1_log_asp.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Logistics Maria Tsenzharik, Ph. D matiac@yandex. ru
Logistics Maria Tsenzharik, Ph. D matiac@yandex. ru
 Plan Logistics: definition and functions Contemporary logistics Transportation system: structure and role Logistics methods and models Supply chain management ICT in logistics
Plan Logistics: definition and functions Contemporary logistics Transportation system: structure and role Logistics methods and models Supply chain management ICT in logistics

 Presentation topics National transportation system (case) Organization of transportation terminal (case) Specificity of supply chain in the manufacturing company Specificity of supply chain in the retail company Application of information system in logistics Case of international logistic company Organization of logistics center (case) Reverse logistics (case)
Presentation topics National transportation system (case) Organization of transportation terminal (case) Specificity of supply chain in the manufacturing company Specificity of supply chain in the retail company Application of information system in logistics Case of international logistic company Organization of logistics center (case) Reverse logistics (case)
 Logistics definition Council of Logistics Management (USA): Logistics is a process of planning, organization and control of effective movement and storage of goods (raw materials, semi-finished, and finished goods), services and related information form the point of origin to the point of consumption aiming meeting customers requirements.
Logistics definition Council of Logistics Management (USA): Logistics is a process of planning, organization and control of effective movement and storage of goods (raw materials, semi-finished, and finished goods), services and related information form the point of origin to the point of consumption aiming meeting customers requirements.
 Logistics definition (France) Logistics is a complex of activities carried with the aim of delivery of necessary quantity (Q) of goods at a certain time (T) to a certain place (P) where a need for this goods exists, with a minimum cost.
Logistics definition (France) Logistics is a complex of activities carried with the aim of delivery of necessary quantity (Q) of goods at a certain time (T) to a certain place (P) where a need for this goods exists, with a minimum cost.
 Logistics definition: Germany Logistics is a determined for any enterprise system of control (optimization) of internal and external material flows at different stages from purchasing via production process to delivery of final goods to the customers, including the information system which relates all tasks indicated
Logistics definition: Germany Logistics is a determined for any enterprise system of control (optimization) of internal and external material flows at different stages from purchasing via production process to delivery of final goods to the customers, including the information system which relates all tasks indicated
 Logistics The concept and the methods of material and related information flows management which are applied: Aim: delivery of certain quantity of materials and goods to certain place in time indicated Criteria: costs minimization or profit maximization Area: in the logistics systems determined for any company Necessary condition: appropriate delivery time and convenience for the client
Logistics The concept and the methods of material and related information flows management which are applied: Aim: delivery of certain quantity of materials and goods to certain place in time indicated Criteria: costs minimization or profit maximization Area: in the logistics systems determined for any company Necessary condition: appropriate delivery time and convenience for the client
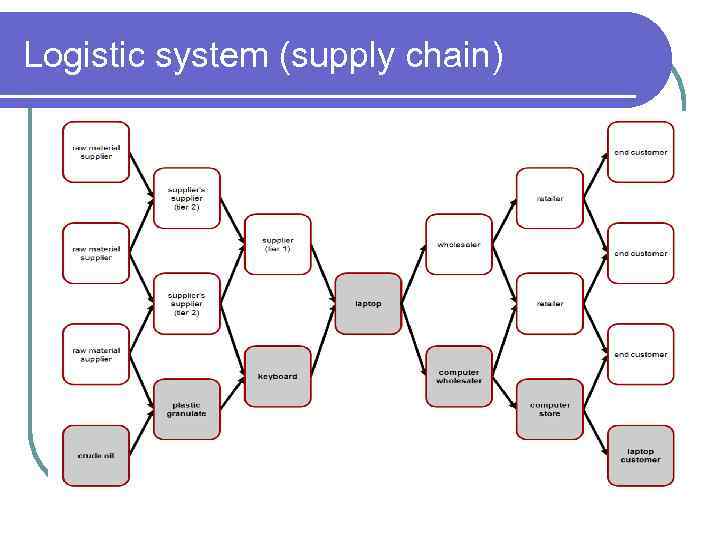 Logistic system (supply chain)
Logistic system (supply chain)
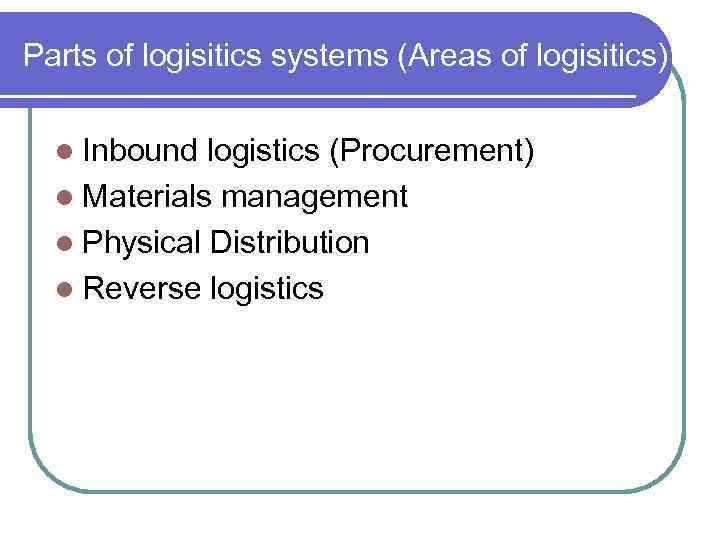 Parts of logisitics systems (Areas of logisitics) l Inbound logistics (Procurement) l Materials management l Physical Distribution l Reverse logistics
Parts of logisitics systems (Areas of logisitics) l Inbound logistics (Procurement) l Materials management l Physical Distribution l Reverse logistics
 Inbound logistics Analysis and choice of suppliers Contracting with suppliers Inventory management Order placement Delivery organization Resources quality control Storage organization Warehouses allocation
Inbound logistics Analysis and choice of suppliers Contracting with suppliers Inventory management Order placement Delivery organization Resources quality control Storage organization Warehouses allocation
 Materials management Production schedules Materials movement inside the enterprise Some authors consider materials management as a part of operations management or production management
Materials management Production schedules Materials movement inside the enterprise Some authors consider materials management as a part of operations management or production management
 Physical distribution Demand forecasting Orders taking Orders processing Finished goods inventory management Goods storage Goods delivery
Physical distribution Demand forecasting Orders taking Orders processing Finished goods inventory management Goods storage Goods delivery
 Reverse logistics Return of goods with the bad quality Return of disposable (for utilization) and reusable (for further usage) packages Return of overdue goods Return of used goods for utilization (recycling, remanufacturing) Return of not sold goods for replacement Return of harmful wastes for utilization
Reverse logistics Return of goods with the bad quality Return of disposable (for utilization) and reusable (for further usage) packages Return of overdue goods Return of used goods for utilization (recycling, remanufacturing) Return of not sold goods for replacement Return of harmful wastes for utilization
 Thus, logistics science of planning, design and support of business operations of procurement, purchasing, inventory, warehousing, distribution, transportation, customer support, financial and human resources
Thus, logistics science of planning, design and support of business operations of procurement, purchasing, inventory, warehousing, distribution, transportation, customer support, financial and human resources
 Logistics operations analytical ü ü ü Orders processing Demand forecasting Document flows organization Economic order quantity calculation Inventory control Optimal transportation schedule calculation physical Packaging and marking of goods Transportation Distribution centers and warehouses management Taking returned goods and packages Loading and reloading Wastes processing
Logistics operations analytical ü ü ü Orders processing Demand forecasting Document flows organization Economic order quantity calculation Inventory control Optimal transportation schedule calculation physical Packaging and marking of goods Transportation Distribution centers and warehouses management Taking returned goods and packages Loading and reloading Wastes processing
 Supply Chain a system of organizations, people, activities, information, and resources involved in moving a product or service from supplier to customer
Supply Chain a system of organizations, people, activities, information, and resources involved in moving a product or service from supplier to customer
 Supply chain strategies require a total systems view of the links in the chain that work together efficiently to create customer satisfaction at the end point of delivery to the consumer. costs must be lowered throughout the chain by driving out unnecessary expenses, movements, and handling main focus - efficiency and added value. Efficiency must be increased, and bottlenecks removed. supply chain system must be responsive to customer requirements
Supply chain strategies require a total systems view of the links in the chain that work together efficiently to create customer satisfaction at the end point of delivery to the consumer. costs must be lowered throughout the chain by driving out unnecessary expenses, movements, and handling main focus - efficiency and added value. Efficiency must be increased, and bottlenecks removed. supply chain system must be responsive to customer requirements
 Total logistics costs preparing goods for transportation · storage · cargo insurance · loading/reloading · customs processing · transportation · containers leasing · information costs · opportunity profit ·
Total logistics costs preparing goods for transportation · storage · cargo insurance · loading/reloading · customs processing · transportation · containers leasing · information costs · opportunity profit ·
 Factors effected logistics development Growth of fuel prices => need to reduce transportation costs Competition =>Growth of product lines number Increasing of warehouses sizes => Changing of inventory management concept Domino effect => logistics methods diffusion Public interest to environment protection => new packages and reverse logistics ICT progress => improving information accumulating, processing and transfer New modes of transportation => raising speed of delivery
Factors effected logistics development Growth of fuel prices => need to reduce transportation costs Competition =>Growth of product lines number Increasing of warehouses sizes => Changing of inventory management concept Domino effect => logistics methods diffusion Public interest to environment protection => new packages and reverse logistics ICT progress => improving information accumulating, processing and transfer New modes of transportation => raising speed of delivery
 Contemporary logistics International logistics ICT in management of movement and storage of goods Logistics intermediaries Transformation of logistics out of secondary function into the key one
Contemporary logistics International logistics ICT in management of movement and storage of goods Logistics intermediaries Transformation of logistics out of secondary function into the key one
 ICT effecting logistics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. To simplify and speed up document flows To process large volumes of data for analysis and calculations To transfer information almost simultaneously To enter information into the information system To facilitate international trade To trace customer preferencies
ICT effecting logistics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. To simplify and speed up document flows To process large volumes of data for analysis and calculations To transfer information almost simultaneously To enter information into the information system To facilitate international trade To trace customer preferencies
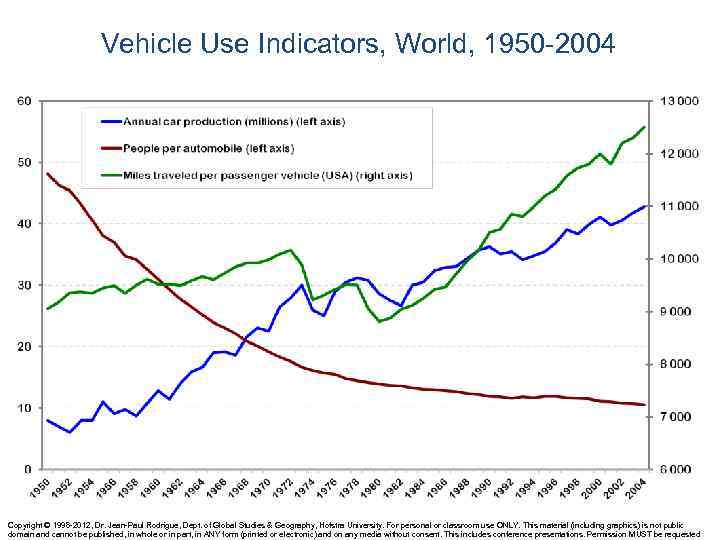 Vehicle Use Indicators, World, 1950 -2004 Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
Vehicle Use Indicators, World, 1950 -2004 Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
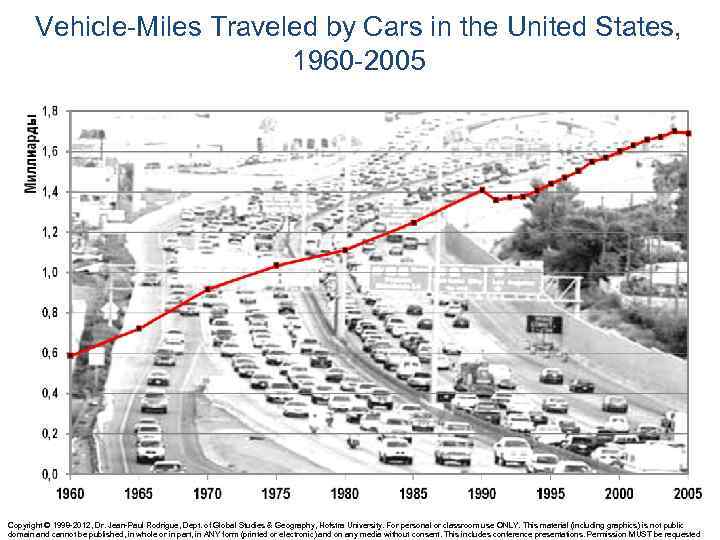 Vehicle-Miles Traveled by Cars in the United States, 1960 -2005 Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
Vehicle-Miles Traveled by Cars in the United States, 1960 -2005 Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
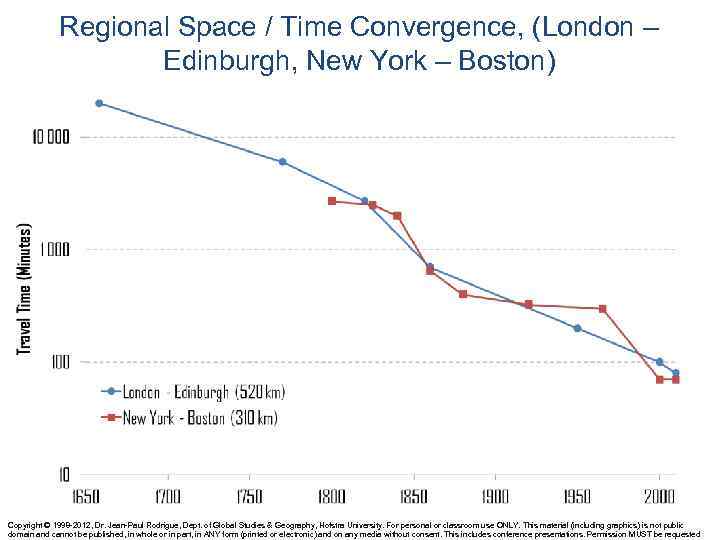 Regional Space / Time Convergence, (London – Edinburgh, New York – Boston) Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
Regional Space / Time Convergence, (London – Edinburgh, New York – Boston) Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
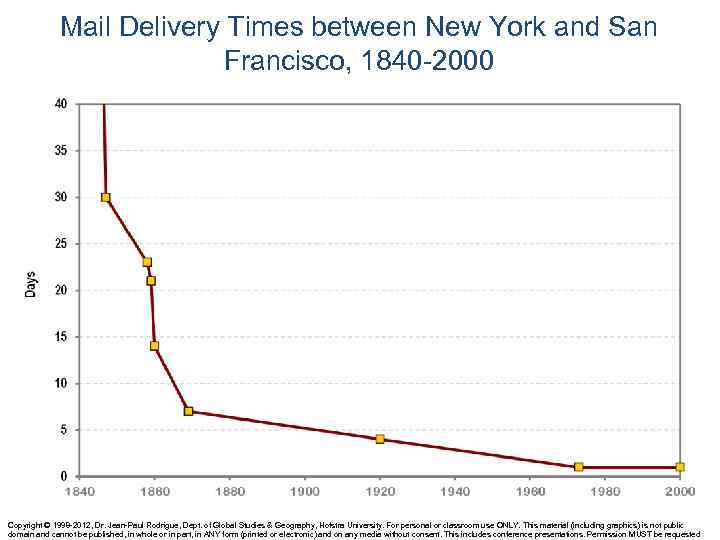 Mail Delivery Times between New York and San Francisco, 1840 -2000 Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
Mail Delivery Times between New York and San Francisco, 1840 -2000 Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
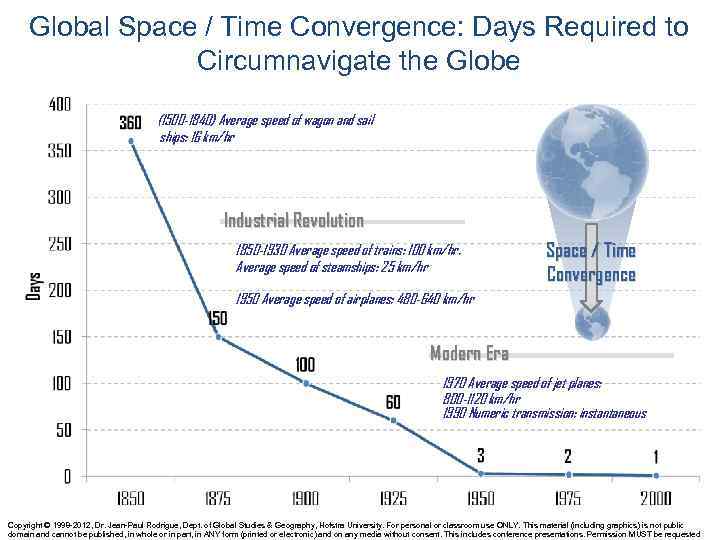 Global Space / Time Convergence: Days Required to Circumnavigate the Globe (1500 -1840) Average speed of wagon and sail ships: 16 km/hr Industrial Revolution 1850 -1930 Average speed of trains: 100 km/hr. Average speed of steamships: 25 km/hr Space / Time Convergence 1950 Average speed of airplanes: 480 -640 km/hr Modern Era 1970 Average speed of jet planes: 800 -1120 km/hr 1990 Numeric transmission: instantaneous Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
Global Space / Time Convergence: Days Required to Circumnavigate the Globe (1500 -1840) Average speed of wagon and sail ships: 16 km/hr Industrial Revolution 1850 -1930 Average speed of trains: 100 km/hr. Average speed of steamships: 25 km/hr Space / Time Convergence 1950 Average speed of airplanes: 480 -640 km/hr Modern Era 1970 Average speed of jet planes: 800 -1120 km/hr 1990 Numeric transmission: instantaneous Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
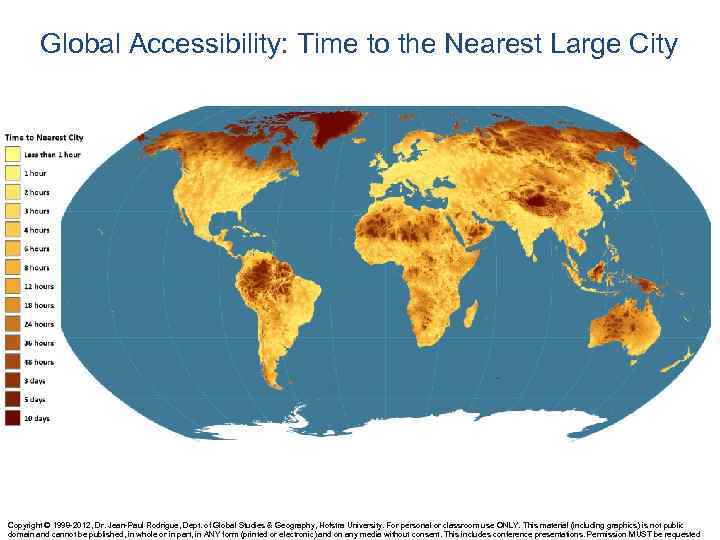 Global Accessibility: Time to the Nearest Large City Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
Global Accessibility: Time to the Nearest Large City Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
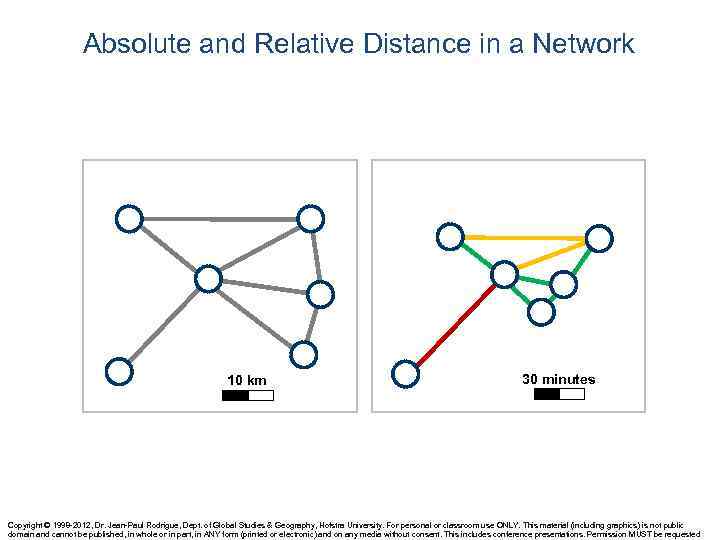 Absolute and Relative Distance in a Network 10 km 30 minutes Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
Absolute and Relative Distance in a Network 10 km 30 minutes Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
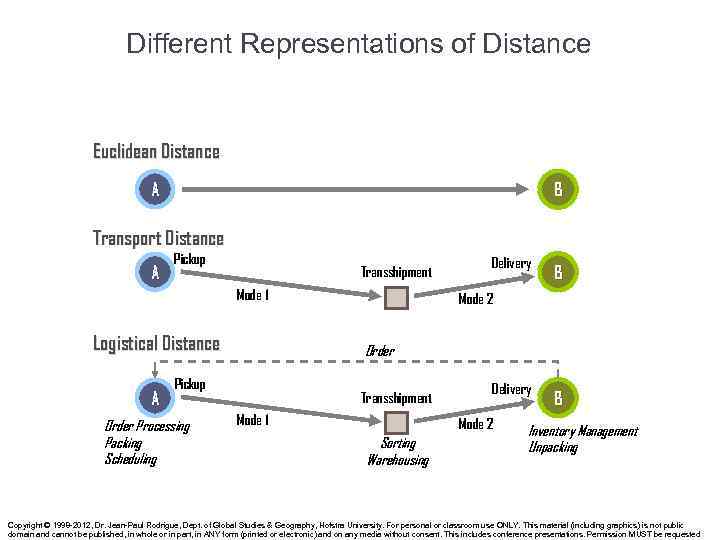 Different Representations of Distance Euclidean Distance A B Transport Distance A Pickup Transshipment Mode 1 Logistical Distance A B Mode 2 Order Pickup Order Processing Packing Scheduling Delivery Transshipment Mode 1 Delivery Mode 2 Sorting Warehousing B Inventory Management Unpacking Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
Different Representations of Distance Euclidean Distance A B Transport Distance A Pickup Transshipment Mode 1 Logistical Distance A B Mode 2 Order Pickup Order Processing Packing Scheduling Delivery Transshipment Mode 1 Delivery Mode 2 Sorting Warehousing B Inventory Management Unpacking Copyright © 1998 -2012, Dr. Jean-Paul Rodrigue, Dept. of Global Studies & Geography, Hofstra University. For personal or classroom use ONLY. This material (including graphics) is not public domain and cannot be published, in whole or in part, in ANY form (printed or electronic) and on any media without consent. This includes conference presentations. Permission MUST be requested
 Market for logistics services in the world • Logistics and transportation share in GDP is about 13 -16% • Logistics costs have 10 -20% in the final price of goods
Market for logistics services in the world • Logistics and transportation share in GDP is about 13 -16% • Logistics costs have 10 -20% in the final price of goods
 Logistic services in Russia • Average transportation costs of national companies 3 times higher than in Germany • Cargo transportation (especially railways) is carried out 4 times slower than in the USA See for instance: ü http: //lenta. ru/articles/2013/02/01/trains/ ü http: //www. vedomosti. ru/companies/news/225 0195/polzkom_po_relsam • Productivity of cargo systems processing is over 2, 5 times less than in Europe
Logistic services in Russia • Average transportation costs of national companies 3 times higher than in Germany • Cargo transportation (especially railways) is carried out 4 times slower than in the USA See for instance: ü http: //lenta. ru/articles/2013/02/01/trains/ ü http: //www. vedomosti. ru/companies/news/225 0195/polzkom_po_relsam • Productivity of cargo systems processing is over 2, 5 times less than in Europe
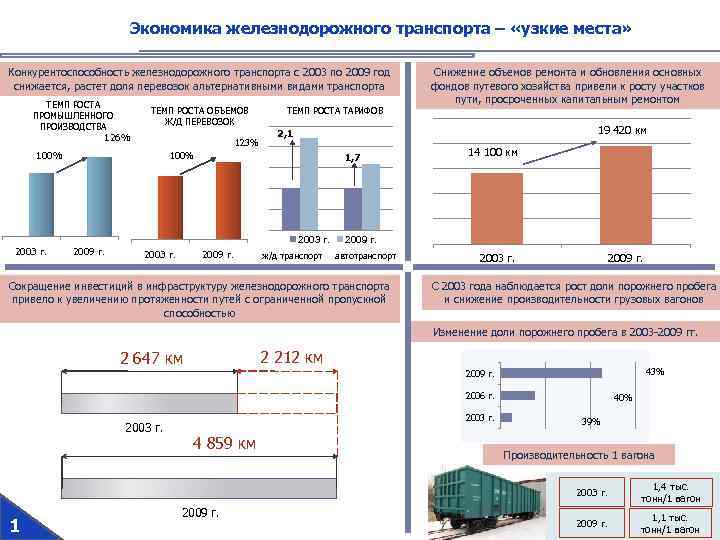 Экономика железнодорожного транспорта – «узкие места» Конкурентоспособность железнодорожного транспорта с 2003 по 2009 год снижается, растет доля перевозок альтернативными видами транспорта ТЕМП РОСТА ПРОМЫШЛЕННОГО ПРОИЗВОДСТВА ТЕМП РОСТА ОБЪЕМОВ Ж/Д ПЕРЕВОЗОК 126% 123% 100% 2003 г. ТЕМП РОСТА ТАРИФОВ 19 420 км 2, 1 100% 2009 г. 1, 7 2003 г. 2009 г. Снижение объемов ремонта и обновления основных фондов путевого хозяйства привели к росту участков пути, просроченных капитальным ремонтом ж/д транспорт 14 100 км 2009 г. автотранспорт Сокращение инвестиций в инфраструктуру железнодорожного транспорта привело к увеличению протяженности путей с ограниченной пропускной способностью 2003 г. 2009 г. С 2003 года наблюдается рост доли порожнего пробега и снижение производительности грузовых вагонов Изменение доли порожнего пробега в 2003 -2009 гг. 2 212 км 2 647 км 43% 2009 г. 2006 г. 2003 г. 4 859 км 40% 39% Производительность 1 вагона 2003 г. 1 2009 г. 1, 4 тыс. тонн/1 вагон 2009 г. 1, 1 тыс. тонн/1 вагон
Экономика железнодорожного транспорта – «узкие места» Конкурентоспособность железнодорожного транспорта с 2003 по 2009 год снижается, растет доля перевозок альтернативными видами транспорта ТЕМП РОСТА ПРОМЫШЛЕННОГО ПРОИЗВОДСТВА ТЕМП РОСТА ОБЪЕМОВ Ж/Д ПЕРЕВОЗОК 126% 123% 100% 2003 г. ТЕМП РОСТА ТАРИФОВ 19 420 км 2, 1 100% 2009 г. 1, 7 2003 г. 2009 г. Снижение объемов ремонта и обновления основных фондов путевого хозяйства привели к росту участков пути, просроченных капитальным ремонтом ж/д транспорт 14 100 км 2009 г. автотранспорт Сокращение инвестиций в инфраструктуру железнодорожного транспорта привело к увеличению протяженности путей с ограниченной пропускной способностью 2003 г. 2009 г. С 2003 года наблюдается рост доли порожнего пробега и снижение производительности грузовых вагонов Изменение доли порожнего пробега в 2003 -2009 гг. 2 212 км 2 647 км 43% 2009 г. 2006 г. 2003 г. 4 859 км 40% 39% Производительность 1 вагона 2003 г. 1 2009 г. 1, 4 тыс. тонн/1 вагон 2009 г. 1, 1 тыс. тонн/1 вагон



