3acc285a6ee7516857b8d19913de7820.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 LSWHO
LSWHO
 ■ Essential Question: Question –What led to the Cold War between the United States & the Soviet Union? ■ Warm-Up Question: Question –Examine the image on the next slide & use it to answer this Q: –What was the Cold War?
■ Essential Question: Question –What led to the Cold War between the United States & the Soviet Union? ■ Warm-Up Question: Question –Examine the image on the next slide & use it to answer this Q: –What was the Cold War?
 Use this image to search for clues What was the Cold War?
Use this image to search for clues What was the Cold War?
 The USA after World War II ■ The end of WWII in 1945, marked a turning point in U. S. history by taking an active role in world affairs –The USA became a leader in the United Nations & World Bank –The U. S. occupied & helped rebuild Japan after the war –The U. S. helped found Israel as a Jewish nation in the Middle East
The USA after World War II ■ The end of WWII in 1945, marked a turning point in U. S. history by taking an active role in world affairs –The USA became a leader in the United Nations & World Bank –The U. S. occupied & helped rebuild Japan after the war –The U. S. helped found Israel as a Jewish nation in the Middle East
 United Nations Member Nations United Nations Headquarters is in New York City
United Nations Member Nations United Nations Headquarters is in New York City

 American Occupation of Japan
American Occupation of Japan
 The Cold War ■ The most important change in U. S. foreign policy after WWII was the beginning of the Cold War –The Cold War was an era of distrust & hostility between the USA & USSR from 1945 -1991 –It was an era of competing ideologies: The USA promoted democracy & capitalism while the USSR tried to spread communism
The Cold War ■ The most important change in U. S. foreign policy after WWII was the beginning of the Cold War –The Cold War was an era of distrust & hostility between the USA & USSR from 1945 -1991 –It was an era of competing ideologies: The USA promoted democracy & capitalism while the USSR tried to spread communism

 Causes of the Cold War During 1920 s, The USA sent In the. Lenin’s After WWII, Vladimir Lenin troopsin 1924, Americans the to & death USAfight led the “Red. Stalin USSR worked feared the Joseph Army” Bolsheviks in togetherof during the spread to became dictator the Russian Communism Russian Civil ofdefeat the & the USSR Revolution in Axis 1917 the during War Powers, started his “Red Scare” but. . . Five Year Plans
Causes of the Cold War During 1920 s, The USA sent In the. Lenin’s After WWII, Vladimir Lenin troopsin 1924, Americans the to & death USAfight led the “Red. Stalin USSR worked feared the Joseph Army” Bolsheviks in togetherof during the spread to became dictator the Russian Communism Russian Civil ofdefeat the & the USSR Revolution in Axis 1917 the during War Powers, started his “Red Scare” but. . . Five Year Plans
 Causes of the Cold War ■ WWII increased hostilities between the USA & the USSR: –The U. S. & USSR emerged from the war as rival superpowers –The development of the atomic bomb gave the USA a monopoly on nuclear weapons
Causes of the Cold War ■ WWII increased hostilities between the USA & the USSR: –The U. S. & USSR emerged from the war as rival superpowers –The development of the atomic bomb gave the USA a monopoly on nuclear weapons
 But Stalin never did; By Stalin agreed WWII increased Conference, the time. USA &to At the Yalta hostilities between of the USSR Potsdam Conference, Stalin began allow self-determination in Eastern Europe extending his control over Eastern Europe Stalin refused to remove his military or allow free election in Eastern Europe As a result, Eastern European nations turned to Communism & became Soviet satellites—nations influenced by the USSR (the “Eastern bloc”)
But Stalin never did; By Stalin agreed WWII increased Conference, the time. USA &to At the Yalta hostilities between of the USSR Potsdam Conference, Stalin began allow self-determination in Eastern Europe extending his control over Eastern Europe Stalin refused to remove his military or allow free election in Eastern Europe As a result, Eastern European nations turned to Communism & became Soviet satellites—nations influenced by the USSR (the “Eastern bloc”)
 At the end of the war, Germany was divided into a zone occupied by the USSR (which became East Germany) & a zone occupied by the USA, Britain, & France (West Germany)
At the end of the war, Germany was divided into a zone occupied by the USSR (which became East Germany) & a zone occupied by the USA, Britain, & France (West Germany)

 The Iron Curtain Capitalism & Democracy Communism & Totalitarianism The USA began to view Stalin in the 1940 s as a new Hitler—a dangerous dictator who wanted to take over the world
The Iron Curtain Capitalism & Democracy Communism & Totalitarianism The USA began to view Stalin in the 1940 s as a new Hitler—a dangerous dictator who wanted to take over the world
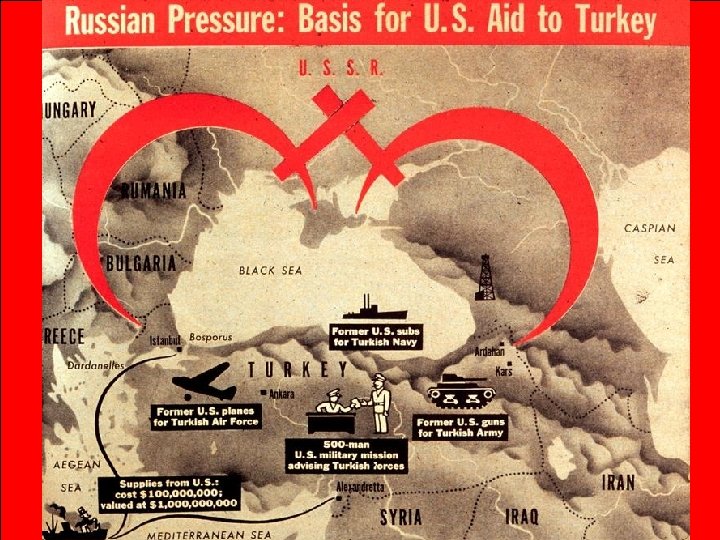
 In 1947, the U. S. began a policy of Containment to stop the spread of Communism by the USSR When the USSR began “A long-term, patient pressuring Greece & Turkey to but firm, and vigilant USA turn communist, the containment of Russian created the Truman Doctrine: expansionist policies… U. S. economic & military aid towill eventually force any country threatened by the USSR to live in communism peace with the West” The Truman Doctrine worked —Secretary of State, & neither Greece nor Turkey George Marshall fell to communism
In 1947, the U. S. began a policy of Containment to stop the spread of Communism by the USSR When the USSR began “A long-term, patient pressuring Greece & Turkey to but firm, and vigilant USA turn communist, the containment of Russian created the Truman Doctrine: expansionist policies… U. S. economic & military aid towill eventually force any country threatened by the USSR to live in communism peace with the West” The Truman Doctrine worked —Secretary of State, & neither Greece nor Turkey George Marshall fell to communism
 In 1947, the U. S. began a policy of Containment to stop the spread of Communism by the USSR European nations had difficulty recovering after WWII which led to fears of communism in Europe The U. S. created the Marshall Plan: offered $13 billion to help rebuild post-war Europe By 1952, Western Europe recovered & Communism never took root
In 1947, the U. S. began a policy of Containment to stop the spread of Communism by the USSR European nations had difficulty recovering after WWII which led to fears of communism in Europe The U. S. created the Marshall Plan: offered $13 billion to help rebuild post-war Europe By 1952, Western Europe recovered & Communism never took root
 Marshall Plan to Aid Europe 1948 -1952
Marshall Plan to Aid Europe 1948 -1952
 In 1947, the U. S. began a policy of Containment to stop the spread of Communism by the USSR In 1948, the USSR used military force to turn Czechoslovakia to communism; This led to fears that Stalin would use similar tactics in Western Europe In 1949, the USA formed the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO): a military alliance among democratic countries
In 1947, the U. S. began a policy of Containment to stop the spread of Communism by the USSR In 1948, the USSR used military force to turn Czechoslovakia to communism; This led to fears that Stalin would use similar tactics in Western Europe In 1949, the USA formed the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO): a military alliance among democratic countries
 NATO was one of many alliances the USA would form with democratic nations over the course of the Cold War NATO Communist Bloc
NATO was one of many alliances the USA would form with democratic nations over the course of the Cold War NATO Communist Bloc
 The Berlin Blockade ■ In 1948, the USSR responded to Containment by cutting off all traffic to Berlin in East Germany –The USA began the Berlin Airlift to bring food, fuel, & supplies to keep West Berlin from turning to Communism –The standoff lasted 2 weeks until Stalin lifted the blockade
The Berlin Blockade ■ In 1948, the USSR responded to Containment by cutting off all traffic to Berlin in East Germany –The USA began the Berlin Airlift to bring food, fuel, & supplies to keep West Berlin from turning to Communism –The standoff lasted 2 weeks until Stalin lifted the blockade

 Reorganizing the Government The new air force was the preferred military ■ By of the War gov’t created 3 agency 1947, Cold U. S. because airplanes new drop nuclear bombs if Cold could agencies during theneeded. War –Dept of Defense to direct the Army & Navy; The military created the Air Force –Central Intelligence Agency to collect & manage information among all gov’t agencies –Nat’l Security Council to advise the president on nat’l security
Reorganizing the Government The new air force was the preferred military ■ By of the War gov’t created 3 agency 1947, Cold U. S. because airplanes new drop nuclear bombs if Cold could agencies during theneeded. War –Dept of Defense to direct the Army & Navy; The military created the Air Force –Central Intelligence Agency to collect & manage information among all gov’t agencies –Nat’l Security Council to advise the president on nat’l security
 The Cold War Expands
The Cold War Expands
 The Soviet atomic bomb. Arms Race USA to The Nuclear motivated the regain its nuclear advantage; In 1952, the U. S. The U. S. monopoly on nuclear weapons tested the 1 st hydrogen bomb (1, 000 USSR times technology ended in 1949 when the more powerful thanown a-bomb) the atomic bomb successfully tested their The Soviets responded with their own hydrogen bomb in 1953
The Soviet atomic bomb. Arms Race USA to The Nuclear motivated the regain its nuclear advantage; In 1952, the U. S. The U. S. monopoly on nuclear weapons tested the 1 st hydrogen bomb (1, 000 USSR times technology ended in 1949 when the more powerful thanown a-bomb) the atomic bomb successfully tested their The Soviets responded with their own hydrogen bomb in 1953
 The Cold War in Asia ■ Containment stopped communism in Europe, but by the late 1940 s the Cold War spread to Asia: –Since the 1930 s, Communist Mao Zedong fought democratic leaders for control of China –In 1949, Mao gained control & turned China to communism –Americans blamed President Truman for “losing China”
The Cold War in Asia ■ Containment stopped communism in Europe, but by the late 1940 s the Cold War spread to Asia: –Since the 1930 s, Communist Mao Zedong fought democratic leaders for control of China –In 1949, Mao gained control & turned China to communism –Americans blamed President Truman for “losing China”
 Based upon this chart, why were Mao & the Communists so popular among the Chinese people?
Based upon this chart, why were Mao & the Communists so popular among the Chinese people?
 The Cold War in Asia ■ America’s response to the fall of China was to more aggressively confront Communism in the world –The U. S. expanded the military & stockpiled nuclear weapons –The USA feared that China would influence its neighbors to turn communist (“domino theory”) –In 1950, the U. S. fought the Korean War to stop communism
The Cold War in Asia ■ America’s response to the fall of China was to more aggressively confront Communism in the world –The U. S. expanded the military & stockpiled nuclear weapons –The USA feared that China would influence its neighbors to turn communist (“domino theory”) –In 1950, the U. S. fought the Korean War to stop communism
 In 1950, North Korea crossed the 38° & attacked South Korea The USA led a United Nations intervention to stop North Korea But, when the USA pushed too close to By. After WWII, Koreastopped the fighting 1953, a ceasefire China, the Chinese was divided along &the 38° with Communists in boundary the 38° was restored Army entered the war as thethe North between North & South Koreas & democracy & helped North Koreain the South
In 1950, North Korea crossed the 38° & attacked South Korea The USA led a United Nations intervention to stop North Korea But, when the USA pushed too close to By. After WWII, Koreastopped the fighting 1953, a ceasefire China, the Chinese was divided along &the 38° with Communists in boundary the 38° was restored Army entered the war as thethe North between North & South Koreas & democracy & helped North Koreain the South
 The USA stopped the spread of Communism into South Korea, but in 1954, Communist Ho Chi Minh began a war to gain independence for Vietnam
The USA stopped the spread of Communism into South Korea, but in 1954, Communist Ho Chi Minh began a war to gain independence for Vietnam
 Conclusions ■ After World War II, U. S. foreign policy changed: –The U. S. became a superpower that actively intervened in world affairs –The Cold War increased military spending, nuclear weapons, & fears of a war with the USSR –President Truman successfully “contained” Communism in Europe but seemed to fail in Asia
Conclusions ■ After World War II, U. S. foreign policy changed: –The U. S. became a superpower that actively intervened in world affairs –The Cold War increased military spending, nuclear weapons, & fears of a war with the USSR –President Truman successfully “contained” Communism in Europe but seemed to fail in Asia


