bfa57bd410f1ea8a40d95be435cabe2d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

LOICZ II The next Generation of Global Coastal Change Science Land-Ocean interactions across multiple interfaces 2003 2012 G. Flöser, LOICZ European Node, GKSS Research Centre, Geesthacht, Germany A core project of the International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme and the International Human Dimensions Programme on Global Environmental Change

What is / was LOICZ? • LOICZ: Land-Ocean Interaction in the Coastal Zone • Core Project of IGBP • Phase I 1993 -2002 concluded, Springer book available June ‘ 05. More than 20 scientific Reports. • Aim: “to determine … the dynamic nature of interaction between land, ocean and atmosphere and how changes in various components of the Earth system are affecting coastal zones …”. • key biogeochemical features of global coastal seas • 2300 scientists in 130 countries • International Project Office in Texel, The Netherlands (hosted by NIOZ), 2 officers
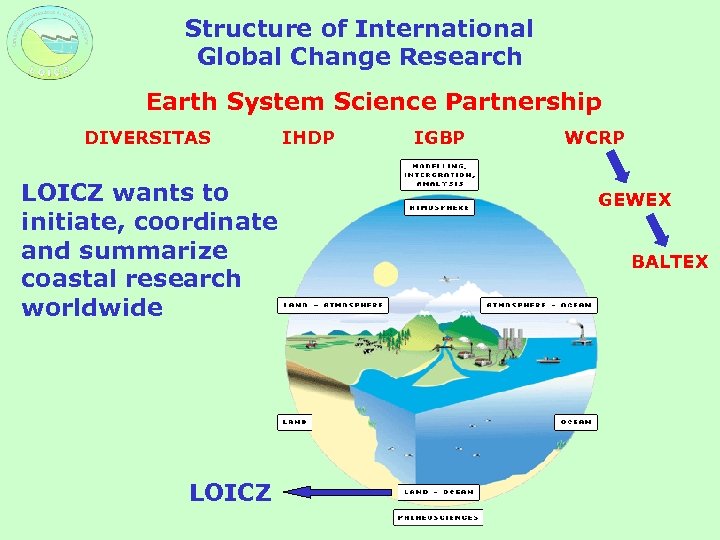
Structure of International Global Change Research Earth System Science Partnership DIVERSITAS LOICZ wants to initiate, coordinate and summarize coastal research worldwide LOICZ IHDP IGBP WCRP GEWEX BALTEX
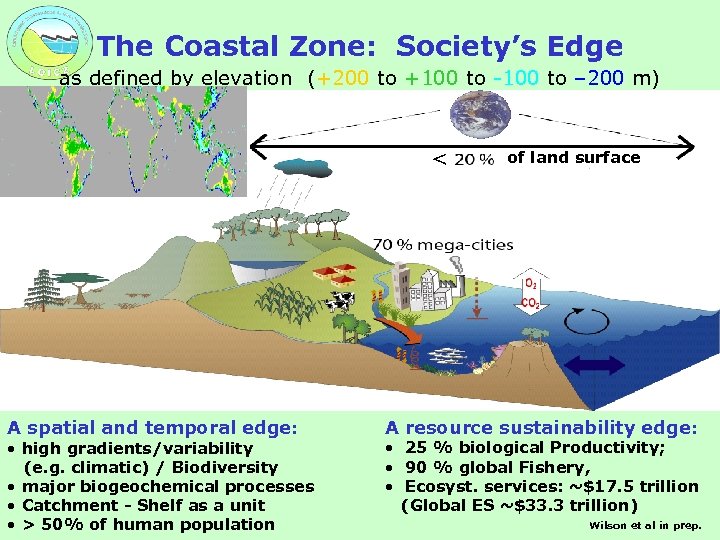
The Coastal Zone: Society’s Edge as defined by elevation (+200 to +100 to -100 to – 200 m) < A spatial and temporal edge: • high gradients/variability (e. g. climatic) / Biodiversity • major biogeochemical processes • Catchment - Shelf as a unit • > 50% of human population of land surface A resource sustainability edge: • 25 % biological Productivity; • 90 % global Fishery, • Ecosyst. services: ~$17. 5 trillion (Global ES ~$33. 3 trillion) Wilson et al in prep.
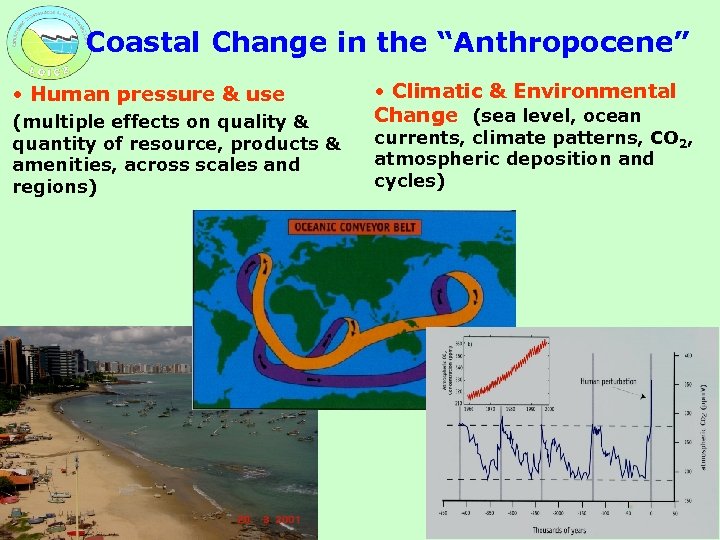
Coastal Change in the “Anthropocene” • Human pressure & use (multiple effects on quality & quantity of resource, products & amenities, across scales and regions) • Climatic & Environmental Change (sea level, ocean currents, climate patterns, CO 2, atmospheric deposition and cycles)
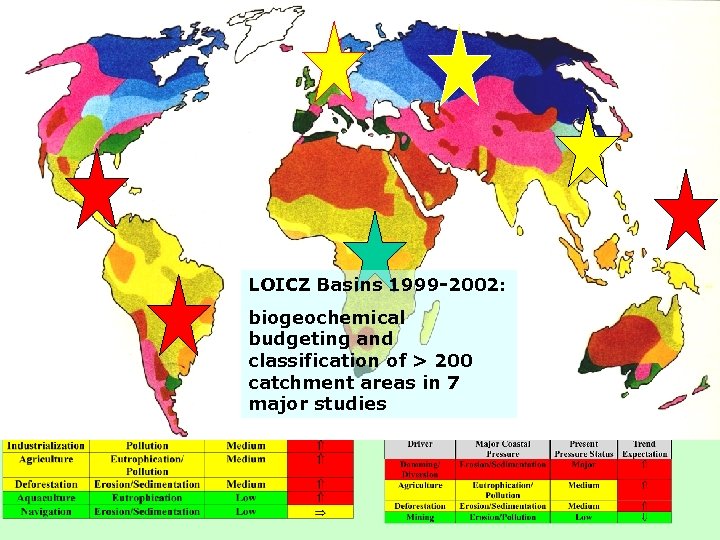
The river-coast continuum: Giving information LOICZ Basins 1999 -2002: in a useful way biogeochemical budgeting and classification of > 200 catchment areas in 7 major studies
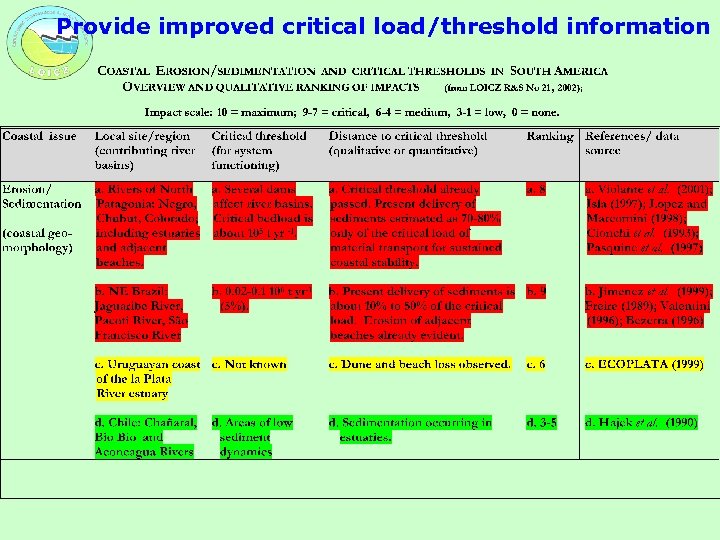
Provide improved critical load/threshold information
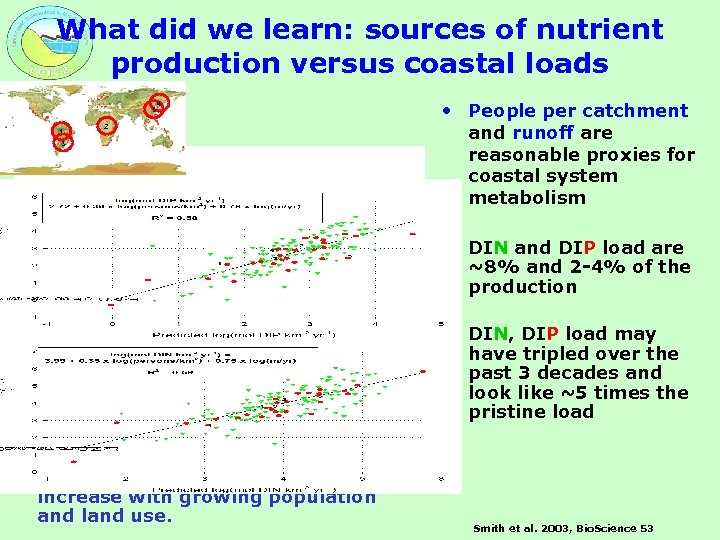
What did we learn: sources of nutrient production versus coastal loads 5 1 4 2 3 • People per catchment and runoff are reasonable proxies for coastal system metabolism • DIN and DIP load are ~8% and 2 -4% of the production • DIN, DIP load may have tripled over the past 3 decades and look like ~5 times the pristine load • Load still seems relatively low; but there is potential of continued increase with growing population and land use. Smith et al. 2003, Bio. Science 53
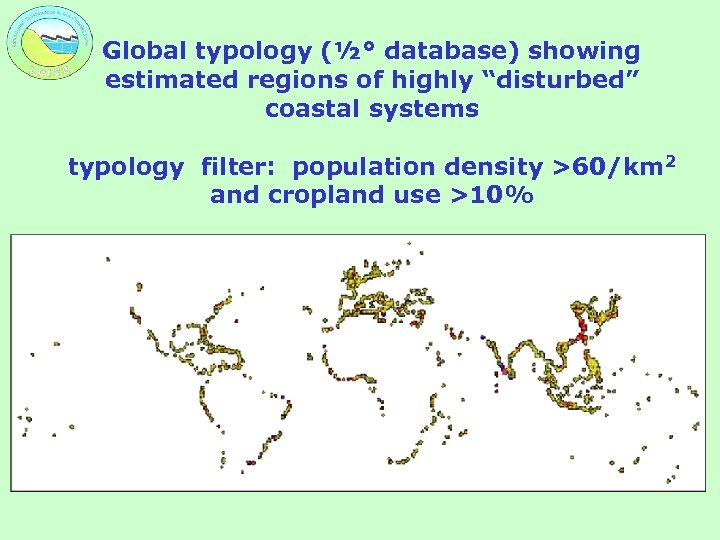
Global typology (½° database) showing estimated regions of highly “disturbed” coastal systems typology filter: population density >60/km 2 and cropland use >10%
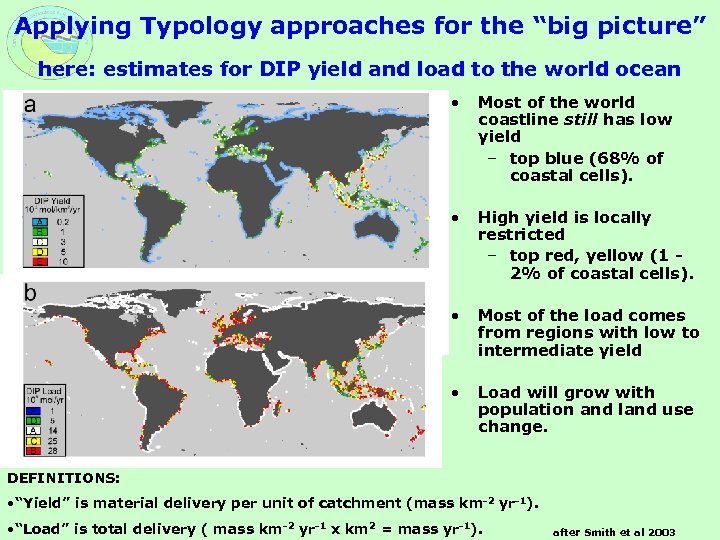
Applying Typology approaches for the “big picture” here: estimates for DIP yield and load to the world ocean • Most of the world coastline still has low yield – top blue (68% of coastal cells). • High yield is locally restricted – top red, yellow (1 2% of coastal cells). • Most of the load comes from regions with low to intermediate yield • Load will grow with population and land use change. DEFINITIONS: • “Yield” is material delivery per unit of catchment (mass km-2 yr-1). • “Load” is total delivery ( mass km-2 yr-1 x km 2 = mass yr-1). after Smith et al 2003

The New LOICZ • Connection to the International Human Dimensions Programme, another Core Project of ESSP • Science plan is finished and available on the web: www. loicz. org • Example: Cooperative Research Center (Australia) brings together decision makers – tourism – economy – nature conservation

Cooperative Research Center, Australia: Bringing together stakeholders interested in the Great Barrier Reef • • • Association of Marine Park Tourism Operators Australian Institute of Marine Science Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority Great Barrier Reef Research Foundation James Cook University Queensland Department of Primary Industries and Fisheries • Queensland Seafood Industry Association Inc. • SUNFISH Queensland Inc.
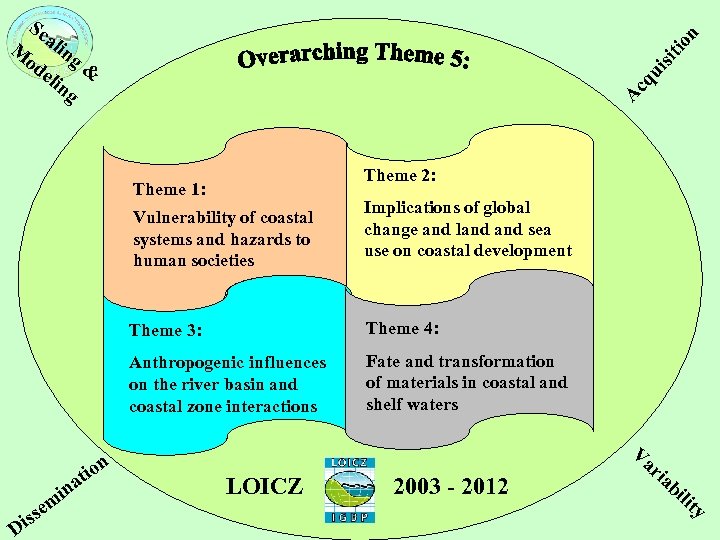
A cq ui sit i on Sc a M ling od eli & ng Theme 2: Theme 1: Vulnerability of coastal systems and hazards to human societies Implications of global change and land sea use on coastal development Theme 3: Anthropogenic influences on the river basin and coastal zone interactions i at n Di m se s ion Theme 4: Fate and transformation of materials in coastal and shelf waters Va LOICZ 2003 - 2012 ria bi lit y

New LOICZ: A process-based rolling synthesis approach Theme 1: Vulnerability of coastal systems and hazards to human societies (exchange with, e. g. , GECHS, GECAFS, GWSP, WCRP) · Sea level rise - Hard vs. soft coastal defences · Natural hazards and life quality · Impacts of global atmospheric / ocean climate change on coastal systems (downscaling) · Variability of coastal vulnerability to environmental changes (Estuaries) · Adaptation strategies to environmental changes and impact on health safety Theme 2: Implications of global change and land sea use on coastal development (exchange with, e. g. , Urbanization, Land (LUCC), IDGEC) · Coastal urbanisation · Changing dynamics (e. g. mangroves, salt marshes, dredging) · Changing sea use [sand gravel mining, windmills, reclamation (including offshore), large scale engineering, oil and gas extraction, aquaculture]

New LOICZ: A process-based rolling synthesis approach Theme 3: Anthropogenic influences on the river basin and coastal zone interactions (exchange with, e. g. , GWSP, IDGEC, Land (LUCC)) · Damming · Catchment modelling on nutrients and pollution; scenarios · Local governance and resource management · Land Use and Cover Change and critical thresholds of mass transport Theme 4: Fate and transformation of materials in coastal BALTEX II Objectives: and shelf waters (exchange with, e. g. , IMBER, SOLAS, …Gradual extension of BALTEX methodologies GLOBEC) to air and water quality studies · Local burial versus long distant export of matter · Use of global (satellite) coastal monitoring data · Coastal & Estuarine software (freeware/shareware) · Interaction between coastal habitats/ecosystems and C/N/P sources/sinks · Refining techniques for coastal biogeochemical budgets including error analysis · Trace gasses in the coastal zone · Geochemical cycling of Hg in the coastal zone

New LOICZ: A process-based rolling synthesis approach Overarching -Theme 5 : Towards coastal system sustainability by managing land-ocean interactions (exchange with, e. g. , IHDP, DIVERSITAS) · Changing economic valuation of coastal ecosystems (also under 2) · Criteria of coastal sustainability (resources, ecological) · Different governance strategies for coastal zone management and Indicators of management efficiency · Contents and tools of adaptive management
The Baltic Sea • was part of LOICZ in the biogeochemical budgeting procedure (Vistula, Gulf of Finland, Odra projects) • is part in the SINCOS EU project
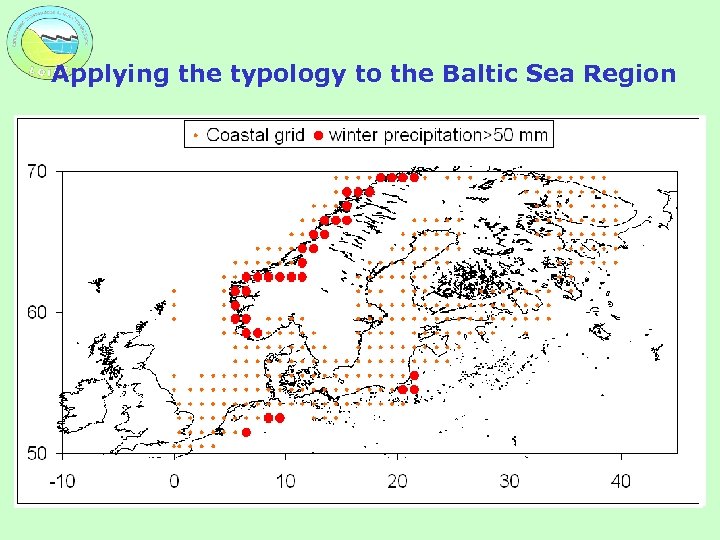
Applying the typology to the Baltic Sea Region
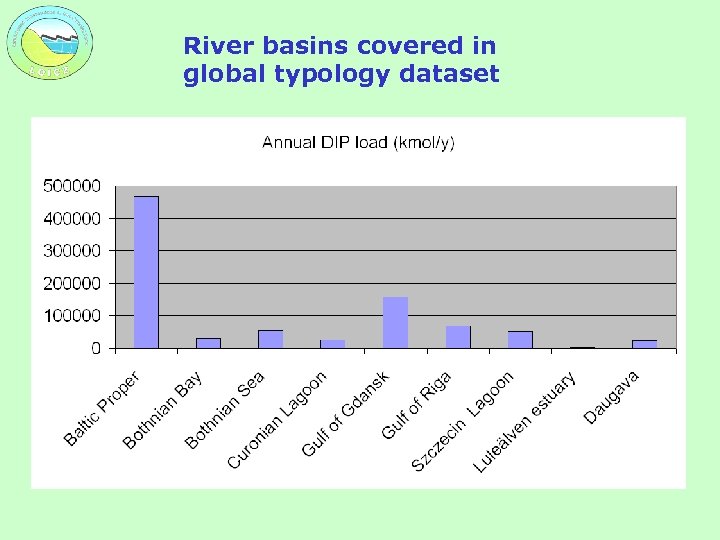
River basins covered in global typology dataset

The Odra Project www. ikzm-oder. de • is a regional project of the New LOICZ • immediately feeds into themes 2, 3 and 5 • is transboundary • includes stakeholders on river basin management • LOICZ wants comparison to other river basins (IOW)

Thank you!
bfa57bd410f1ea8a40d95be435cabe2d.ppt