d7fe6cca3dd37f225d3d21b590e2b388.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Little Data: Next. Gen Info Storage in DNA 3: 55 -4: 50 PM CBA 7 -Mar-2013 12: 12 -12: 21 PM Thanks to: . gov NHGRI || NIGMS ||. edu || Arm. Rev. org || Oppenheimer . org Foundation || ||. com Azco || || Read LSRF Gen 9 = = = = I/O = = = = Write A
Little Data: Next. Gen Info Storage in DNA 3: 55 -4: 50 PM CBA 7 -Mar-2013 12: 12 -12: 21 PM Thanks to: . gov NHGRI || NIGMS ||. edu || Arm. Rev. org || Oppenheimer . org Foundation || ||. com Azco || || Read LSRF Gen 9 = = = = I/O = = = = Write A
 Next-generation Digital Information Storage in DNA 1. Read/write DNA 10 -fold/yr: Next = FISSeq 2. E. coli & human genome engineering 3. DNA data archiving 4. Brain Activity Map I/O: Polymerase Biologically Inspired Engineering
Next-generation Digital Information Storage in DNA 1. Read/write DNA 10 -fold/yr: Next = FISSeq 2. E. coli & human genome engineering 3. DNA data archiving 4. Brain Activity Map I/O: Polymerase Biologically Inspired Engineering
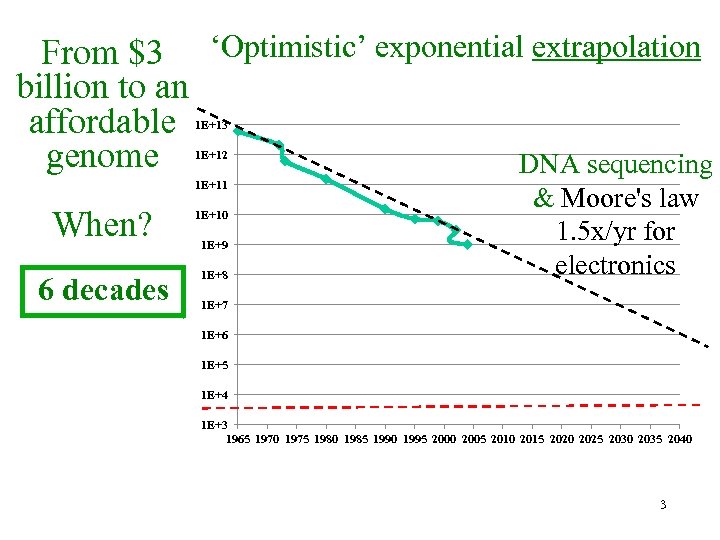 From $3 ‘Optimistic’ exponential extrapolation billion to an affordable genome DNA sequencing 1 E+13 1 E+12 1 E+11 When? 1 E+10 6 decades 1 E+8 1 E+9 & Moore's law 1. 5 x/yr for electronics 1 E+7 1 E+6 1 E+5 1 E+4 1 E+3 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 2025 2030 2035 2040 3
From $3 ‘Optimistic’ exponential extrapolation billion to an affordable genome DNA sequencing 1 E+13 1 E+12 1 E+11 When? 1 E+10 6 decades 1 E+8 1 E+9 & Moore's law 1. 5 x/yr for electronics 1 E+7 1 E+6 1 E+5 1 E+4 1 E+3 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 2025 2030 2035 2040 3
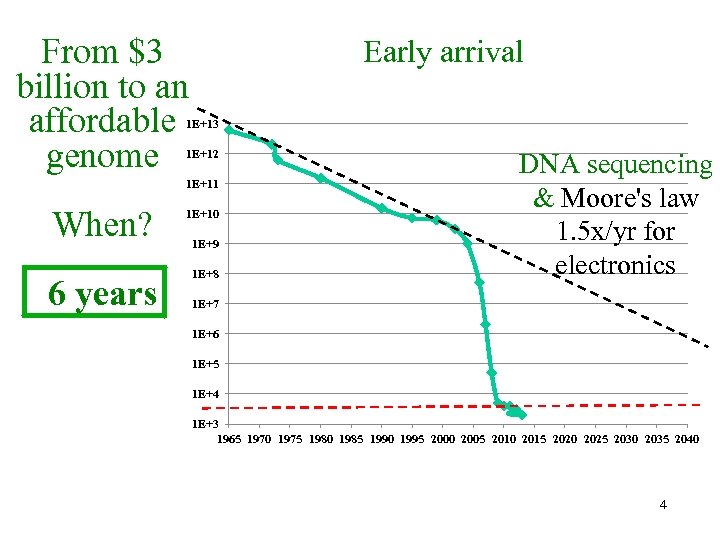 From $3 billion to an affordable genome Early arrival 1 E+13 1 E+12 1 E+11 When? 1 E+10 6 years 1 E+8 1 E+9 DNA sequencing & Moore's law 1. 5 x/yr for electronics 1 E+7 1 E+6 1 E+5 1 E+4 1 E+3 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 2025 2030 2035 2040 4
From $3 billion to an affordable genome Early arrival 1 E+13 1 E+12 1 E+11 When? 1 E+10 6 years 1 E+8 1 E+9 DNA sequencing & Moore's law 1. 5 x/yr for electronics 1 E+7 1 E+6 1 E+5 1 E+4 1 E+3 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 2025 2030 2035 2040 4
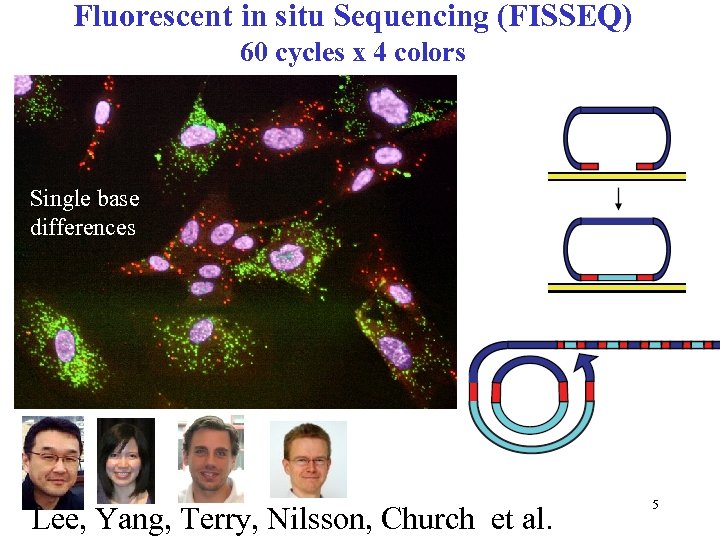 Fluorescent in situ Sequencing (FISSEQ) 60 cycles x 4 colors Single base differences Lee, Yang, Terry, Nilsson, Church et al. 5
Fluorescent in situ Sequencing (FISSEQ) 60 cycles x 4 colors Single base differences Lee, Yang, Terry, Nilsson, Church et al. 5
 Next-generation Digital Information Storage in DNA 1. Read/write DNA 10 -fold/yr: Next = FISSeq 2. E. coli & human genome engineering 3. DNA data archiving 4. Brain Activity Map I/O: Polymerase Biologically Inspired Engineering
Next-generation Digital Information Storage in DNA 1. Read/write DNA 10 -fold/yr: Next = FISSeq 2. E. coli & human genome engineering 3. DNA data archiving 4. Brain Activity Map I/O: Polymerase Biologically Inspired Engineering
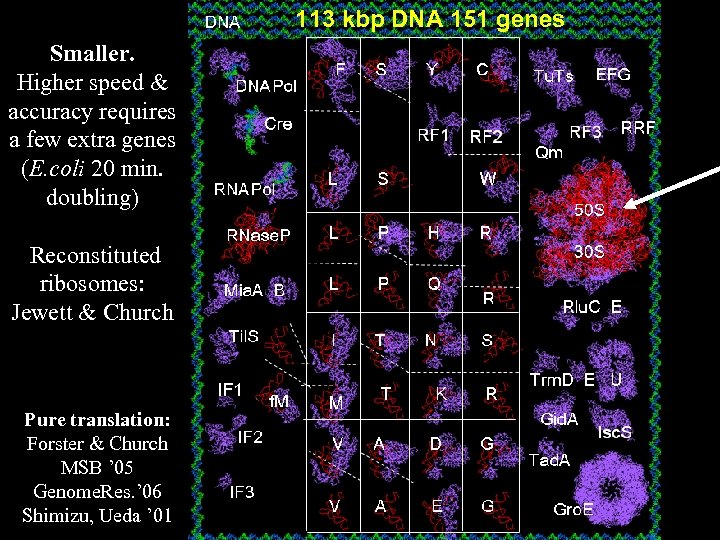 113 kbp DNA 151 genes Smaller. Higher speed & accuracy requires a few extra genes (E. coli 20 min. doubling) Reconstituted ribosomes: Jewett & Church Pure translation: Forster & Church MSB ’ 05 Genome. Res. ’ 06 Shimizu, Ueda ’ 01 7
113 kbp DNA 151 genes Smaller. Higher speed & accuracy requires a few extra genes (E. coli 20 min. doubling) Reconstituted ribosomes: Jewett & Church Pure translation: Forster & Church MSB ’ 05 Genome. Res. ’ 06 Shimizu, Ueda ’ 01 7
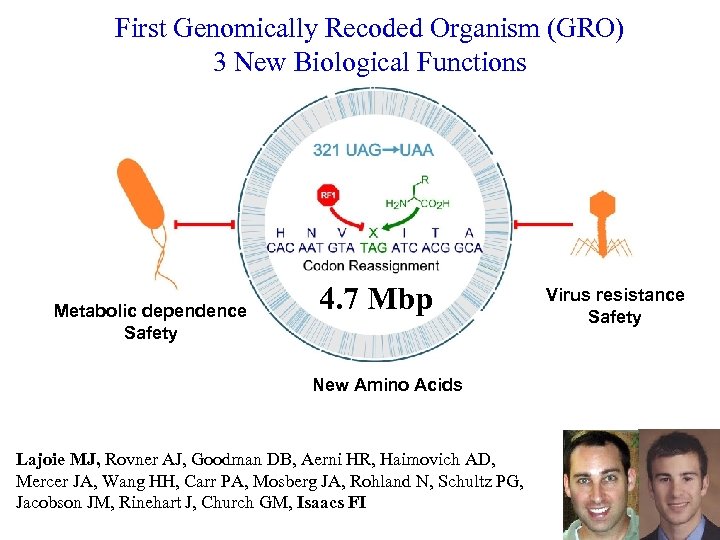 First Genomically Recoded Organism (GRO) 3 New Biological Functions Metabolic dependence Safety 4. 7 Mbp New Amino Acids Lajoie MJ, Rovner AJ, Goodman DB, Aerni HR, Haimovich AD, Mercer JA, Wang HH, Carr PA, Mosberg JA, Rohland N, Schultz PG, Jacobson JM, Rinehart J, Church GM, Isaacs FI Virus resistance Safety
First Genomically Recoded Organism (GRO) 3 New Biological Functions Metabolic dependence Safety 4. 7 Mbp New Amino Acids Lajoie MJ, Rovner AJ, Goodman DB, Aerni HR, Haimovich AD, Mercer JA, Wang HH, Carr PA, Mosberg JA, Rohland N, Schultz PG, Jacobson JM, Rinehart J, Church GM, Isaacs FI Virus resistance Safety
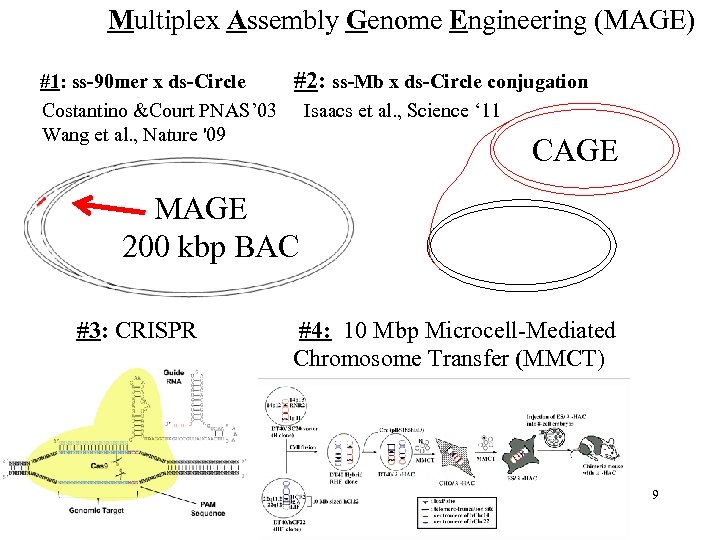 Multiplex Assembly Genome Engineering (MAGE) #1: ss-90 mer x ds-Circle #2: ss-Mb x ds-Circle conjugation Costantino &Court PNAS’ 03 Isaacs et al. , Science ‘ 11 Wang et al. , Nature '09 CAGE MAGE 200 kbp BAC #3: CRISPR #4: 10 Mbp Microcell-Mediated Chromosome Transfer (MMCT) 9
Multiplex Assembly Genome Engineering (MAGE) #1: ss-90 mer x ds-Circle #2: ss-Mb x ds-Circle conjugation Costantino &Court PNAS’ 03 Isaacs et al. , Science ‘ 11 Wang et al. , Nature '09 CAGE MAGE 200 kbp BAC #3: CRISPR #4: 10 Mbp Microcell-Mediated Chromosome Transfer (MMCT) 9
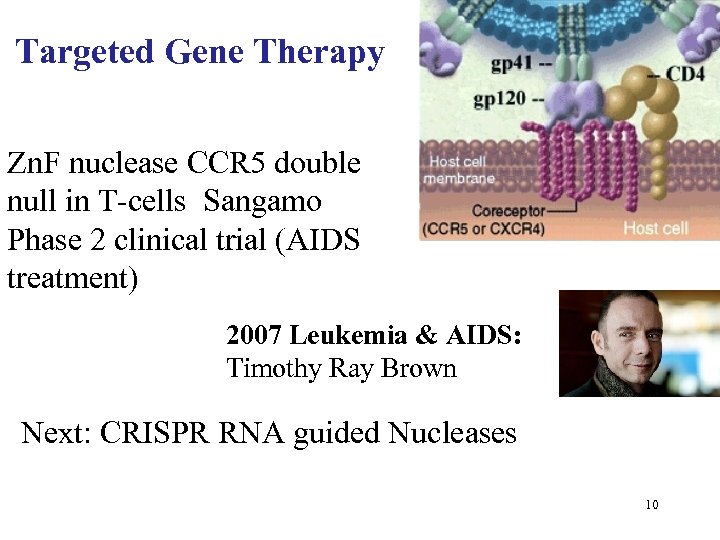 Targeted Gene Therapy Zn. F nuclease CCR 5 double null in T-cells Sangamo Phase 2 clinical trial (AIDS treatment) 2007 Leukemia & AIDS: Timothy Ray Brown Next: CRISPR RNA guided Nucleases 10
Targeted Gene Therapy Zn. F nuclease CCR 5 double null in T-cells Sangamo Phase 2 clinical trial (AIDS treatment) 2007 Leukemia & AIDS: Timothy Ray Brown Next: CRISPR RNA guided Nucleases 10
 Next-generation Digital Information Storage in DNA 1. Read/write DNA 10 -fold/yr: Next = FISSeq 2. E. coli & human genome engineering 3. DNA data archiving 4. Brain Activity Map I/O: Polymerase Biologically Inspired Engineering
Next-generation Digital Information Storage in DNA 1. Read/write DNA 10 -fold/yr: Next = FISSeq 2. E. coli & human genome engineering 3. DNA data archiving 4. Brain Activity Map I/O: Polymerase Biologically Inspired Engineering
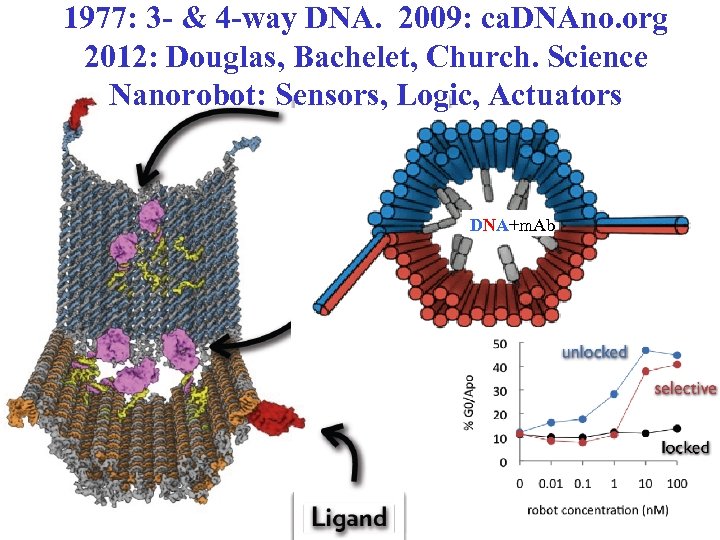 1977: 3 - & 4 -way DNA. 2009: ca. DNAno. org 2012: Douglas, Bachelet, Church. Science Nanorobot: Sensors, Logic, Actuators DNA+m. Ab
1977: 3 - & 4 -way DNA. 2009: ca. DNAno. org 2012: Douglas, Bachelet, Church. Science Nanorobot: Sensors, Logic, Actuators DNA+m. Ab
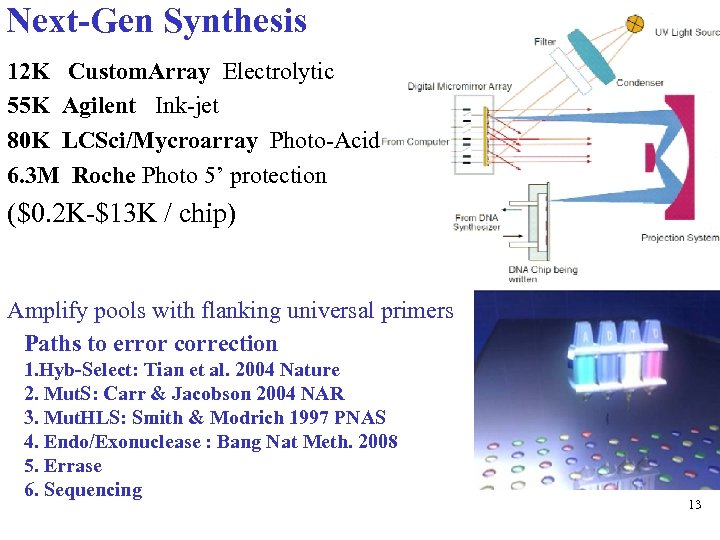 Next-Gen Synthesis 12 K Custom. Array Electrolytic 55 K Agilent Ink-jet 80 K LCSci/Mycroarray Photo-Acid 6. 3 M Roche Photo 5’ protection ($0. 2 K-$13 K / chip) Amplify pools with flanking universal primers Paths to error correction 1. Hyb-Select: Tian et al. 2004 Nature 2. Mut. S: Carr & Jacobson 2004 NAR 3. Mut. HLS: Smith & Modrich 1997 PNAS 4. Endo/Exonuclease : Bang Nat Meth. 2008 5. Errase 6. Sequencing 13
Next-Gen Synthesis 12 K Custom. Array Electrolytic 55 K Agilent Ink-jet 80 K LCSci/Mycroarray Photo-Acid 6. 3 M Roche Photo 5’ protection ($0. 2 K-$13 K / chip) Amplify pools with flanking universal primers Paths to error correction 1. Hyb-Select: Tian et al. 2004 Nature 2. Mut. S: Carr & Jacobson 2004 NAR 3. Mut. HLS: Smith & Modrich 1997 PNAS 4. Endo/Exonuclease : Bang Nat Meth. 2008 5. Errase 6. Sequencing 13
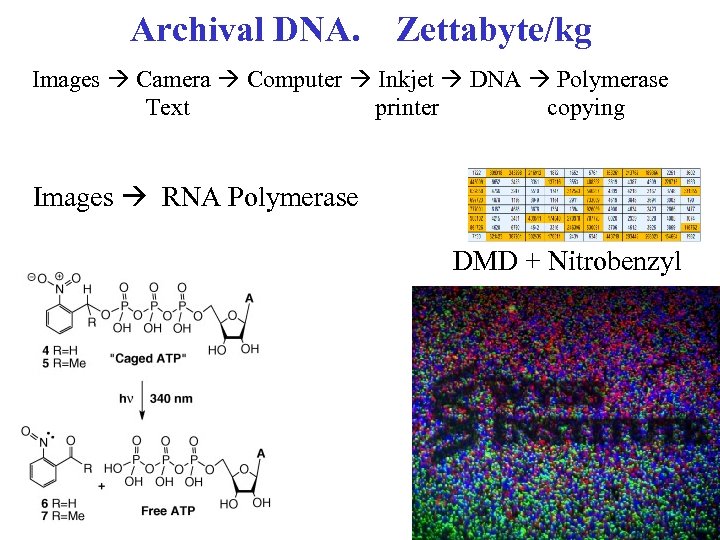 Archival DNA. Zettabyte/kg Images Camera Computer Inkjet DNA Polymerase Text printer copying Images RNA Polymerase DMD + Nitrobenzyl
Archival DNA. Zettabyte/kg Images Camera Computer Inkjet DNA Polymerase Text printer copying Images RNA Polymerase DMD + Nitrobenzyl
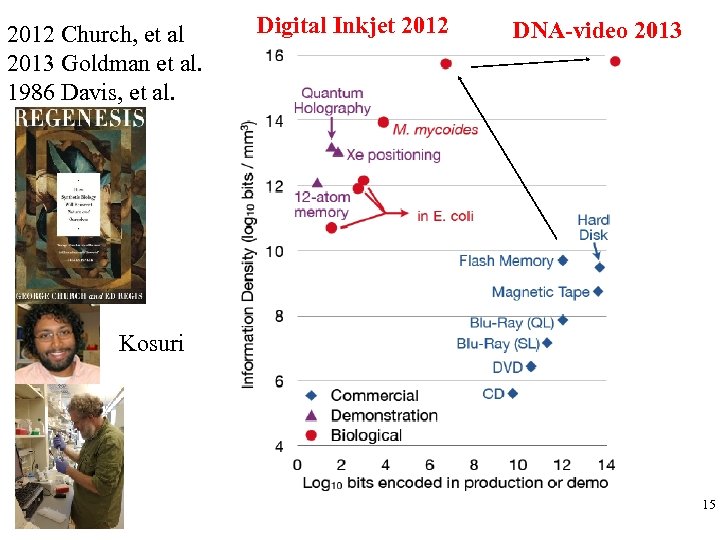 2012 Church, et al 2013 Goldman et al. 1986 Davis, et al. Digital Inkjet 2012 DNA-video 2013 Kosuri 15
2012 Church, et al 2013 Goldman et al. 1986 Davis, et al. Digital Inkjet 2012 DNA-video 2013 Kosuri 15
 Next-generation Digital Information Storage in DNA 1. 2. 3. 4. Read/write DNA 8 -fold/yr Fluorescent In Situ Sequencing (FISSeq) Nanorobots & DNA data archiving Brain Activity Map I/O: Polymerase Biologically Inspired Engineering
Next-generation Digital Information Storage in DNA 1. 2. 3. 4. Read/write DNA 8 -fold/yr Fluorescent In Situ Sequencing (FISSeq) Nanorobots & DNA data archiving Brain Activity Map I/O: Polymerase Biologically Inspired Engineering
 Brain Activity Map (BAM) Sep 2011: Kavli, Gatsby, Allen: Chun Imaging: Greenspan, Yuste, Zhaung, Reid Optical fibers: Roukes, Boyden, Scherer Nano: Alivisatos, Park, Weiss, Mc. Euen Stimulation: Donoghue, Deisseroth Computation: Kording, Sejnowski Polymerase: Zamft, Marblestone, Schmidt, Tyo, Martín-Alarcón, Marcus 17
Brain Activity Map (BAM) Sep 2011: Kavli, Gatsby, Allen: Chun Imaging: Greenspan, Yuste, Zhaung, Reid Optical fibers: Roukes, Boyden, Scherer Nano: Alivisatos, Park, Weiss, Mc. Euen Stimulation: Donoghue, Deisseroth Computation: Kording, Sejnowski Polymerase: Zamft, Marblestone, Schmidt, Tyo, Martín-Alarcón, Marcus 17
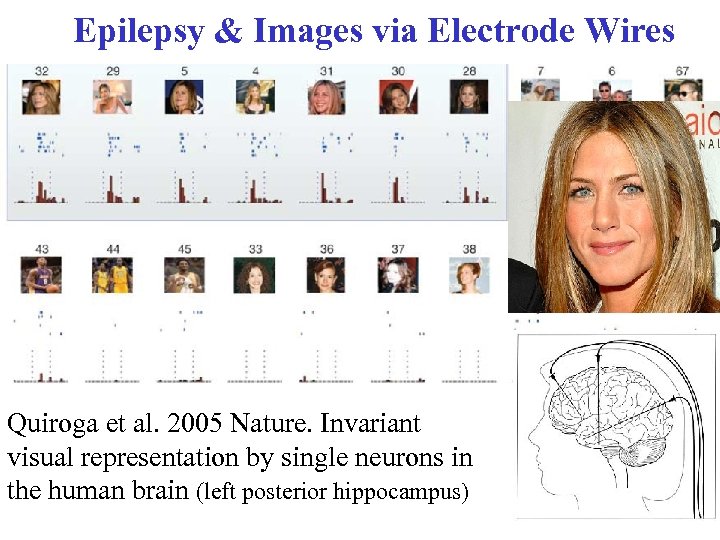 Epilepsy & Images via Electrode Wires Quiroga et al. 2005 Nature. Invariant visual representation by single neurons in the human brain (left posterior hippocampus) 18
Epilepsy & Images via Electrode Wires Quiroga et al. 2005 Nature. Invariant visual representation by single neurons in the human brain (left posterior hippocampus) 18
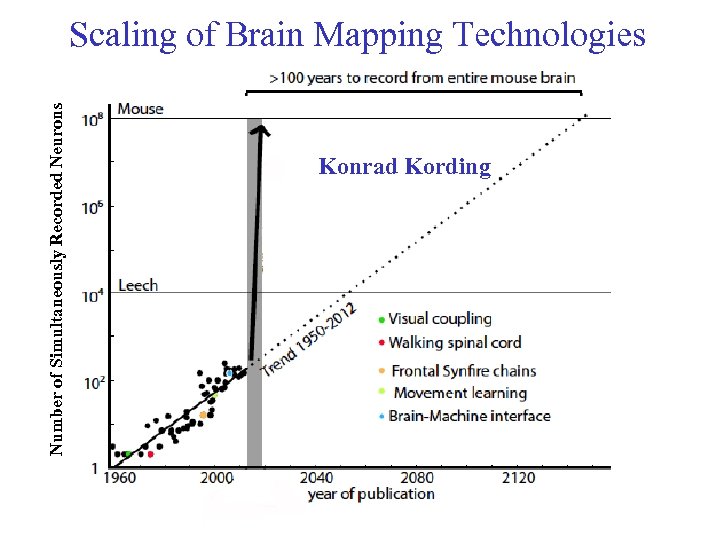 Number of Simultaneously Recorded Neurons Scaling of Brain Mapping Technologies Konrad Kording
Number of Simultaneously Recorded Neurons Scaling of Brain Mapping Technologies Konrad Kording
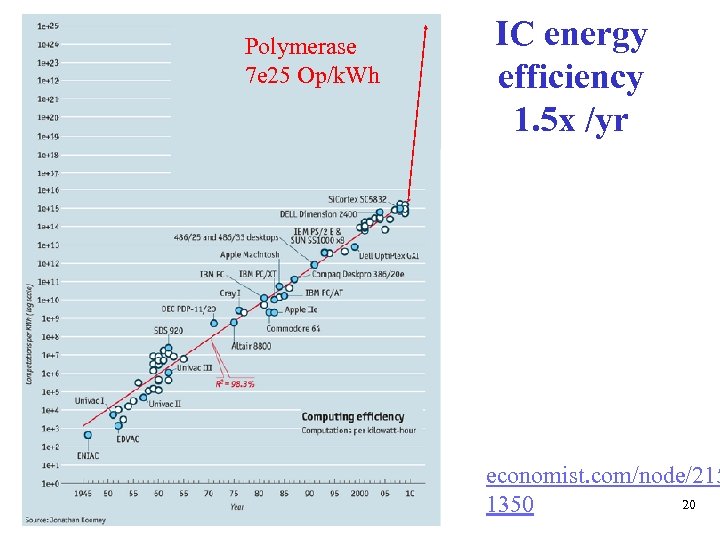 Polymerase 7 e 25 Op/k. Wh IC energy efficiency 1. 5 x /yr economist. com/node/215 20 1350
Polymerase 7 e 25 Op/k. Wh IC energy efficiency 1. 5 x /yr economist. com/node/215 20 1350
 Ions to DNA Light to DNA ATP to DNA Pol
Ions to DNA Light to DNA ATP to DNA Pol
 Ions to DNA Zamft, Marblestone et al. PLo. S One 2012 DNA Pol Dpo 4 Pol
Ions to DNA Zamft, Marblestone et al. PLo. S One 2012 DNA Pol Dpo 4 Pol
 .
.
 .
.
 Brain Activity Map I/O Why? Blindness, deafness, stroke, traumatic brain injuries, spinal cord injuries, Parkinson’s, chronic pain, depression, locked-in syndrome, dystonia, essential tremor, epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseases. Alivisatos, Chun, Church, Donoghue, Greenspan, Roukes, Yuste; The Brain Activity Map Project and the Challenge of Functional Connectomics. Neuron 2012 25
Brain Activity Map I/O Why? Blindness, deafness, stroke, traumatic brain injuries, spinal cord injuries, Parkinson’s, chronic pain, depression, locked-in syndrome, dystonia, essential tremor, epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseases. Alivisatos, Chun, Church, Donoghue, Greenspan, Roukes, Yuste; The Brain Activity Map Project and the Challenge of Functional Connectomics. Neuron 2012 25
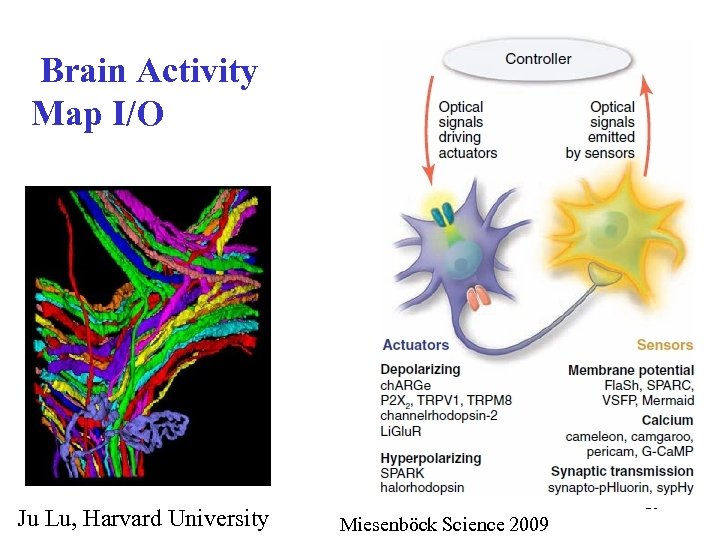 Brain Activity Map I/O Ju Lu, Harvard University 26 Miesenböck Science 2009
Brain Activity Map I/O Ju Lu, Harvard University 26 Miesenböck Science 2009
 Wireless molecular I/O. 100 M Neural cells 27
Wireless molecular I/O. 100 M Neural cells 27
 Next-generation Digital Information Storage in DNA 1. 2. 3. 4. Read/write DNA 8 -fold/yr Fluorescent In Situ Sequencing (FISSeq) Nanorobots & DNA data archiving Brain Activity Map I/O: Polymerase Biologically Inspired Engineering
Next-generation Digital Information Storage in DNA 1. 2. 3. 4. Read/write DNA 8 -fold/yr Fluorescent In Situ Sequencing (FISSeq) Nanorobots & DNA data archiving Brain Activity Map I/O: Polymerase Biologically Inspired Engineering
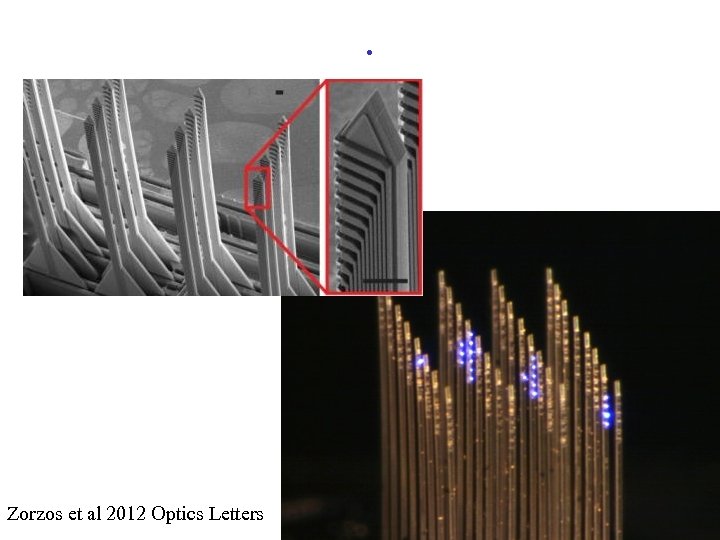 . Zorzos et al 2012 Optics Letters
. Zorzos et al 2012 Optics Letters
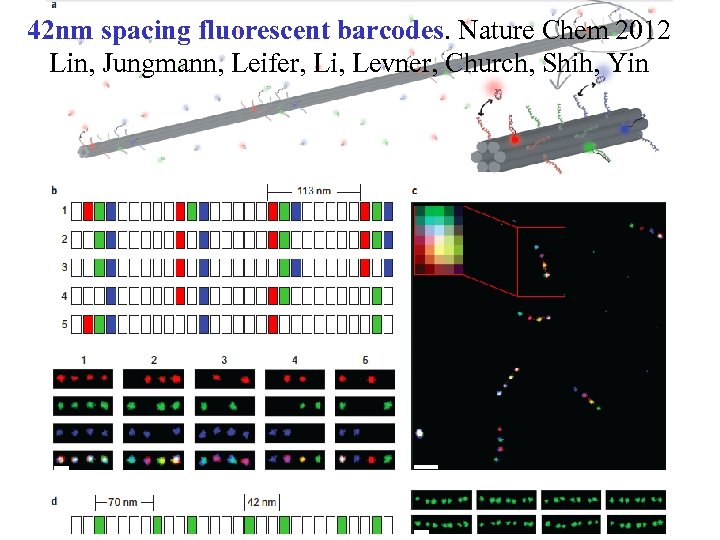 42 nm spacing fluorescent barcodes. Nature Chem 2012 Lin, Jungmann, Leifer, Li, Levner, Church, Shih, Yin
42 nm spacing fluorescent barcodes. Nature Chem 2012 Lin, Jungmann, Leifer, Li, Levner, Church, Shih, Yin
 Fluorescent In situ Sequencing FISSEQ RNA & DNA Jay Lee Evan Daugharthy Reza Kalhor Jonathan Scheiman Michael Sismour Joyce Yang John Aach Kun Zhang Yoav Mayshar Polonator & Advanced Technology Team: Nicholas Conway Daniel Levner Chao Li Richard Terry Brian Turczyk Frederick Vigneault
Fluorescent In situ Sequencing FISSEQ RNA & DNA Jay Lee Evan Daugharthy Reza Kalhor Jonathan Scheiman Michael Sismour Joyce Yang John Aach Kun Zhang Yoav Mayshar Polonator & Advanced Technology Team: Nicholas Conway Daniel Levner Chao Li Richard Terry Brian Turczyk Frederick Vigneault
 Generic Health Advice • Exercise • Drink your milk • Eat your grains • & beans • & iron • & meat • Get more rest
Generic Health Advice • Exercise • Drink your milk • Eat your grains • & beans • & iron • & meat • Get more rest
 UNLESS … • Exercise • Drink your milk • Eat your grains • & beans • & iron • & meat • Get more rest HCM (cardiac arrest) MCM 6 (gastric distress) HLA-DQ 2 (diarrhoea) G 6 PD (red cell lysis) HFE (Liver damage) LDLR (clogged arteries) HLA-DR 2 (excessive sleep)
UNLESS … • Exercise • Drink your milk • Eat your grains • & beans • & iron • & meat • Get more rest HCM (cardiac arrest) MCM 6 (gastric distress) HLA-DQ 2 (diarrhoea) G 6 PD (red cell lysis) HFE (Liver damage) LDLR (clogged arteries) HLA-DR 2 (excessive sleep)
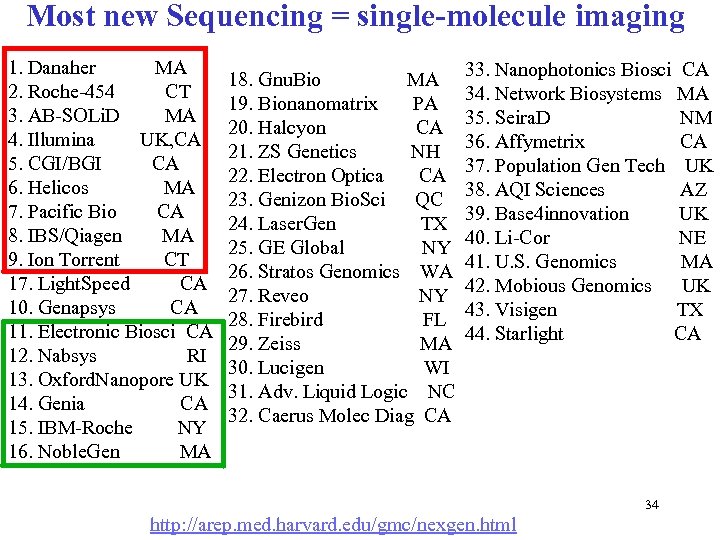 Most new Sequencing = single-molecule imaging 1. Danaher MA 2. Roche-454 CT 3. AB-SOLi. D MA 4. Illumina UK, CA 5. CGI/BGI CA 6. Helicos MA 7. Pacific Bio CA 8. IBS/Qiagen MA 9. Ion Torrent CT 17. Light. Speed CA 10. Genapsys CA 11. Electronic Biosci CA 12. Nabsys RI 13. Oxford. Nanopore UK 14. Genia CA 15. IBM-Roche NY 16. Noble. Gen MA 18. Gnu. Bio MA 19. Bionanomatrix PA 20. Halcyon CA 21. ZS Genetics NH 22. Electron Optica CA 23. Genizon Bio. Sci QC 24. Laser. Gen TX 25. GE Global NY 26. Stratos Genomics WA 27. Reveo NY 28. Firebird FL 29. Zeiss MA 30. Lucigen WI 31. Adv. Liquid Logic NC 32. Caerus Molec Diag CA 33. Nanophotonics Biosci CA 34. Network Biosystems MA 35. Seira. D NM 36. Affymetrix CA 37. Population Gen Tech UK 38. AQI Sciences AZ 39. Base 4 innovation UK 40. Li-Cor NE 41. U. S. Genomics MA 42. Mobious Genomics UK 43. Visigen TX 44. Starlight CA 34 http: //arep. med. harvard. edu/gmc/nexgen. html
Most new Sequencing = single-molecule imaging 1. Danaher MA 2. Roche-454 CT 3. AB-SOLi. D MA 4. Illumina UK, CA 5. CGI/BGI CA 6. Helicos MA 7. Pacific Bio CA 8. IBS/Qiagen MA 9. Ion Torrent CT 17. Light. Speed CA 10. Genapsys CA 11. Electronic Biosci CA 12. Nabsys RI 13. Oxford. Nanopore UK 14. Genia CA 15. IBM-Roche NY 16. Noble. Gen MA 18. Gnu. Bio MA 19. Bionanomatrix PA 20. Halcyon CA 21. ZS Genetics NH 22. Electron Optica CA 23. Genizon Bio. Sci QC 24. Laser. Gen TX 25. GE Global NY 26. Stratos Genomics WA 27. Reveo NY 28. Firebird FL 29. Zeiss MA 30. Lucigen WI 31. Adv. Liquid Logic NC 32. Caerus Molec Diag CA 33. Nanophotonics Biosci CA 34. Network Biosystems MA 35. Seira. D NM 36. Affymetrix CA 37. Population Gen Tech UK 38. AQI Sciences AZ 39. Base 4 innovation UK 40. Li-Cor NE 41. U. S. Genomics MA 42. Mobious Genomics UK 43. Visigen TX 44. Starlight CA 34 http: //arep. med. harvard. edu/gmc/nexgen. html
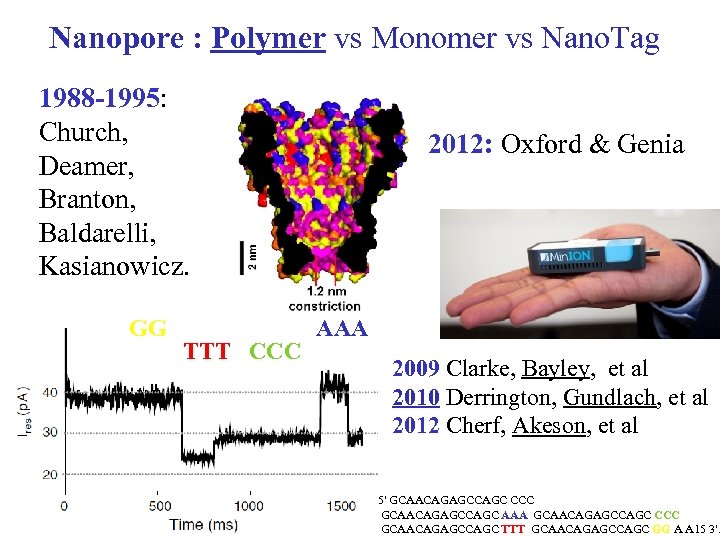 Nanopore : Polymer vs Monomer vs Nano. Tag 1988 -1995: Church, Deamer, Branton, Baldarelli, Kasianowicz. GG TTT CCC 2012: Oxford & Genia AAA 2009 Clarke, Bayley, et al 2010 Derrington, Gundlach, et al 2012 Cherf, Akeson, et al 5′ GCAACAGAGCCAGC CCC 35 GCAACAGAGCCAGC AAA GCAACAGAGCCAGC CCC GCAACAGAGCCAGC TTT GCAACAGAGCCAGC GG A A 15 3′.
Nanopore : Polymer vs Monomer vs Nano. Tag 1988 -1995: Church, Deamer, Branton, Baldarelli, Kasianowicz. GG TTT CCC 2012: Oxford & Genia AAA 2009 Clarke, Bayley, et al 2010 Derrington, Gundlach, et al 2012 Cherf, Akeson, et al 5′ GCAACAGAGCCAGC CCC 35 GCAACAGAGCCAGC AAA GCAACAGAGCCAGC CCC GCAACAGAGCCAGC TTT GCAACAGAGCCAGC GG A A 15 3′.
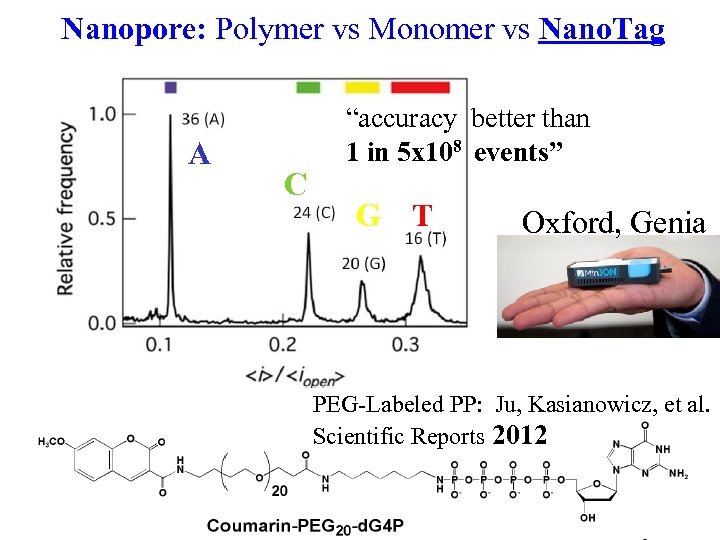 Nanopore: Polymer vs Monomer vs Nano. Tag A C “accuracy better than 1 in 5 x 108 events” G T Oxford, Genia PEG-Labeled PP: Ju, Kasianowicz, et al. Scientific Reports 2012
Nanopore: Polymer vs Monomer vs Nano. Tag A C “accuracy better than 1 in 5 x 108 events” G T Oxford, Genia PEG-Labeled PP: Ju, Kasianowicz, et al. Scientific Reports 2012


