Liver and blood biochemistry.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

LIVER BIOCHEMISTRY
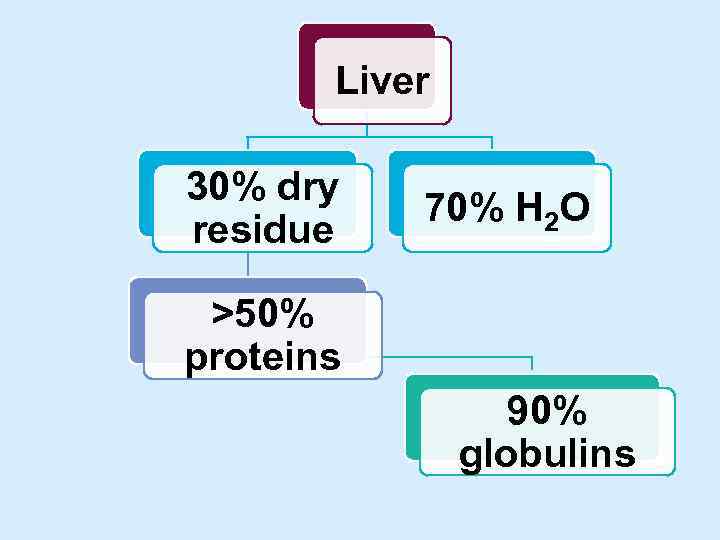
Liver 30% dry residue 70% H 2 O >50% proteins 90% globulins

Liver functions Metabolic function Storage Detoxification Digestive function Excretory function Homeostatic function
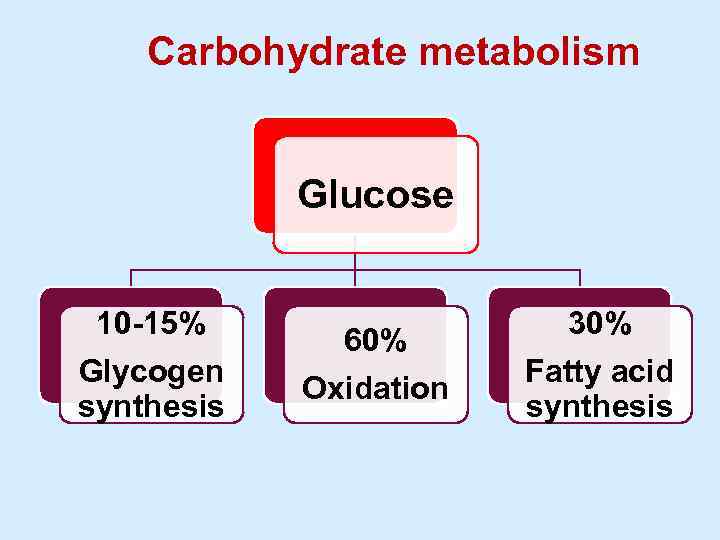
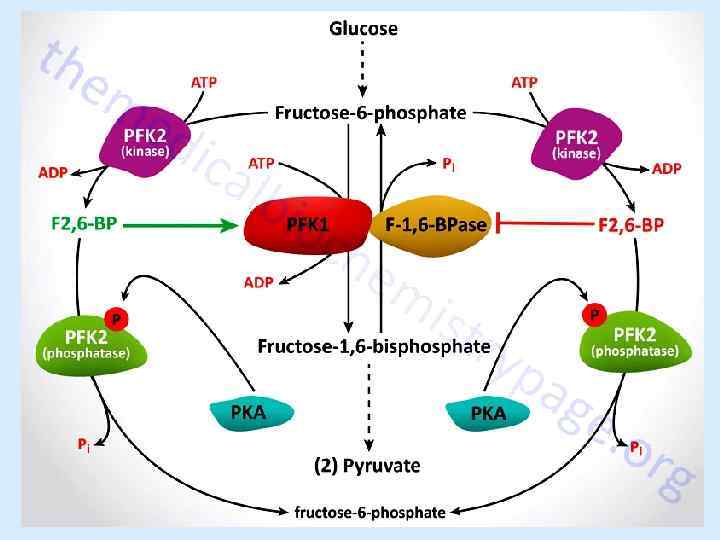
Carbohydrate metabolism Glucose 10 -15% Glycogen synthesis 60% Oxidation 30% Fatty acid synthesis
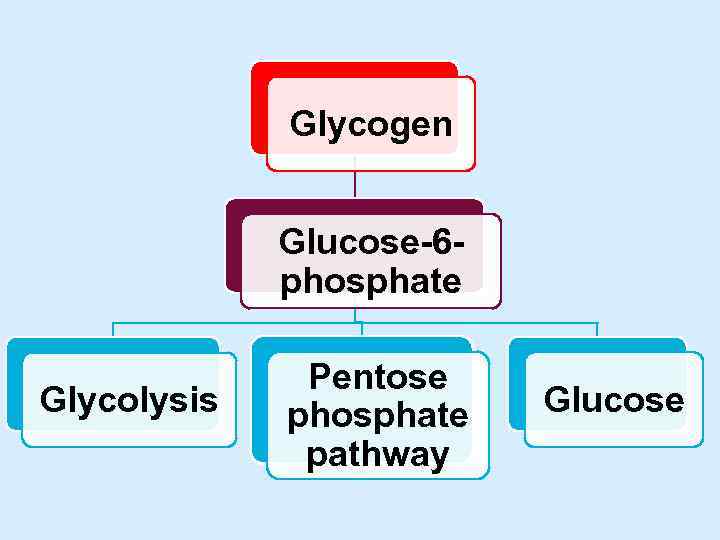
Glycogen Glucose-6 phosphate Glycolysis Pentose phosphate pathway Glucose
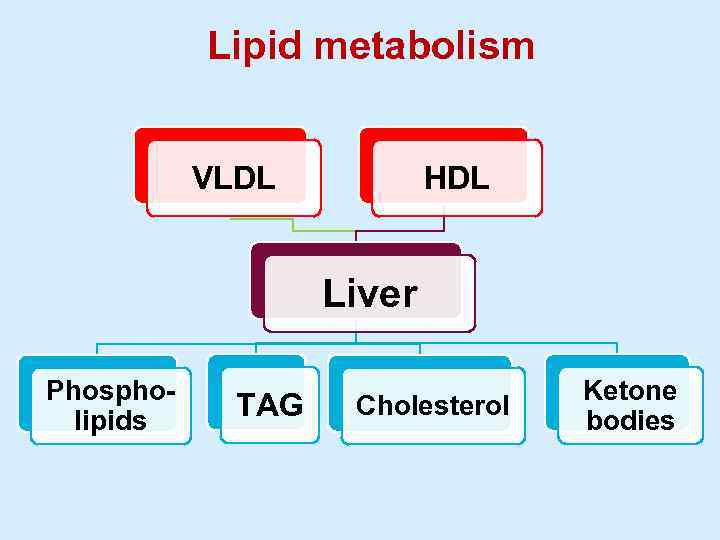
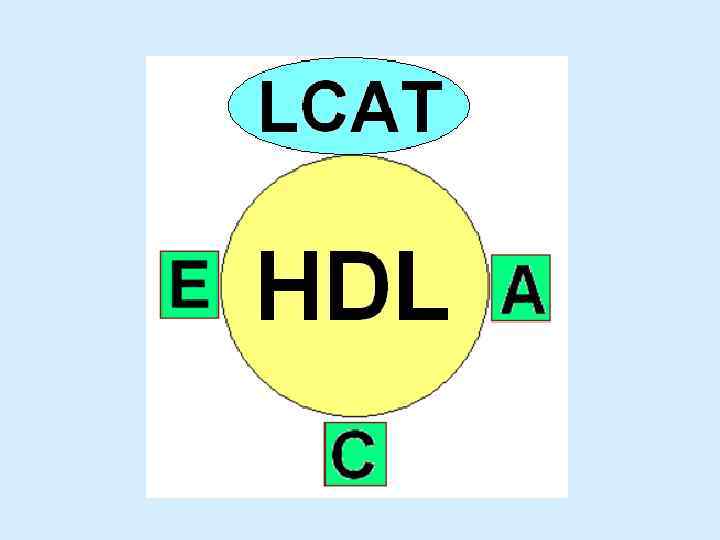
Lipid metabolism VLDL HDL Liver Phospholipids TAG Cholesterol Ketone bodies
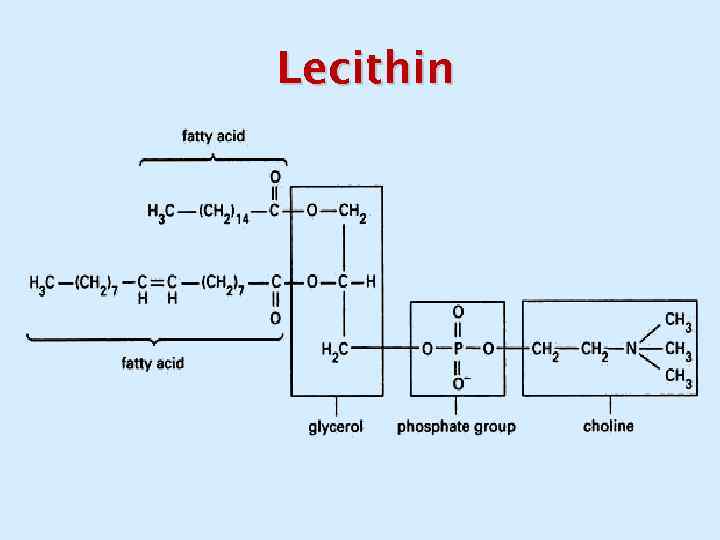
Lecithin

Niemann - Pick disease is caused by mutations in a gene of lysosomal sphingomyelinase. Gaucher disease is caused by deficiency of the enzyme glucocerebrosidase.
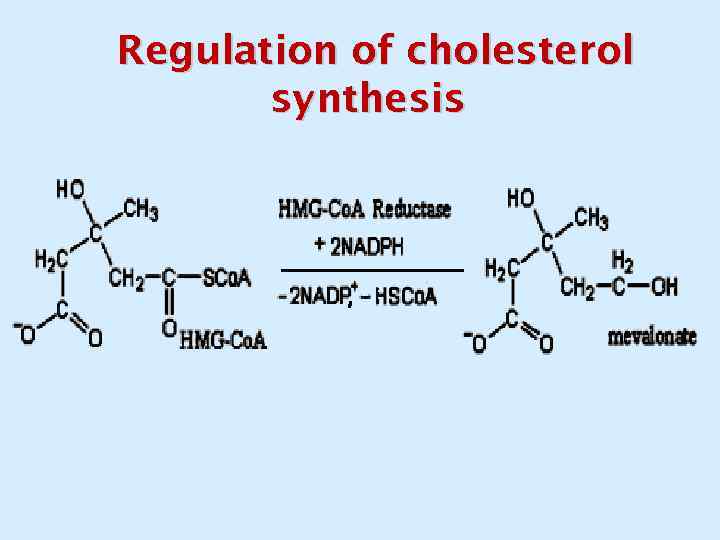
Regulation of cholesterol synthesis
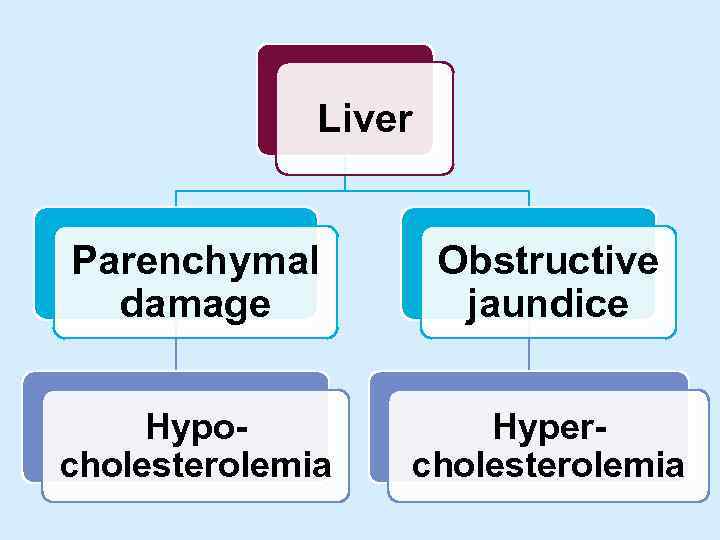
Liver Parenchymal damage Obstructive jaundice Hypocholesterolemia Hypercholesterolemia
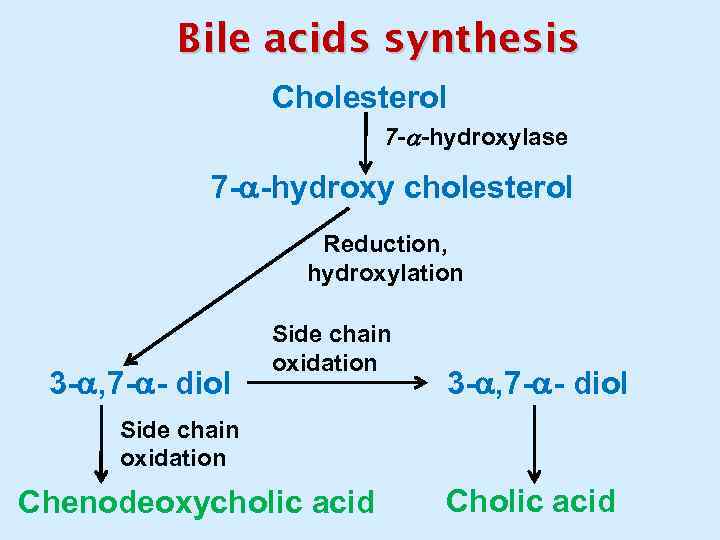
Bile acids synthesis Cholesterol 7 - -hydroxylase 7 - -hydroxy cholesterol Reduction, hydroxylation 3 - , 7 - - diol Side chain oxidation Chenodeoxycholic acid Cholic acid
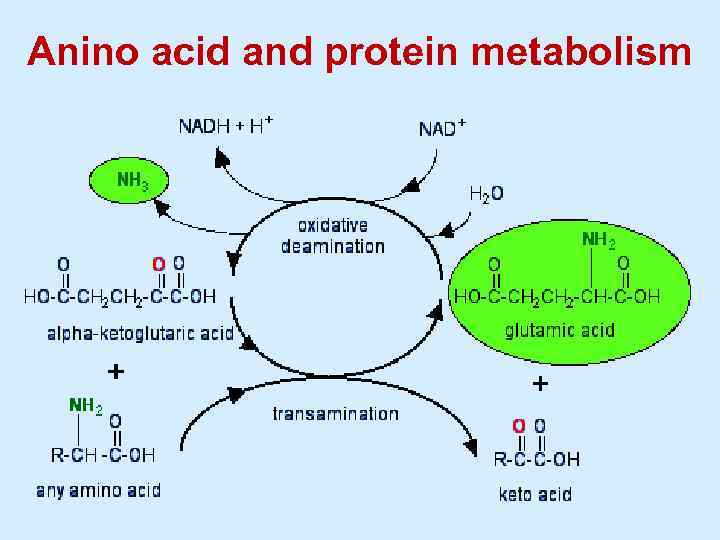
Anino acid and protein metabolism
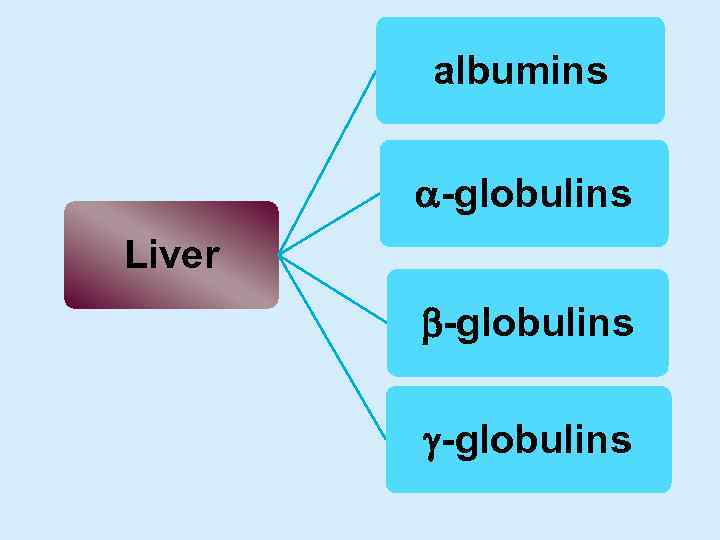
albumins -globulins Liver -globulins

Ceruloplasmin catalyzes the oxidation of polyphenols and polyamines. It’s concentration is increased in inflammatory processes. Wilson's disease (hepatolenticular disease) is an inborn error of copper metabolism. Menkes disease ("disease of curly hair”) is a violation of the cellular transport of copper due to a defect of ATPase.

α-1 -antitrypsin inhibits proteases in biological fluids of the body. Deficiency of α-1 -antitrypsin is associated with emphysema and liver cirrhosis. Plasma clotting factors: prothrombin, fibrinogen, prothrombin conversion factor (proconvertin) Elements of anticoagulation system: heparin, antithrombin, antiplasmin.
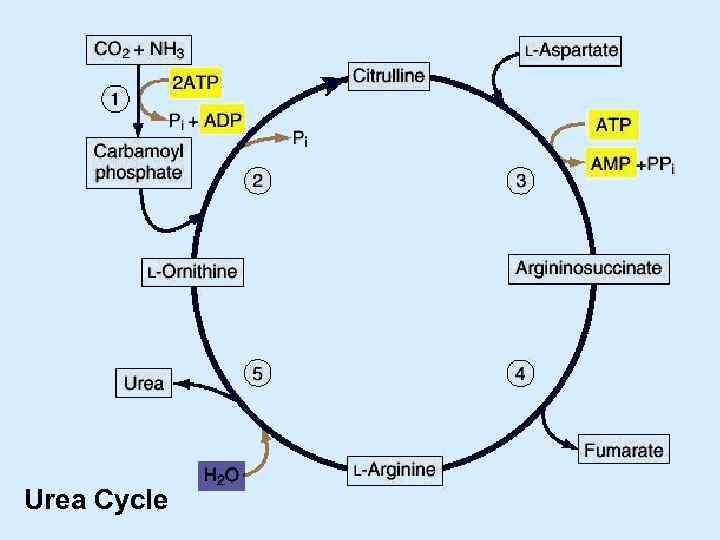
Urea Cycle

Vitamins Absorption: А, D, Е, К Deposition: А, В 1, Р, Е, К, РР Activation: В 1, В 2, В 6 Participation in chemical reactions: В 1, В 2, В 5, В 12, С, К
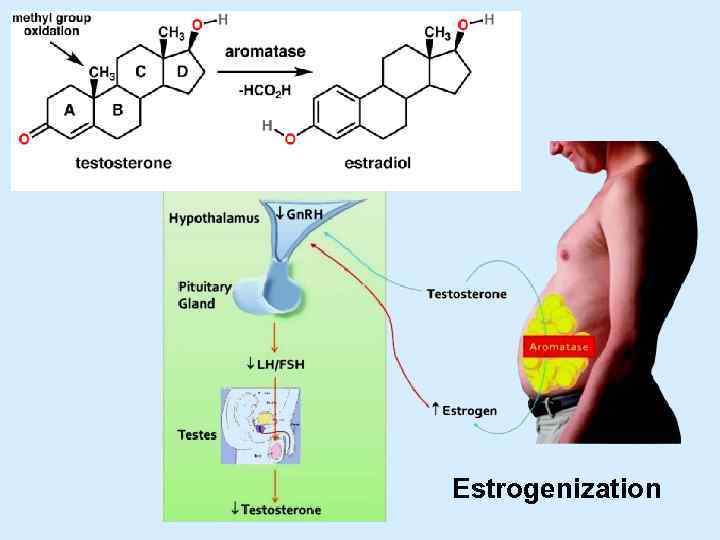
Estrogenization
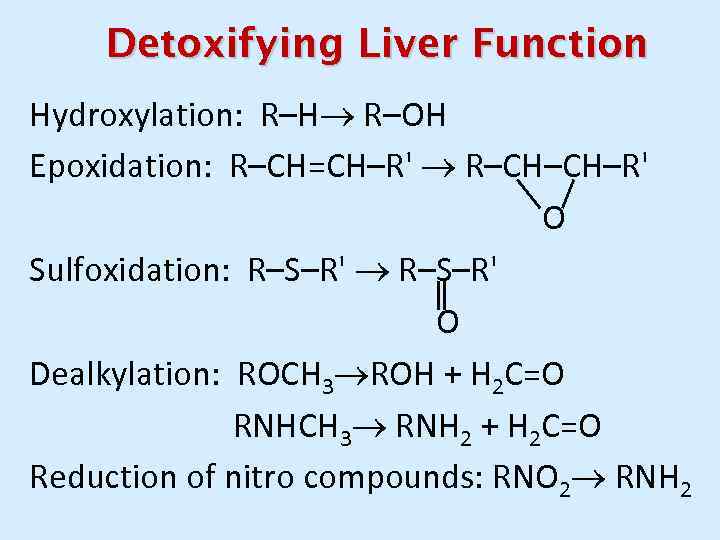
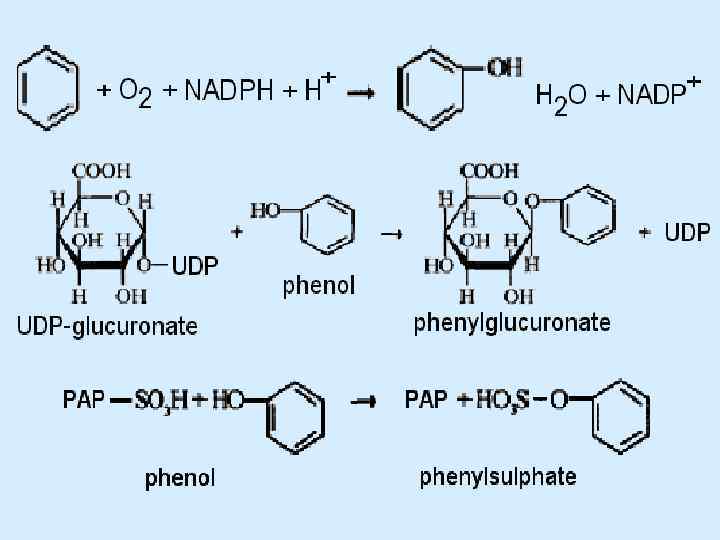
Detoxifying Liver Function Hydroxylation: R–Н R–ОН Epoxidation: R–CН=СН–R' R–CH–CH–R' O Sulfoxidation: R–S–R' О Dealkylation: RОСН 3 RОН + Н 2 С=О RNHСН 3 RNH 2 + Н 2 С=О Reduction of nitro compounds: RNО 2 RNH 2
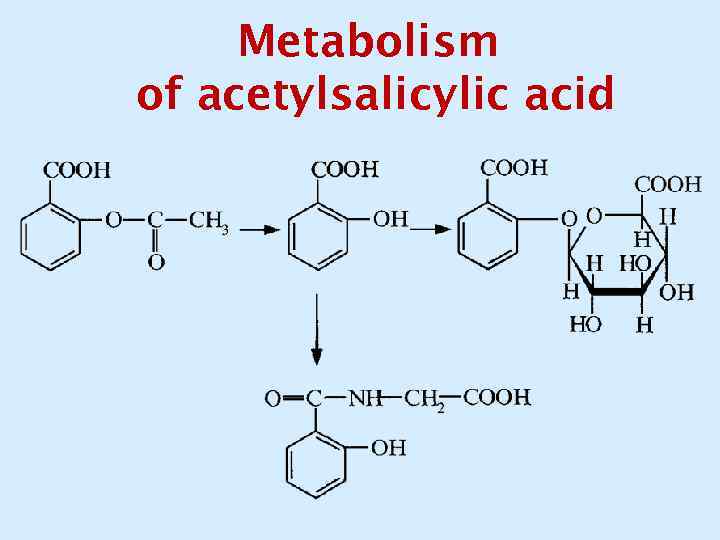
Metabolism of acetylsalicylic acid

BLOOD BIOCHEMISTRY

Chemical composition of blood Proteins: albumin, globulins Functions: - , V, p. H - Viscosity - Transport - Blood clotting - Immunity - Amino acids
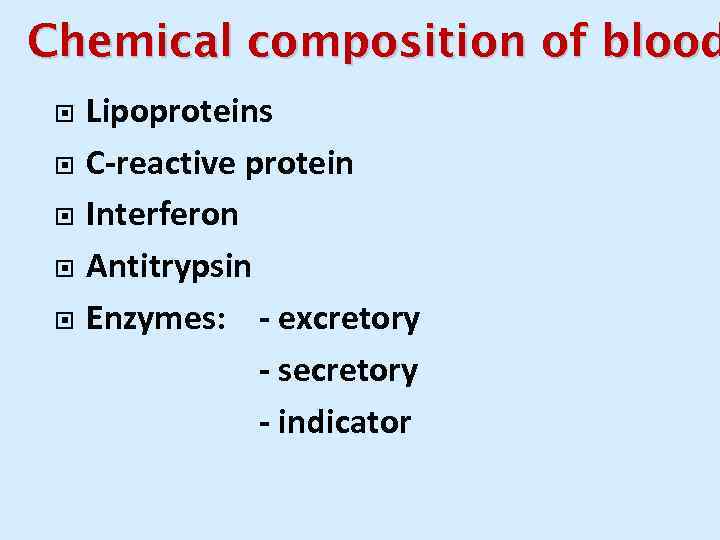
Chemical composition of blood Lipoproteins C-reactive protein Interferon Antitrypsin Enzymes: - excretory - secretory - indicator

Chemical composition of blood Non-protein nitrogen components Nitrogen-free organic compounds Electrolytes Micronutrients
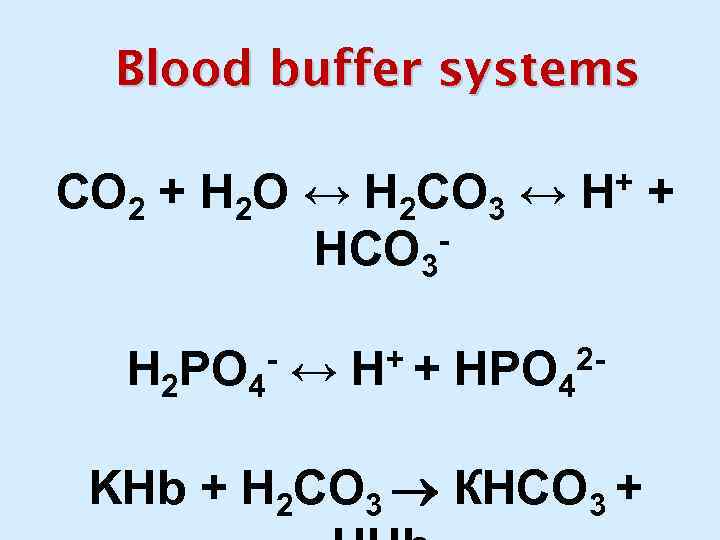
Blood buffer systems СО 2 + Н 2 О ↔ Н 2 СО 3 ↔ Н+ + НСО 3 - ↔ Н+ + НРО 2 Н 2 РО 4 4 KHb + Н 2 СО 3 КНСО 3 +
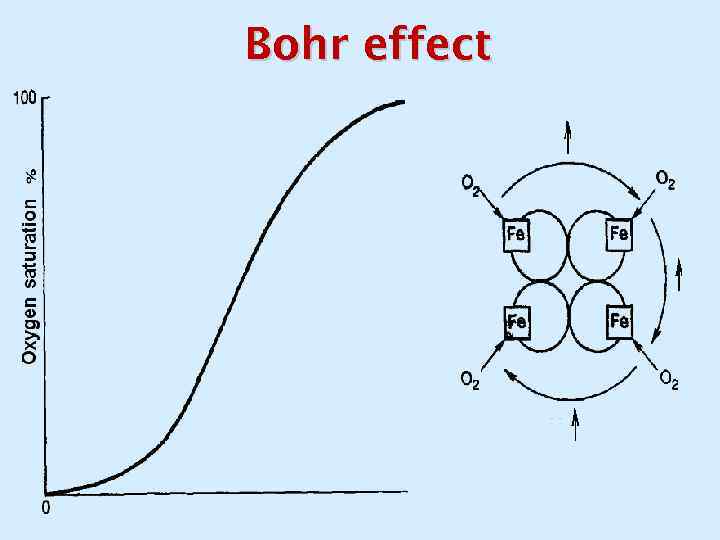
Bohr effect
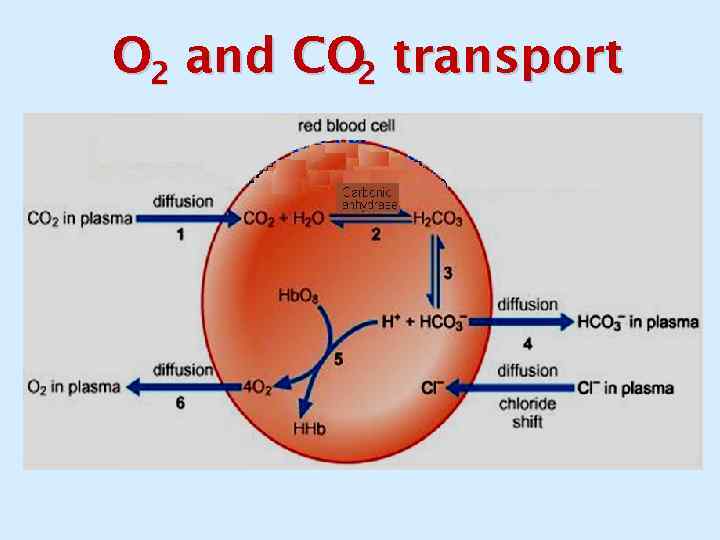
O 2 and CO 2 transport
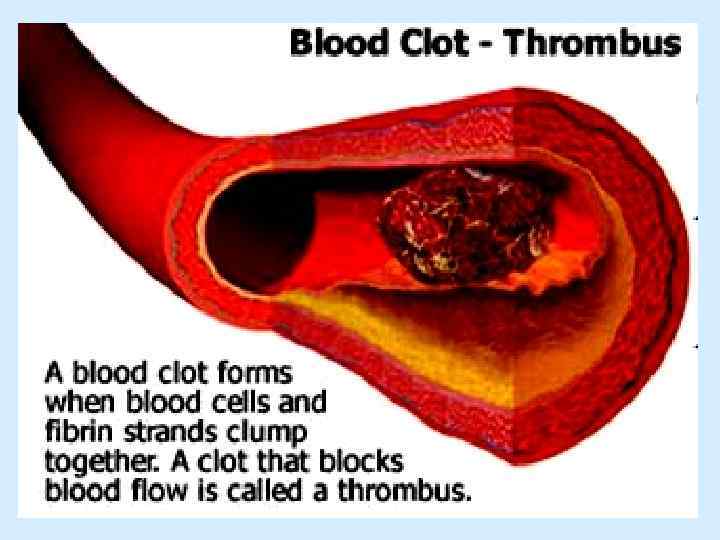
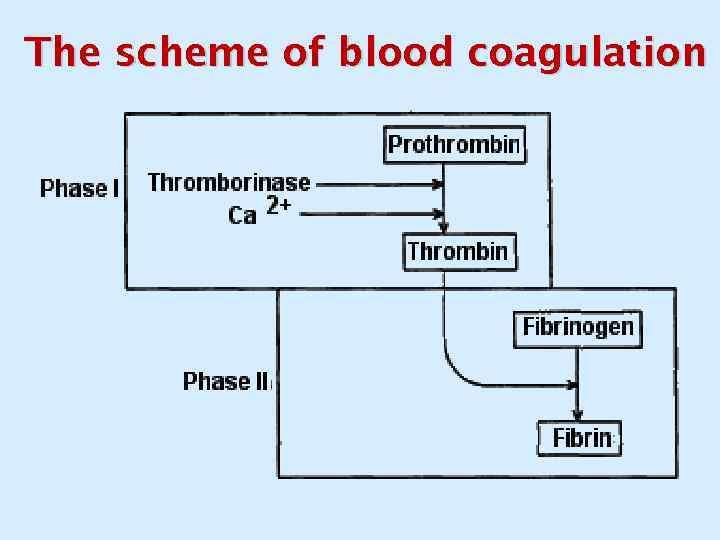
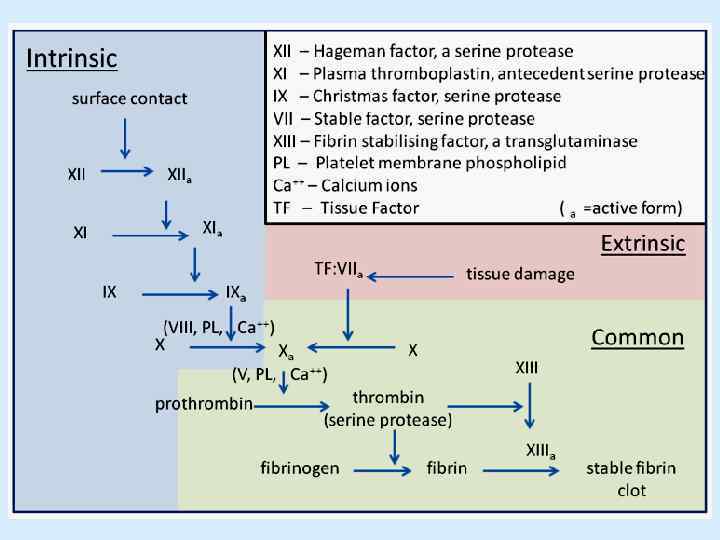
The scheme of blood coagulation

Blood clotting factors Factor I (fibrinogen) Factor II (prothrombin) Factor III (tissue factor, or tissue thromboplastin) Factor IV (Ca 2 + ions) Factor V (proaccelerin) Factor VII (prothrombinogen, proconvertin) Factor VIII (antihemophylic globulin A)

Blood clotting factors Factor IX (antihemophylic globulin B, Christmas factor) Factor X (Stuart - Power factor) Factor XI (Rosenthal factor, plasma thromboplastin) Factor XII (Hageman factor) Factor XIII (fibrin-stabilizing factor, transglutaminase) Factors of platelets.
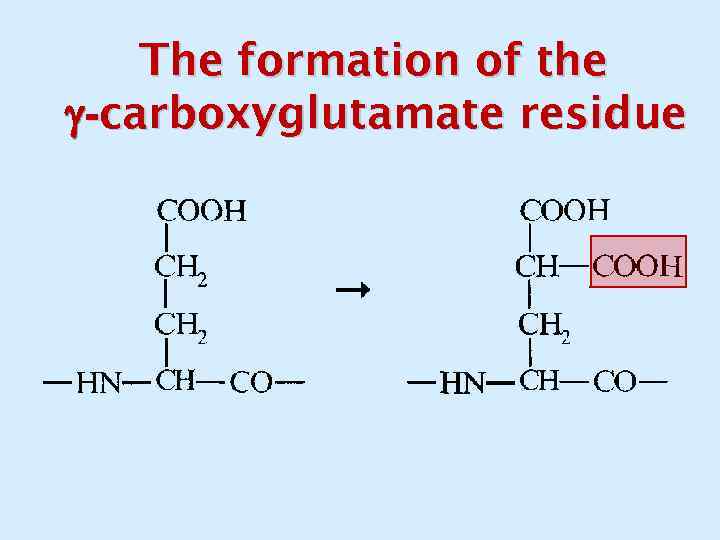
The formation of the -carboxyglutamate residue
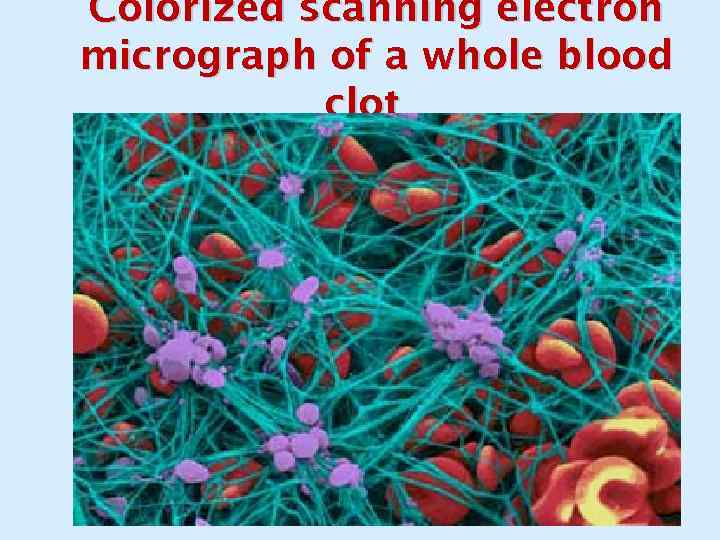
Colorized scanning electron micrograph of a whole blood clot
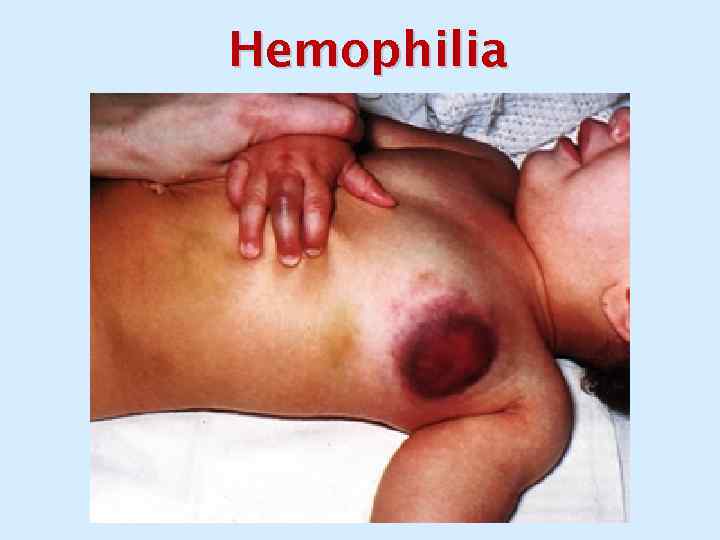
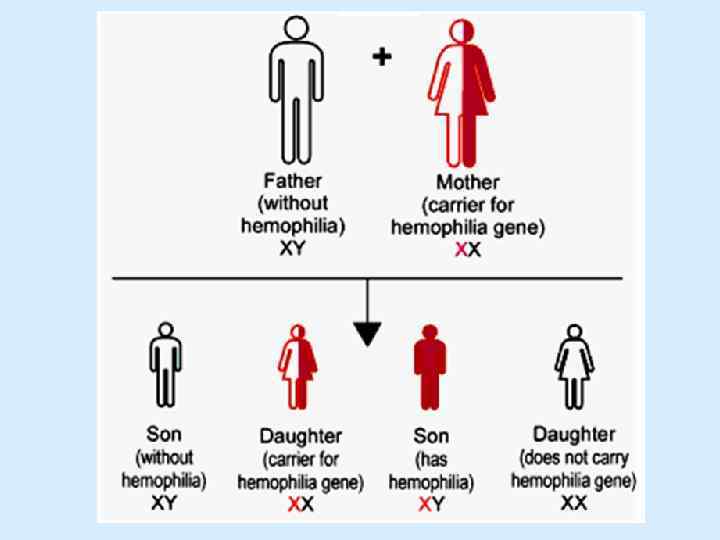
Hemophilia
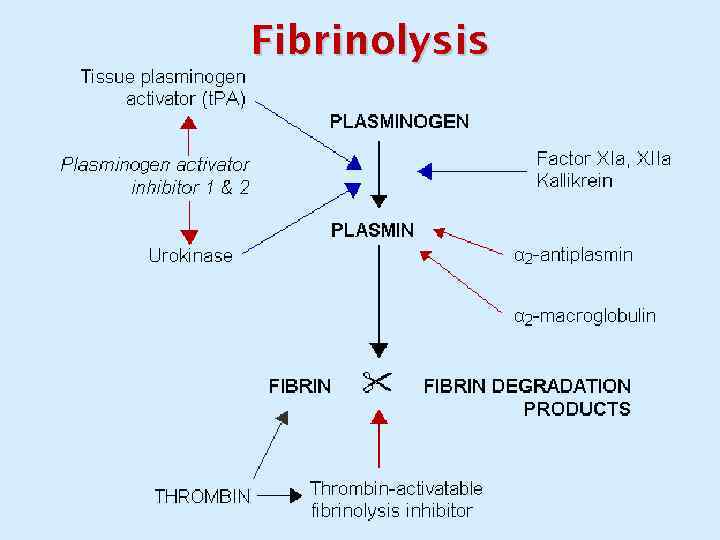
Fibrinolysis
Liver and blood biochemistry.ppt