364eeee7a1756fbcd6b8f2716e2cb93c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Low Cost ATM Technology and Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks Rolf Kraemer Philips Gmb. H Research Laboratories Aachen kraemer@pfa. research. philips. com Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 1 P
Low Cost ATM Technology and Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks Rolf Kraemer Philips Gmb. H Research Laboratories Aachen kraemer@pfa. research. philips. com Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 1 P
 Content • Vision of an In Home Digital Network • End to End View • Embedded ATM Switching for Low Cost Networks – Functional Switch Decomposition – Single Chip Approach – Distributed Software System • Wireless ATM as extension of Embedded Switching • Ad-Hoc W-ATM-LAN for Low Cost Broadband IHDN Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 2 P
Content • Vision of an In Home Digital Network • End to End View • Embedded ATM Switching for Low Cost Networks – Functional Switch Decomposition – Single Chip Approach – Distributed Software System • Wireless ATM as extension of Embedded Switching • Ad-Hoc W-ATM-LAN for Low Cost Broadband IHDN Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 2 P
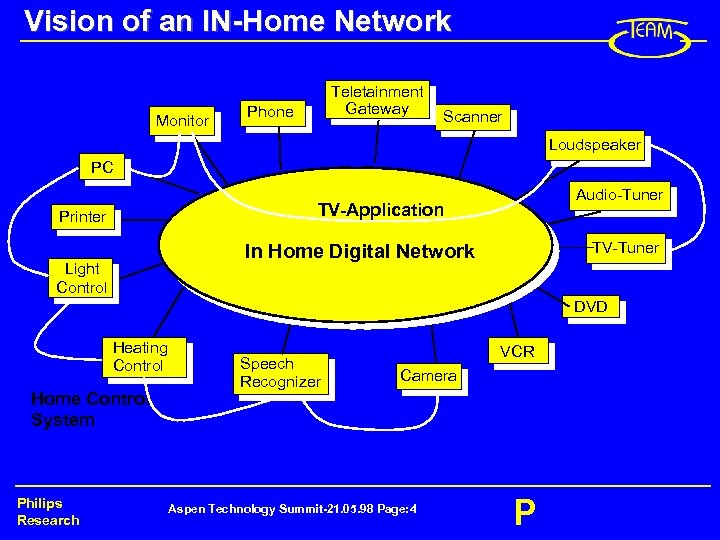 Vision of an IN-Home Network Monitor Teletainment Gateway Phone Scanner Loudspeaker PC Audio-Tuner TV-Application Printer TV-Tuner In Home Digital Network Light Control DVD Heating Control Home Control System Philips Research Speech Recognizer VCR Camera Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 4 P
Vision of an IN-Home Network Monitor Teletainment Gateway Phone Scanner Loudspeaker PC Audio-Tuner TV-Application Printer TV-Tuner In Home Digital Network Light Control DVD Heating Control Home Control System Philips Research Speech Recognizer VCR Camera Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 4 P
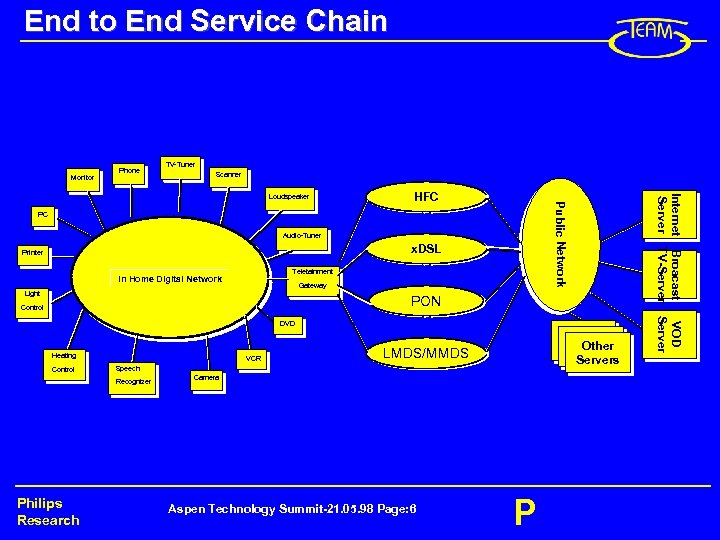 End to End Service Chain Monitor Phone TV-Tuner Scanner Public Network HFC PC Audio-Tuner x. DSL Printer Teletainment In Home Digital Network Gateway Light PON Control Heating Control VCR LMDS/MMDS Speech Recognizer Philips Research Other Servers Camera Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 6 P VOD Server DVD Internet Broacast Server TV-Server Loudspeaker
End to End Service Chain Monitor Phone TV-Tuner Scanner Public Network HFC PC Audio-Tuner x. DSL Printer Teletainment In Home Digital Network Gateway Light PON Control Heating Control VCR LMDS/MMDS Speech Recognizer Philips Research Other Servers Camera Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 6 P VOD Server DVD Internet Broacast Server TV-Server Loudspeaker
 “Embedded Switching System”: Requirements • • • Scalability of System Size Linear Scalability of Cost with Number of Ports No Cost Offset Scalability of Service Architecture Decentralised Signalling and Switch Control “Graceful Degradation” Behaviour in Case of Faults Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 7 P
“Embedded Switching System”: Requirements • • • Scalability of System Size Linear Scalability of Cost with Number of Ports No Cost Offset Scalability of Service Architecture Decentralised Signalling and Switch Control “Graceful Degradation” Behaviour in Case of Faults Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 7 P
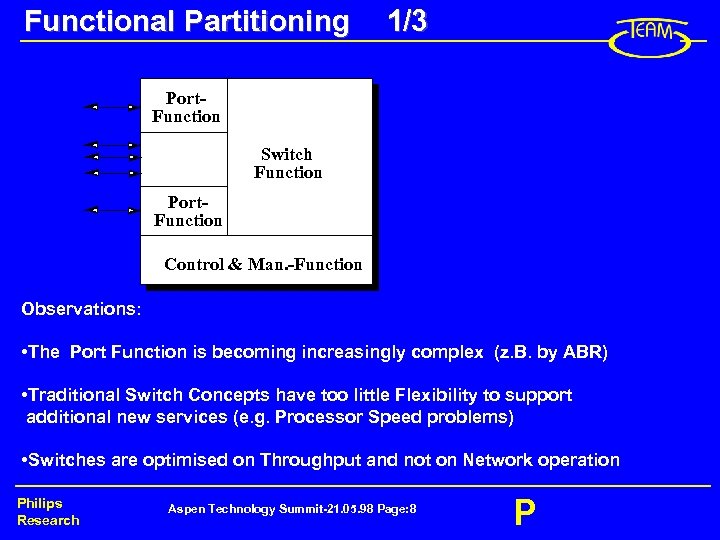 Functional Partitioning 1/3 Port. Function Switch Function Port. Function Control & Man. -Function Observations: • The Port Function is becoming increasingly complex (z. B. by ABR) • Traditional Switch Concepts have too little Flexibility to support additional new services (e. g. Processor Speed problems) • Switches are optimised on Throughput and not on Network operation Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 8 P
Functional Partitioning 1/3 Port. Function Switch Function Port. Function Control & Man. -Function Observations: • The Port Function is becoming increasingly complex (z. B. by ABR) • Traditional Switch Concepts have too little Flexibility to support additional new services (e. g. Processor Speed problems) • Switches are optimised on Throughput and not on Network operation Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 8 P
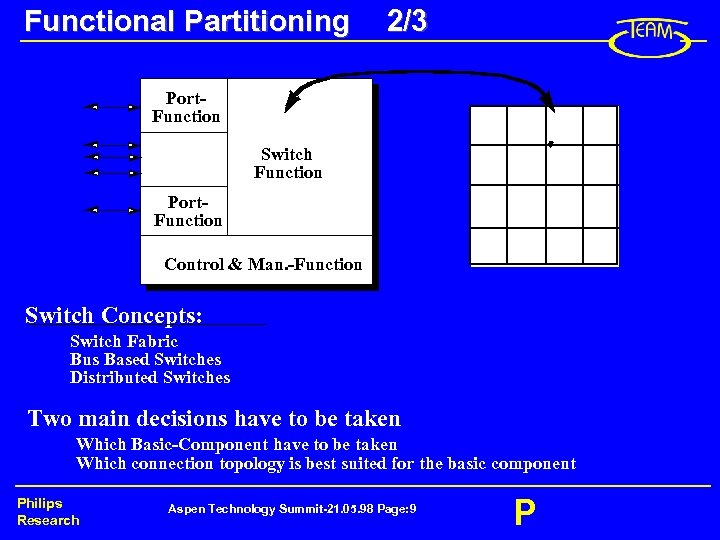 Functional Partitioning 2/3 Port. Function Switch Function Port. Function Control & Man. -Function Switch Concepts: Switch Fabric Bus Based Switches Distributed Switches Two main decisions have to be taken Which Basic-Component have to be taken Which connection topology is best suited for the basic component Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 9 P
Functional Partitioning 2/3 Port. Function Switch Function Port. Function Control & Man. -Function Switch Concepts: Switch Fabric Bus Based Switches Distributed Switches Two main decisions have to be taken Which Basic-Component have to be taken Which connection topology is best suited for the basic component Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 9 P
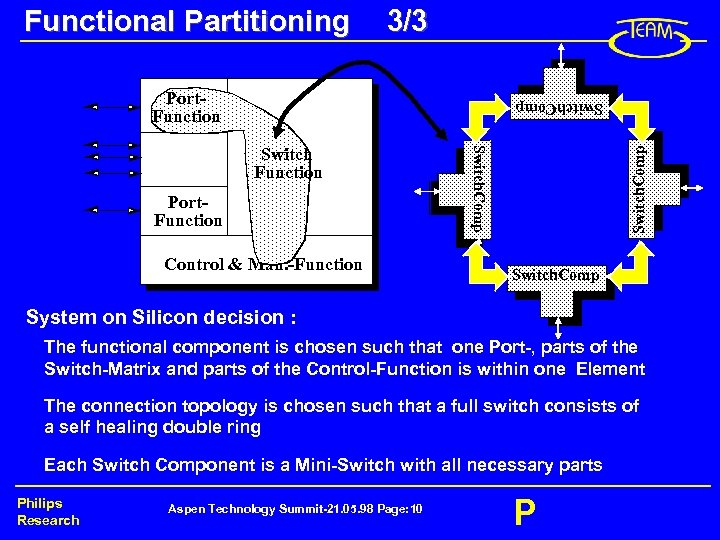 Functional Partitioning 3/3 Port. Function Control & Man. -Function Switch. Comp Transceiver Port. Function Switch. Comp Transceiver Switch Function Switch. Comp Transceiver System on Silicon decision : The functional component is chosen such that one Port-, parts of the Switch-Matrix and parts of the Control-Function is within one Element The connection topology is chosen such that a full switch consists of a self healing double ring Each Switch Component is a Mini-Switch with all necessary parts Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 10 P
Functional Partitioning 3/3 Port. Function Control & Man. -Function Switch. Comp Transceiver Port. Function Switch. Comp Transceiver Switch Function Switch. Comp Transceiver System on Silicon decision : The functional component is chosen such that one Port-, parts of the Switch-Matrix and parts of the Control-Function is within one Element The connection topology is chosen such that a full switch consists of a self healing double ring Each Switch Component is a Mini-Switch with all necessary parts Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 10 P
 Sample Device Connections Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 11 P
Sample Device Connections Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 11 P
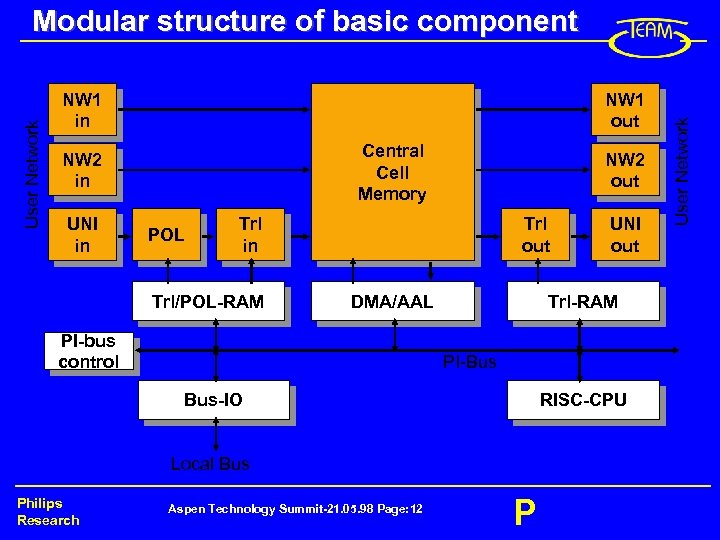 NW 1 in NW 1 out Central Cell Memory NW 2 in UNI in POL NW 2 out Trl in Trl/POL-RAM Trl out DMA/AAL PI-bus control Trl-RAM PI-Bus Bus-IO RISC-CPU Local Bus Philips Research UNI out Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 12 P User Network Modular structure of basic component
NW 1 in NW 1 out Central Cell Memory NW 2 in UNI in POL NW 2 out Trl in Trl/POL-RAM Trl out DMA/AAL PI-bus control Trl-RAM PI-Bus Bus-IO RISC-CPU Local Bus Philips Research UNI out Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 12 P User Network Modular structure of basic component
 CMC-155 Chip Size: Transistors: Memory: Frequency: Pins: Technology: Supply Voltage: Current: Philips Research 144 mm 2 1. 98*106 200 kb 20 MHz 208 0. 5 m 3. 3 V 0. 4 A Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 13 P
CMC-155 Chip Size: Transistors: Memory: Frequency: Pins: Technology: Supply Voltage: Current: Philips Research 144 mm 2 1. 98*106 200 kb 20 MHz 208 0. 5 m 3. 3 V 0. 4 A Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 13 P
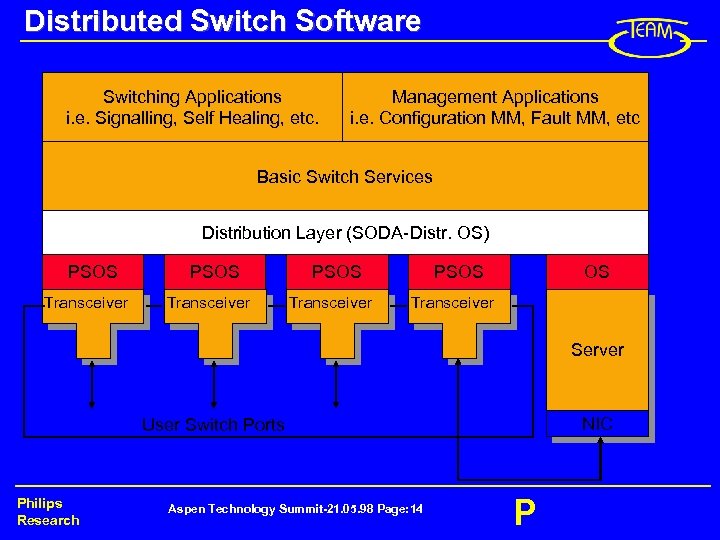 Distributed Switch Software Switching Applications i. e. Signalling, Self Healing, etc. Management Applications i. e. Configuration MM, Fault MM, etc Basic Switch Services Distribution Layer (SODA-Distr. OS) PSOS Transceiver PSOS OS Transceiver Server NIC User Switch Ports Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 14 P
Distributed Switch Software Switching Applications i. e. Signalling, Self Healing, etc. Management Applications i. e. Configuration MM, Fault MM, etc Basic Switch Services Distribution Layer (SODA-Distr. OS) PSOS Transceiver PSOS OS Transceiver Server NIC User Switch Ports Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 14 P
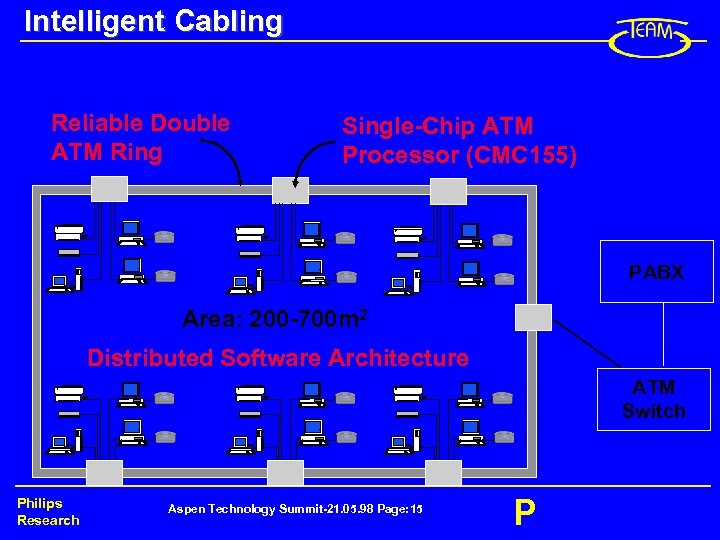 Intelligent Cabling Reliable Double ATM Ring Single-Chip ATM Processor (CMC 155) PABX Area: 200 -700 m 2 Distributed Software Architecture ATM Switch Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 15 P
Intelligent Cabling Reliable Double ATM Ring Single-Chip ATM Processor (CMC 155) PABX Area: 200 -700 m 2 Distributed Software Architecture ATM Switch Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 15 P
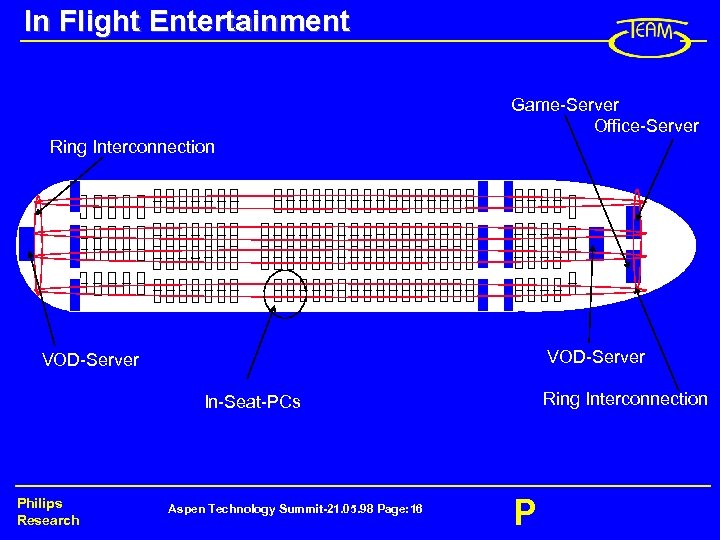 In Flight Entertainment Game-Server Office-Server Ring Interconnection VOD-Server Ring Interconnection In-Seat-PCs Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 16 P
In Flight Entertainment Game-Server Office-Server Ring Interconnection VOD-Server Ring Interconnection In-Seat-PCs Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 16 P
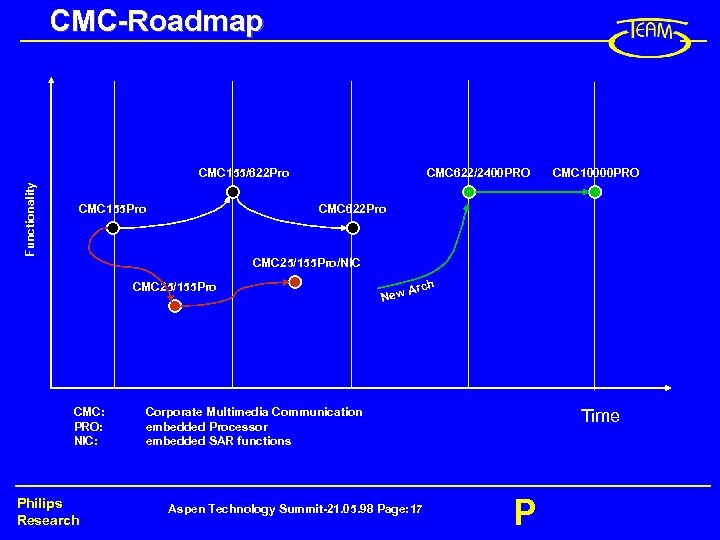 CMC-Roadmap Functionality CMC 155/622 Pro CMC 155 Pro CMC 622/2400 PRO CMC 10000 PRO CMC 622 Pro CMC 25/155 Pro/NIC CMC 25/155 Pro CMC: PRO: NIC: Philips Research New Arch Time Corporate Multimedia Communication embedded Processor embedded SAR functions Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 17 P
CMC-Roadmap Functionality CMC 155/622 Pro CMC 155 Pro CMC 622/2400 PRO CMC 10000 PRO CMC 622 Pro CMC 25/155 Pro/NIC CMC 25/155 Pro CMC: PRO: NIC: Philips Research New Arch Time Corporate Multimedia Communication embedded Processor embedded SAR functions Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 17 P
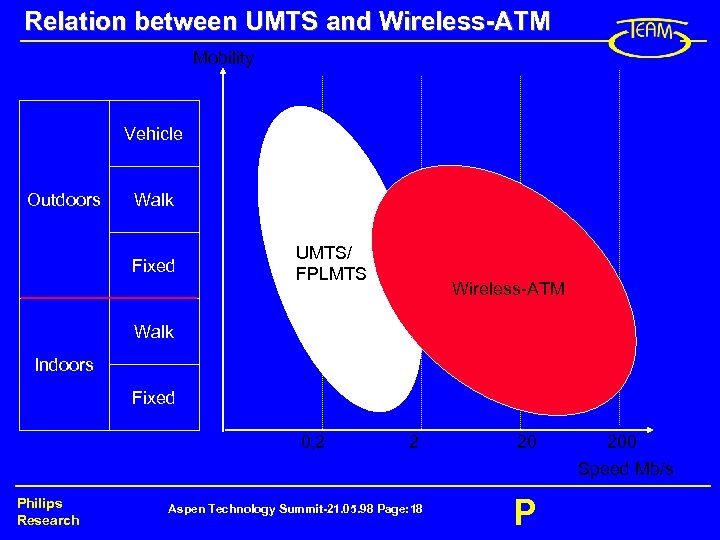 Relation between UMTS and Wireless-ATM Mobility Vehicle Outdoors Walk Fixed UMTS/ FPLMTS Wireless-ATM Walk Indoors Fixed 0, 2 2 20 200 Speed Mb/s Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 18 P
Relation between UMTS and Wireless-ATM Mobility Vehicle Outdoors Walk Fixed UMTS/ FPLMTS Wireless-ATM Walk Indoors Fixed 0, 2 2 20 200 Speed Mb/s Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 18 P
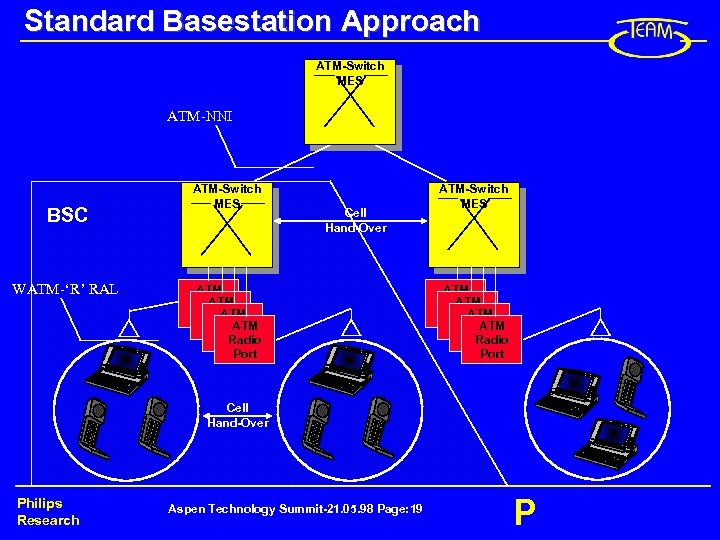 Standard Basestation Approach ATM-Switch MES ATM-NNI BSC WATM-‘R’ RAL ATM-Switch MES Cell Hand-Over ATM Radio Port ATM-Switch MES ATM Radio Port Cell Hand-Over Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 19 P
Standard Basestation Approach ATM-Switch MES ATM-NNI BSC WATM-‘R’ RAL ATM-Switch MES Cell Hand-Over ATM Radio Port ATM-Switch MES ATM Radio Port Cell Hand-Over Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 19 P
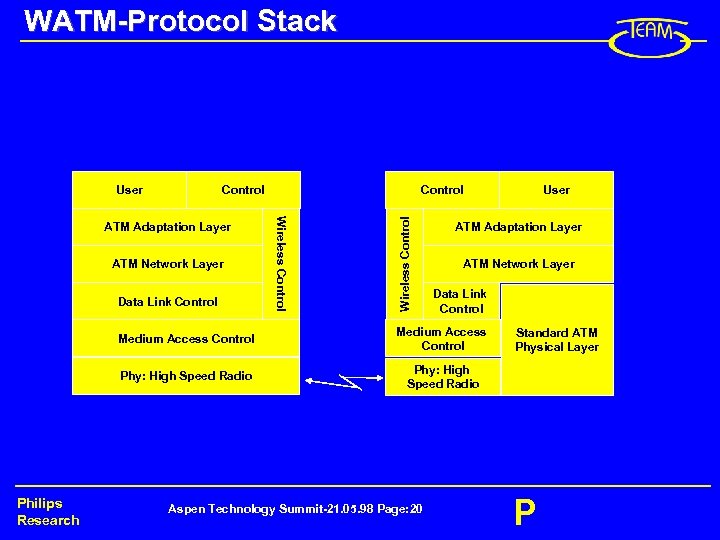 WATM-Protocol Stack Control ATM Network Layer Data Link Control Wireless Control ATM Adaptation Layer Control Wireless Control User ATM Adaptation Layer ATM Network Layer Data Link Control Medium Access Control Phy: High Speed Radio Philips Research User Phy: High Speed Radio Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 20 Standard ATM Physical Layer P
WATM-Protocol Stack Control ATM Network Layer Data Link Control Wireless Control ATM Adaptation Layer Control Wireless Control User ATM Adaptation Layer ATM Network Layer Data Link Control Medium Access Control Phy: High Speed Radio Philips Research User Phy: High Speed Radio Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 20 Standard ATM Physical Layer P
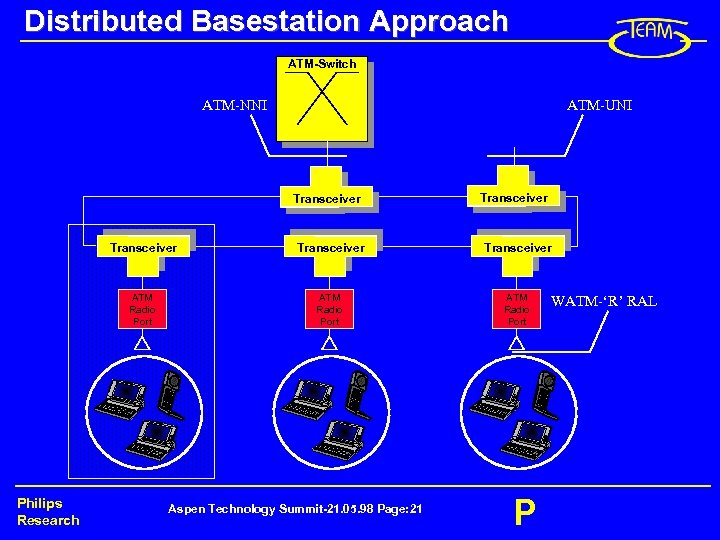 Distributed Basestation Approach ATM-Switch ATM-UNI ATM-NNI Transceiver ATM Radio Port Philips Research Transceiver ATM Radio Port Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 21 P WATM-‘R’ RAL
Distributed Basestation Approach ATM-Switch ATM-UNI ATM-NNI Transceiver ATM Radio Port Philips Research Transceiver ATM Radio Port Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 21 P WATM-‘R’ RAL
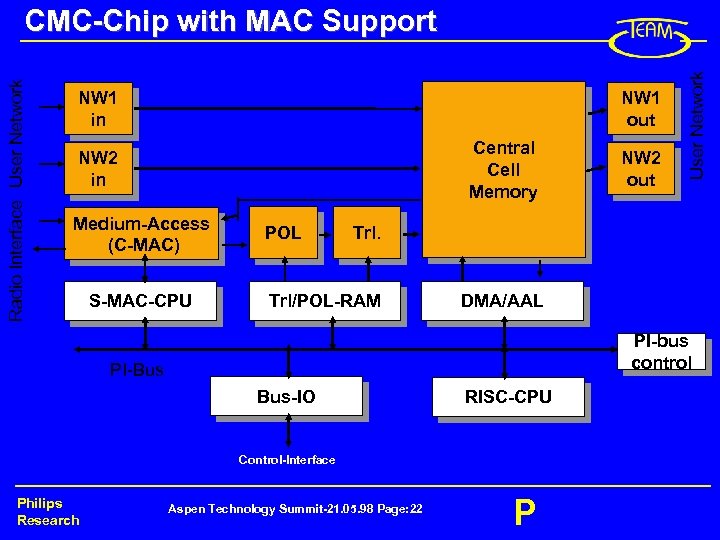 NW 1 in NW 1 out Central Cell Memory NW 2 in Medium-Access (C-MAC) S-MAC-CPU POL Trl/POL-RAM DMA/AAL PI-bus control PI-Bus Bus-IO RISC-CPU Control-Interface Philips Research NW 2 out User Network Radio Interface User Network CMC-Chip with MAC Support Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 22 P
NW 1 in NW 1 out Central Cell Memory NW 2 in Medium-Access (C-MAC) S-MAC-CPU POL Trl/POL-RAM DMA/AAL PI-bus control PI-Bus Bus-IO RISC-CPU Control-Interface Philips Research NW 2 out User Network Radio Interface User Network CMC-Chip with MAC Support Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 22 P
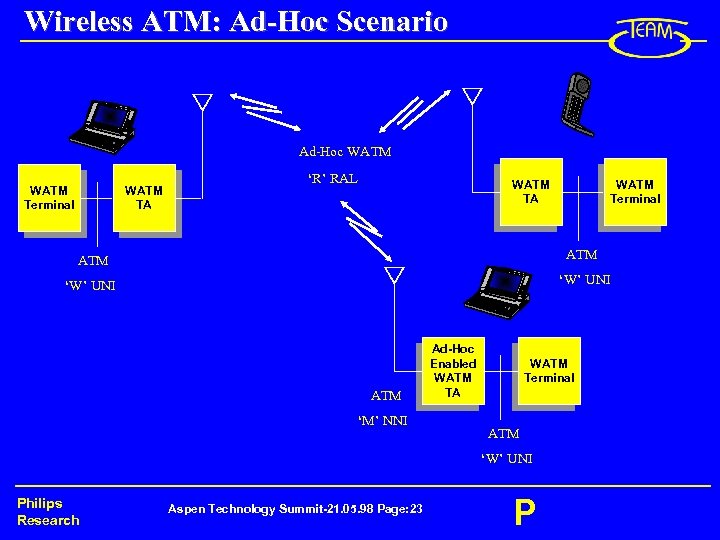 Wireless ATM: Ad-Hoc Scenario Ad-Hoc WATM Terminal WATM TA ‘R’ RAL WATM TA WATM Terminal ATM ‘W’ UNI ATM ‘M’ NNI Ad-Hoc Enabled WATM TA WATM Terminal ATM ‘W’ UNI Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 23 P
Wireless ATM: Ad-Hoc Scenario Ad-Hoc WATM Terminal WATM TA ‘R’ RAL WATM TA WATM Terminal ATM ‘W’ UNI ATM ‘M’ NNI Ad-Hoc Enabled WATM TA WATM Terminal ATM ‘W’ UNI Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 23 P
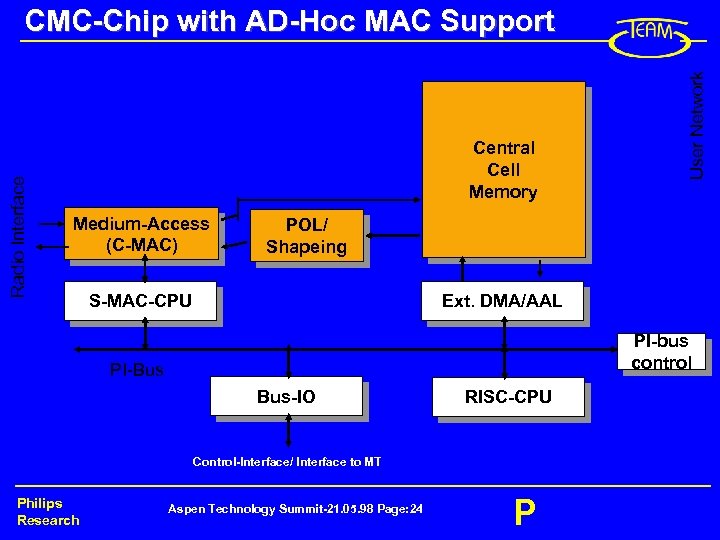 Central Cell Memory Medium-Access (C-MAC) POL/ Shapeing S-MAC-CPU Ext. DMA/AAL PI-bus control PI-Bus Bus-IO RISC-CPU Control-Interface/ Interface to MT Philips Research User Network Radio Interface CMC-Chip with AD-Hoc MAC Support Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 24 P
Central Cell Memory Medium-Access (C-MAC) POL/ Shapeing S-MAC-CPU Ext. DMA/AAL PI-bus control PI-Bus Bus-IO RISC-CPU Control-Interface/ Interface to MT Philips Research User Network Radio Interface CMC-Chip with AD-Hoc MAC Support Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 24 P
 Conclusion • Low Cost ATM is not only feasible but already available (CMC concept) • The distributed CMC-Concept allows the extension to WATM • The building block approach of the CMC concept supports the stepwise extension towards full AD-HOC WATM systems • A first CMC based WATM demonstrator has been implemented (10 Mb/s) • First application will be in the office environment • The final goal to support IHDN is in reach Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 25 P
Conclusion • Low Cost ATM is not only feasible but already available (CMC concept) • The distributed CMC-Concept allows the extension to WATM • The building block approach of the CMC concept supports the stepwise extension towards full AD-HOC WATM systems • A first CMC based WATM demonstrator has been implemented (10 Mb/s) • First application will be in the office environment • The final goal to support IHDN is in reach Philips Research Aspen Technology Summit-21. 05. 98 Page: 25 P


