f906b4d34b3847261ea0dfcb39460c91.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 LOCKSS/CLOCKSS and Portico What does that content look like? Coalition for Networked Information Fall 2006 Task Force Meeting December 4, 2006
LOCKSS/CLOCKSS and Portico What does that content look like? Coalition for Networked Information Fall 2006 Task Force Meeting December 4, 2006
 Presented by Geneva L. Henry Executive Director, Digital Library Initiative Rice University Carolyn Walters Executive Associate Dean Indiana University Libraries Phyllis Davidson Assistant Dean of Digital & Information Technology Services Indiana University Libraries Kerry A. Keck Assistant University Librarian, Collections Rice University
Presented by Geneva L. Henry Executive Director, Digital Library Initiative Rice University Carolyn Walters Executive Associate Dean Indiana University Libraries Phyllis Davidson Assistant Dean of Digital & Information Technology Services Indiana University Libraries Kerry A. Keck Assistant University Librarian, Collections Rice University
 Agenda w Overview/Background w Content -- What’s the difference? w Costs w Additional uses of the systems w Summary
Agenda w Overview/Background w Content -- What’s the difference? w Costs w Additional uses of the systems w Summary
 Overview/Background
Overview/Background
 Why are we up here? w Warning: WE’RE NOT EXPERTS! w Rice and Indiana Universities are both users and members of LOCKSS, CLOCKSS and Portico w We hear people from various libraries and publishers say the darnedest things about these solutions w We thought you might want to hear an unbiased review and comparison from the library community w These efforts are important for libraries and should be taken very seriously if you subscribe to any electronic journals and would like to ensure that they are preserved for future access
Why are we up here? w Warning: WE’RE NOT EXPERTS! w Rice and Indiana Universities are both users and members of LOCKSS, CLOCKSS and Portico w We hear people from various libraries and publishers say the darnedest things about these solutions w We thought you might want to hear an unbiased review and comparison from the library community w These efforts are important for libraries and should be taken very seriously if you subscribe to any electronic journals and would like to ensure that they are preserved for future access
 Some background information w LOCKSS, CLOCKSS and Portico are solutions for preserving electronic journal content w LOCKSS (Lots of Copies Keep Stuff Safe) developed by Stanford. Began in 1999, beta tested through 2002, production system developed 2002 - 2004, released April 2004 w CLOCKSS (Controlled LOCKSS) based on LOCKSS s/w, started early 2006, piloting with a small number of libraries and publishers for 2 years w Portico launched by JSTOR in 2002 with funding from Mellon, became part of Ithaka Harbors, Inc. in 2004, then launched as Portico in 2005
Some background information w LOCKSS, CLOCKSS and Portico are solutions for preserving electronic journal content w LOCKSS (Lots of Copies Keep Stuff Safe) developed by Stanford. Began in 1999, beta tested through 2002, production system developed 2002 - 2004, released April 2004 w CLOCKSS (Controlled LOCKSS) based on LOCKSS s/w, started early 2006, piloting with a small number of libraries and publishers for 2 years w Portico launched by JSTOR in 2002 with funding from Mellon, became part of Ithaka Harbors, Inc. in 2004, then launched as Portico in 2005
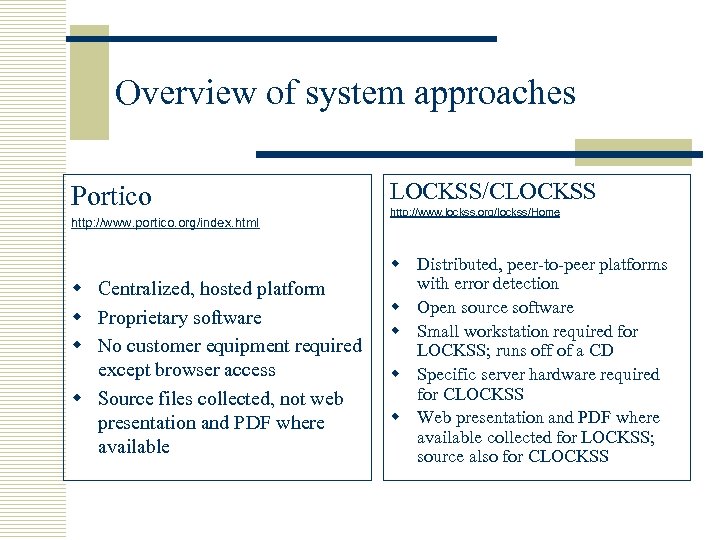 Overview of system approaches Portico http: //www. portico. org/index. html w Centralized, hosted platform w Proprietary software w No customer equipment required except browser access w Source files collected, not web presentation and PDF where available LOCKSS/CLOCKSS http: //www. lockss. org/lockss/Home w Distributed, peer-to-peer platforms with error detection w Open source software w Small workstation required for LOCKSS; runs off of a CD w Specific server hardware required for CLOCKSS w Web presentation and PDF where available collected for LOCKSS; source also for CLOCKSS
Overview of system approaches Portico http: //www. portico. org/index. html w Centralized, hosted platform w Proprietary software w No customer equipment required except browser access w Source files collected, not web presentation and PDF where available LOCKSS/CLOCKSS http: //www. lockss. org/lockss/Home w Distributed, peer-to-peer platforms with error detection w Open source software w Small workstation required for LOCKSS; runs off of a CD w Specific server hardware required for CLOCKSS w Web presentation and PDF where available collected for LOCKSS; source also for CLOCKSS
 Content - what’s the difference?
Content - what’s the difference?
 How the systems support perpetual access to content w Default access is always to the publisher’s existing website w Only in the event that the publisher’s website is unavailable, does access revert to the archival site
How the systems support perpetual access to content w Default access is always to the publisher’s existing website w Only in the event that the publisher’s website is unavailable, does access revert to the archival site
 How the archival sites differ in supporting requests Portico/CLOCKSS Systems provide qualifying libraries supporting the archive with campus-wide access to archived content when specific trigger events occur, and when titles are no longer available from the publisher or other source. Trigger events include: w w A publisher stops operations; or A publisher ceases to publish a title; or A publisher no longer offers back issues; or Upon catastrophic and sustained failure of a publisher's delivery platform LOCKSS n n n The institution must cache archive units (journal volumes) to their local box as they are released by the publisher Institutions often run web proxies, to allow off-campus access to subscriptions and to reduce the bandwidth cost of Web access. The LOCKSS Box integrates with these systems, intercepting requests from the community's browsers to the journals being preserved. When a request for a page from a preserved journal arrives, it is first forwarded to the publisher. If the publisher returns content, that is what the browser gets. Otherwise the browser gets the preserved copy.
How the archival sites differ in supporting requests Portico/CLOCKSS Systems provide qualifying libraries supporting the archive with campus-wide access to archived content when specific trigger events occur, and when titles are no longer available from the publisher or other source. Trigger events include: w w A publisher stops operations; or A publisher ceases to publish a title; or A publisher no longer offers back issues; or Upon catastrophic and sustained failure of a publisher's delivery platform LOCKSS n n n The institution must cache archive units (journal volumes) to their local box as they are released by the publisher Institutions often run web proxies, to allow off-campus access to subscriptions and to reduce the bandwidth cost of Web access. The LOCKSS Box integrates with these systems, intercepting requests from the community's browsers to the journals being preserved. When a request for a page from a preserved journal arrives, it is first forwarded to the publisher. If the publisher returns content, that is what the browser gets. Otherwise the browser gets the preserved copy.
 And then there is CLOCKSS… w CLOCKSS differs from LOCKSS by both its structure and purpose: it is conceived as a small, responsible network providing a safety net - or dark archive - of subscription-based journals on behalf of a much broader community. w Will be made available if needed through a 3 rd party TBD (e. g. Google) w Publishers and archiving libraries will have to pay to participate w Participating pilot libraries: Indiana University, New York Public Library, OCLC, Rice University, Stanford University, University of Virginia, University of Edinburgh
And then there is CLOCKSS… w CLOCKSS differs from LOCKSS by both its structure and purpose: it is conceived as a small, responsible network providing a safety net - or dark archive - of subscription-based journals on behalf of a much broader community. w Will be made available if needed through a 3 rd party TBD (e. g. Google) w Publishers and archiving libraries will have to pay to participate w Participating pilot libraries: Indiana University, New York Public Library, OCLC, Rice University, Stanford University, University of Virginia, University of Edinburgh
 What content is available? w There is substantial overlap in the publishers announcing content via Portico and via LOCKSS/CLOCKSS w There is notably less overlap in the serial titles and/or issues available for preservation via the Portico and LOCKSS
What content is available? w There is substantial overlap in the publishers announcing content via Portico and via LOCKSS/CLOCKSS w There is notably less overlap in the serial titles and/or issues available for preservation via the Portico and LOCKSS
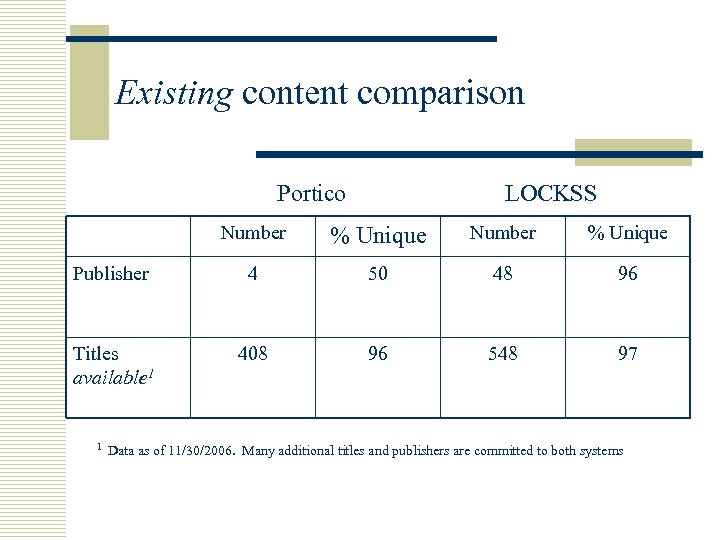 Existing content comparison Portico LOCKSS Number % Unique Publisher 4 50 48 96 Titles available 1 408 96 548 97 1 Data as of 11/30/2006. Many additional titles and publishers are committed to both systems
Existing content comparison Portico LOCKSS Number % Unique Publisher 4 50 48 96 Titles available 1 408 96 548 97 1 Data as of 11/30/2006. Many additional titles and publishers are committed to both systems
 And then there is CLOCKSS w 12 publishers are participating in the CLOCKSS initiative: n n n American Chemical Society American Medical Association American Physiological Society Blackwell Publishing Elsevier Institute of Physics Nature Publishing Group Oxford University Press SAGE Publications Springer Taylor and Francis John Wiley & Sons.
And then there is CLOCKSS w 12 publishers are participating in the CLOCKSS initiative: n n n American Chemical Society American Medical Association American Physiological Society Blackwell Publishing Elsevier Institute of Physics Nature Publishing Group Oxford University Press SAGE Publications Springer Taylor and Francis John Wiley & Sons.
 Sample displays from Audit menus Note that these do not represent the experience of the user in event of “publisher failure”
Sample displays from Audit menus Note that these do not represent the experience of the user in event of “publisher failure”
 Portico’s display for available issues of a journal title w Portico has a very navigable auditing interface, comparable to end user resources
Portico’s display for available issues of a journal title w Portico has a very navigable auditing interface, comparable to end user resources
 Portico’s display for an individual article w An individual article entry provides the DOI and links to the html and PDF files
Portico’s display for an individual article w An individual article entry provides the DOI and links to the html and PDF files
 Viewing the article in Portico In html Ø Note that internal hyperlinks are all active and links to separately maintained images are present Ø External links (e. g. back to table of contents) may not be active within the audit view As a PDF (where present)
Viewing the article in Portico In html Ø Note that internal hyperlinks are all active and links to separately maintained images are present Ø External links (e. g. back to table of contents) may not be active within the audit view As a PDF (where present)
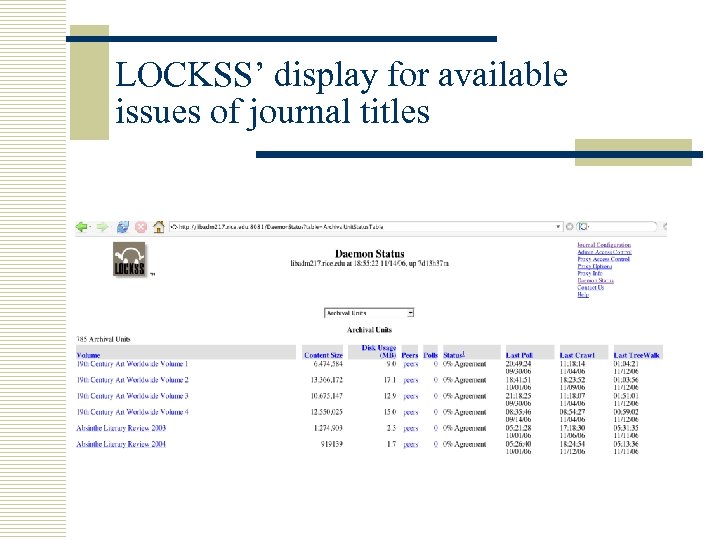 LOCKSS’ display for available issues of journal titles
LOCKSS’ display for available issues of journal titles
 LOCKSS display for components from the journal volume… Each article and image component of a volume is listed An auditor must determine an appropriate ‘starting’ point links from a table of contents screen may fail
LOCKSS display for components from the journal volume… Each article and image component of a volume is listed An auditor must determine an appropriate ‘starting’ point links from a table of contents screen may fail
 LOCKSS display of an abstract-level screen from Oxford University Press w See a typical abstract record from the list w And the article html full text Ø Ø Note internal links and separate images And the PDF (where present)
LOCKSS display of an abstract-level screen from Oxford University Press w See a typical abstract record from the list w And the article html full text Ø Ø Note internal links and separate images And the PDF (where present)
 Costs
Costs
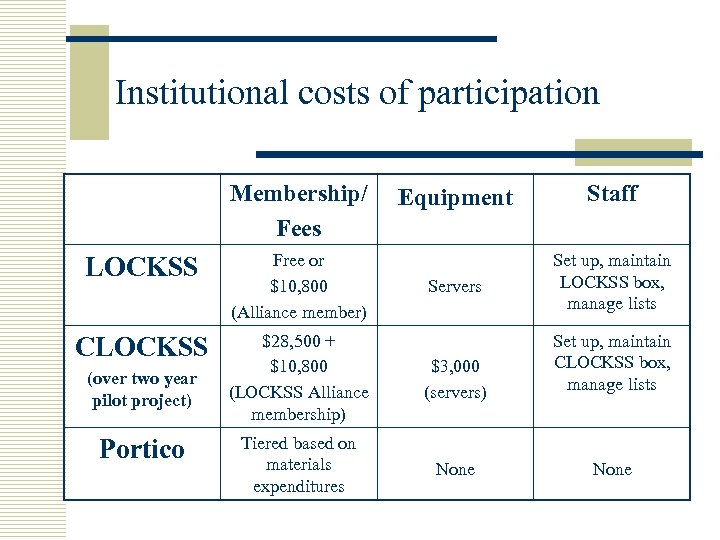 Institutional costs of participation Membership/ Fees Equipment Staff Servers Set up, maintain LOCKSS box, manage lists LOCKSS Free or $10, 800 (Alliance member) CLOCKSS $28, 500 + $10, 800 (LOCKSS Alliance membership) $3, 000 (servers) Set up, maintain CLOCKSS box, manage lists Tiered based on materials expenditures None (over two year pilot project) Portico
Institutional costs of participation Membership/ Fees Equipment Staff Servers Set up, maintain LOCKSS box, manage lists LOCKSS Free or $10, 800 (Alliance member) CLOCKSS $28, 500 + $10, 800 (LOCKSS Alliance membership) $3, 000 (servers) Set up, maintain CLOCKSS box, manage lists Tiered based on materials expenditures None (over two year pilot project) Portico
 Our cost experience w LOCKSS costs: n n Alliance Member Three Servers Programmer Technical Services $10, 800 annually $3, 085 one-time Two hours/week 2 -12 hours/month
Our cost experience w LOCKSS costs: n n Alliance Member Three Servers Programmer Technical Services $10, 800 annually $3, 085 one-time Two hours/week 2 -12 hours/month
 Our cost experience w CLOCKSS (Two year pilot) * n n Programmer support Servers Programmer Technical Services $28, 500 $ 3, 000 One hour/week One hour/month * Must be a member of the LOCKSS Alliance
Our cost experience w CLOCKSS (Two year pilot) * n n Programmer support Servers Programmer Technical Services $28, 500 $ 3, 000 One hour/week One hour/month * Must be a member of the LOCKSS Alliance
 Our cost experience w Portico - Indiana n n n Annual Membership $15, 200 Portico Archive Founder* (-25%) - 3, 800 w Portico - Rice n n n $11, 400 n n No equipment No ongoing expenses *Discount for five years if joined in 2006 10% discount for five years if joining in 2007 Annual Membership $13, 000 Portico Archive Founder* (-25%) - 3, 250 $9, 750 n n No equipment No ongoing expenses *Discount for five years if joined in 2006 10% discount for five years if joining in 2007
Our cost experience w Portico - Indiana n n n Annual Membership $15, 200 Portico Archive Founder* (-25%) - 3, 800 w Portico - Rice n n n $11, 400 n n No equipment No ongoing expenses *Discount for five years if joined in 2006 10% discount for five years if joining in 2007 Annual Membership $13, 000 Portico Archive Founder* (-25%) - 3, 250 $9, 750 n n No equipment No ongoing expenses *Discount for five years if joined in 2006 10% discount for five years if joining in 2007
 Additional Uses of the LOCKSS software
Additional Uses of the LOCKSS software
 Other current applications for the LOCKSS software w Preserving federal digital publications n GPO LOCKSS Pilot Project http: //www. access. gpo. gov/su_docs/fdlp/lockss/index. html n State of Alaska Project http: //www. library. state. ak. us/asp/shippinglists/fy_2007_shippinglists. html w Preserving born-digital, freely available humanities journals n Humanities Project http: //www. lockss. org/lockss/Related_Projects#Humanities_Project
Other current applications for the LOCKSS software w Preserving federal digital publications n GPO LOCKSS Pilot Project http: //www. access. gpo. gov/su_docs/fdlp/lockss/index. html n State of Alaska Project http: //www. library. state. ak. us/asp/shippinglists/fy_2007_shippinglists. html w Preserving born-digital, freely available humanities journals n Humanities Project http: //www. lockss. org/lockss/Related_Projects#Humanities_Project
 Other current applications for the LOCKSS software w Electronic theses and dissertations repositories n Association of Southeast Research Libraries http: //scholar. lib. vt. edu/theses/ETDs. ASERLLOCKSS 20050711 PR. pdf (project announcement) n The ASERL LOCKSS-ETD INITIATIVE: Developing Preservation Strategies for Libraries that Publish E-Scholarship http: //www. cni. org/tfms/2005 b. fall/abstracts/handouts/CNI_ASERL_Mc. Donald. ppt n International ETDs Preservation http: //www 6. bibl. ulaval. ca: 8080/etd 2006/pages/papers/SP 10_ Kamini_Santhanagopalan. ppt n Meta. Archive of Southern Digital Culture http: //www. metaarchive. org/index. html
Other current applications for the LOCKSS software w Electronic theses and dissertations repositories n Association of Southeast Research Libraries http: //scholar. lib. vt. edu/theses/ETDs. ASERLLOCKSS 20050711 PR. pdf (project announcement) n The ASERL LOCKSS-ETD INITIATIVE: Developing Preservation Strategies for Libraries that Publish E-Scholarship http: //www. cni. org/tfms/2005 b. fall/abstracts/handouts/CNI_ASERL_Mc. Donald. ppt n International ETDs Preservation http: //www 6. bibl. ulaval. ca: 8080/etd 2006/pages/papers/SP 10_ Kamini_Santhanagopalan. ppt n Meta. Archive of Southern Digital Culture http: //www. metaarchive. org/index. html
 Summary
Summary
 In summary … w These are three highest profile preservation solutions available at this time for subscriptionbased library content w Others may be coming w Institutions have a responsibility to participate, contributing to developing solutions for preservation of the digital cultural record just as we have done in the earlier, print-based era w There’s a solution for everyone, whether or not you have an IT staff
In summary … w These are three highest profile preservation solutions available at this time for subscriptionbased library content w Others may be coming w Institutions have a responsibility to participate, contributing to developing solutions for preservation of the digital cultural record just as we have done in the earlier, print-based era w There’s a solution for everyone, whether or not you have an IT staff
 Considerations in selecting a solution w We currently preserve print journals, but quantity of electronic journals is much greater. The cost is still lower supporting all of these initiatives. w When looking at the options, where is the overlap with your titles? w Do faculty have interests in specific niche journals? These may be the most vulnerable. w Libraries can have tremendous influence with publishers in educating them about the need to preserve publications. LOCKSS, CLOCKSS and Portico provide an easy avenue for them to preserve their content.
Considerations in selecting a solution w We currently preserve print journals, but quantity of electronic journals is much greater. The cost is still lower supporting all of these initiatives. w When looking at the options, where is the overlap with your titles? w Do faculty have interests in specific niche journals? These may be the most vulnerable. w Libraries can have tremendous influence with publishers in educating them about the need to preserve publications. LOCKSS, CLOCKSS and Portico provide an easy avenue for them to preserve their content.
 Presented by Geneva L. Henry Executive Director, Digital Library Initiative Rice University ghenry@rice. edu Carolyn Walters Executive Associate Dean Indiana University Libraries cwalters@indiana. edu Phyllis Davidson Assistant Dean of Digital & Information Technology Services Indiana University Libraries pdavidso@indiana. edu Kerry A. Keck Assistant University Librarian, Collections Rice University keckker@rice. edu
Presented by Geneva L. Henry Executive Director, Digital Library Initiative Rice University ghenry@rice. edu Carolyn Walters Executive Associate Dean Indiana University Libraries cwalters@indiana. edu Phyllis Davidson Assistant Dean of Digital & Information Technology Services Indiana University Libraries pdavidso@indiana. edu Kerry A. Keck Assistant University Librarian, Collections Rice University keckker@rice. edu


