25276089987abdf400019082c73e191e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Logics for Data and Knowledge Representation Application of DLs: Rel. BAC
Logics for Data and Knowledge Representation Application of DLs: Rel. BAC
 Outline q New Challenges for Access Control q Model and Logic q Automated Reasoning q Reasoning tasks q So. D 2
Outline q New Challenges for Access Control q Model and Logic q Automated Reasoning q Reasoning tasks q So. D 2
 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING New Challenges q Objects q q q Files, documents, pictures … Various scales: e. Business, e. Science … Various types: Blogs, Wiki, Flickr, Youtube … q Subjects q Social networks: My. Space, Facebook, Google+ q Permissions q 3 Read, Write …
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING New Challenges q Objects q q q Files, documents, pictures … Various scales: e. Business, e. Science … Various types: Blogs, Wiki, Flickr, Youtube … q Subjects q Social networks: My. Space, Facebook, Google+ q Permissions q 3 Read, Write …
 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Dynamic Permissions q Time q Access time, duration, frequency, etc. q Location q Physical address q System condition such as load, connection number, priority, etc. 4
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Dynamic Permissions q Time q Access time, duration, frequency, etc. q Location q Physical address q System condition such as load, connection number, priority, etc. 4
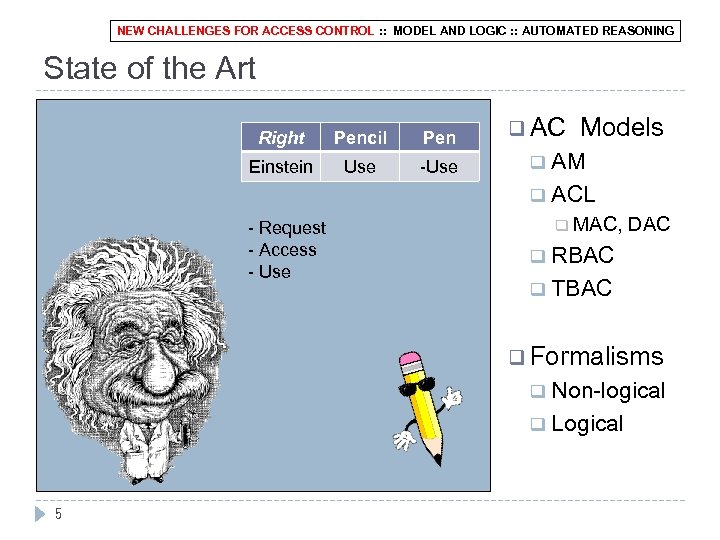 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING State of the Art Right Pencil Pen q AC Einstein Use -Use q - Request - Access - Use Models AM q ACL q MAC, DAC RBAC q TBAC q q Formalisms Non-logical q Logical q 5
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING State of the Art Right Pencil Pen q AC Einstein Use -Use q - Request - Access - Use Models AM q ACL q MAC, DAC RBAC q TBAC q q Formalisms Non-logical q Logical q 5
 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Motivations q Natural q Friendly to ordinary user q Automated tools for management q Flexible q Coverage of various domains q Extensible for new requests q Formal q Compact syntax and semantics q Security Analysis 6
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Motivations q Natural q Friendly to ordinary user q Automated tools for management q Flexible q Coverage of various domains q Extensible for new requests q Formal q Compact syntax and semantics q Security Analysis 6
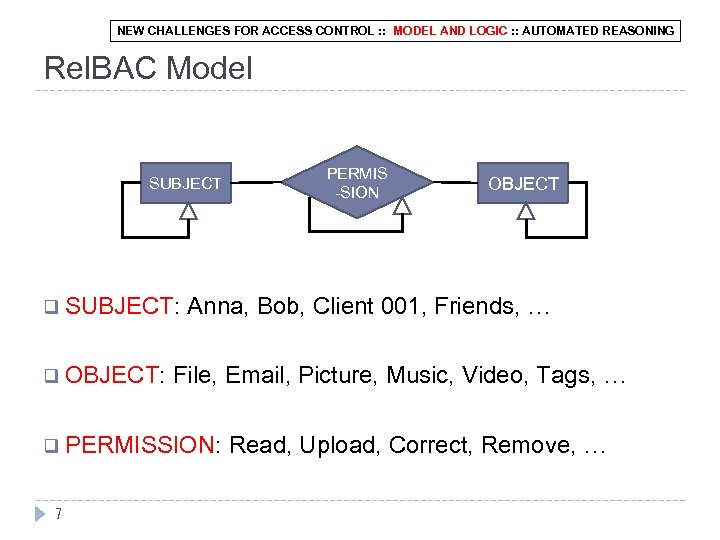 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Rel. BAC Model SUBJECT q SUBJECT: q OBJECT: OBJECT Anna, Bob, Client 001, Friends, … File, Email, Picture, Music, Video, Tags, … q PERMISSION: 7 PERMIS -SION Read, Upload, Correct, Remove, …
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Rel. BAC Model SUBJECT q SUBJECT: q OBJECT: OBJECT Anna, Bob, Client 001, Friends, … File, Email, Picture, Music, Video, Tags, … q PERMISSION: 7 PERMIS -SION Read, Upload, Correct, Remove, …
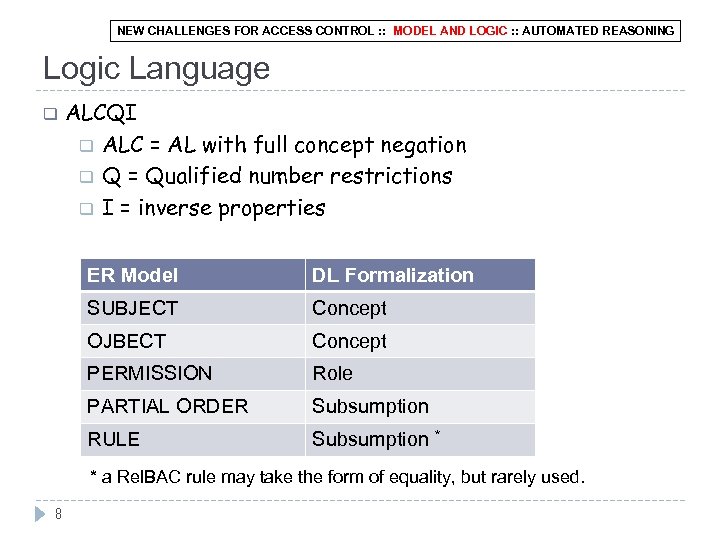 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Logic Language q ALCQI q ALC = AL with full concept negation q Q = Qualified number restrictions q I = inverse properties ER Model DL Formalization SUBJECT Concept OJBECT Concept PERMISSION Role PARTIAL ORDER Subsumption RULE Subsumption * * a Rel. BAC rule may take the form of equality, but rarely used. 8
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Logic Language q ALCQI q ALC = AL with full concept negation q Q = Qualified number restrictions q I = inverse properties ER Model DL Formalization SUBJECT Concept OJBECT Concept PERMISSION Role PARTIAL ORDER Subsumption RULE Subsumption * * a Rel. BAC rule may take the form of equality, but rarely used. 8
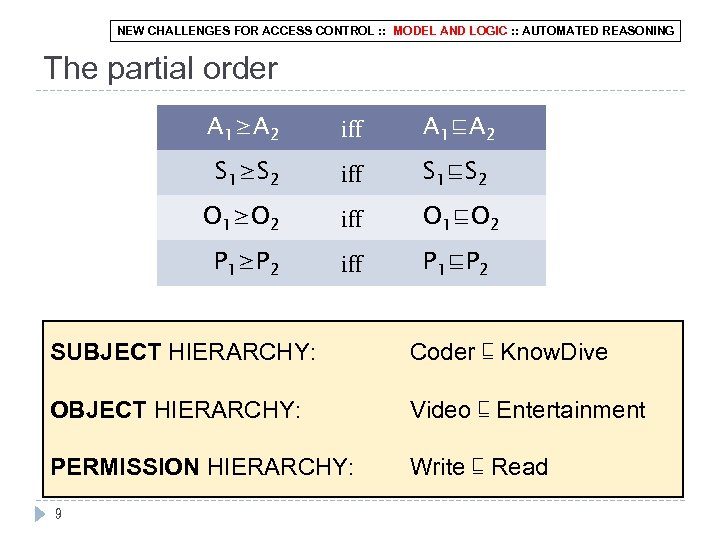 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING The partial order A 1≥A 2 iff A 1⊑A 2 S 1≥S 2 iff S 1⊑S 2 O 1≥O 2 iff O 1⊑O 2 P 1≥P 2 iff P 1⊑P 2 SUBJECT HIERARCHY: Coder ⊑ Know. Dive OBJECT HIERARCHY: Video ⊑ Entertainment PERMISSION HIERARCHY: Write ⊑ Read 9
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING The partial order A 1≥A 2 iff A 1⊑A 2 S 1≥S 2 iff S 1⊑S 2 O 1≥O 2 iff O 1⊑O 2 P 1≥P 2 iff P 1⊑P 2 SUBJECT HIERARCHY: Coder ⊑ Know. Dive OBJECT HIERARCHY: Video ⊑ Entertainment PERMISSION HIERARCHY: Write ⊑ Read 9
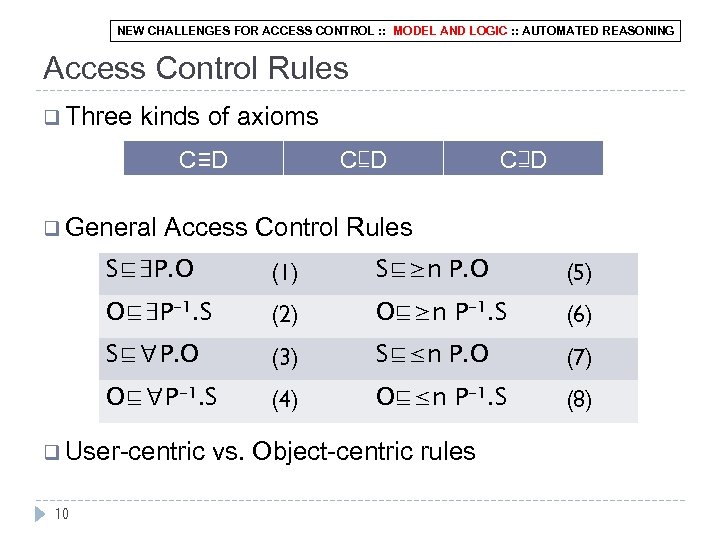 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Access Control Rules q Three kinds of axioms C≡D q General C⊑D C⊒D Access Control Rules S⊑∃P. O (1) S⊑≥n P. O (5) O⊑∃P-1. S (2) O⊑≥n P-1. S (6) S⊑∀P. O (3) S⊑≤n P. O (7) O⊑∀P-1. S (4) O⊑≤n P-1. S (8) q User-centric 10 vs. Object-centric rules
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Access Control Rules q Three kinds of axioms C≡D q General C⊑D C⊒D Access Control Rules S⊑∃P. O (1) S⊑≥n P. O (5) O⊑∃P-1. S (2) O⊑≥n P-1. S (6) S⊑∀P. O (3) S⊑≤n P. O (7) O⊑∀P-1. S (4) O⊑≤n P-1. S (8) q User-centric 10 vs. Object-centric rules
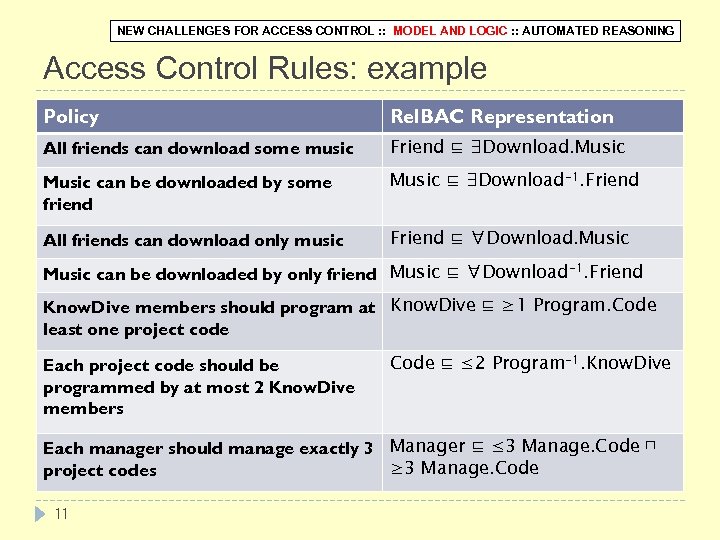 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Access Control Rules: example Policy Rel. BAC Representation All friends can download some music Friend ⊑ ∃Download. Music can be downloaded by some friend Music ⊑ ∃Download-1. Friend All friends can download only music Friend ⊑ ∀Download. Music can be downloaded by only friend Music ⊑ ∀Download-1. Friend Know. Dive members should program at Know. Dive ⊑ ≥ 1 Program. Code least one project code Each project code should be programmed by at most 2 Know. Dive members Code ⊑ ≤ 2 Program-1. Know. Dive Each manager should manage exactly 3 Manager ⊑ ≤ 3 Manage. Code ⊓ ≥ 3 Manage. Code project codes 11
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Access Control Rules: example Policy Rel. BAC Representation All friends can download some music Friend ⊑ ∃Download. Music can be downloaded by some friend Music ⊑ ∃Download-1. Friend All friends can download only music Friend ⊑ ∀Download. Music can be downloaded by only friend Music ⊑ ∀Download-1. Friend Know. Dive members should program at Know. Dive ⊑ ≥ 1 Program. Code least one project code Each project code should be programmed by at most 2 Know. Dive members Code ⊑ ≤ 2 Program-1. Know. Dive Each manager should manage exactly 3 Manager ⊑ ≤ 3 Manage. Code ⊓ ≥ 3 Manage. Code project codes 11
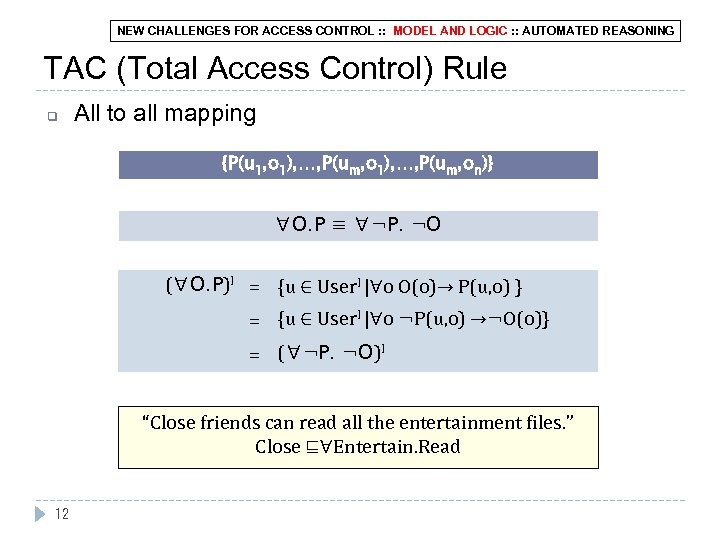 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING TAC (Total Access Control) Rule q All to all mapping {P(u 1, o 1), …, P(um, on)} ∀O. P ≡ ∀¬P. ¬O (∀O. P)I = {u ∈ User. I |∀o O(o)→ P(u, o) } = {u ∈ User. I |∀o ¬P(u, o) →¬O(o)} = (∀¬P. ¬O)I “Close friends can read all the entertainment files. ” Close ⊑∀Entertain. Read 12
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING TAC (Total Access Control) Rule q All to all mapping {P(u 1, o 1), …, P(um, on)} ∀O. P ≡ ∀¬P. ¬O (∀O. P)I = {u ∈ User. I |∀o O(o)→ P(u, o) } = {u ∈ User. I |∀o ¬P(u, o) →¬O(o)} = (∀¬P. ¬O)I “Close friends can read all the entertainment files. ” Close ⊑∀Entertain. Read 12
 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Correspondences to Motivations q Natural q permission binary relation q partial order subsumption axiom q rule formula(e) q Flexible q hierarchy partial order q attribute binary relation q Formal q Description 13 logics
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Correspondences to Motivations q Natural q permission binary relation q partial order subsumption axiom q rule formula(e) q Flexible q hierarchy partial order q attribute binary relation q Formal q Description 13 logics
 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Reasoning Services q TBox ‘A business friend can update some entries. ’ q ABox ‘Bob is a business friend. ’ q ABox + TBox ‘Bob is a business friend so that he can update some entries. ’ q Design 14 vs. Run time Reasoning
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Reasoning Services q TBox ‘A business friend can update some entries. ’ q ABox ‘Bob is a business friend. ’ q ABox + TBox ‘Bob is a business friend so that he can update some entries. ’ q Design 14 vs. Run time Reasoning
 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Reasoning Tasks: Design q Hierarchy IPod ⊑ Digital. Device q Membership Digital. Device(ipod-2 g 0903) q Separation of duties ‘customer and sales manager are to be separated. ’ q High-level Concern ‘the 3 users to commit an order should include 1 customer, 1 sales agent and 1 sales manager. ’ 15
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Reasoning Tasks: Design q Hierarchy IPod ⊑ Digital. Device q Membership Digital. Device(ipod-2 g 0903) q Separation of duties ‘customer and sales manager are to be separated. ’ q High-level Concern ‘the 3 users to commit an order should include 1 customer, 1 sales agent and 1 sales manager. ’ 15
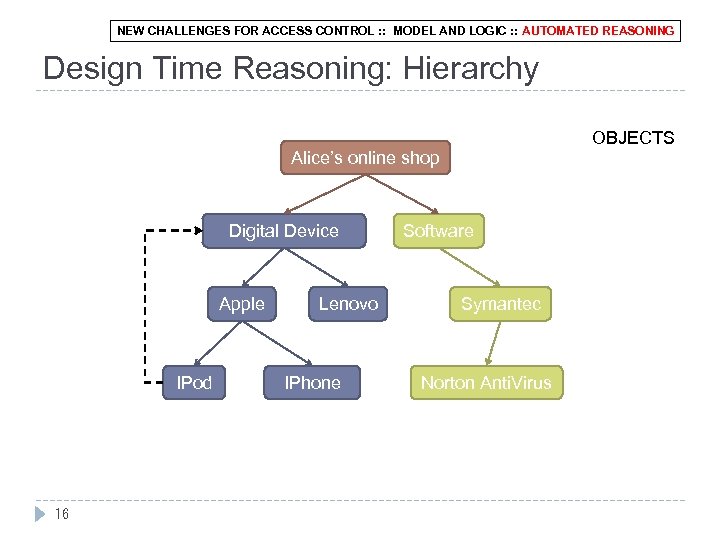 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Design Time Reasoning: Hierarchy OBJECTS Alice’s online shop Digital Device Apple IPod 16 Lenovo IPhone Software Symantec Norton Anti. Virus
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Design Time Reasoning: Hierarchy OBJECTS Alice’s online shop Digital Device Apple IPod 16 Lenovo IPhone Software Symantec Norton Anti. Virus
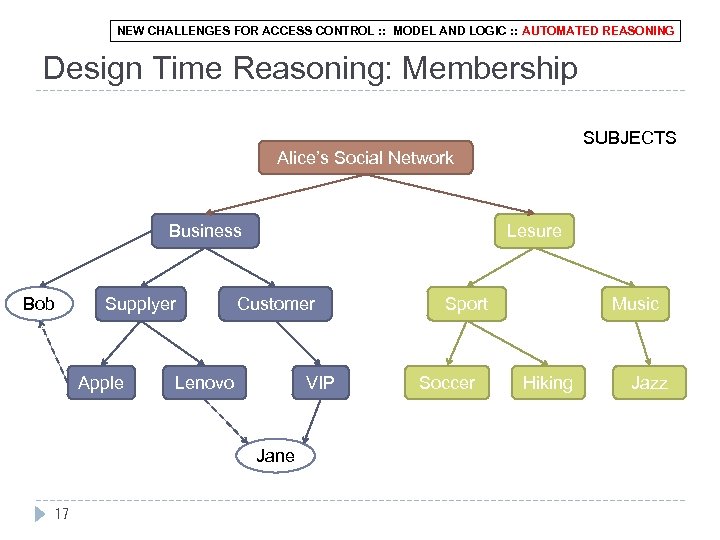 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Design Time Reasoning: Membership SUBJECTS Alice’s Social Network Business Bob Supplyer Apple Lesure Customer Lenovo VIP Jane 17 Sport Soccer Music Hiking Jazz
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Design Time Reasoning: Membership SUBJECTS Alice’s Social Network Business Bob Supplyer Apple Lesure Customer Lenovo VIP Jane 17 Sport Soccer Music Hiking Jazz
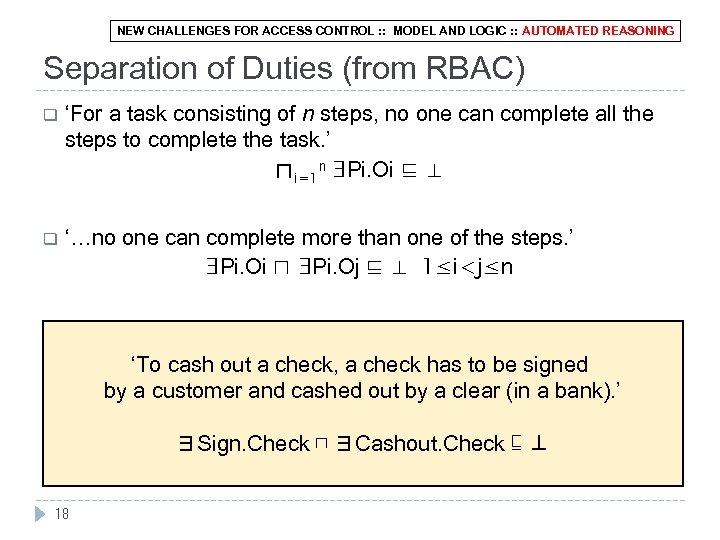 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Separation of Duties (from RBAC) q ‘For a task consisting of n steps, no one can complete all the steps to complete the task. ’ ⊓i=1 n ∃Pi. Oi ⊑ ⊥ q ‘…no one can complete more than one of the steps. ’ ∃Pi. Oi ⊓ ∃Pi. Oj ⊑ ⊥ 1≤i
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Separation of Duties (from RBAC) q ‘For a task consisting of n steps, no one can complete all the steps to complete the task. ’ ⊓i=1 n ∃Pi. Oi ⊑ ⊥ q ‘…no one can complete more than one of the steps. ’ ∃Pi. Oi ⊓ ∃Pi. Oj ⊑ ⊥ 1≤i
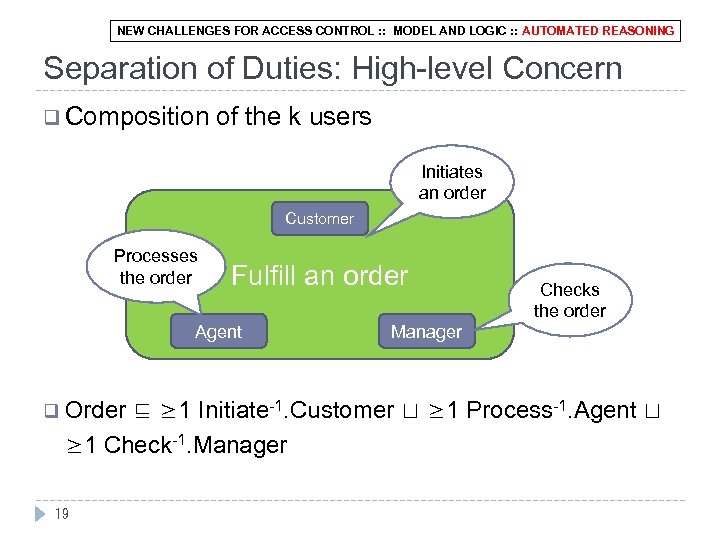 NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Separation of Duties: High-level Concern q Composition of the k users Initiates an order Customer Processes the order Fulfill an order Agent Checks the order Manager ⊑ ≥ 1 Initiate-1. Customer ⊔ ≥ 1 Process-1. Agent ⊔ ≥ 1 Check-1. Manager q Order 19
NEW CHALLENGES FOR ACCESS CONTROL : : MODEL AND LOGIC : : AUTOMATED REASONING Separation of Duties: High-level Concern q Composition of the k users Initiates an order Customer Processes the order Fulfill an order Agent Checks the order Manager ⊑ ≥ 1 Initiate-1. Customer ⊔ ≥ 1 Process-1. Agent ⊔ ≥ 1 Check-1. Manager q Order 19


