a9f7bcb8050e2ac73cb60367ef2ceab7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 good style • Write each statement on a new line. • Add plenty of comments. There are three styles of comments in a PHP program – // the rest of the line is a comment – # the rest of a line is a comment – /* this is a comment */ • Only last style can be used over several lines. • Do you recognize two of the commenting styles?
good style • Write each statement on a new line. • Add plenty of comments. There are three styles of comments in a PHP program – // the rest of the line is a comment – # the rest of a line is a comment – /* this is a comment */ • Only last style can be used over several lines. • Do you recognize two of the commenting styles?
$greeting
 Forms • Forms are parts of an HTML document that users can fill in. They may include buttons, checkboxes, text areas, file selections. • The thing that users fill in are called the controls of the form. • Some controls are hidden. • Controls are submitted to PHP in the form of variables. Each control in the HTML form becomes a variable in PHP. This is seen later.
Forms • Forms are parts of an HTML document that users can fill in. They may include buttons, checkboxes, text areas, file selections. • The thing that users fill in are called the controls of the form. • Some controls are hidden. • Controls are submitted to PHP in the form of variables. Each control in the HTML form becomes a variable in PHP. This is seen later.
 forms examples • Here is an example in http: //wotan. liu. edu/home/krichel/coures/lis 651/ex amples/forms • Elements used in forms use a special attribute group that I will call the “form attributes”. I will discuss them now.
forms examples • Here is an example in http: //wotan. liu. edu/home/krichel/coures/lis 651/ex amples/forms • Elements used in forms use a special attribute group that I will call the “form attributes”. I will discuss them now.
 form attribute: tabindex= • Stupid users use the mouse to fill in form. Smart users use the tab character on the keyboard. It is much quicker. • if you set the tabindex= on a in input, you can set the order. The value of the attribute is a number between 0 and 32767. The input with a lower number will be dealt with before the one with a higher number.
form attribute: tabindex= • Stupid users use the mouse to fill in form. Smart users use the tab character on the keyboard. It is much quicker. • if you set the tabindex= on a in input, you can set the order. The value of the attribute is a number between 0 and 32767. The input with a lower number will be dealt with before the one with a higher number.
 form attribute: readonly= • If you set readonly="readonly" the control can only be read but not set. This means – It can receive focus but cannot be modified by the user. – It is included in tabbing navigation. – It is transmitted to the server for processing. • readonly= is not set by default.
form attribute: readonly= • If you set readonly="readonly" the control can only be read but not set. This means – It can receive focus but cannot be modified by the user. – It is included in tabbing navigation. – It is transmitted to the server for processing. • readonly= is not set by default.
 form attribute: disabled= • If you set disabled="disabled" the control can only be read but not set. This means – it can not receive focus and can not be modified – it is excluded in tabbing – it is not transmitted to the server for processing. • disabled= in not set by default.
form attribute: disabled= • If you set disabled="disabled" the control can only be read but not set. This means – it can not receive focus and can not be modified – it is excluded in tabbing – it is not transmitted to the server for processing. • disabled= in not set by default.

 the action= attribute of
the action= attribute of
 method= of
method= of
 method="get" • If you use GET, the form data is transmitted by appending it to the URL of the script. Google's Web search does it that way, for example. • There is a standard way to write the data in the URL knows as Common Gateway Interface, CGI. It is of no further interest to us. • Advantage: you can bookmark the form. • Problem: there is a limit of 1024 chars for the URL, therefore only a limited information can be transmitted in this way.
method="get" • If you use GET, the form data is transmitted by appending it to the URL of the script. Google's Web search does it that way, for example. • There is a standard way to write the data in the URL knows as Common Gateway Interface, CGI. It is of no further interest to us. • Advantage: you can bookmark the form. • Problem: there is a limit of 1024 chars for the URL, therefore only a limited information can be transmitted in this way.
 method="post" • If you use post, the user agent sends the form as a POST message to the server. • The data is sent in the body of the http request. • Thus it can be as long as you want. • If you use POST you can set the MIME type of the data with a special attribute enctype=
method="post" • If you use post, the user agent sends the form as a POST message to the server. • The data is sent in the body of the http request. • Thus it can be as long as you want. • If you use POST you can set the MIME type of the data with a special attribute enctype=
 more attributes to
more attributes to
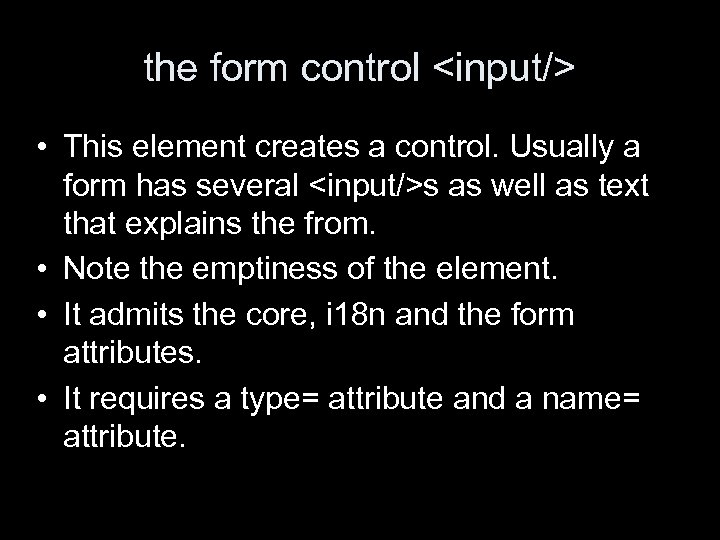 the form control • This element creates a control. Usually a form has several s as well as text that explains the from. • Note the emptiness of the element. • It admits the core, i 18 n and the form attributes. • It requires a type= attribute and a name= attribute.
the form control • This element creates a control. Usually a form has several s as well as text that explains the from. • Note the emptiness of the element. • It admits the core, i 18 n and the form attributes. • It requires a type= attribute and a name= attribute.
 the type= attribute of • This attribute can only take the following values – – – – – ‘text’ enter text ‘password’ enter text, but don't echo on screen ‘checkbox’ enter checks on boxes ‘radio’ check one select ‘submit’ press to submit form ‘reset’ reset form ‘file’ upload file (can only be done with POST) ‘hidden’ hidden form data, not shown ‘image’ image map submission, not covered further ‘button’ a button
the type= attribute of • This attribute can only take the following values – – – – – ‘text’ enter text ‘password’ enter text, but don't echo on screen ‘checkbox’ enter checks on boxes ‘radio’ check one select ‘submit’ press to submit form ‘reset’ reset form ‘file’ upload file (can only be done with POST) ‘hidden’ hidden form data, not shown ‘image’ image map submission, not covered further ‘button’ a button
 the name= attribute of • This give a name to the control that the users are setting. • The script that is found by the action= attribute will identify the controls by name. Therefore every control should have a different name.
the name= attribute of • This give a name to the control that the users are setting. • The script that is found by the action= attribute will identify the controls by name. Therefore every control should have a different name.
 control name and PHP variable • When the form is passed to the PHP script named with the action= attribute of the form, the controls are accessible as PHP variables. • If name is the name of the control, and if the method is POST, the control is read as the variable $_POST['name']. • If name is the name of the control, and if the method is GET, the control is read as the variable $_GET['name'].
control name and PHP variable • When the form is passed to the PHP script named with the action= attribute of the form, the controls are accessible as PHP variables. • If name is the name of the control, and if the method is POST, the control is read as the variable $_POST['name']. • If name is the name of the control, and if the method is GET, the control is read as the variable $_GET['name'].
 the size= attribute of • It lets you set the size of the input field. • Note that the size of the field may not limit the input to that size. • When the type is ‘text’ or ‘password’ the value you give to this field is the number of characters. • Otherwise it is the number of pixels.
the size= attribute of • It lets you set the size of the input field. • Note that the size of the field may not limit the input to that size. • When the type is ‘text’ or ‘password’ the value you give to this field is the number of characters. • Otherwise it is the number of pixels.
 the maxlength= attribute of • This sets the maximum length on the value. • Note that this is different from the size of the input field because there is scrolling. • If you don't specify a maximum length there is no limit. • But it is good security to have a limit.
the maxlength= attribute of • This sets the maximum length on the value. • Note that this is different from the size of the input field because there is scrolling. • If you don't specify a maximum length there is no limit. • But it is good security to have a limit.
 the value= attribute of • This gives the initial value of the . • The initial value is shown to the user. • value= is optional but should be given for the radio and checkbox type.
the value= attribute of • This gives the initial value of the . • The initial value is shown to the user. • value= is optional but should be given for the radio and checkbox type.
 the checked= attributes of • When the input is of type 'radio', setting the checked= attribute to any value will tell the browser what button is initially set. Of course there can only be one of them. • When the input is of type 'checkbox', setting the checked= attribute to any value will make sure it is checked initially.
the checked= attributes of • When the input is of type 'radio', setting the checked= attribute to any value will tell the browser what button is initially set. Of course there can only be one of them. • When the input is of type 'checkbox', setting the checked= attribute to any value will make sure it is checked initially.
 the src= attribute of • When the input is of type 'image' the src= attribute gives the URL of the image. • This is for input using image maps.
the src= attribute of • When the input is of type 'image' the src= attribute gives the URL of the image. • This is for input using image maps.
your last name:" src="https://present5.com/presentation/a9f7bcb8050e2ac73cb60367ef2ceab7/image-38.jpg" alt="example • HTML file greet. html has
• PHP file greet. php has in addition to the usual HTML stuff. the push button
the push button
 creating menus • This is done with
creating menus • This is done with
 attributes to
attributes to
 selectable choice:
selectable choice:
 value= attribute to
value= attribute to
 label= attribute to
label= attribute to

 the element • This creates a text area where you can put a large chunk of text. • It takes some attributes – name= sets the name of the control that is set. – cols= sets the number of columns in the text area. – rows= sets the number of rows in the text area. • also admits the i 18 n, core and form attributes.
the element • This creates a text area where you can put a large chunk of text. • It takes some attributes – name= sets the name of the control that is set. – cols= sets the number of columns in the text area. – rows= sets the number of rows in the text area. • also admits the i 18 n, core and form attributes.

 summary • Forms deliver data to the server. The server can then process the data and deliver a response. • Active effects can also be done client-side. This is done using the
summary • Forms deliver data to the server. The server can then process the data and deliver a response. • Active effects can also be done client-side. This is done using the




















![saar_bier. php, part 1 <? php $gross_pils=$_POST['gw_pils']; $p_gross_pils=$_POST['p_gw_pils']; $t_gross_pils=$p_gross_pils*$gross_pils; $gross_expo=$_POST['gw_expo']; $p_gross_expo=$_POST['p_gw_expo']; $t_gross_expo=$p_gross_expo*$gross_expo; $bruch_land=$_POST['bruch_land']; $p_bruch_land=$_POST['p_bruch_land']; saar_bier. php, part 1 <? php $gross_pils=$_POST['gw_pils']; $p_gross_pils=$_POST['p_gw_pils']; $t_gross_pils=$p_gross_pils*$gross_pils; $gross_expo=$_POST['gw_expo']; $p_gross_expo=$_POST['p_gw_expo']; $t_gross_expo=$p_gross_expo*$gross_expo; $bruch_land=$_POST['bruch_land']; $p_bruch_land=$_POST['p_bruch_land'];](https://present5.com/presentation/a9f7bcb8050e2ac73cb60367ef2ceab7/image-55.jpg)

