
Lobular pneumonia.

Plan • • • Lobular pneumonia Causes of lobar pneumonia. Symptoms of lobar pneumonia. Diagnosis of lobar pneumonia. Complications of lobar pneumonia. Treatment of lobar pneumonia.
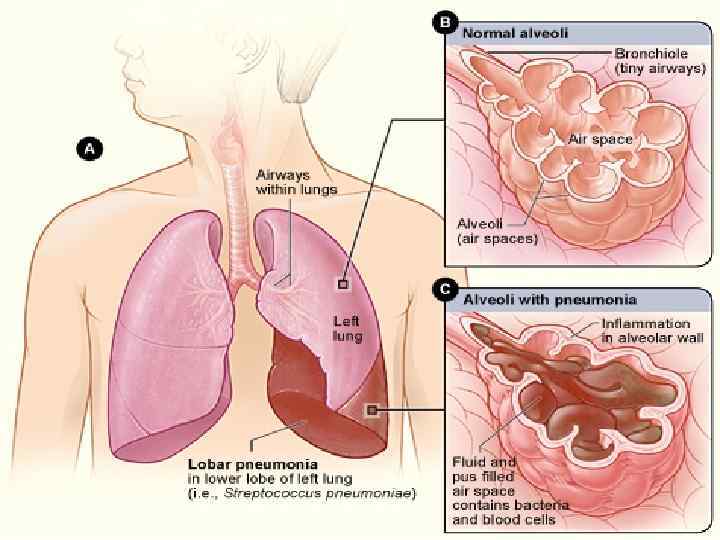
Lobular pneumonia. Lobar pneumonia - an acute inflammation of infectious-allergic, which covers one or a number of shares, as well as the pleura. The disease is manifested by chills, pain in the head and chest, fever, weakness of the body, shortness of breath, sweating, moist cough.
Stages: Lobar pneumonia developed in four stages: • • tide; red hepatization; gray hepatization; resolution.

Causes: The causative agent in the majority of cases - one of the pneumococcal strains. There are other mikroorgazmy. They fall into the lung, usually through the bronchi, but can lymphogenous or hematogenous route. Streptococcus pneumoniae is capable of long-term survival in the human nasopharynx. The acute phase of the disease can occur even when a person is healthy. The threat of disease increases as supercooling, and in the case of transferring diseases such as SARS and influenza. Other factors may act injuries, loss of immunity, excessive exercise. Disease contributes background pathological conditions: • diabetes; • COPD; • coronary artery disease; • tuberculosis; • oncological diseases; • regular consumption of alcohol. • Also plays a significant role heredity.

Symptoms: Getting the disease is characterized by a number of general intoxication and bronchopulmonary symptoms. Overall intoxication: • shivering; • headache; • general weakness; • the temperature rise above 39 degrees; • sweating. bronchopulmonary: • pain in the chest when breathing movements; • dyspnea; • cough; • expectoration.
The patient feels a sharp pain in the chest with a clear localization, the pain increases with a deep breath, the body is tilted. Cough dry observed, accompanied by pain in the chest, for 3 -4 hours may be fibrous exudate (discharge), stands viscous or yellowish sputum with blood splashes. Intoxication leads to neurological manifestations of the disease: • insomnia; • hallucinations and delusions; • loss of consciousness; • increased agitation.

Diagnostics: First, you need to consult a physician, and later to make an appointment to the lung. The survey begins with a survey of the patient, as well as to identify the symptoms of physical examination: • tachycardia; • rapid shallow breathing; • asynchrony movements of the chest; • chest pain; • noises and wheezing. Necessary is radiography. Planting of sputum allows to allocate the causative agent, and set the sensitivity to antibiotics.

Treatment: During the course of acute lobar pneumonia should be followed with bed rest, drink plenty of warm liquid, high-grade feed. If there is an infectious-toxic shock, carried out the stabilization of blood pressure, infusion therapy, metabolism correction, and others. Taking antibiotics is appointed before the sowing of bacteriological analysis. Duration of drugs is determined by the degree of severity of the disease, as well as his character development. Important timely and adequate response to the pathological state. Depending on these factors determined cycle of medication, it may vary from one to three weeks. In addition, prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs, antihistamines, anti-pyretic drugs, immunostimulants and mucolytics. From physiotherapy carried out: • iontophoresis; • inhalation drugs; • UHF; • physical therapy; • chest compressions

Prevention: The prevention is based on maintaining the protective functions of the body, so effectively hardening, active exercise, timely treatment of chronic diseases. It is also important to avoid hypothermia and stress.