 Long-Range Effects in Layered Spin Structures Ramaz Khomeriki 1, 3, David Mukamel 2, Stefano Ruffo 1 1)Dipartimento di Energetica ‘‘S. Stecco’’ and CSDC, Università di Firenze, and INFN, Via S. Marta, 3, 50139 Firenze, ITALY 2)Department of Physics of Complex Systems, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot 76100, ISRAEL 3)Physics Department, Tbilisi State University, 0128 Tbilisi, GEORGIA
Long-Range Effects in Layered Spin Structures Ramaz Khomeriki 1, 3, David Mukamel 2, Stefano Ruffo 1 1)Dipartimento di Energetica ‘‘S. Stecco’’ and CSDC, Università di Firenze, and INFN, Via S. Marta, 3, 50139 Firenze, ITALY 2)Department of Physics of Complex Systems, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot 76100, ISRAEL 3)Physics Department, Tbilisi State University, 0128 Tbilisi, GEORGIA
 ABSTRACT The layered spin structures are studied theoretically with the aim of predicting realistic testable effects of long range dipolar interactions. As shown, dipolar interaction between the spin layers open gaps in allowable energy versus magnetization phase diagram. The consequences of this behavior, particularly, the response of the system state under application of periodical external magnetic field is investigated.
ABSTRACT The layered spin structures are studied theoretically with the aim of predicting realistic testable effects of long range dipolar interactions. As shown, dipolar interaction between the spin layers open gaps in allowable energy versus magnetization phase diagram. The consequences of this behavior, particularly, the response of the system state under application of periodical external magnetic field is investigated.
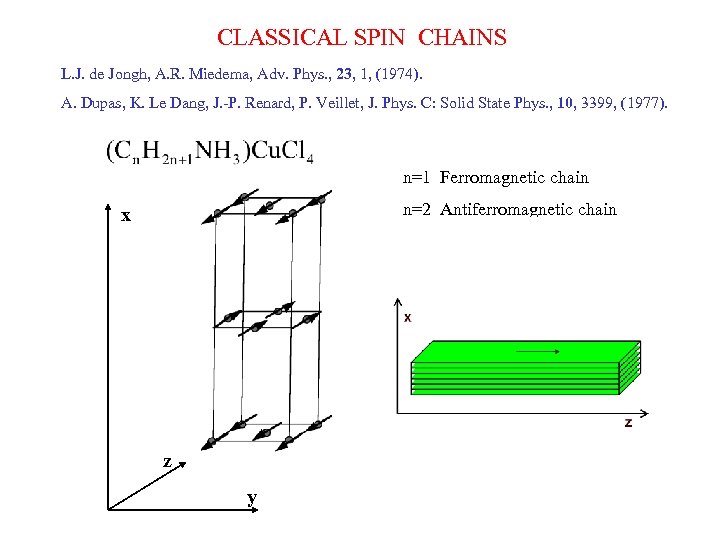 CLASSICAL SPIN CHAINS L. J. de Jongh, A. R. Miedema, Adv. Phys. , 23, 1, (1974). A. Dupas, K. Le Dang, J. -P. Renard, P. Veillet, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. , 10, 3399, (1977). n=1 Ferromagnetic chain n=2 Antiferromagnetic chain x z y
CLASSICAL SPIN CHAINS L. J. de Jongh, A. R. Miedema, Adv. Phys. , 23, 1, (1974). A. Dupas, K. Le Dang, J. -P. Renard, P. Veillet, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. , 10, 3399, (1977). n=1 Ferromagnetic chain n=2 Antiferromagnetic chain x z y
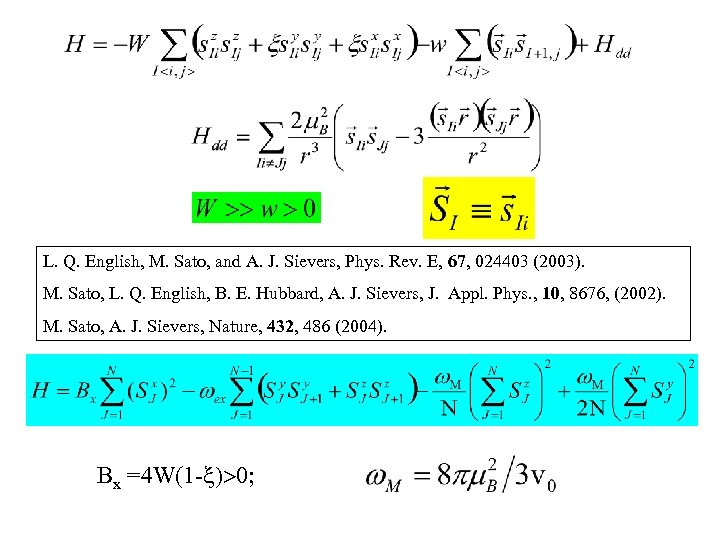 L. Q. English, M. Sato, and A. J. Sievers, Phys. Rev. E, 67, 024403 (2003). M. Sato, L. Q. English, B. E. Hubbard, A. J. Sievers, J. Appl. Phys. , 10, 8676, (2002). M. Sato, A. J. Sievers, Nature, 432, 486 (2004). Bx =4 W(1 -x)>0;
L. Q. English, M. Sato, and A. J. Sievers, Phys. Rev. E, 67, 024403 (2003). M. Sato, L. Q. English, B. E. Hubbard, A. J. Sievers, J. Appl. Phys. , 10, 8676, (2002). M. Sato, A. J. Sievers, Nature, 432, 486 (2004). Bx =4 W(1 -x)>0;
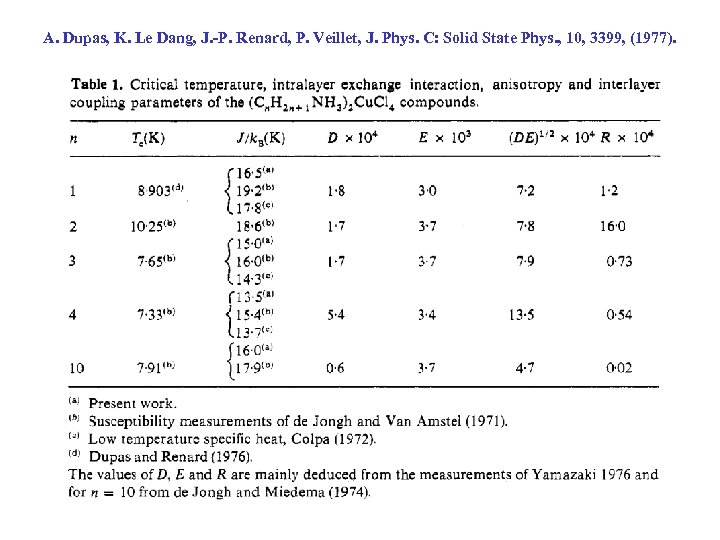 A. Dupas, K. Le Dang, J. -P. Renard, P. Veillet, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. , 10, 3399, (1977).
A. Dupas, K. Le Dang, J. -P. Renard, P. Veillet, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. , 10, 3399, (1977).