dea1e0f4d3a983e8e8bc572283edc78c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Literacies for Learning in Further Education Research Project From Plumbing to Punctuation: What do we mean by ‘embedded’? North West Sf. L Research Forum Lancaster University 7 June 2006
Literacies for Learning in Further Education Research Project From Plumbing to Punctuation: What do we mean by ‘embedded’? North West Sf. L Research Forum Lancaster University 7 June 2006
 Lf. LFE Research Project www. lancs. ac. uk/lflfe/
Lf. LFE Research Project www. lancs. ac. uk/lflfe/
 Literacies for Learning in FE Project structure 2 universities 4 colleges 16 curriculum areas 32 units 100 students
Literacies for Learning in FE Project structure 2 universities 4 colleges 16 curriculum areas 32 units 100 students
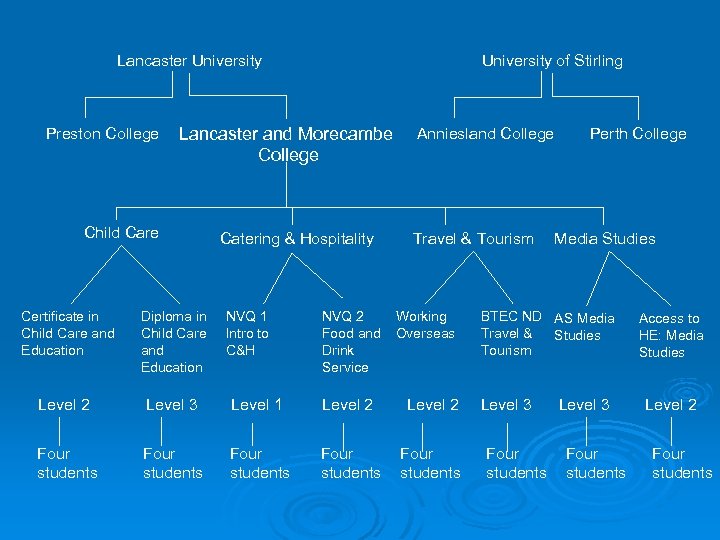 Lancaster University Preston College University of Stirling Lancaster and Morecambe College Child Care Catering & Hospitality NVQ 1 Intro to C&H NVQ 2 Food and Drink Service Anniesland College Travel & Tourism Certificate in Child Care and Education Diploma in Child Care and Education Working Overseas Level 2 Level 3 Level 1 Level 2 Four students Four students Perth College Media Studies BTEC ND AS Media Travel & Studies Tourism Level 3 Four students Access to HE: Media Studies Level 2 Four students
Lancaster University Preston College University of Stirling Lancaster and Morecambe College Child Care Catering & Hospitality NVQ 1 Intro to C&H NVQ 2 Food and Drink Service Anniesland College Travel & Tourism Certificate in Child Care and Education Diploma in Child Care and Education Working Overseas Level 2 Level 3 Level 1 Level 2 Four students Four students Perth College Media Studies BTEC ND AS Media Travel & Studies Tourism Level 3 Four students Access to HE: Media Studies Level 2 Four students
 Categories of literacy practices in learning vocational subjects in Further Education Literacy practices for learning (e. g. reading and making notes from a text book) Ø Literacy practices for assessment (e. g. producing an essay or a report) Ø Evidence-providing literacy practices (e. g. completing a log book or portfolio) Ø Literacy practices relating to the workplace (e. g. writing food orders; reading to children) Ø
Categories of literacy practices in learning vocational subjects in Further Education Literacy practices for learning (e. g. reading and making notes from a text book) Ø Literacy practices for assessment (e. g. producing an essay or a report) Ø Evidence-providing literacy practices (e. g. completing a log book or portfolio) Ø Literacy practices relating to the workplace (e. g. writing food orders; reading to children) Ø
 Literacy practices for learning
Literacy practices for learning
 Literacy practices for assessment
Literacy practices for assessment
 Evidence-providing literacy practices
Evidence-providing literacy practices
 Literacy practices in the workplace
Literacy practices in the workplace
 Literacy practices in the workplace (on placement)
Literacy practices in the workplace (on placement)
 Literacy practices in the workplace (a Real Work Environment)
Literacy practices in the workplace (a Real Work Environment)
 Literacy practices in the workplace (interactive literacies)
Literacy practices in the workplace (interactive literacies)
 Texts in Catering and Hospitality The following 11 slides represent some of the texts with which students interacted during ONE session in the restaurant at Lancaster and Morecambe College. Ø These texts all involved the students reading and/or writing in the course of working in the restaurant. Ø Almost all of these texts are similar to those they would use in a “real” workplace – with some notable exceptions. Ø
Texts in Catering and Hospitality The following 11 slides represent some of the texts with which students interacted during ONE session in the restaurant at Lancaster and Morecambe College. Ø These texts all involved the students reading and/or writing in the course of working in the restaurant. Ø Almost all of these texts are similar to those they would use in a “real” workplace – with some notable exceptions. Ø
 Student’s Powerpoint Presentation
Student’s Powerpoint Presentation
 Stillroom Duties Checklist and Stock Order Book
Stillroom Duties Checklist and Stock Order Book
 Diary page with table plan, and Indemnity Card
Diary page with table plan, and Indemnity Card
 Menus
Menus
 Daily Restaurant List and Bar Till
Daily Restaurant List and Bar Till
 Wine list
Wine list
 Whiteboard in kitchen
Whiteboard in kitchen
 Cash Summary Sheet and Customer Bill
Cash Summary Sheet and Customer Bill
 Customer Comment Card
Customer Comment Card
 Pages from tutor-produced text to supplement log book
Pages from tutor-produced text to supplement log book
 Log book
Log book
 Evidence-providing literacy foregrounded
Evidence-providing literacy foregrounded
 Methods for collecting data pertaining to FE students’ literacy practices outside college include: Ø The ‘clock activity’ to give an overview of students’ activities over a 24 -hour period. Ø Student-taken photographs, representing literacy-related activities during one week. Ø Individual or group interviews leading on from the clock activities and/or the student-taken photographs. Ø Possible observation of, or other data related to, students during an out-of-college activity, e. g. at work, at a club, or at home.
Methods for collecting data pertaining to FE students’ literacy practices outside college include: Ø The ‘clock activity’ to give an overview of students’ activities over a 24 -hour period. Ø Student-taken photographs, representing literacy-related activities during one week. Ø Individual or group interviews leading on from the clock activities and/or the student-taken photographs. Ø Possible observation of, or other data related to, students during an out-of-college activity, e. g. at work, at a club, or at home.

 Literacies in everyday life
Literacies in everyday life
 Paul
Paul
 Paul’s Home Literacies Works as a nightclub DJ: ‘my girlfriend bought me some decks … she bought me two or three records a week and then I started collecting them’ ‘I do it on my mate’s computer, go on certain websites… He gets us on, I just pick my vinyl’ Calculates how much entrance fees to charge: ‘I got my mum to do that because I can’t do maths…’ Designs flyers to advertise his DJ functions: ‘I got a lad at the University at Preston to do it. ’ Owns property: ‘the house that I am in at the moment with my dad, I own I think it’s a quarter of it, I gave him a lump sum towards that. ’ ‘we’ll buy that, do that up and then hopefully sell it. ’ Does things with his partner’s children: ‘Yeah I do a lot of reading with the kids. ’ ‘We got a cornflake box, cut it out and made wheels and that … from a plan …she had to write it in and then I had to write underneath…’
Paul’s Home Literacies Works as a nightclub DJ: ‘my girlfriend bought me some decks … she bought me two or three records a week and then I started collecting them’ ‘I do it on my mate’s computer, go on certain websites… He gets us on, I just pick my vinyl’ Calculates how much entrance fees to charge: ‘I got my mum to do that because I can’t do maths…’ Designs flyers to advertise his DJ functions: ‘I got a lad at the University at Preston to do it. ’ Owns property: ‘the house that I am in at the moment with my dad, I own I think it’s a quarter of it, I gave him a lump sum towards that. ’ ‘we’ll buy that, do that up and then hopefully sell it. ’ Does things with his partner’s children: ‘Yeah I do a lot of reading with the kids. ’ ‘We got a cornflake box, cut it out and made wheels and that … from a plan …she had to write it in and then I had to write underneath…’
 Increasing resonance between home and pedagogic literacy practices To be more congenial to the “Pauls” who are trying to obtain a qualification: Ø Resonance may be encouraged by offering 1: 1 help with portfolio building or even introducing ‘study buddies’; Ø The requirements for ‘demonstrating competence’ might be brought more in line with the literacy demands of the industry.
Increasing resonance between home and pedagogic literacy practices To be more congenial to the “Pauls” who are trying to obtain a qualification: Ø Resonance may be encouraged by offering 1: 1 help with portfolio building or even introducing ‘study buddies’; Ø The requirements for ‘demonstrating competence’ might be brought more in line with the literacy demands of the industry.
 Comparison of workplace, home and pedagogic literacy practices Ø Ø Ø Ø Workplace and home literacy practices Mostly multi-modal Mostly multi-media Shared, interactive, participatory Non-linear Agentic Purposeful Clear audience Generative Ø Ø Ø Ø Pedagogic literacy practices Mostly mono-modal Mostly paper-based Individual, non-interactive, solitary Linear Non-Agentic Ambiguous purpose Ambiguous audience Information provided
Comparison of workplace, home and pedagogic literacy practices Ø Ø Ø Ø Workplace and home literacy practices Mostly multi-modal Mostly multi-media Shared, interactive, participatory Non-linear Agentic Purposeful Clear audience Generative Ø Ø Ø Ø Pedagogic literacy practices Mostly mono-modal Mostly paper-based Individual, non-interactive, solitary Linear Non-Agentic Ambiguous purpose Ambiguous audience Information provided
 Differences and overlaps among literacy practices
Differences and overlaps among literacy practices


