84190c59782a3e1524af3269c27e2e1b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
 Load Testing Templates: Artifacts of NYU’s Load Testing Implementation Max Whitney & Erik Froese NYU/ITS/e. Services
Load Testing Templates: Artifacts of NYU’s Load Testing Implementation Max Whitney & Erik Froese NYU/ITS/e. Services
 Repeatable Load Testing Wow, it really is that time consuming. Max Whitney NYU/ITS/e. Services max@nyu. edu
Repeatable Load Testing Wow, it really is that time consuming. Max Whitney NYU/ITS/e. Services max@nyu. edu
 Context
Context
 Current Environment • Blackboard Learning System – Fall 2006 • 5, 219 sections • 127, 899 enrollments • 3, 964 instructors & 38, 624 students – Spring 2007 • 4, 952 sections • 146, 889 enrollments • 4, 329 instructors & 38, 559 students
Current Environment • Blackboard Learning System – Fall 2006 • 5, 219 sections • 127, 899 enrollments • 3, 964 instructors & 38, 624 students – Spring 2007 • 4, 952 sections • 146, 889 enrollments • 4, 329 instructors & 38, 559 students
 Under-served Communities • School of Medicine • Math and Sciences • School of Continuing and Professional Studies: The Virtual College, 100% online program • School of Law: LL. M. in Tax, hybrid online and in person program
Under-served Communities • School of Medicine • Math and Sciences • School of Continuing and Professional Studies: The Virtual College, 100% online program • School of Law: LL. M. in Tax, hybrid online and in person program
 Long Time Listener First Time Caller • NYU joined as a Sakai Educational Partner in Summer 2004 • Local pilots – Stern School of Business – Computer Science Department of Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences • Enterprise Pilot: September 2006
Long Time Listener First Time Caller • NYU joined as a Sakai Educational Partner in Summer 2004 • Local pilots – Stern School of Business – Computer Science Department of Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences • Enterprise Pilot: September 2006
 Phased Pilot Lacking the roll out support of commercial software, NYU is rolling out in phases, building the service with each phase: • • Documentation User Support Pedagogy Support Critical System Support: – – – Security Integration High Availability Performance Assurance Disaster Recovery
Phased Pilot Lacking the roll out support of commercial software, NYU is rolling out in phases, building the service with each phase: • • Documentation User Support Pedagogy Support Critical System Support: – – – Security Integration High Availability Performance Assurance Disaster Recovery
 Snowballing to Production
Snowballing to Production
 January 2007 Phase 1 Dashboard (My Workspace) Announcements Syllabus Roster Course Site Statistics Help Web Content Resources Assignments Default Discussion Board Gradebook Email Archive 23 Course Sites 20 Faculty 891 Students Backup & Disaster Recovery Implemented Penetration Testing Passed & Security Report Filed Smaller Summer Sets - 2 Phases
January 2007 Phase 1 Dashboard (My Workspace) Announcements Syllabus Roster Course Site Statistics Help Web Content Resources Assignments Default Discussion Board Gradebook Email Archive 23 Course Sites 20 Faculty 891 Students Backup & Disaster Recovery Implemented Penetration Testing Passed & Security Report Filed Smaller Summer Sets - 2 Phases
 Critical System Support for Phase 3 - September 2007 • Integration with Student Information System • Performance Assurance
Critical System Support for Phase 3 - September 2007 • Integration with Student Information System • Performance Assurance
 Repeatable Load Testing • • Select Software Select Hardware Identify Network Requirements Identify Ancillary System Requirements Commit to Long-term Retention Method for Tests, Results & Configurations Describe Test Cases Identify User and Site Characteristics Identify Executive Stakeholders • • • Identify Load Characteristics Implement Test Cases Create Test Users Create Test Site Content Test Store Configuration and Results Reset Analyze Results Report to Executive Stakeholders
Repeatable Load Testing • • Select Software Select Hardware Identify Network Requirements Identify Ancillary System Requirements Commit to Long-term Retention Method for Tests, Results & Configurations Describe Test Cases Identify User and Site Characteristics Identify Executive Stakeholders • • • Identify Load Characteristics Implement Test Cases Create Test Users Create Test Site Content Test Store Configuration and Results Reset Analyze Results Report to Executive Stakeholders
 Load Testing Software • Key questions – Is there a budget? – Are there reasons to go with a proprietary or an open source tool? – Does it matter if you can share your test case code? – Where should it be in the adoption cycle? – What internal expertise exists?
Load Testing Software • Key questions – Is there a budget? – Are there reasons to go with a proprietary or an open source tool? – Does it matter if you can share your test case code? – Where should it be in the adoption cycle? – What internal expertise exists?
 NYU’s Choice • The Grinder 3 – – – No budget Charged with using open source where mature Others can use the resulting test cases Neither bleeding edge nor nearing obsolescence Jython/Python scripting in a Java framework
NYU’s Choice • The Grinder 3 – – – No budget Charged with using open source where mature Others can use the resulting test cases Neither bleeding edge nor nearing obsolescence Jython/Python scripting in a Java framework
 Artifacts • Installation and Configuration Cheat Sheet – In progress – Shared
Artifacts • Installation and Configuration Cheat Sheet – In progress – Shared
 Load Testing Hardware • Key questions – Buy or borrow? – Where should machines live? – How many? • Bleeds into Network Requirements
Load Testing Hardware • Key questions – Buy or borrow? – Where should machines live? – How many? • Bleeds into Network Requirements
 • Console NYU’s Choices – Borrow – Least secure network consistent with data stored – Long term (near-permanent) cname • Agents – Borrow – On same subnet as application, on NYU-NET, off NYU-NET, across VPN, across NYU-DIAL, on NYU-ROAM – Number desired will be derived from test case characteristics – Number used will be negotiated with ‘volunteer’ organizations • Network Requirements – Remember to handshake with the NOC early
• Console NYU’s Choices – Borrow – Least secure network consistent with data stored – Long term (near-permanent) cname • Agents – Borrow – On same subnet as application, on NYU-NET, off NYU-NET, across VPN, across NYU-DIAL, on NYU-ROAM – Number desired will be derived from test case characteristics – Number used will be negotiated with ‘volunteer’ organizations • Network Requirements – Remember to handshake with the NOC early
 Artifacts • Derivation of agent machine counts – In progress – Shared • Machinery – Not shared
Artifacts • Derivation of agent machine counts – In progress – Shared • Machinery – Not shared
 Ancillary Systems • Key questions – What are you really testing? – Are the any non-Sakai systems in the mix?
Ancillary Systems • Key questions – What are you really testing? – Are the any non-Sakai systems in the mix?
 • LDAP NYU’s Answers – Not testing the speed of our LDAP response – Don’t slow other production systems – Don’t expose real user data Set up an independent LDAP system with well specified test accounts and test passwords • Automated data processes – Future issue – Disable non-core processes for duration of load testing – Schedule specific load tests to learn the impact of batch processes on user response times
• LDAP NYU’s Answers – Not testing the speed of our LDAP response – Don’t slow other production systems – Don’t expose real user data Set up an independent LDAP system with well specified test accounts and test passwords • Automated data processes – Future issue – Disable non-core processes for duration of load testing – Schedule specific load tests to learn the impact of batch processes on user response times
 Artifacts • None – Share test account specifications – Missing something shareable?
Artifacts • None – Share test account specifications – Missing something shareable?
 Long Term Retention • Key questions – – – Retain results? Retain test scripts? Retain network and machine specs? Retain configuration data? Who is the data steward? Where to keep it all?
Long Term Retention • Key questions – – – Retain results? Retain test scripts? Retain network and machine specs? Retain configuration data? Who is the data steward? Where to keep it all?
 NYU’s Choices • • • Retain Network and Machine Specs Retain Test Scripts Retain Results Retain a Record of Versions and Configuration Settings Without a formal QA department, Dev is the Steward Subversion repository
NYU’s Choices • • • Retain Network and Machine Specs Retain Test Scripts Retain Results Retain a Record of Versions and Configuration Settings Without a formal QA department, Dev is the Steward Subversion repository
 Artifacts • Subversion repository recommendations – Will share own best practices for tagging/branching svn repository – Missing something shareable?
Artifacts • Subversion repository recommendations – Will share own best practices for tagging/branching svn repository – Missing something shareable?
 Itemize Test Cases • Derived from existing Learning Management Systems in production • Derived from actual Sakai usage in production • Theorized for new tools
Itemize Test Cases • Derived from existing Learning Management Systems in production • Derived from actual Sakai usage in production • Theorized for new tools
 Blackboard Usage • Statistics information is exported to offline database schema (bb_bb 60_stats) • Query for counts – Time blocks: pre-semester, first week, midterms, reading week, finals, one-time events • Analyze events • Translate to Sakai equivalents • Derive relative counts of each activity for each time block “Administrators have open access to the statistics database to use for analysis and creating reports. ” at http: //library. blackboard. com/docs/r 7/70/en_US/admin/bbas_r 7_0_admin/ advanced_system_reporting. htm and http: //library. blackboard. com/docs/cp/learning_system/ release 6/administrator/advanced_system_reporting. htm
Blackboard Usage • Statistics information is exported to offline database schema (bb_bb 60_stats) • Query for counts – Time blocks: pre-semester, first week, midterms, reading week, finals, one-time events • Analyze events • Translate to Sakai equivalents • Derive relative counts of each activity for each time block “Administrators have open access to the statistics database to use for analysis and creating reports. ” at http: //library. blackboard. com/docs/r 7/70/en_US/admin/bbas_r 7_0_admin/ advanced_system_reporting. htm and http: //library. blackboard. com/docs/cp/learning_system/ release 6/administrator/advanced_system_reporting. htm
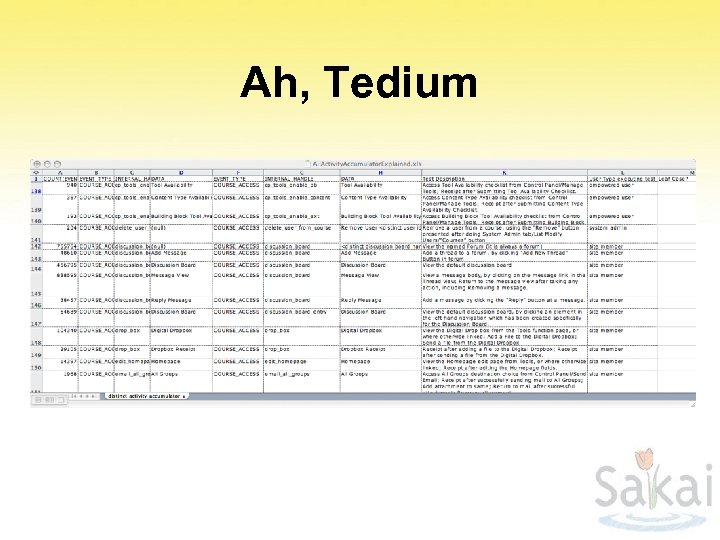 Ah, Tedium
Ah, Tedium
 Artifacts • Queries • Transliteration from leaf case to Sakai test • Multiplication factor from leaf case to event – In progress – Shared
Artifacts • Queries • Transliteration from leaf case to Sakai test • Multiplication factor from leaf case to event – In progress – Shared
 Sakai Usage • In pilot, little valid data • Biggest usage results turned out to reflect our pen testing
Sakai Usage • In pilot, little valid data • Biggest usage results turned out to reflect our pen testing
 Theoretical Usage • New tool means no historical data • Key is to identify and document all assumptions • Update assumptions as data accumulates
Theoretical Usage • New tool means no historical data • Key is to identify and document all assumptions • Update assumptions as data accumulates
 Artifacts • Sakai site statistics queries – In progress – Shared • Assumptions worksheet – Not quite on the radar yet
Artifacts • Sakai site statistics queries – In progress – Shared • Assumptions worksheet – Not quite on the radar yet
 Elements of a Test Case • • • Name Number - for correspondence to Grinder test Human readable description User type executing test case Data assumed to exist before the test case starts Success criteria - only successful tests are counted in timing statistics • Categorization - login, logout, content read, content create, discussion read, discussion write
Elements of a Test Case • • • Name Number - for correspondence to Grinder test Human readable description User type executing test case Data assumed to exist before the test case starts Success criteria - only successful tests are counted in timing statistics • Categorization - login, logout, content read, content create, discussion read, discussion write
 Artifacts • Test Case Documentation – Not started – Shared
Artifacts • Test Case Documentation – Not started – Shared
 Implement Test Cases • The Grinder proxy captures clicks of a test case • Programmer effort – – Clean up proxy output Parameterize user data Parameterize course site data Check for success criteria • Not to be sneezed at • Test the Test Cases
Implement Test Cases • The Grinder proxy captures clicks of a test case • Programmer effort – – Clean up proxy output Parameterize user data Parameterize course site data Check for success criteria • Not to be sneezed at • Test the Test Cases
 Artifacts • The Grinder Test Case Scripts – Not started – Shared
Artifacts • The Grinder Test Case Scripts – Not started – Shared
 Create Test Users and Sites • Now know user types required and relative counts of each type. • Now know data requirements for each test case, and the course sites and starting contents required. • Script the generation of users and sites, and of the data files used by The Grinder agents – LDAP account allocation – Permissioning within course sites – Content creation within course sites: seed content files, lorem ipsum
Create Test Users and Sites • Now know user types required and relative counts of each type. • Now know data requirements for each test case, and the course sites and starting contents required. • Script the generation of users and sites, and of the data files used by The Grinder agents – LDAP account allocation – Permissioning within course sites – Content creation within course sites: seed content files, lorem ipsum
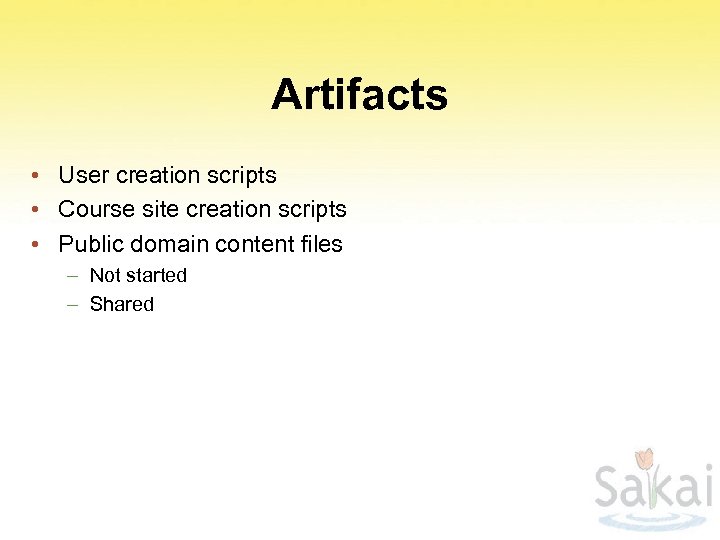 Artifacts • User creation scripts • Course site creation scripts • Public domain content files – Not started – Shared
Artifacts • User creation scripts • Course site creation scripts • Public domain content files – Not started – Shared
 Test • Set up grinder configuration: counts, ramp up speed, duration • Install The Grinder on agent machines to speak to common console • Check in to subversion all documentation, test cases and configuration data • Take a full back up of the target system Run the test.
Test • Set up grinder configuration: counts, ramp up speed, duration • Install The Grinder on agent machines to speak to common console • Check in to subversion all documentation, test cases and configuration data • Take a full back up of the target system Run the test.
 Test bit anticlimactic really
Test bit anticlimactic really
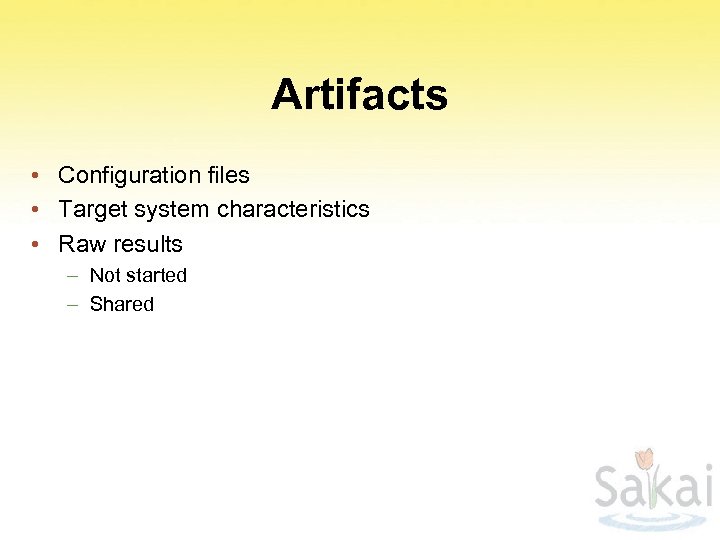 Artifacts • Configuration files • Target system characteristics • Raw results – Not started – Shared
Artifacts • Configuration files • Target system characteristics • Raw results – Not started – Shared
 Reset the System • Restore from the full backup
Reset the System • Restore from the full backup
 Results • Commit the raw results to subversion alongside the tests and configurations used to generate the results
Results • Commit the raw results to subversion alongside the tests and configurations used to generate the results
 Report • Report to stakeholders
Report • Report to stakeholders
 Repeat Until Done
Repeat Until Done
 Test • Set up grinder configuration: counts, ramp up speed, duration • Install The Grinder on agent machines to speak to common console • Check in to subversion all documentation, test cases and configuration data • Take a full back up of the target system Run the test.
Test • Set up grinder configuration: counts, ramp up speed, duration • Install The Grinder on agent machines to speak to common console • Check in to subversion all documentation, test cases and configuration data • Take a full back up of the target system Run the test.
 Reset the System • Restore from the full backup
Reset the System • Restore from the full backup
 Results • Commit the raw results to subversion alongside the tests and configurations used to generate the results
Results • Commit the raw results to subversion alongside the tests and configurations used to generate the results
 Report • Report to stakeholders
Report • Report to stakeholders
 Repeat Until Done
Repeat Until Done
 Test • Set up grinder configuration: counts, ramp up speed, duration • Install The Grinder on agent machines to speak to common console • Check in to subversion all documentation, test cases and configuration data • Take a full back up of the target system Run the test.
Test • Set up grinder configuration: counts, ramp up speed, duration • Install The Grinder on agent machines to speak to common console • Check in to subversion all documentation, test cases and configuration data • Take a full back up of the target system Run the test.
 Reset the System • Restore from the full backup
Reset the System • Restore from the full backup
 Results • Commit the raw results to subversion alongside the tests and configurations used to generate the results
Results • Commit the raw results to subversion alongside the tests and configurations used to generate the results
 Report • Report to stakeholders
Report • Report to stakeholders
 Repeat Until Done
Repeat Until Done
 Thank You and good day
Thank You and good day


