3262163ea7adbb61d0b1fad151aab30b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 LOSE LESS AND SELL MORE: Using the ECR Europe Approach to Manage Shrinkage Adrian Beck Reader in Criminology University of Leicester, UK
LOSE LESS AND SELL MORE: Using the ECR Europe Approach to Manage Shrinkage Adrian Beck Reader in Criminology University of Leicester, UK
 Structure • Defining Shrinkage • The Scale of the Problem • Key Principles of Effective Shrinkage Management • A Case Study in Success
Structure • Defining Shrinkage • The Scale of the Problem • Key Principles of Effective Shrinkage Management • A Case Study in Success
 Defining Shrinkage
Defining Shrinkage
 Original ECR Europe Definition Shrinkage Process failures Intercompany fraud Internal theft External theft
Original ECR Europe Definition Shrinkage Process failures Intercompany fraud Internal theft External theft
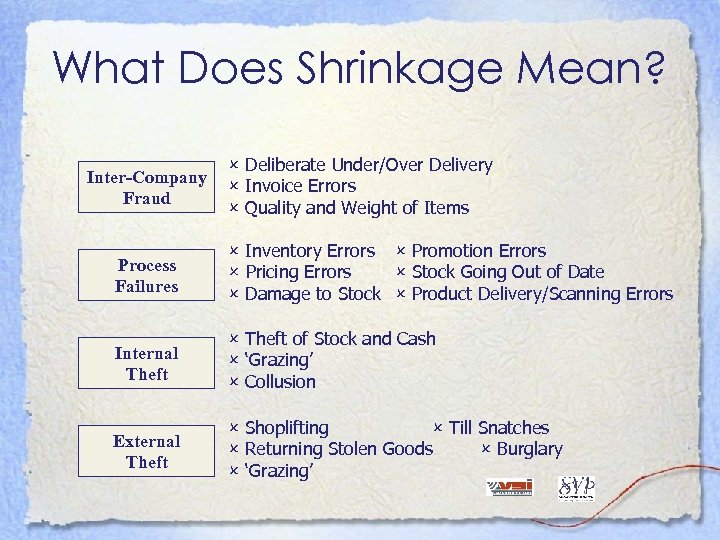 What Does Shrinkage Mean? Inter-Company Fraud Deliberate Under/Over Delivery Invoice Errors Quality and Weight of Items Process Failures Inventory Errors Promotion Errors Pricing Errors Stock Going Out of Date Damage to Stock Product Delivery/Scanning Errors Internal Theft of Stock and Cash ‘Grazing’ Collusion External Theft Shoplifting Till Snatches Returning Stolen Goods Burglary ‘Grazing’
What Does Shrinkage Mean? Inter-Company Fraud Deliberate Under/Over Delivery Invoice Errors Quality and Weight of Items Process Failures Inventory Errors Promotion Errors Pricing Errors Stock Going Out of Date Damage to Stock Product Delivery/Scanning Errors Internal Theft of Stock and Cash ‘Grazing’ Collusion External Theft Shoplifting Till Snatches Returning Stolen Goods Burglary ‘Grazing’
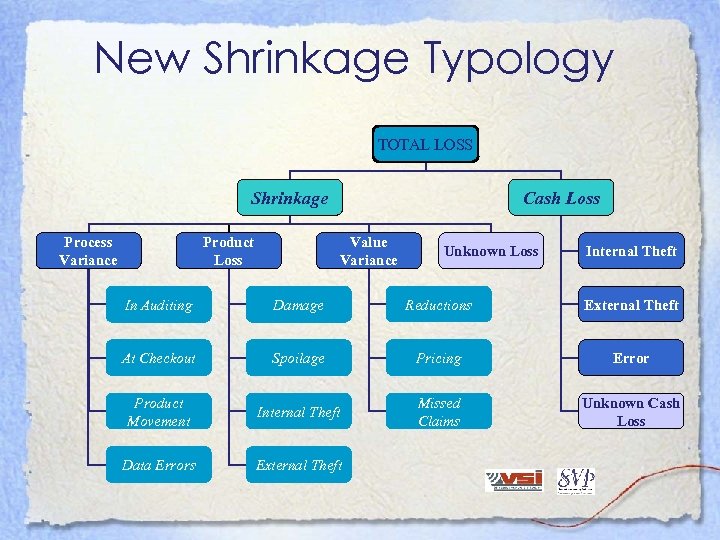 New Shrinkage Typology TOTAL LOSS Shrinkage Process Variance Product Loss Cash Loss Value Variance Unknown Loss Internal Theft In Auditing Damage Reductions External Theft At Checkout Spoilage Pricing Error Product Movement Internal Theft Missed Claims Unknown Cash Loss Data Errors External Theft
New Shrinkage Typology TOTAL LOSS Shrinkage Process Variance Product Loss Cash Loss Value Variance Unknown Loss Internal Theft In Auditing Damage Reductions External Theft At Checkout Spoilage Pricing Error Product Movement Internal Theft Missed Claims Unknown Cash Loss Data Errors External Theft
 Scale of the Problem
Scale of the Problem
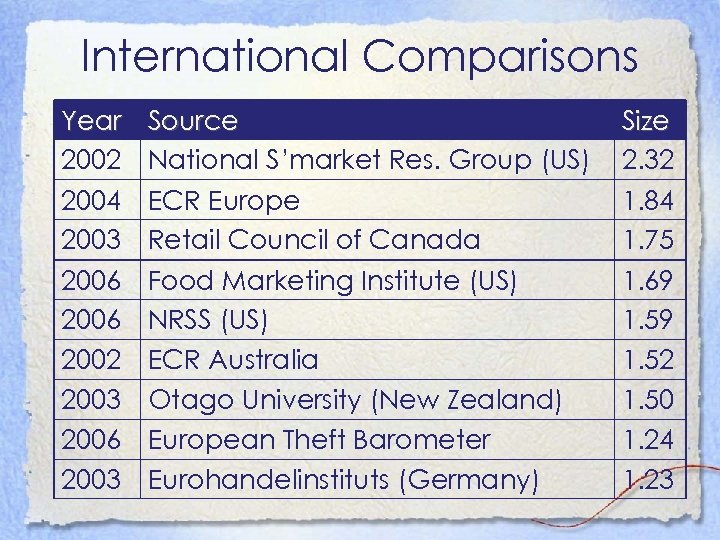 International Comparisons Year 2002 2004 2003 2006 2002 2003 2006 2003 Source National S’market Res. Group (US) ECR Europe Retail Council of Canada Food Marketing Institute (US) NRSS (US) ECR Australia Otago University (New Zealand) European Theft Barometer Eurohandelinstituts (Germany) Size 2. 32 1. 84 1. 75 1. 69 1. 52 1. 50 1. 24 1. 23
International Comparisons Year 2002 2004 2003 2006 2002 2003 2006 2003 Source National S’market Res. Group (US) ECR Europe Retail Council of Canada Food Marketing Institute (US) NRSS (US) ECR Australia Otago University (New Zealand) European Theft Barometer Eurohandelinstituts (Germany) Size 2. 32 1. 84 1. 75 1. 69 1. 52 1. 50 1. 24 1. 23
 Shrinkage Retail Iceberg • Lack of visibility • Lack of awareness 49% – When did it happen? – Where did it happen? – How did it happen? – Who was responsible? 51% • Lack of accountability • Prioritisation of the most visible/acceptable
Shrinkage Retail Iceberg • Lack of visibility • Lack of awareness 49% – When did it happen? – Where did it happen? – How did it happen? – Who was responsible? 51% • Lack of accountability • Prioritisation of the most visible/acceptable
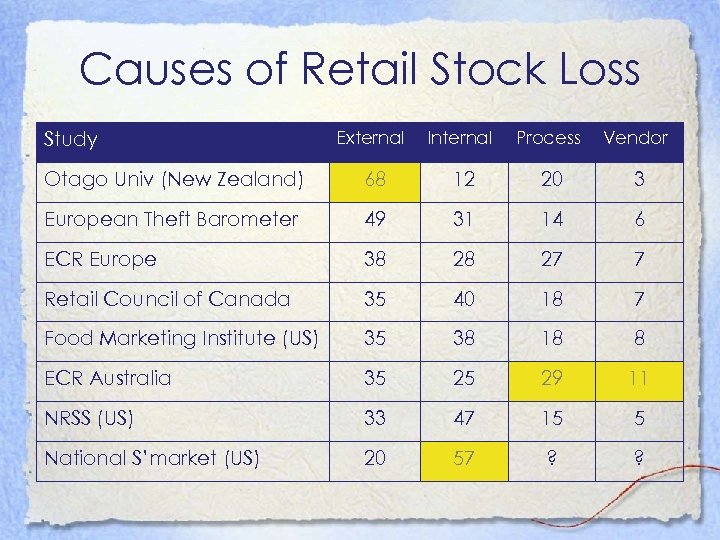 Causes of Retail Stock Loss External Internal Process Vendor Otago Univ (New Zealand) 68 12 20 3 European Theft Barometer 49 31 14 6 ECR Europe 38 28 27 7 Retail Council of Canada 35 40 18 7 Food Marketing Institute (US) 35 38 18 8 ECR Australia 35 25 29 11 NRSS (US) 33 47 15 5 National S’market (US) 20 57 ? ? Study
Causes of Retail Stock Loss External Internal Process Vendor Otago Univ (New Zealand) 68 12 20 3 European Theft Barometer 49 31 14 6 ECR Europe 38 28 27 7 Retail Council of Canada 35 40 18 7 Food Marketing Institute (US) 35 38 18 8 ECR Australia 35 25 29 11 NRSS (US) 33 47 15 5 National S’market (US) 20 57 ? ? Study
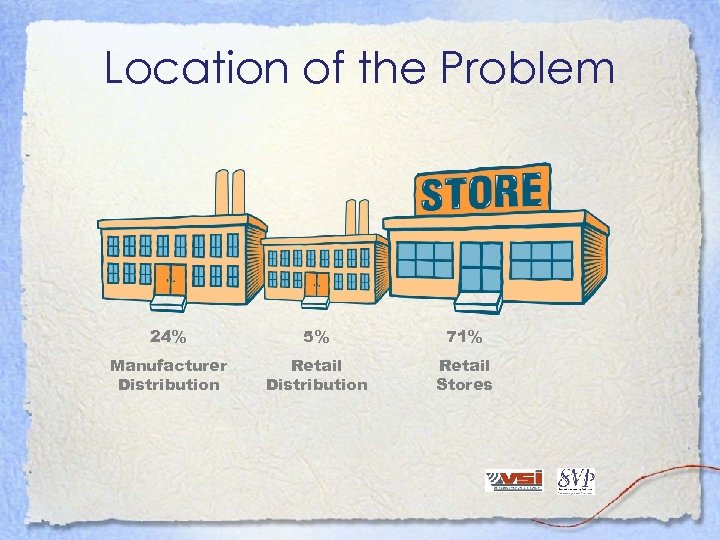 Location of the Problem 24% 5% 71% Manufacturer Distribution Retail Stores
Location of the Problem 24% 5% 71% Manufacturer Distribution Retail Stores
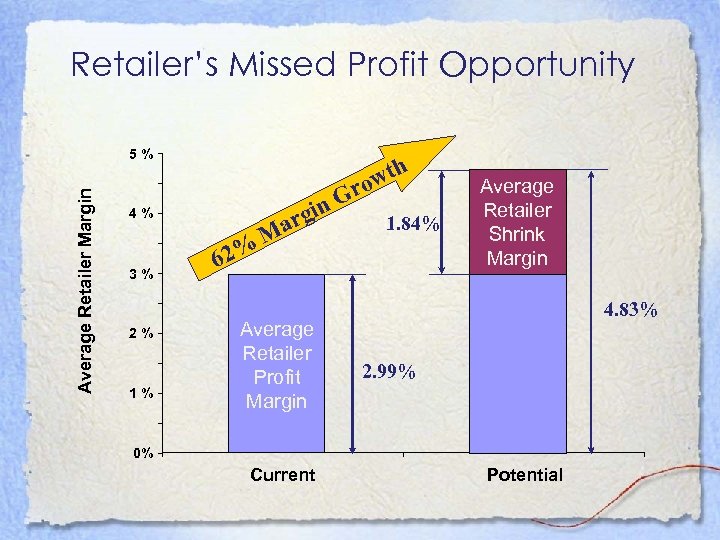 Retailer’s Missed Profit Opportunity Average Retailer Margin 5% 4% 3% 2% 1% 62% arg M in G wth ro Average Retailer Profit Margin 1. 84% Average Retailer Shrink Margin 4. 83% 2. 99% 0% Current Potential
Retailer’s Missed Profit Opportunity Average Retailer Margin 5% 4% 3% 2% 1% 62% arg M in G wth ro Average Retailer Profit Margin 1. 84% Average Retailer Shrink Margin 4. 83% 2. 99% 0% Current Potential
 Shareholder Value Net Income Shareholder Value € 1 Incremental Sales € 0. 15 € 3. 00 € 1 Inventory Reduction € 0. 20 € 4. 00 € 1 Shrinkage Reduction € 0. 70 € 14. 00 Calculated by the Cranfield School of Management based upon the following assumptions Sales Margin = 15%; Inventory Holding Costs = 20%; Net Overhead Cost = 30%; Share Price is a Multiple of 20 on Net Income.
Shareholder Value Net Income Shareholder Value € 1 Incremental Sales € 0. 15 € 3. 00 € 1 Inventory Reduction € 0. 20 € 4. 00 € 1 Shrinkage Reduction € 0. 70 € 14. 00 Calculated by the Cranfield School of Management based upon the following assumptions Sales Margin = 15%; Inventory Holding Costs = 20%; Net Overhead Cost = 30%; Share Price is a Multiple of 20 on Net Income.
 Principles of Effective Shrinkage Management
Principles of Effective Shrinkage Management
 Guiding Principles • Engage senior management • Convince them of the opportunity • Show the impact on the consumer • Persuade them that a multi functional approach is required • Secure resource
Guiding Principles • Engage senior management • Convince them of the opportunity • Show the impact on the consumer • Persuade them that a multi functional approach is required • Secure resource
 Guiding Principles • Measure the problem • Data accessibility, timeliness and granularity • Mining the data warehouse • Monitor and generate transparency
Guiding Principles • Measure the problem • Data accessibility, timeliness and granularity • Mining the data warehouse • Monitor and generate transparency
 Data mining. . . 14, 836, 947 products 10 p report Cashier error? £ 12, 000 shrinkage 1. 48 billion kr
Data mining. . . 14, 836, 947 products 10 p report Cashier error? £ 12, 000 shrinkage 1. 48 billion kr
 Guiding Principles • Promote inter and intra company collaboration • Who needed to be involved? – Manufacturer • • • Design team Production Supply Chain Marketing Sales – Retailer • • Buyer/Merchandising Loss Prevention Supply Chain Store Operations – Environmental agency
Guiding Principles • Promote inter and intra company collaboration • Who needed to be involved? – Manufacturer • • • Design team Production Supply Chain Marketing Sales – Retailer • • Buyer/Merchandising Loss Prevention Supply Chain Store Operations – Environmental agency
 End to End Solutions Before After
End to End Solutions Before After
 Guiding Principles • Adopt a systemic and systematic approach – The ECR Europe Road Map
Guiding Principles • Adopt a systemic and systematic approach – The ECR Europe Road Map
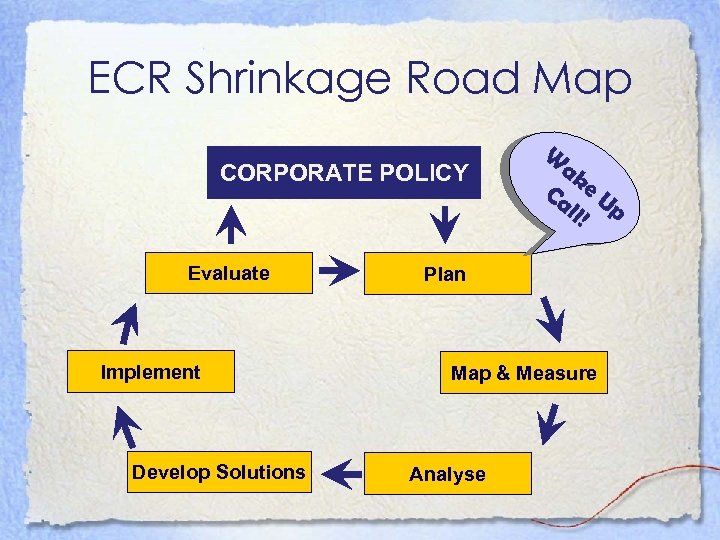 ECR Shrinkage Road Map CORPORATE POLICY Evaluate Implement Develop Solutions W ak Ca e U ll! p Plan Map & Measure Analyse
ECR Shrinkage Road Map CORPORATE POLICY Evaluate Implement Develop Solutions W ak Ca e U ll! p Plan Map & Measure Analyse
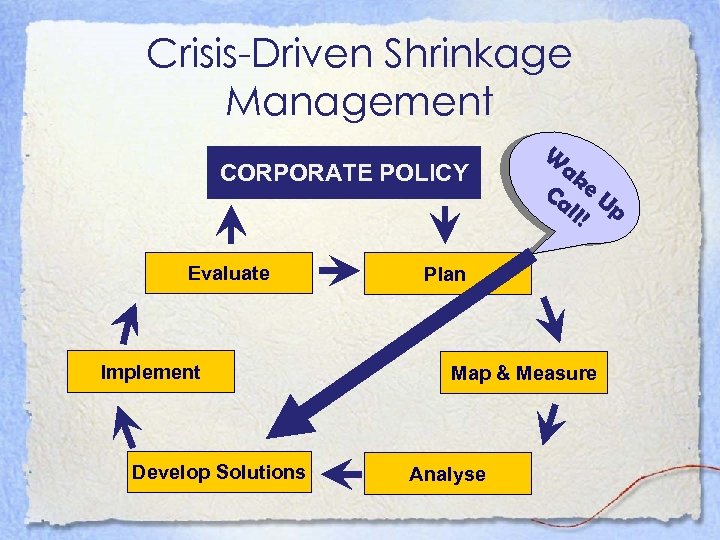 Crisis-Driven Shrinkage Management CORPORATE POLICY Evaluate Implement Develop Solutions W ak Ca e U ll! p Plan Map & Measure Analyse
Crisis-Driven Shrinkage Management CORPORATE POLICY Evaluate Implement Develop Solutions W ak Ca e U ll! p Plan Map & Measure Analyse
 Example Tool: 5 Whys Problem n There is no product on the shelf 1. Why? Because it is in the back room 2. Why? Replenishment team cannot find it 3. Why? All packs seem to look the same 4. Why? No differentiation except by barcode 5. Why? Pack designed to suit DC operation
Example Tool: 5 Whys Problem n There is no product on the shelf 1. Why? Because it is in the back room 2. Why? Replenishment team cannot find it 3. Why? All packs seem to look the same 4. Why? No differentiation except by barcode 5. Why? Pack designed to suit DC operation
 ECR Road Map Principles • Collaborate and engage all stakeholders • Focus effort on the processes: Products/Information/Money • Identify greatest oppportunities then target root causes • Remove the opportunity for loss or error • Encourage evaluation & learning
ECR Road Map Principles • Collaborate and engage all stakeholders • Focus effort on the processes: Products/Information/Money • Identify greatest oppportunities then target root causes • Remove the opportunity for loss or error • Encourage evaluation & learning
 ECR Road Map Benefits • Ensures the right resources and people engaged • Better and more sustainable results • Less daunting • More cost efficient • Higher probability of success • Quicker to implement • Lessons can be reapplied to other problems
ECR Road Map Benefits • Ensures the right resources and people engaged • Better and more sustainable results • Less daunting • More cost efficient • Higher probability of success • Quicker to implement • Lessons can be reapplied to other problems
 Guiding Principles • Unlock the value of the 'hot' concept – – Products Places People Processes Places People Products Processes
Guiding Principles • Unlock the value of the 'hot' concept – – Products Places People Processes Places People Products Processes
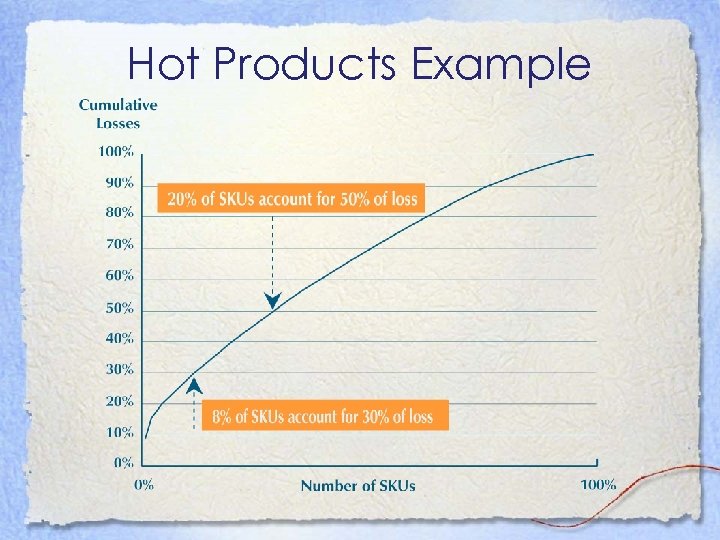 Hot Products Example
Hot Products Example
 Benefits of the ‘Hot’ Concept • Avoids spreading valuable resources too thinly • Focus on the vital few amongst the trivial many • Rapid impact • Greatest return • Possible diffusion of benefits
Benefits of the ‘Hot’ Concept • Avoids spreading valuable resources too thinly • Focus on the vital few amongst the trivial many • Rapid impact • Greatest return • Possible diffusion of benefits
 Guiding Principles • Focus on process failures first – Removes opportunity • Receipt process • Returns – Masks malicious activity – Delivers • Quick wins • Cost effective wins • Sustainable solutions
Guiding Principles • Focus on process failures first – Removes opportunity • Receipt process • Returns – Masks malicious activity – Delivers • Quick wins • Cost effective wins • Sustainable solutions
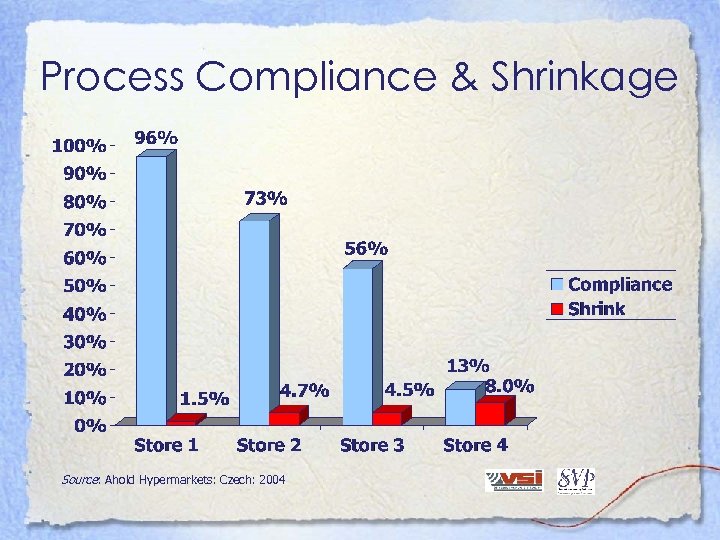 Process Compliance & Shrinkage Source: Ahold Hypermarkets: Czech: 2004
Process Compliance & Shrinkage Source: Ahold Hypermarkets: Czech: 2004
 Guiding Principles • Encourage innovation and experimentation – Keep ahead of the game – Initiate……. • Pilot Studies on new ideas • Road Map projects with suppliers • Benchmarking against industry surveys – Experiment…. . • New solutions • New store layouts – ECR survey showed that retailers who innovated and experimented most had 20% lower shrinkage
Guiding Principles • Encourage innovation and experimentation – Keep ahead of the game – Initiate……. • Pilot Studies on new ideas • Road Map projects with suppliers • Benchmarking against industry surveys – Experiment…. . • New solutions • New store layouts – ECR survey showed that retailers who innovated and experimented most had 20% lower shrinkage
 Guiding Principles • Document learning and disseminate success
Guiding Principles • Document learning and disseminate success
 Guiding Principles Disseminate Document Learning Adherence to Use the Road ECR Road Map Procedures Motivate Staff Collaborate Measure Innovate Experiment Focus on Hot Concept Engage Senior Management Adopt Systemic a Systematic Approach Start with Non Malicious Shrink
Guiding Principles Disseminate Document Learning Adherence to Use the Road ECR Road Map Procedures Motivate Staff Collaborate Measure Innovate Experiment Focus on Hot Concept Engage Senior Management Adopt Systemic a Systematic Approach Start with Non Malicious Shrink
 The ECR Road Map in Action: Tesco and P&G Case Study
The ECR Road Map in Action: Tesco and P&G Case Study
 The Problem - 2003 • Products Locked Up • Shelf “out of stocks” Failing to serve the customer and failing to support their businesses
The Problem - 2003 • Products Locked Up • Shelf “out of stocks” Failing to serve the customer and failing to support their businesses
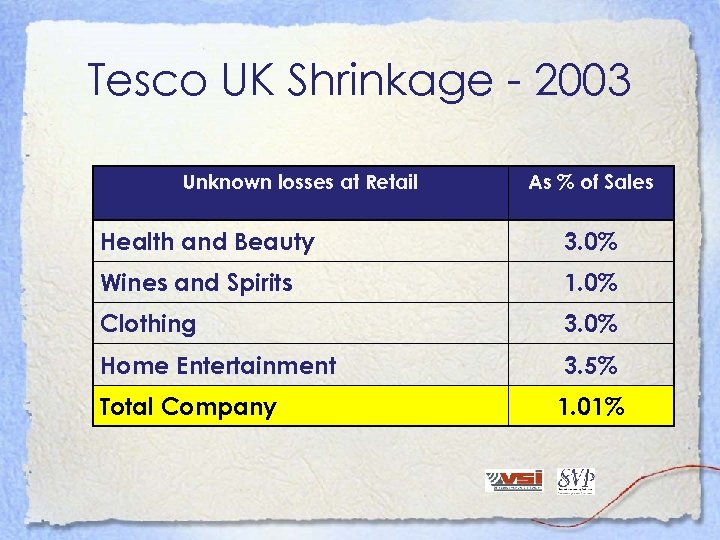 Tesco UK Shrinkage - 2003 Unknown losses at Retail As % of Sales Health and Beauty 3. 0% Wines and Spirits 1. 0% Clothing 3. 0% Home Entertainment 3. 5% Total Company 1. 01%
Tesco UK Shrinkage - 2003 Unknown losses at Retail As % of Sales Health and Beauty 3. 0% Wines and Spirits 1. 0% Clothing 3. 0% Home Entertainment 3. 5% Total Company 1. 01%
 Tesco - Call to Action • “Got the call” from the very top • “Licence” to work across functions to reduce shrinkage • Permission granted to take drastic action if needed
Tesco - Call to Action • “Got the call” from the very top • “Licence” to work across functions to reduce shrinkage • Permission granted to take drastic action if needed
 Plan • Hot Products • Hot Stores • Look for Internal Process Failures
Plan • Hot Products • Hot Stores • Look for Internal Process Failures
 Hot Products. . . Health & Beauty
Hot Products. . . Health & Beauty
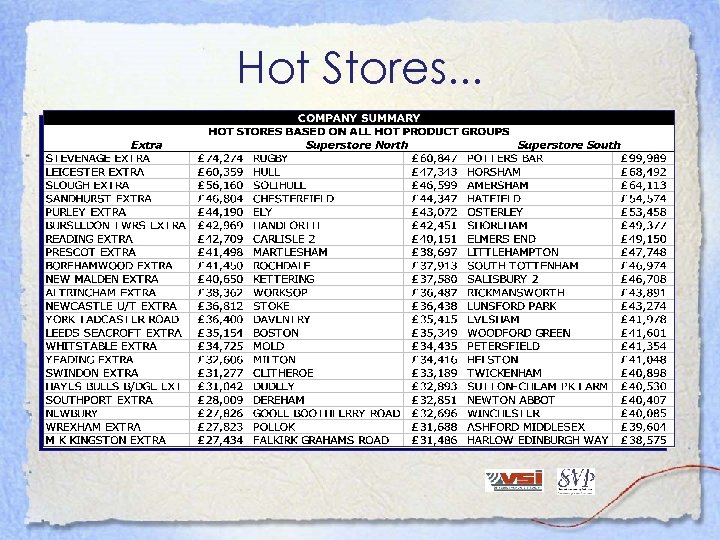 Hot Stores. . .
Hot Stores. . .
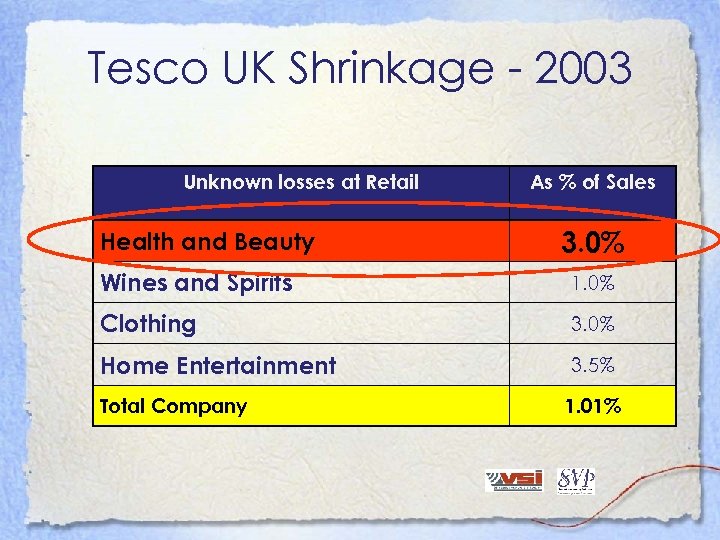 Tesco UK Shrinkage - 2003 Unknown losses at Retail Health and Beauty As % of Sales 3. 0% Wines and Spirits 1. 0% Clothing 3. 0% Home Entertainment 3. 5% Total Company 1. 01%
Tesco UK Shrinkage - 2003 Unknown losses at Retail Health and Beauty As % of Sales 3. 0% Wines and Spirits 1. 0% Clothing 3. 0% Home Entertainment 3. 5% Total Company 1. 01%
 P&G Hot Products - 2003 Unknown losses at Retail As % of Sales MACH 3 9% Oral. B Braun 15% Duracell 20%
P&G Hot Products - 2003 Unknown losses at Retail As % of Sales MACH 3 9% Oral. B Braun 15% Duracell 20%
 Map & Measure Picking Shelf
Map & Measure Picking Shelf
 Analyse • What could go wrong? • Scored each risk – Severity – Occurrence – Detection • Assessed root causes for key risks
Analyse • What could go wrong? • Scored each risk – Severity – Occurrence – Detection • Assessed root causes for key risks
 Solutions Developed • Secure Supply Chain for top 500 hot products
Solutions Developed • Secure Supply Chain for top 500 hot products
 Solutions Developed • Secure storage in top 200 stores • This has become “design” standard and is rolled out in all stores
Solutions Developed • Secure storage in top 200 stores • This has become “design” standard and is rolled out in all stores
 Solutions Developed • Modified Packaging to enable product protection in all stores
Solutions Developed • Modified Packaging to enable product protection in all stores
 Solutions Developed • Introduced regular counting of hot products to measure results
Solutions Developed • Introduced regular counting of hot products to measure results
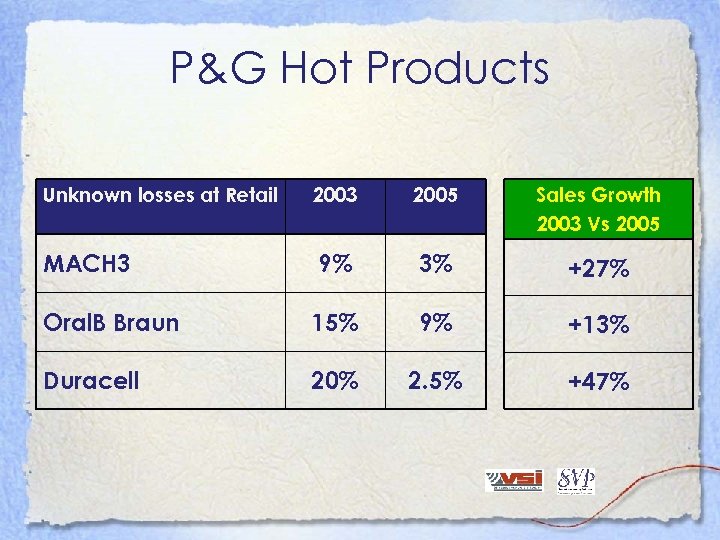 P&G Hot Products Unknown losses at Retail 2003 2005 Sales Growth 2003 Vs 2005 MACH 3 9% 3% +27% Oral. B Braun 15% 9% +13% Duracell 20% 2. 5% +47%
P&G Hot Products Unknown losses at Retail 2003 2005 Sales Growth 2003 Vs 2005 MACH 3 9% 3% +27% Oral. B Braun 15% 9% +13% Duracell 20% 2. 5% +47%
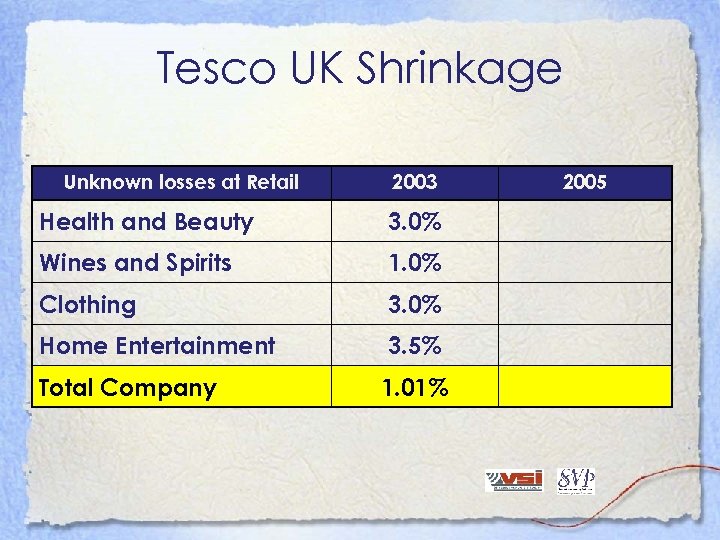 Tesco UK Shrinkage Unknown losses at Retail 2003 Health and Beauty 3. 0% Wines and Spirits 1. 0% Clothing 3. 0% Home Entertainment 3. 5% Total Company 1. 01% 2005
Tesco UK Shrinkage Unknown losses at Retail 2003 Health and Beauty 3. 0% Wines and Spirits 1. 0% Clothing 3. 0% Home Entertainment 3. 5% Total Company 1. 01% 2005
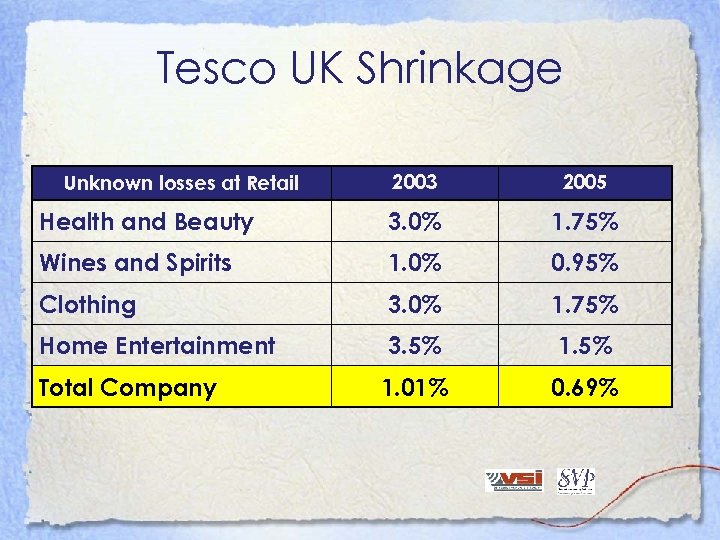 Tesco UK Shrinkage 2003 2005 Health and Beauty 3. 0% 1. 75% Wines and Spirits 1. 0% 0. 95% Clothing 3. 0% 1. 75% Home Entertainment 3. 5% 1. 5% Total Company 1. 01% 0. 69% Unknown losses at Retail
Tesco UK Shrinkage 2003 2005 Health and Beauty 3. 0% 1. 75% Wines and Spirits 1. 0% 0. 95% Clothing 3. 0% 1. 75% Home Entertainment 3. 5% 1. 5% Total Company 1. 01% 0. 69% Unknown losses at Retail
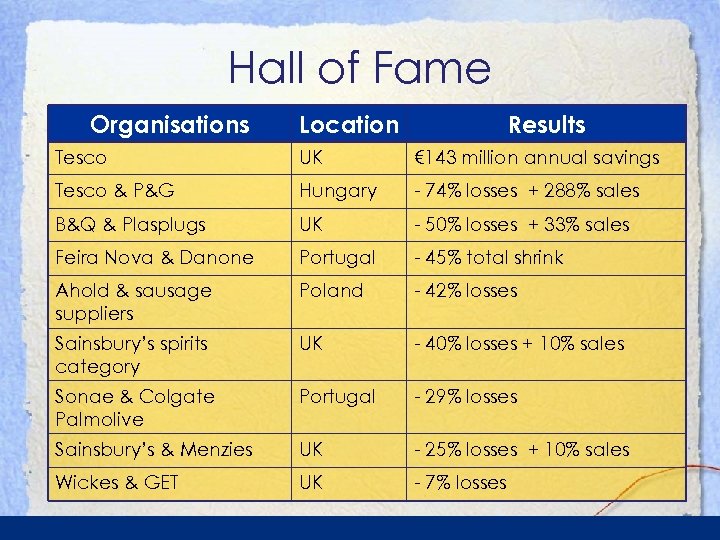 Hall of Fame Organisations Location Results Tesco UK € 143 million annual savings Tesco & P&G Hungary - 74% losses + 288% sales B&Q & Plasplugs UK - 50% losses + 33% sales Feira Nova & Danone Portugal - 45% total shrink Ahold & sausage suppliers Poland - 42% losses Sainsbury’s spirits category UK - 40% losses + 10% sales Sonae & Colgate Palmolive Portugal - 29% losses Sainsbury’s & Menzies UK - 25% losses + 10% sales Wickes & GET UK - 7% losses
Hall of Fame Organisations Location Results Tesco UK € 143 million annual savings Tesco & P&G Hungary - 74% losses + 288% sales B&Q & Plasplugs UK - 50% losses + 33% sales Feira Nova & Danone Portugal - 45% total shrink Ahold & sausage suppliers Poland - 42% losses Sainsbury’s spirits category UK - 40% losses + 10% sales Sonae & Colgate Palmolive Portugal - 29% losses Sainsbury’s & Menzies UK - 25% losses + 10% sales Wickes & GET UK - 7% losses
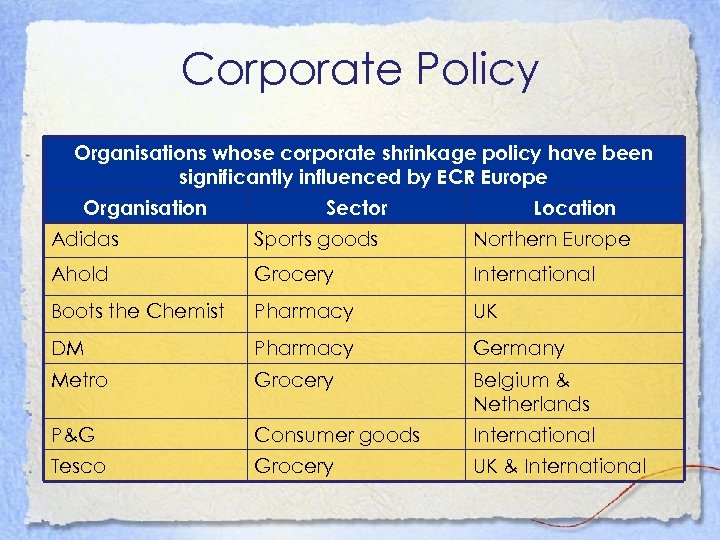 Corporate Policy Organisations whose corporate shrinkage policy have been significantly influenced by ECR Europe Organisation Sector Location Adidas Sports goods Northern Europe Ahold Grocery International Boots the Chemist Pharmacy UK DM Pharmacy Germany Metro Grocery Belgium & Netherlands P&G Consumer goods International Tesco Grocery UK & International
Corporate Policy Organisations whose corporate shrinkage policy have been significantly influenced by ECR Europe Organisation Sector Location Adidas Sports goods Northern Europe Ahold Grocery International Boots the Chemist Pharmacy UK DM Pharmacy Germany Metro Grocery Belgium & Netherlands P&G Consumer goods International Tesco Grocery UK & International
 Concluding Thoughts • Shrinkage offers an enormous opportunity • Need to measure the problem accurately • Need to adopt a systematic and systemic approach • Collaboration is key • Solutions need to be ‘fit for purpose’ • Shrinkage is the last free money on the table
Concluding Thoughts • Shrinkage offers an enormous opportunity • Need to measure the problem accurately • Need to adopt a systematic and systemic approach • Collaboration is key • Solutions need to be ‘fit for purpose’ • Shrinkage is the last free money on the table
 Thank you for listening!
Thank you for listening!


