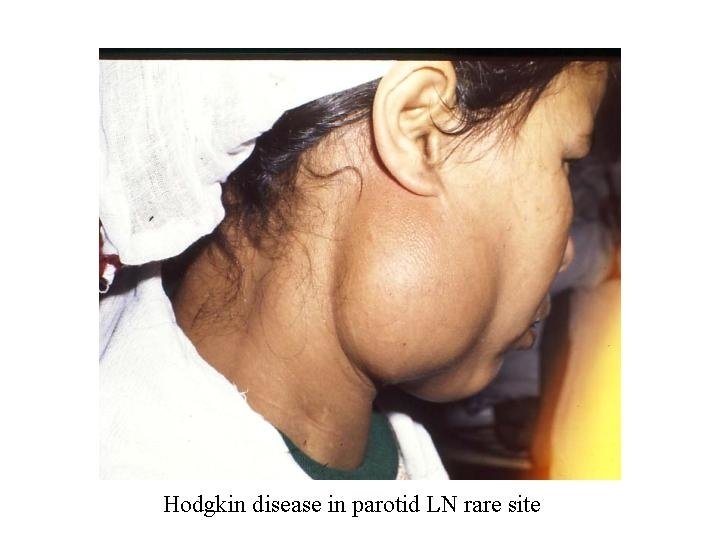
 Hodgkin Disease
Hodgkin Disease
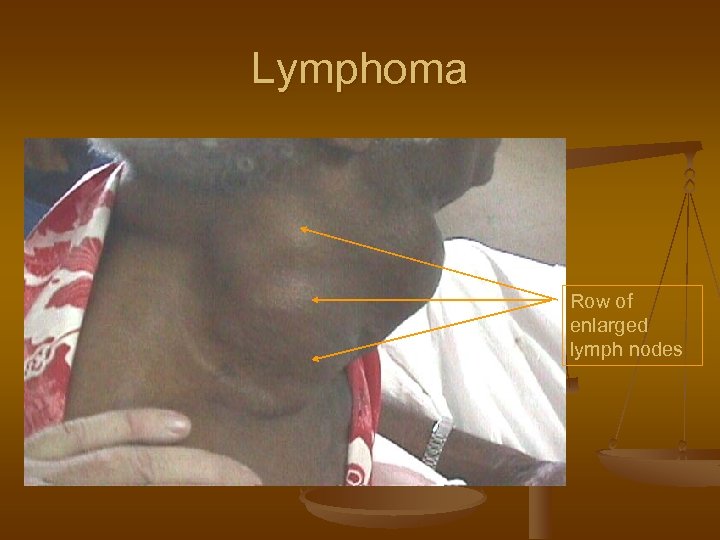 Lymphoma Row of enlarged lymph nodes
Lymphoma Row of enlarged lymph nodes
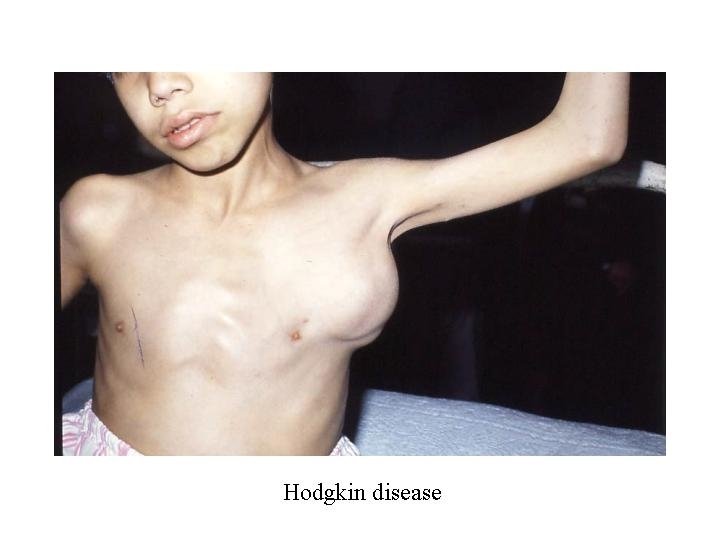
 Diagnosis:
Diagnosis:
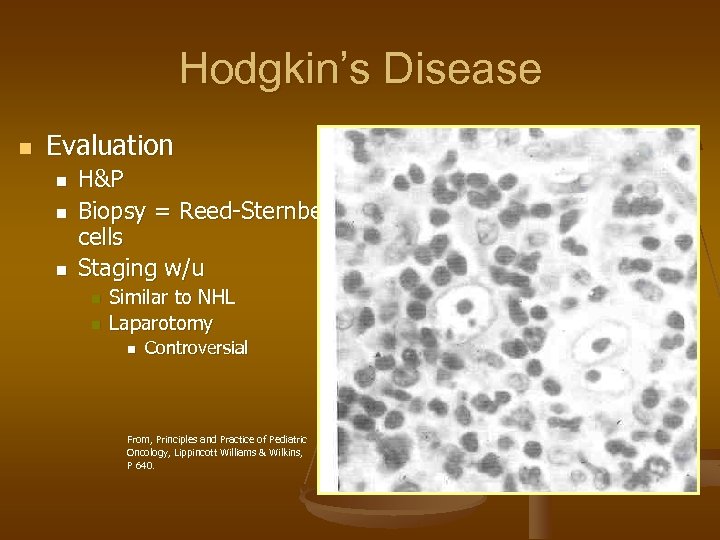 Hodgkin’s Disease n Evaluation n H&P Biopsy = Reed-Sternberg cells Staging w/u n n Similar to NHL Laparotomy n Controversial From, Principles and Practice of Pediatric Oncology, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, P 640.
Hodgkin’s Disease n Evaluation n H&P Biopsy = Reed-Sternberg cells Staging w/u n n Similar to NHL Laparotomy n Controversial From, Principles and Practice of Pediatric Oncology, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, P 640.
 Hodgkin’s Disease n Localized disease n n Extended field XRT Disseminated disease MOPP = nitrogen mustard, vinblastine, procarbazine, prednisone n ABVD = adriamycin bleomycin, vincristine, dacarbazine n
Hodgkin’s Disease n Localized disease n n Extended field XRT Disseminated disease MOPP = nitrogen mustard, vinblastine, procarbazine, prednisone n ABVD = adriamycin bleomycin, vincristine, dacarbazine n
 Laboratory Diagnosis: n Haematological: n n Bone marrow: n n n Normocytic normochromic anemia, High ESR* Leucocytosis, Eosinophilia, lymphopenia Leukoerythroblastic picture - BM infiltration* Normal, or late involvement. Trephine biopsy- diffuse or follicular infiltration Biochemical: n n n High serum LDH – poor prognosis Hypercalcemia, Alkaline phosphatase, Uric acid. Serum transaminases & Bilirubin – Liver
Laboratory Diagnosis: n Haematological: n n Bone marrow: n n n Normocytic normochromic anemia, High ESR* Leucocytosis, Eosinophilia, lymphopenia Leukoerythroblastic picture - BM infiltration* Normal, or late involvement. Trephine biopsy- diffuse or follicular infiltration Biochemical: n n n High serum LDH – poor prognosis Hypercalcemia, Alkaline phosphatase, Uric acid. Serum transaminases & Bilirubin – Liver
 Laboratory Diagnosis: n Haematological: n n Bone marrow: n n n Normocytic normochromic anemia, High ESR* Leucocytosis, Eosinophilia, lymphopenia Leukoerythroblastic picture - BM infiltration* Normal, or late involvement. Trephine biopsy- diffuse or follicular infiltration Biochemical: n n n High serum LDH – poor prognosis Hypercalcemia, Alkaline phosphatase, Uric acid. Serum transaminases & Bilirubin – Liver
Laboratory Diagnosis: n Haematological: n n Bone marrow: n n n Normocytic normochromic anemia, High ESR* Leucocytosis, Eosinophilia, lymphopenia Leukoerythroblastic picture - BM infiltration* Normal, or late involvement. Trephine biopsy- diffuse or follicular infiltration Biochemical: n n n High serum LDH – poor prognosis Hypercalcemia, Alkaline phosphatase, Uric acid. Serum transaminases & Bilirubin – Liver
 Laboratory Diagnosis: n Immunological: Monoclonal gammopathy –B cell NHL, Myeloma n Low normal gammaglobulins n Autoimmune hemolytic anemia – auto ab. n n Karyotypic/Genetic: t(14; 18) – B cell follicular (14* heavy chain) n t(11; 14) – diffuse NHL n
Laboratory Diagnosis: n Immunological: Monoclonal gammopathy –B cell NHL, Myeloma n Low normal gammaglobulins n Autoimmune hemolytic anemia – auto ab. n n Karyotypic/Genetic: t(14; 18) – B cell follicular (14* heavy chain) n t(11; 14) – diffuse NHL n
 Radiological n n n Chest x ray Bone scan Bone x ray if +ve bone scan or bone pains CT scan of chest & abdomen & pelvis Ga 67 scan SPRCT n PET to evaluate residuals n
Radiological n n n Chest x ray Bone scan Bone x ray if +ve bone scan or bone pains CT scan of chest & abdomen & pelvis Ga 67 scan SPRCT n PET to evaluate residuals n
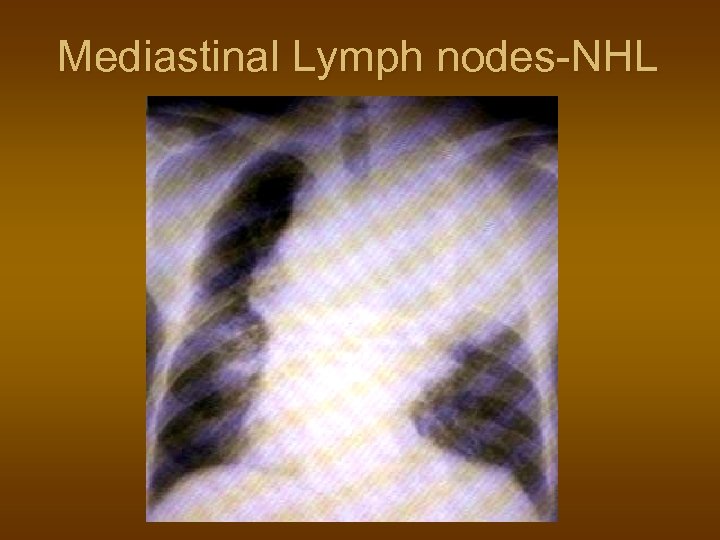 Mediastinal Lymph nodes-NHL
Mediastinal Lymph nodes-NHL
 LN biopsy n Must whole LN as destruction of the architecture is of diagnostic value and n also Reed Sternberg in HL id diagnostic n
LN biopsy n Must whole LN as destruction of the architecture is of diagnostic value and n also Reed Sternberg in HL id diagnostic n
 Additional work up in NHL n Flow cytometry Peripheral blood n Bone marrow detect haematological involvement n n Diagnostic spinal tab in Lymphoblastic lymphoma n Burkitt’s lymphoma n n Upper GIT& small bowel series & endoscopy in S&S of GIT
Additional work up in NHL n Flow cytometry Peripheral blood n Bone marrow detect haematological involvement n n Diagnostic spinal tab in Lymphoblastic lymphoma n Burkitt’s lymphoma n n Upper GIT& small bowel series & endoscopy in S&S of GIT
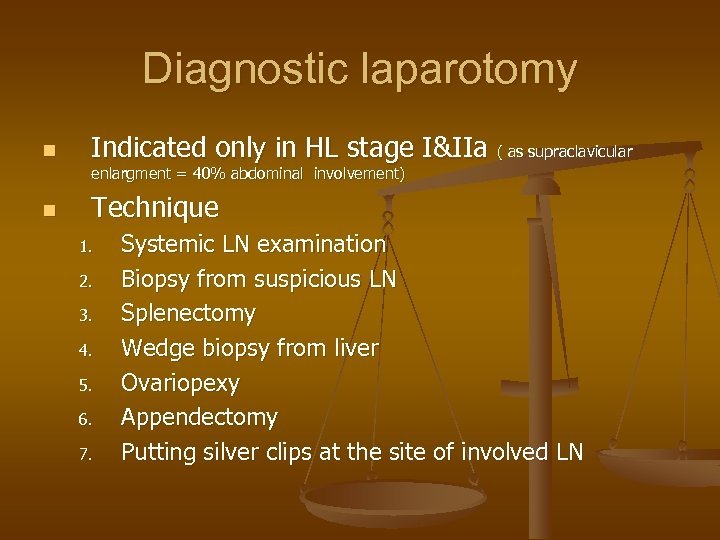 Diagnostic laparotomy n Indicated only in HL stage I&IIa ( as supraclavicular enlargment = 40% abdominal involvement) n Technique 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Systemic LN examination Biopsy from suspicious LN Splenectomy Wedge biopsy from liver Ovariopexy Appendectomy Putting silver clips at the site of involved LN
Diagnostic laparotomy n Indicated only in HL stage I&IIa ( as supraclavicular enlargment = 40% abdominal involvement) n Technique 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Systemic LN examination Biopsy from suspicious LN Splenectomy Wedge biopsy from liver Ovariopexy Appendectomy Putting silver clips at the site of involved LN
 Hodgkin’s Disease n Localized disease (Stage I & II) n Extended field XRT n n Recently IFRT + new modality chemotherapy ABVD Stage III a n n Above diaphragm ---- Mantle below diaphragm ----Inverted Y Extended field RT IFRT + ABVD Multi agent chemotherapy ABVD or MOPP Disseminated disease (Stage III b & IV ) n n MOPP = nitrogen mustard, vinblastine, procarbazine, prednisone ABVD = adriamycin bleomycin, vincristine, dacarbazine
Hodgkin’s Disease n Localized disease (Stage I & II) n Extended field XRT n n Recently IFRT + new modality chemotherapy ABVD Stage III a n n Above diaphragm ---- Mantle below diaphragm ----Inverted Y Extended field RT IFRT + ABVD Multi agent chemotherapy ABVD or MOPP Disseminated disease (Stage III b & IV ) n n MOPP = nitrogen mustard, vinblastine, procarbazine, prednisone ABVD = adriamycin bleomycin, vincristine, dacarbazine
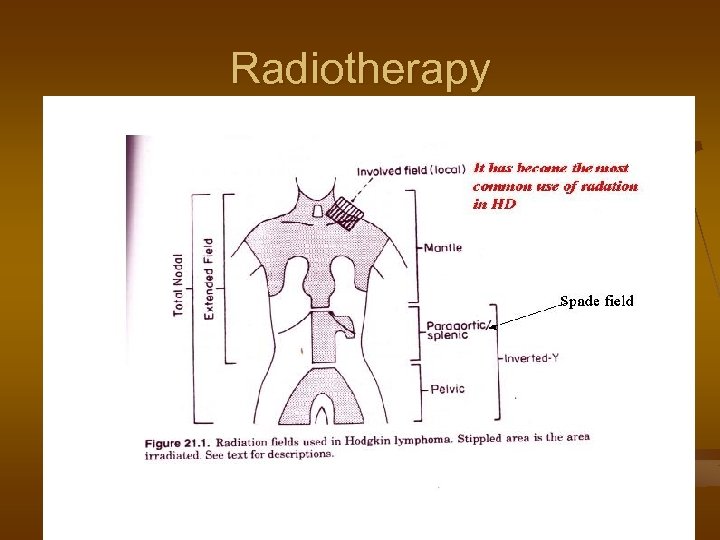 Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy
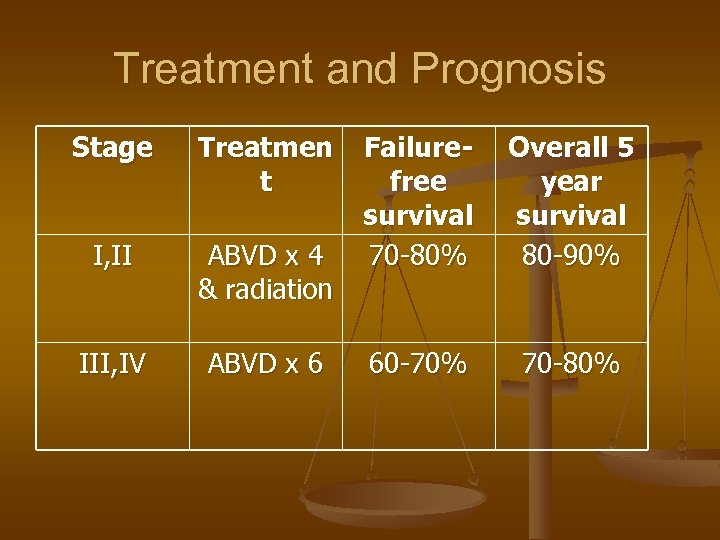 Treatment and Prognosis Stage Treatmen t I, II ABVD x 4 & radiation III, IV ABVD x 6 Failurefree survival 70 -80% Overall 5 year survival 80 -90% 60 -70% 70 -80%
Treatment and Prognosis Stage Treatmen t I, II ABVD x 4 & radiation III, IV ABVD x 6 Failurefree survival 70 -80% Overall 5 year survival 80 -90% 60 -70% 70 -80%
 Hodgkin’s Disease n Survival Stages I, II, and III = 90% n Stage IV = 75 -80% n
Hodgkin’s Disease n Survival Stages I, II, and III = 90% n Stage IV = 75 -80% n
 Long term complications of treatment n infertility MOPP > ABVD; males > females n sperm banking should be discussed n premature menopause n n secondary malignancy n n skin, AML, lung, MDS, NHL, thyroid, breast. . . cardiac disease
Long term complications of treatment n infertility MOPP > ABVD; males > females n sperm banking should be discussed n premature menopause n n secondary malignancy n n skin, AML, lung, MDS, NHL, thyroid, breast. . . cardiac disease
 Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma (NHL)
Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma (NHL)
 Mechanisms of lymphomagenesis n n Genetic alterations Infection Antigen stimulation Immuno-suppression
Mechanisms of lymphomagenesis n n Genetic alterations Infection Antigen stimulation Immuno-suppression
 NHL – Classification: n n n According to cell type n T cell, B cell, Histiocytic & Misc. NHL According to Clinical grade n Low grade, Intermediate & High grade NHL. Histopathological n Diffuse/Follicular NHL, n Small, Intermediate & Large cell NHL Ex: Lennert’s lymphoma is a low grade T cell NHL. Burkitt’s lymphoma, a high grade B cell NHL
NHL – Classification: n n n According to cell type n T cell, B cell, Histiocytic & Misc. NHL According to Clinical grade n Low grade, Intermediate & High grade NHL. Histopathological n Diffuse/Follicular NHL, n Small, Intermediate & Large cell NHL Ex: Lennert’s lymphoma is a low grade T cell NHL. Burkitt’s lymphoma, a high grade B cell NHL
 Kiel Classification of NHL n B Cell NHL: Low Grade: lymphocytic, plasmacytic, centrocytic, mixed centrocytic centroblastic. n High Grade: Centroblastic, Immunoblastic, Burkitts, lymphoblastic. n n T Cell NHL: Low Grade: lymphocytic, mycosis, Lennerts n High Grade: immunoblastic, lymphoblastic etc. n n Rare types:
Kiel Classification of NHL n B Cell NHL: Low Grade: lymphocytic, plasmacytic, centrocytic, mixed centrocytic centroblastic. n High Grade: Centroblastic, Immunoblastic, Burkitts, lymphoblastic. n n T Cell NHL: Low Grade: lymphocytic, mycosis, Lennerts n High Grade: immunoblastic, lymphoblastic etc. n n Rare types:
 NCI – Working Formulation n Low-grade NHL: n n n Intermediate-grade NHL: n n n Follicular large cell Diffuse small cleaved High-grade NHL: n n n Small lymphocytic Follicular small cleaved Immunoblastic Lymphoblastic Miscellaneous: Histiocytic, Mycosis etc.
NCI – Working Formulation n Low-grade NHL: n n n Intermediate-grade NHL: n n n Follicular large cell Diffuse small cleaved High-grade NHL: n n n Small lymphocytic Follicular small cleaved Immunoblastic Lymphoblastic Miscellaneous: Histiocytic, Mycosis etc.
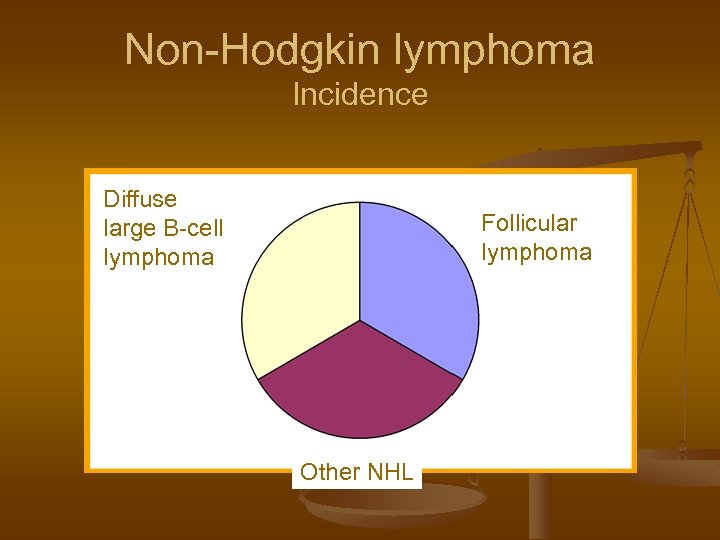 Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Incidence Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma Follicular lymphoma Other NHL
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Incidence Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma Follicular lymphoma Other NHL
 Follicular lymphoma n n n most common type of “indolent” lymphoma usually widespread at presentation often asymptomatic not curable (some exceptions) associated with BCL-2 gene rearrangement [t(14; 18)] cell of origin: germinal center B-cell
Follicular lymphoma n n n most common type of “indolent” lymphoma usually widespread at presentation often asymptomatic not curable (some exceptions) associated with BCL-2 gene rearrangement [t(14; 18)] cell of origin: germinal center B-cell
 Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma n n n most common type of “aggressive” lymphoma usually symptomatic extranodal involvement is common cell of origin: germinal center B-cell treatment should be offered curable in ~ 40%
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma n n n most common type of “aggressive” lymphoma usually symptomatic extranodal involvement is common cell of origin: germinal center B-cell treatment should be offered curable in ~ 40%
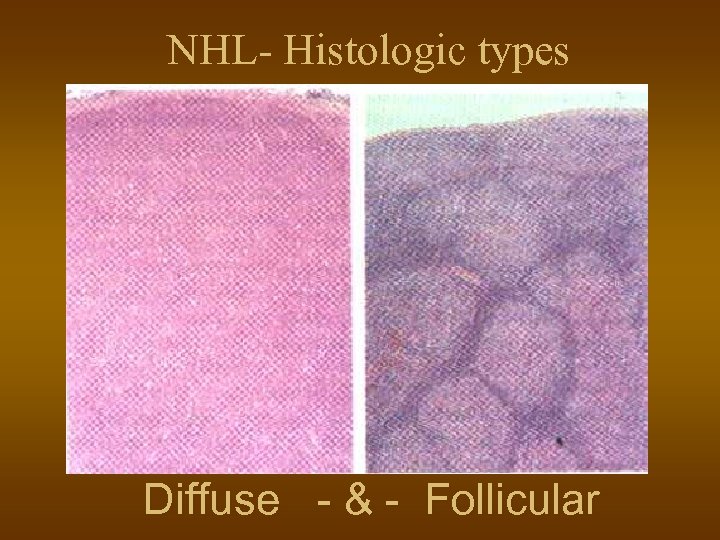 NHL- Histologic types Diffuse - & - Follicular
NHL- Histologic types Diffuse - & - Follicular
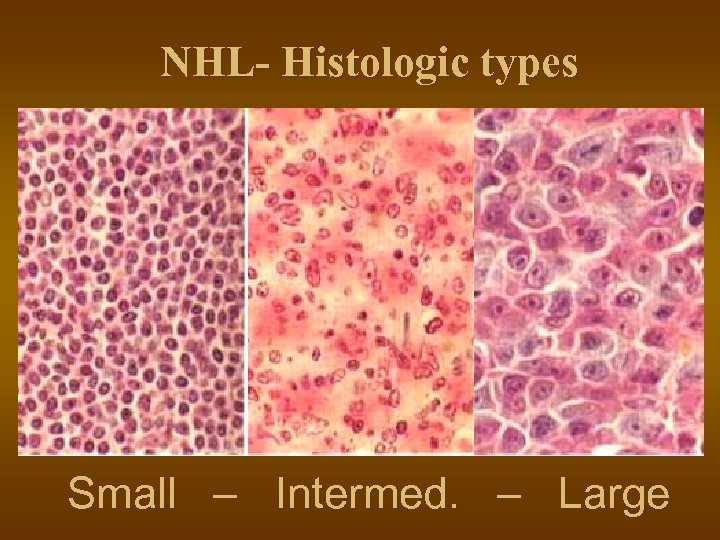 NHL- Histologic types Small – Intermed. – Large
NHL- Histologic types Small – Intermed. – Large
 Lymphoma classification n (based on 2001 WHO) B-cell neoplasms n n T-cell & NK-cell neoplasms n n Precursor B-cell neoplasms (2 types) Mature B-cell neoplasms (19) B-cell proliferations of uncertain malignant potential (2) Precursor T-cell neoplasms (3) Mature T-cell and NK-cell neoplasms (14) T-cell proliferation of uncertain malignant potential (1) Hodgkin lymphoma n n Classical Hodgkin lymphomas (4) Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (1)
Lymphoma classification n (based on 2001 WHO) B-cell neoplasms n n T-cell & NK-cell neoplasms n n Precursor B-cell neoplasms (2 types) Mature B-cell neoplasms (19) B-cell proliferations of uncertain malignant potential (2) Precursor T-cell neoplasms (3) Mature T-cell and NK-cell neoplasms (14) T-cell proliferation of uncertain malignant potential (1) Hodgkin lymphoma n n Classical Hodgkin lymphomas (4) Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (1)
 Clinical manifestations n Variable severity: asymptomatic to extremely ill n time course: evolution over weeks, months, or years n n Systemic manifestations n n fever, night sweats, weight loss, anorexia, pruritis Local manifestations lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly most common n any tissue potentially can be infiltrated n
Clinical manifestations n Variable severity: asymptomatic to extremely ill n time course: evolution over weeks, months, or years n n Systemic manifestations n n fever, night sweats, weight loss, anorexia, pruritis Local manifestations lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly most common n any tissue potentially can be infiltrated n
 Lymphadenopathy in NHL n n n n n Number multiple Site mostly extra nodal Size usually large Shape matted Consistency hard & cystic Fixed skin stretched & red tender fixation
Lymphadenopathy in NHL n n n n n Number multiple Site mostly extra nodal Size usually large Shape matted Consistency hard & cystic Fixed skin stretched & red tender fixation
 Extranodal manifestations (a) SVC compression --dilated Neck veins (b) RLN ---hoarsness of voice (3) Mediastinal (c) Trachea & bronchi--cough& dyspnea (d) Lung--- Dyspnea & effusion (5) Hepatomegally--- Ascites dt • Hepatic dysfunction • Peritoneal invasion (6) jaundice Prehepatic • hemolytic autoimmune • hypersplenism Hepatic– • cholestatic • hepatitis Posthepatic – LN at porta hepatis (1) Cervical lymphadenopathy (2) Hilar LN bronchial compression which cause segmental atelectasis (4) Splenomegally dt infiltration or hyperplasia (7) Stomach & bowel malabsorption syndromes (8) Bone deposites • Sever pain • Pathological fractures (9) Neurological (12) • cord compression Anaemia • Cranial nerve palsy Hypersplenism • Root pains BM infiltration Cytotoxic drugs (11) Mycosis fungoids (10) Skin nodules
Extranodal manifestations (a) SVC compression --dilated Neck veins (b) RLN ---hoarsness of voice (3) Mediastinal (c) Trachea & bronchi--cough& dyspnea (d) Lung--- Dyspnea & effusion (5) Hepatomegally--- Ascites dt • Hepatic dysfunction • Peritoneal invasion (6) jaundice Prehepatic • hemolytic autoimmune • hypersplenism Hepatic– • cholestatic • hepatitis Posthepatic – LN at porta hepatis (1) Cervical lymphadenopathy (2) Hilar LN bronchial compression which cause segmental atelectasis (4) Splenomegally dt infiltration or hyperplasia (7) Stomach & bowel malabsorption syndromes (8) Bone deposites • Sever pain • Pathological fractures (9) Neurological (12) • cord compression Anaemia • Cranial nerve palsy Hypersplenism • Root pains BM infiltration Cytotoxic drugs (11) Mycosis fungoids (10) Skin nodules
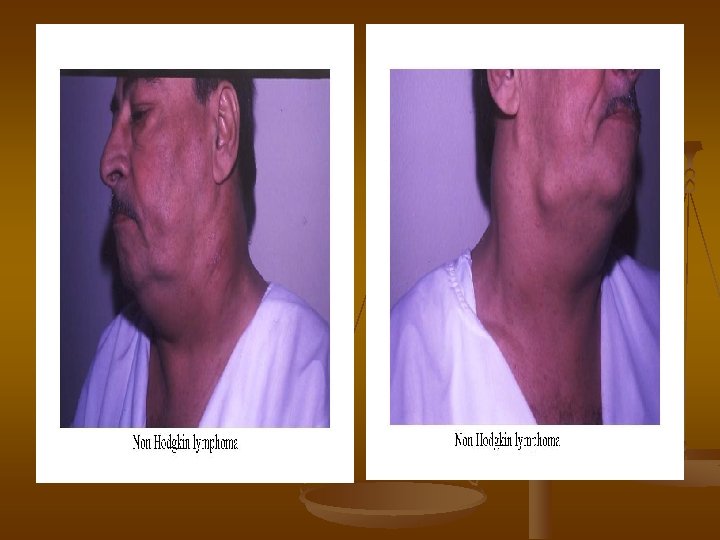
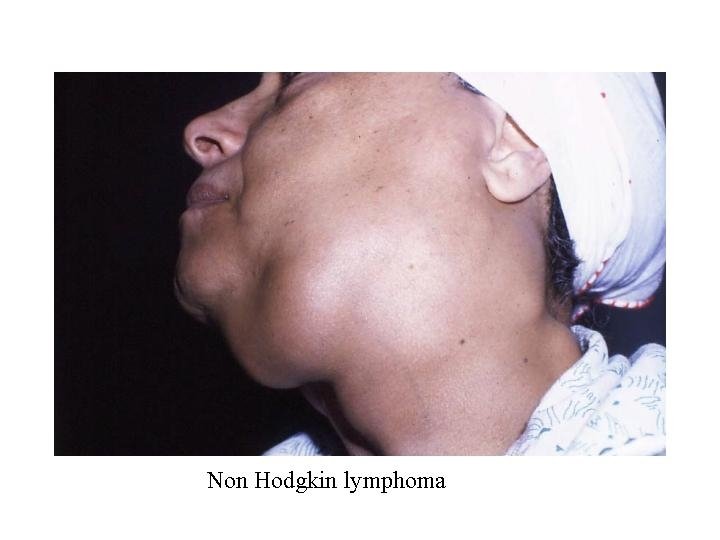
 Non Hodgkin
Non Hodgkin
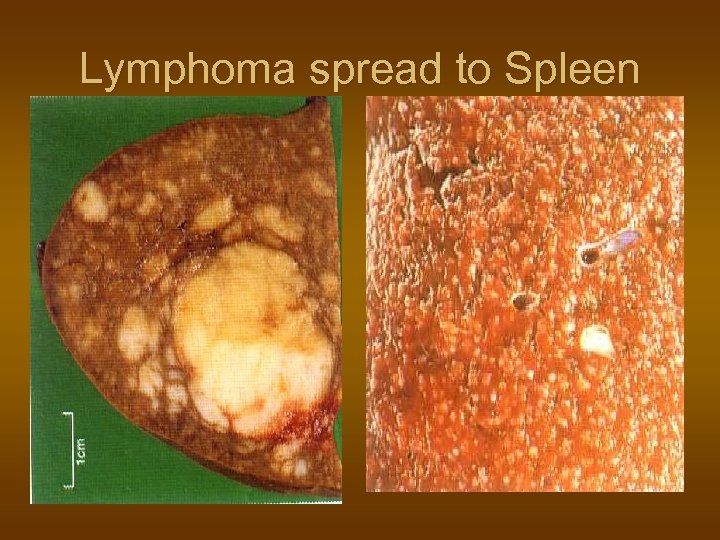 Lymphoma spread to Spleen
Lymphoma spread to Spleen
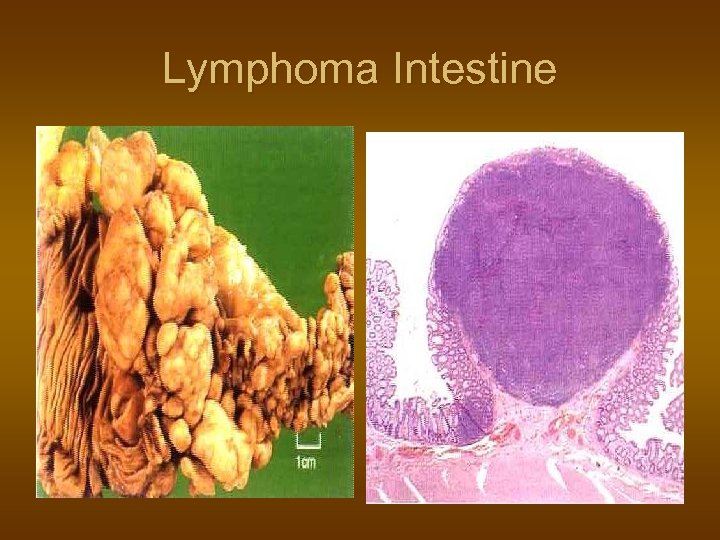 Lymphoma Intestine
Lymphoma Intestine
 A practical way to think of lymphoma Category Non. Hodgkin lymphoma Survival of untreated patients Curability To treat or not to treat Generally defer Rx if asymptomat ic Treat Years Generally not curable Aggressive Months Curable in some Very aggressive Hodgkin lymphoma Indolent Weeks Curable in some Treat All types Variable – months to years Curable in most Treat
A practical way to think of lymphoma Category Non. Hodgkin lymphoma Survival of untreated patients Curability To treat or not to treat Generally defer Rx if asymptomat ic Treat Years Generally not curable Aggressive Months Curable in some Very aggressive Hodgkin lymphoma Indolent Weeks Curable in some Treat All types Variable – months to years Curable in most Treat
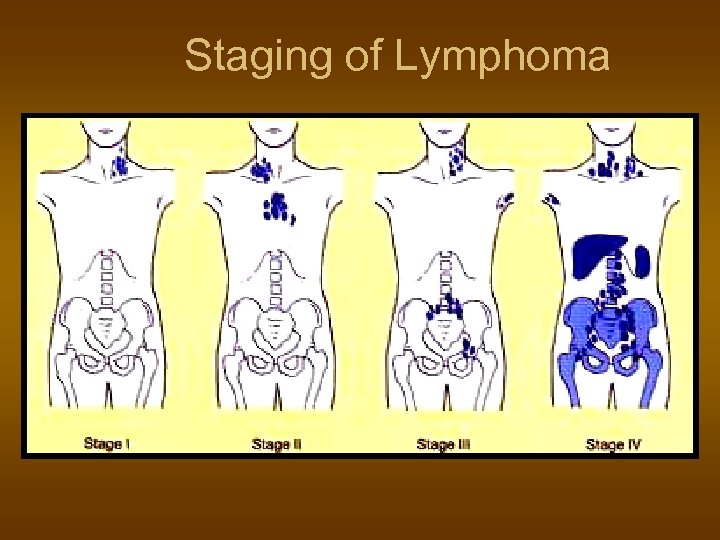 Staging of Lymphoma
Staging of Lymphoma
 Burkitt’s Lymphoma n n n Unusual, B-Lymphoblastic high grade Young african children, jaw bones Isolated histiocytes, starry sky pattern EBV infection related. t(8; 14) Chemotherapy – good response But relapse usual, 30% cure.
Burkitt’s Lymphoma n n n Unusual, B-Lymphoblastic high grade Young african children, jaw bones Isolated histiocytes, starry sky pattern EBV infection related. t(8; 14) Chemotherapy – good response But relapse usual, 30% cure.
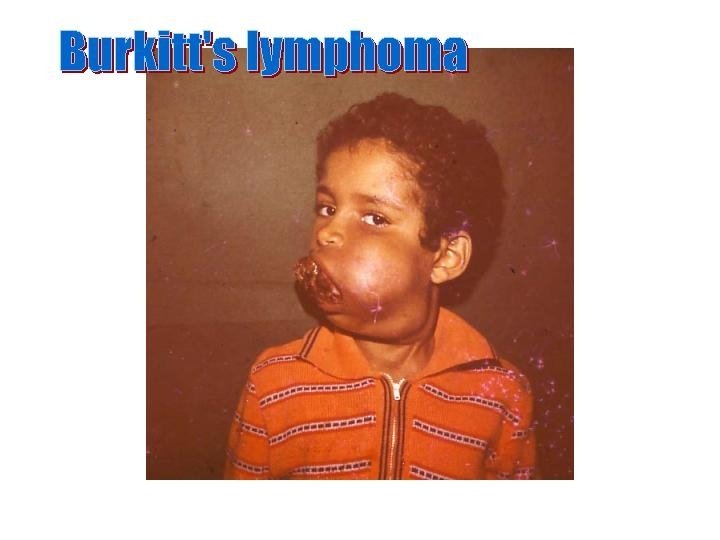
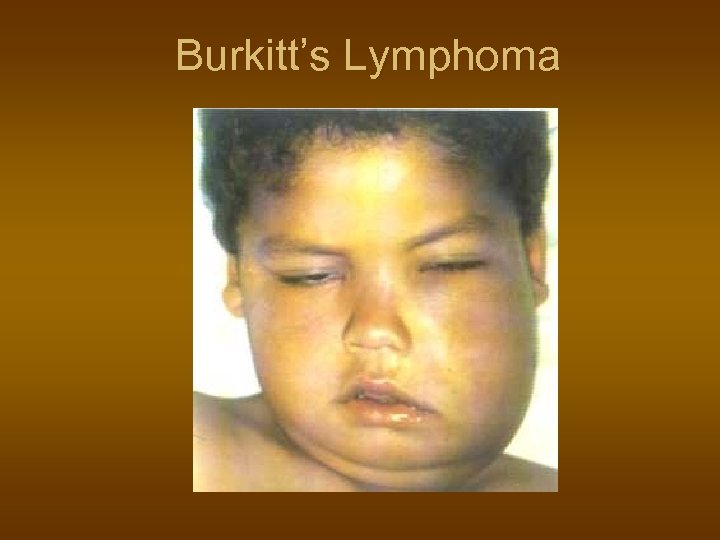 Burkitt’s Lymphoma
Burkitt’s Lymphoma
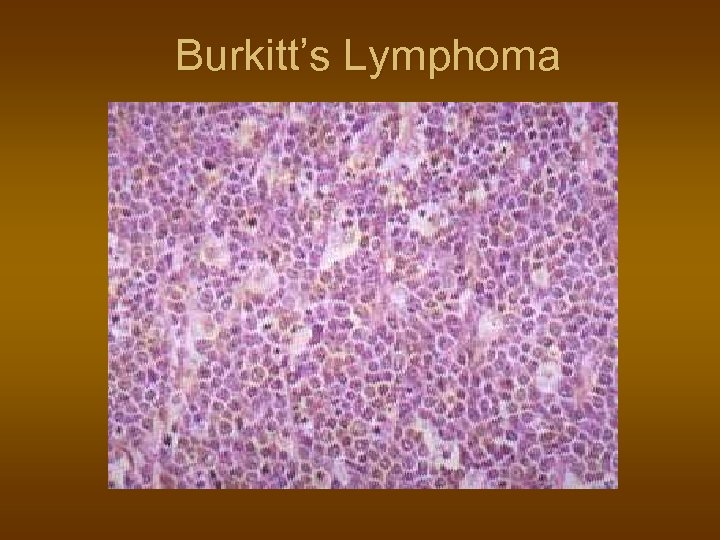 Burkitt’s Lymphoma
Burkitt’s Lymphoma
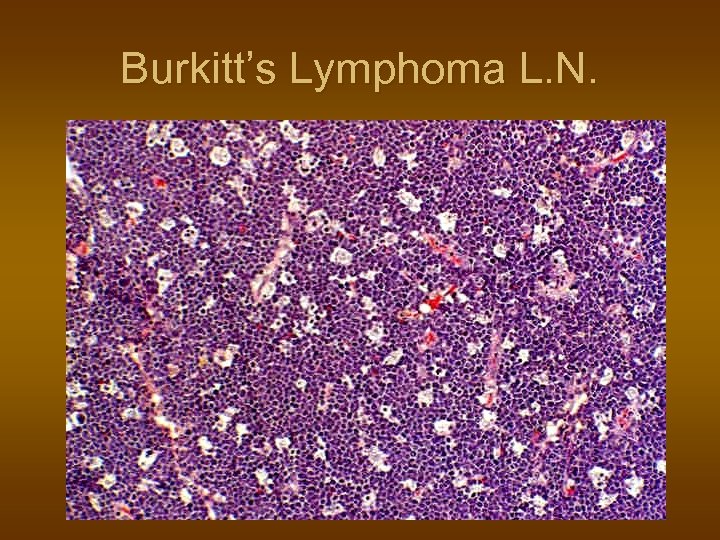 Burkitt’s Lymphoma L. N.
Burkitt’s Lymphoma L. N.
 Non specific LN
Non specific LN
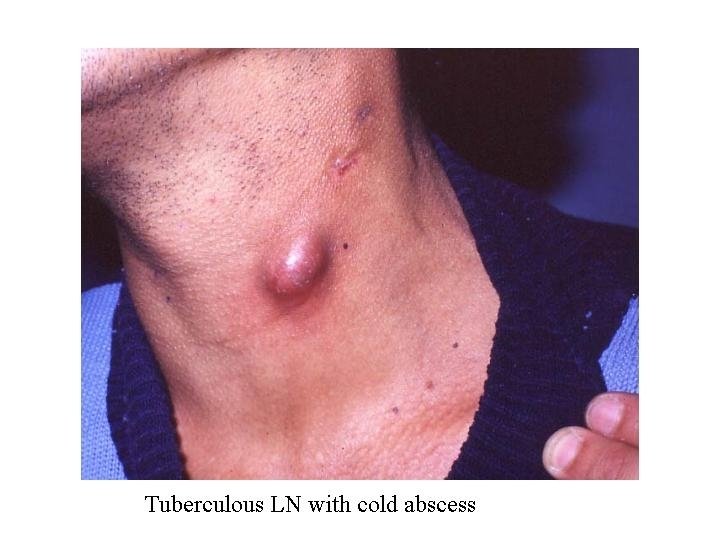
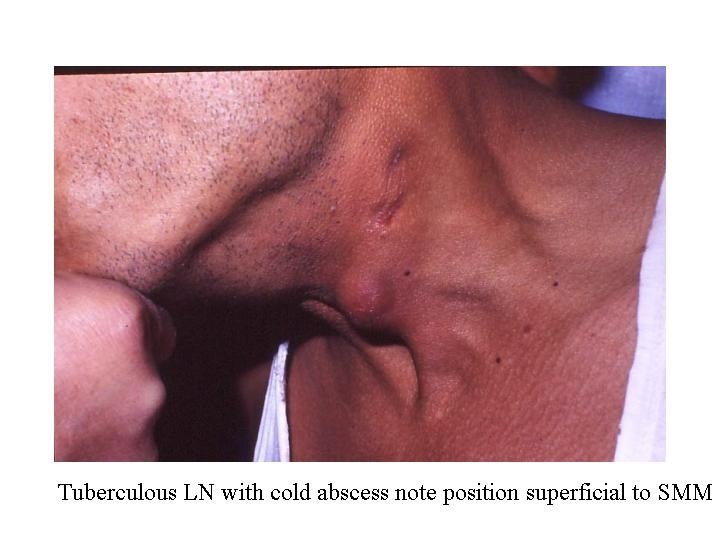
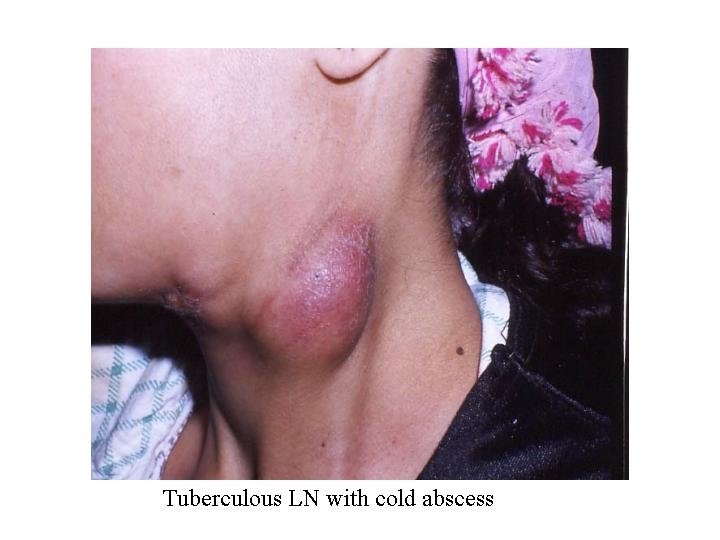
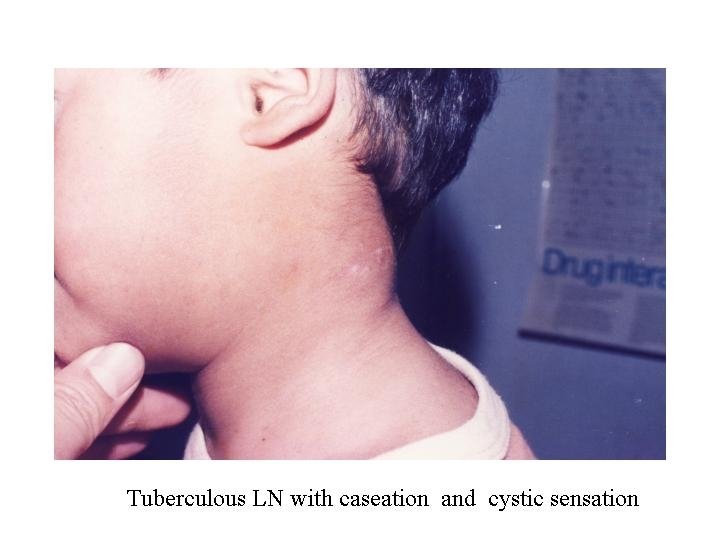
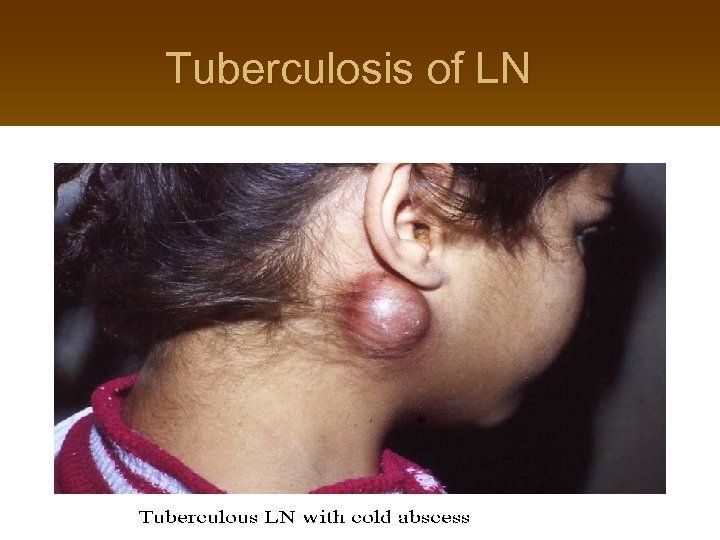 Tuberculosis of LN
Tuberculosis of LN
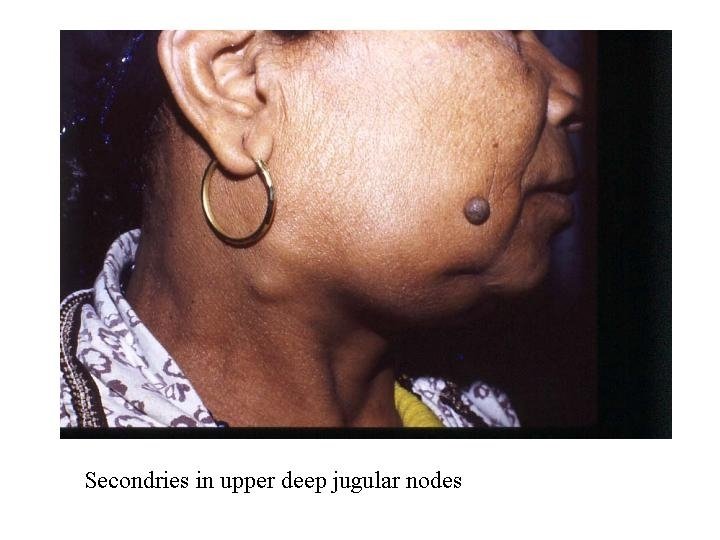
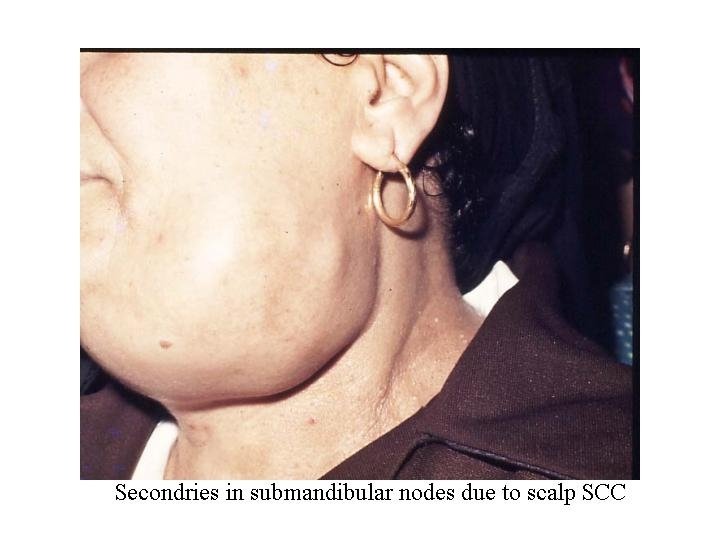
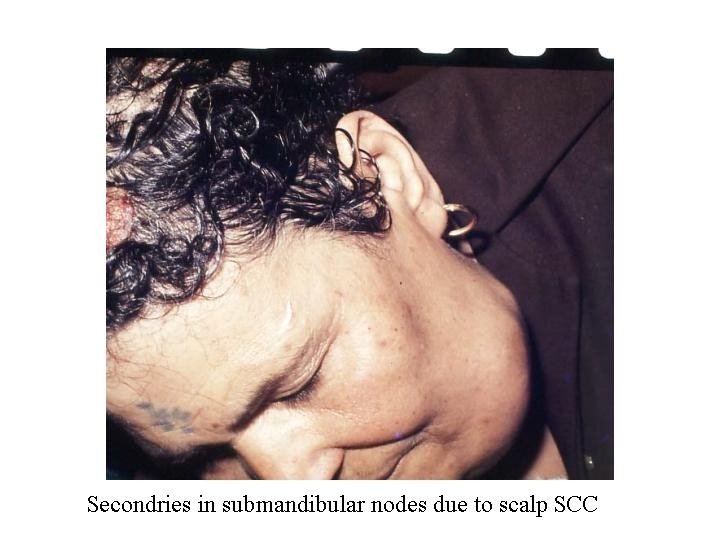
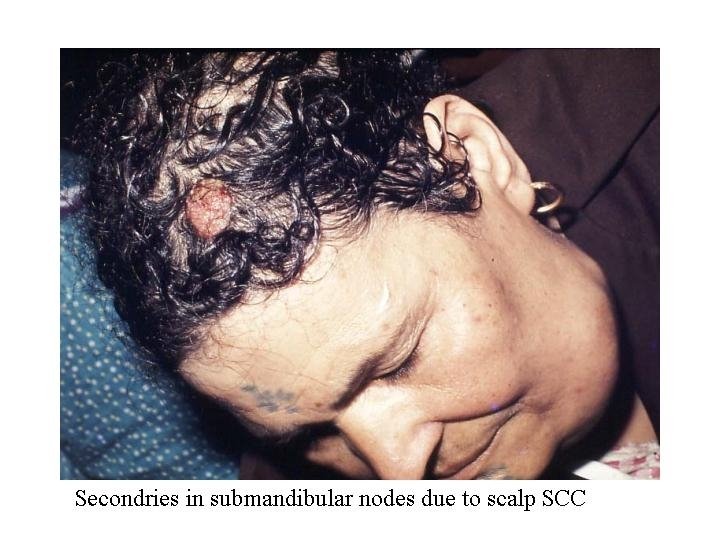
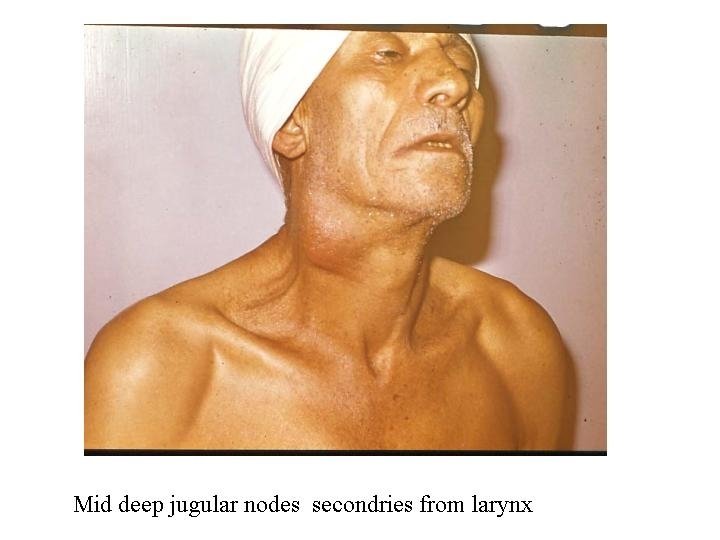
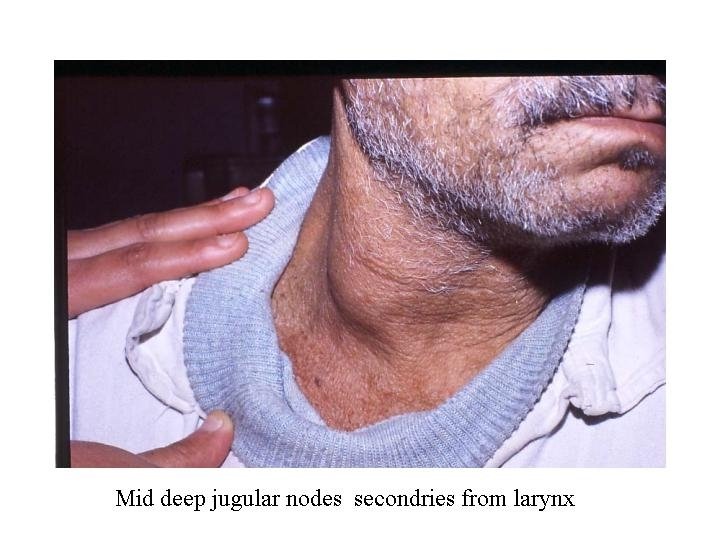
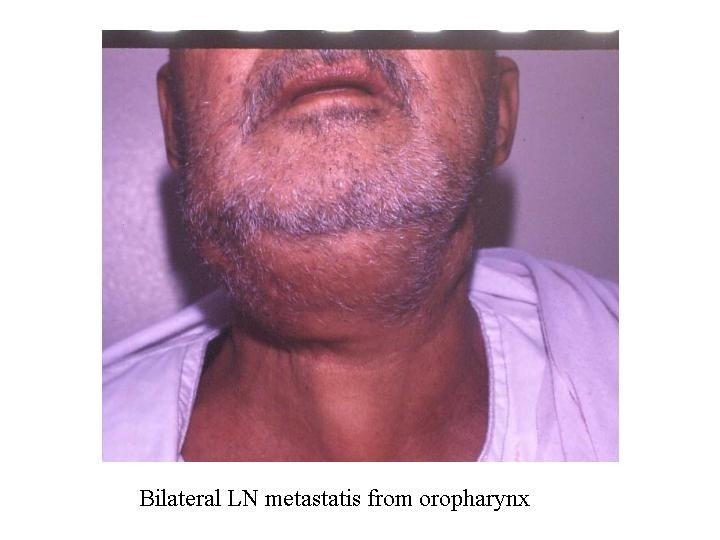
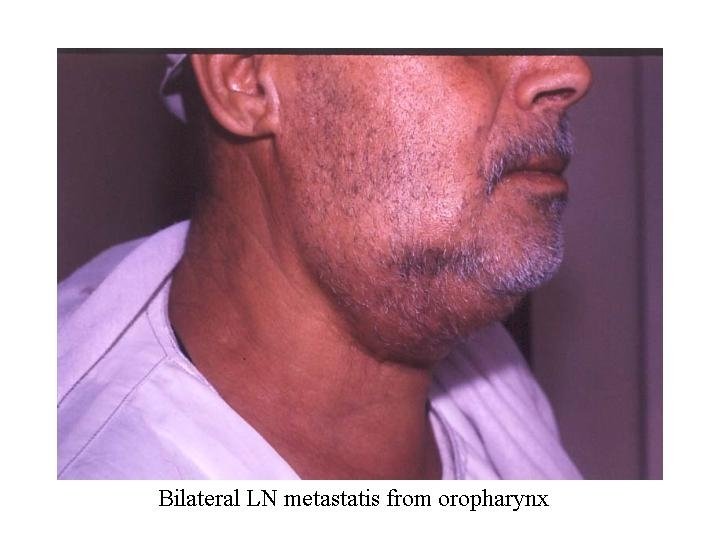
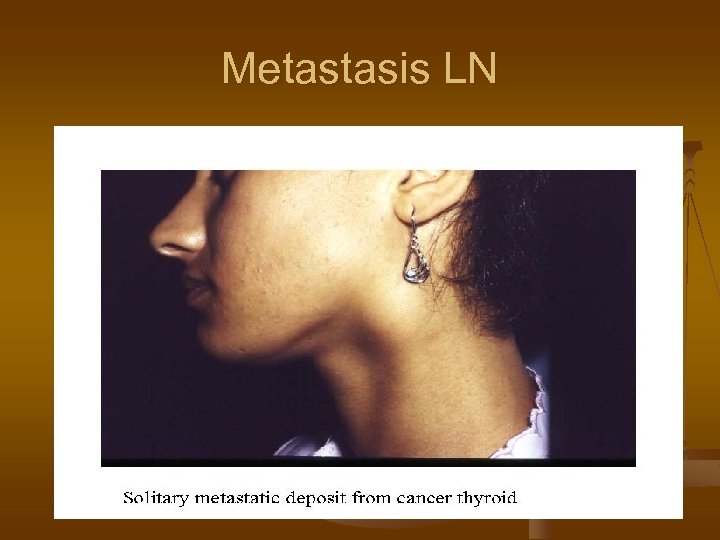 Metastasis LN
Metastasis LN