f430da0ba023a6c835dc923bbcb25c8d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53

LIPIDS An over view of Normal and Abnormal Lipids Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 1

All are One • This not about the GOD • There is only one disease – Over nutrition • Its faces are many such as – – – Over weight / Obesity Diabetes mellitus, IR, Syndrome X Atherosclerosis – HT- CHD – CVD – RVD – PVD Hyper lipidemias – endothelial dysfunction Wear and tear of joints …. So on • What are we to do ? - Avoid over-indulgence Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 2

How much is much ? BMI = Weight in kgs Height 2 in mts 70 BMI = = 25. 71 1. 65 x 1. 65 Underweight < 20 Over weight > 25 to 30 Normal 20 to 25 Obesity >30 Waist / Hip ratio = 35” /38” = 0. 92 Normal for Males < 0. 90, Females <0. 80 Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 3
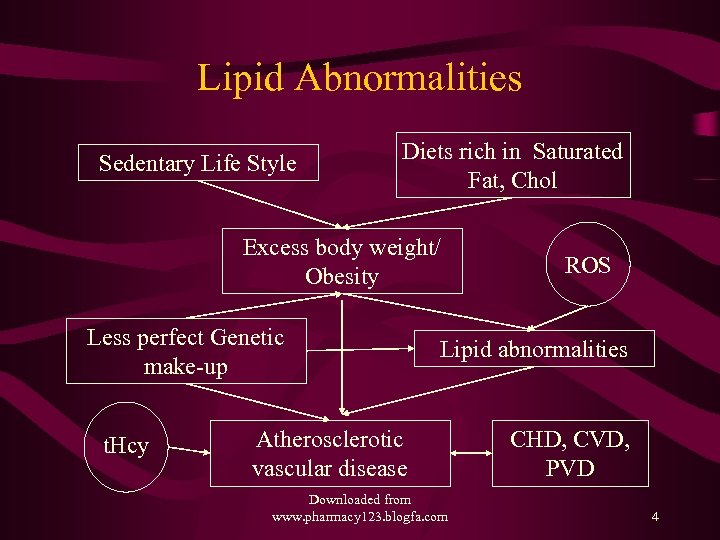
Lipid Abnormalities Sedentary Life Style Diets rich in Saturated Fat, Chol Excess body weight/ Obesity Less perfect Genetic make-up t. Hcy ROS Lipid abnormalities Atherosclerotic vascular disease Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com CHD, CVD, PVD 4

Why are lipids important ? • Complications of Atherosclerosis are – CHD (Coronary Heart Disease) – CVD (Cerebro Vascular Disease) – RVD (Reno Vascular Disease) – PVD (Peripheral Vascular Disease) – These cause > 50% of all deaths - mortality – The Angina, MI, - TIA, Stroke, - HT, RF, - IC, Gangrene all reduce the Quality of Life morbidity Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 5
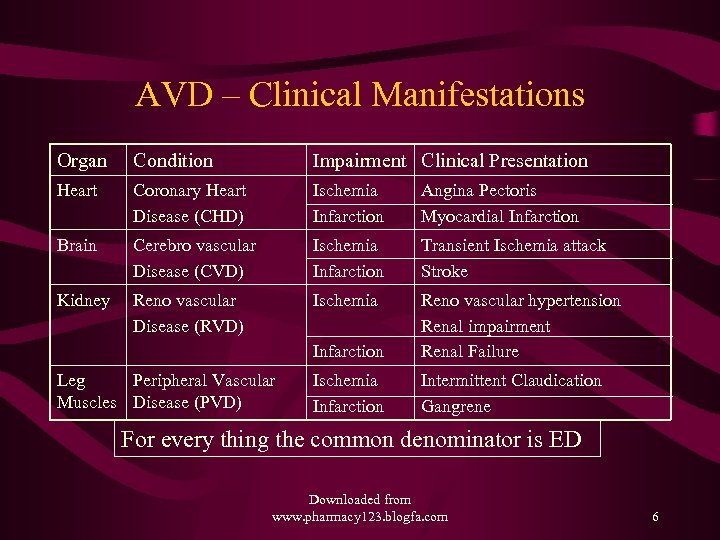
AVD – Clinical Manifestations Organ Condition Impairment Clinical Presentation Heart Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Ischemia Infarction Angina Pectoris Myocardial Infarction Brain Cerebro vascular Disease (CVD) Ischemia Infarction Transient Ischemia attack Stroke Kidney Reno vascular Disease (RVD) Ischemia Infarction Reno vascular hypertension Renal impairment Renal Failure Ischemia Infarction Intermittent Claudication Gangrene Leg Peripheral Vascular Muscles Disease (PVD) For every thing the common denominator is ED Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 6
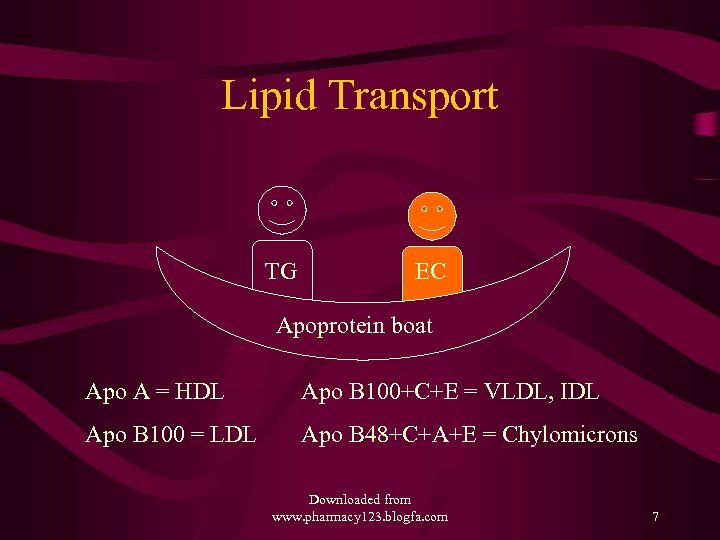
Lipid Transport TG EC Apoprotein boat Apo A = HDL Apo B 100+C+E = VLDL, IDL Apo B 100 = LDL Apo B 48+C+A+E = Chylomicrons Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 7

Lipids and Lipoproteins • Lipids or Fats in our body are mainly • The non polar, hydrophobic, inner core of – Triglycerides (TG) – Cholesterol Esters (EC) • The polar, surface monolayer – Phospholipids (PL) and Free Cholesterol (C) • Apoproteins are the outer coat -amphiphatic Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 8
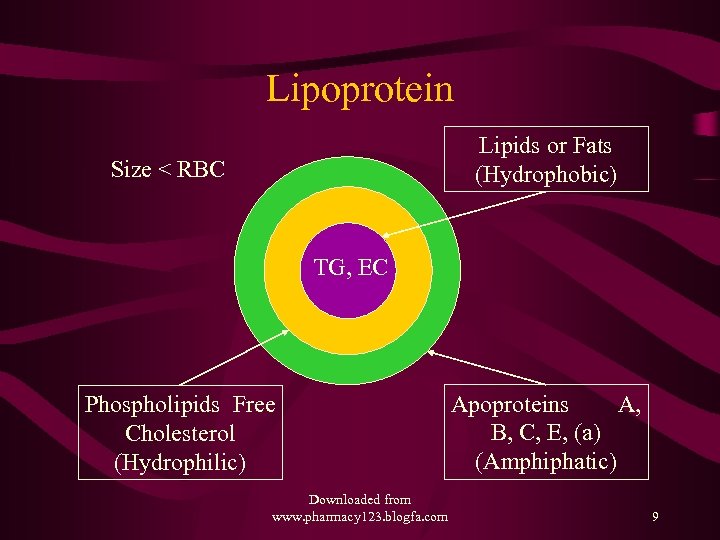
Lipoprotein Lipids or Fats (Hydrophobic) Size < RBC TG, EC Phospholipids Free Cholesterol (Hydrophilic) Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com Apoproteins A, B, C, E, (a) (Amphiphatic) 9
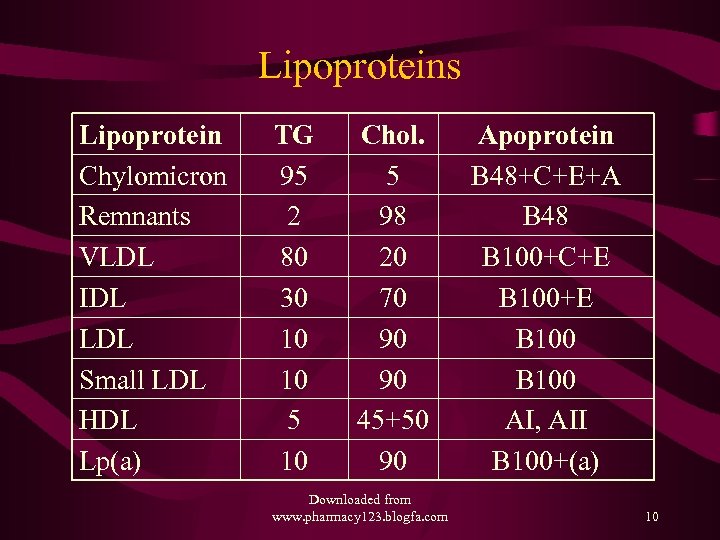
Lipoproteins Lipoprotein Chylomicron Remnants VLDL IDL LDL Small LDL HDL Lp(a) TG 95 2 80 30 10 10 5 10 Chol. 5 98 20 70 90 90 45+50 90 Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com Apoprotein B 48+C+E+A B 48 B 100+C+E B 100 AI, AII B 100+(a) 10
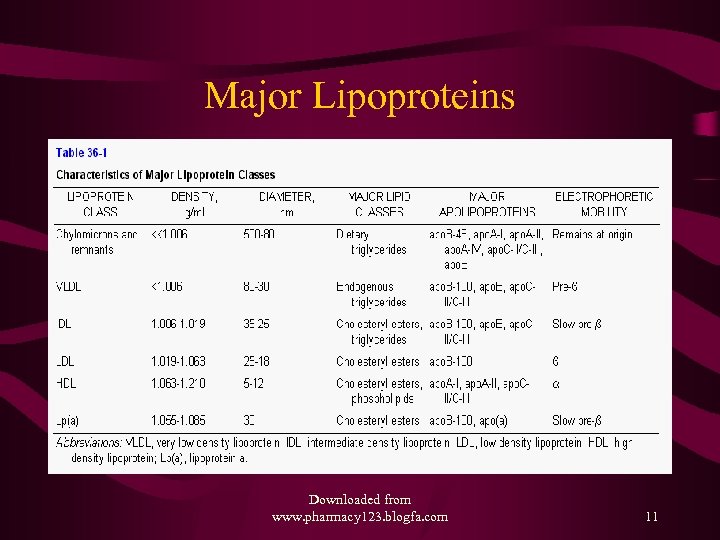
Major Lipoproteins Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 11

Lipoprotein Metabolism • Exogenous – Transport of dietary fats – TG to Adipose tissue, Muscle and Cholesterol to Liver as Chylomicrons • Endogenous – Transport of TG and CE from Liver to the peripheral tissues like muscle, adipose tissues and vascular endothelium via VLDL, IDL, LDL • Reverse Cholesterol transport –HDL Path – from the vessels and periphery to liver Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 12

Enzymes 1. Lipo Protein Lipase (LPL) – Synthesized in Adipose and Muscle tissues – Essential for TG metabol – FFA and Glycerol – Insulin activates LPL, - CII apo binds to LPL 2. Hepatic TG Lipase (HGTL) – Removes TG from VLDL, IDL LDL – Clears the Cholesterol remnants into liver – Converts HDL 2 to HDL 3 in the liver Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 13

Enzymes contd. . 3. Lecithin Chol Acyl Transferase (LCAT) • • Secreted into plasma by the liver Binds to HDL and transfers linoleate from lecithin to free Chol and converts it into EC- 4. Cholesterol Ester Transfer Protein (CETP) – Secreted into plasma from liver – Transfers EC from HDL to VLDL – Converts LDL to small Dense LDL Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 14
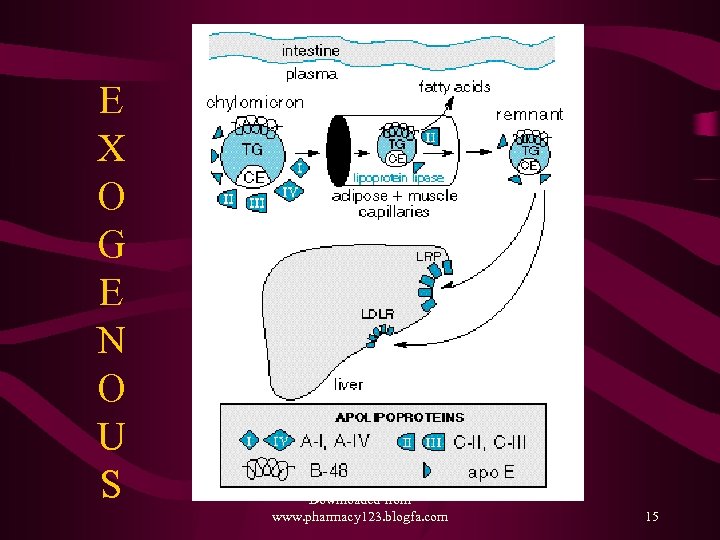
E X O G E N O U S Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 15
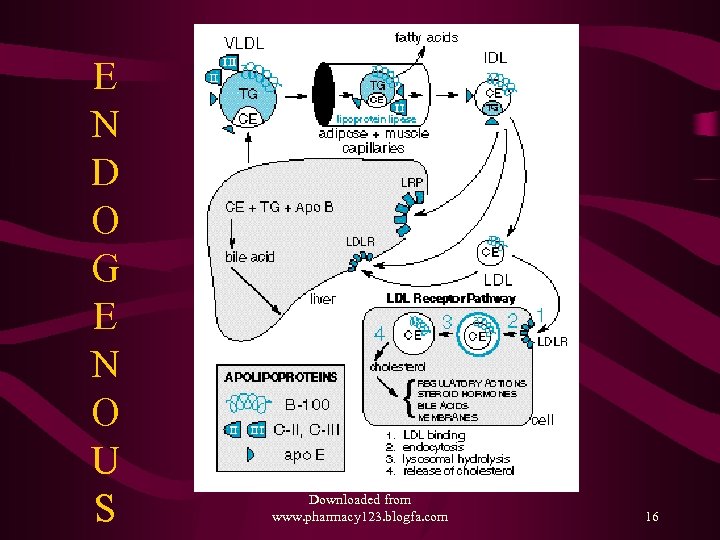
E N D O G E N O U S Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 16
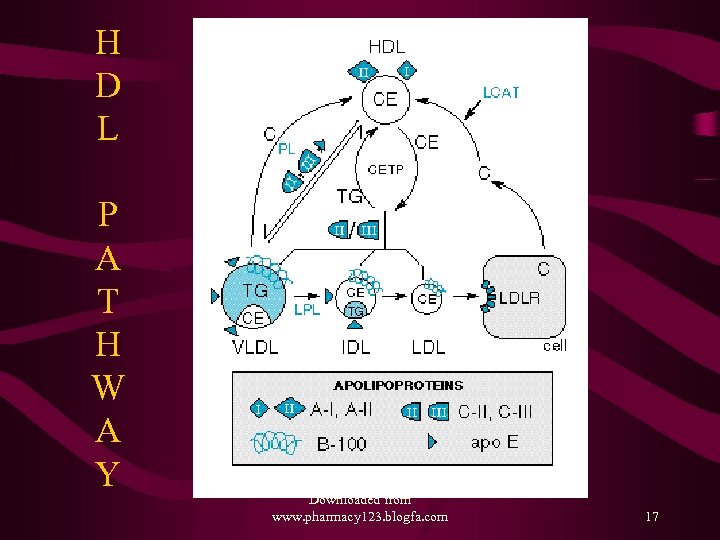
H D L P A T H W A Y Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 17
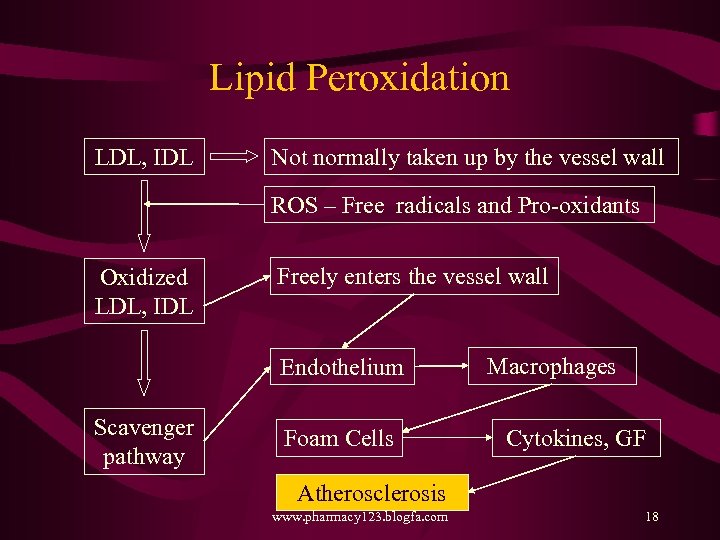
Lipid Peroxidation LDL, IDL Not normally taken up by the vessel wall ROS – Free radicals and Pro-oxidants Oxidized LDL, IDL Freely enters the vessel wall Endothelium Scavenger pathway Foam Cells Macrophages Cytokines, GF Atherosclerosis Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 18

Synthesis of VLDL (TG) • In the liver VLDL is synthesized – – – – It is dependent on substrate flow Obesity Excessive consumption of simple sugars Increased intake of saturated fats Inactivity Alcoholism Insulin resistance Low HDL Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 19
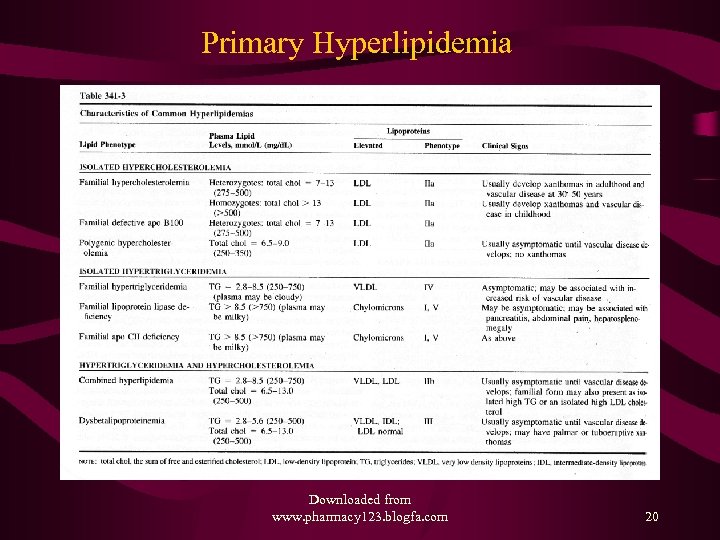
Primary Hyperlipidemia Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 20

Secondary Hyperlipidemia TG EC Obesity Nephrotic syndrome. Diabetes Hypothyroidism Uraemia Obstr. liver disease Alcoholism Anorexia nervosa Oral contraceptives Acute Int. Porphyria Beta blockers Progestogens Pregnancy Thiazides Steroids, Thiazides Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 21

Clinical Action • Presence of secondary causes of Hyperlipidemia – Order for full lipid profile (LP) – HT also • Presence of Hyperlipidemia – increased TG or EC – Investigate for all secondary causes • For all above 20 years once in every 5 years – LP • For those above 45 yrs – once in 2 years • For those with already known lipid abnormality follow-up every 3 -6 months Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 22
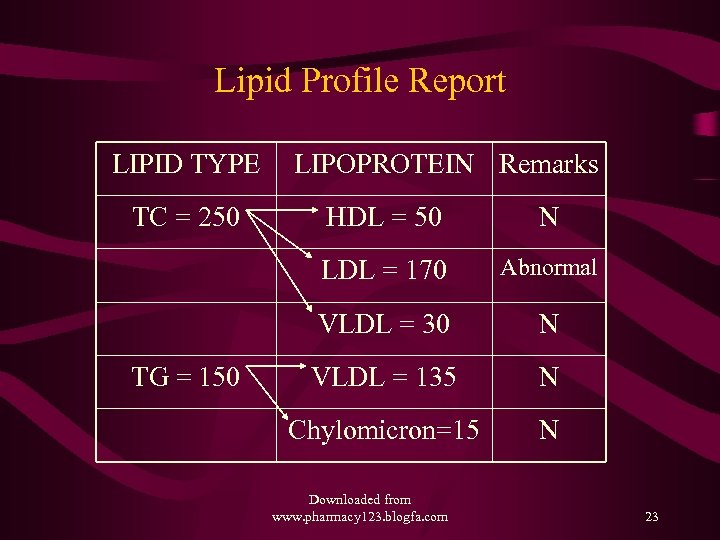
Lipid Profile Report LIPID TYPE TC = 250 LIPOPROTEIN Remarks N LDL = 170 Abnormal VLDL = 30 TG = 150 HDL = 50 N VLDL = 135 N Chylomicron=15 N Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 23
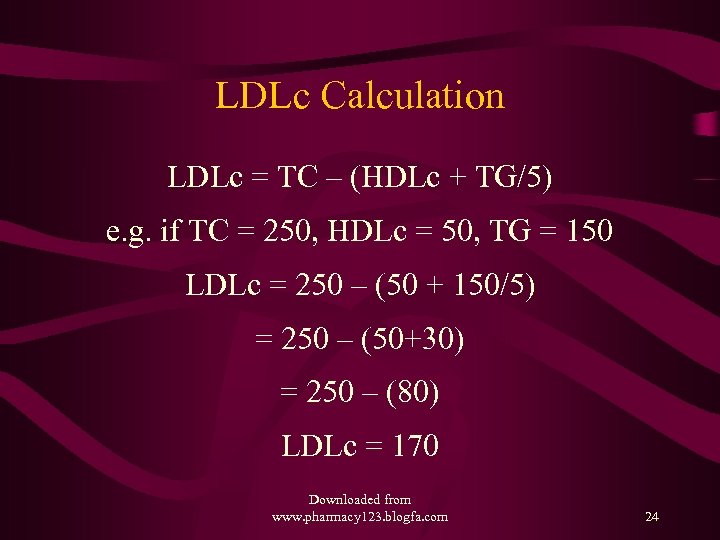
LDLc Calculation LDLc = TC – (HDLc + TG/5) e. g. if TC = 250, HDLc = 50, TG = 150 LDLc = 250 – (50 + 150/5) = 250 – (50+30) = 250 – (80) LDLc = 170 Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 24

Risk Factors for CHD Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 25

Treatment Plan - LDLc Clinical Status Diet Drugs Goal No CHD < 2 RF >160 >190 <160 No CHD 2 or more RF >130 >160 <130 CHD Present >100 >130 <100 Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 26
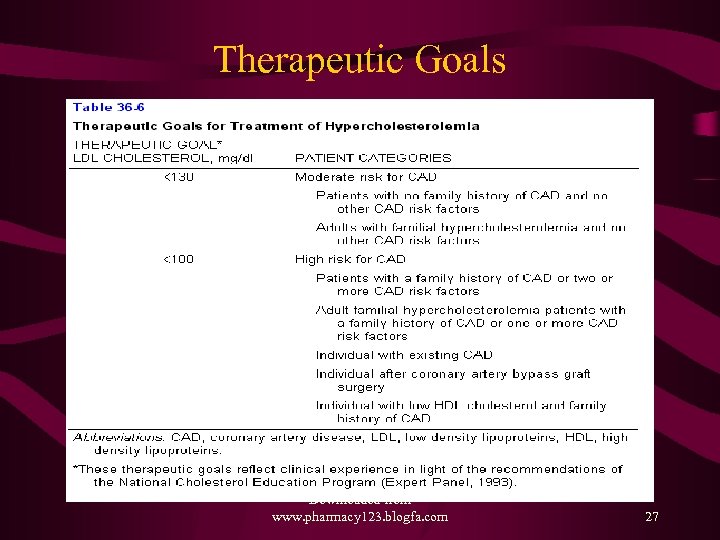
Therapeutic Goals Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 27
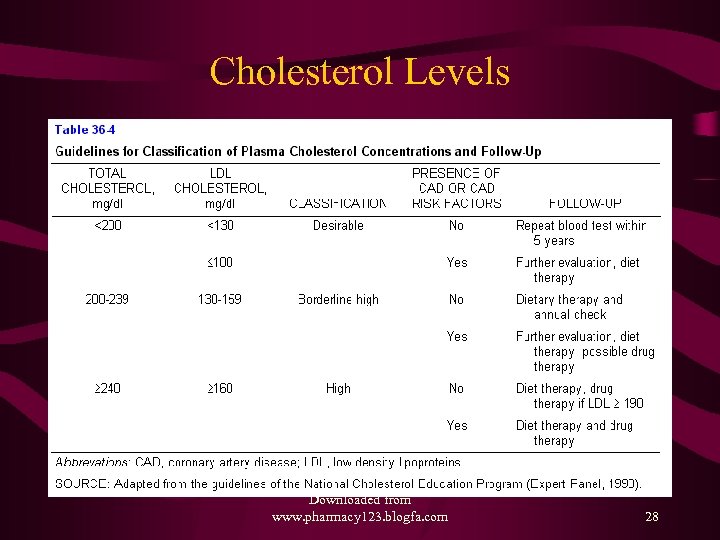
Cholesterol Levels Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 28
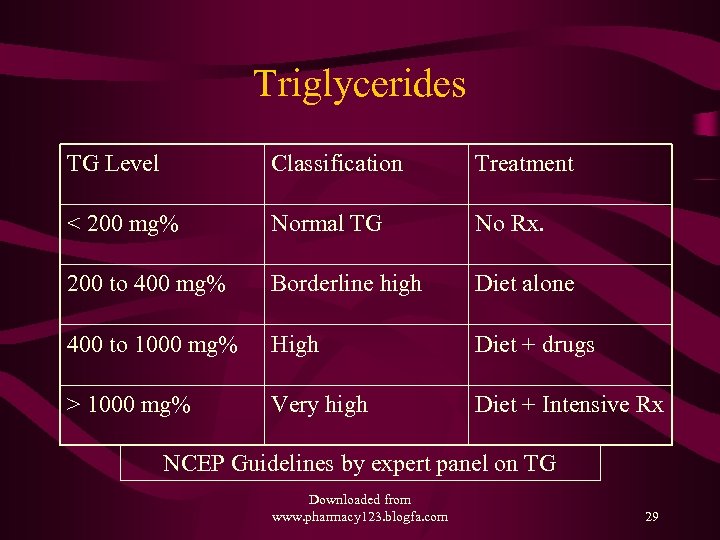
Triglycerides TG Level Classification Treatment < 200 mg% Normal TG No Rx. 200 to 400 mg% Borderline high Diet alone 400 to 1000 mg% High Diet + drugs > 1000 mg% Very high Diet + Intensive Rx NCEP Guidelines by expert panel on TG Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 29

Diet Regimen Nutrient Step II Total Fats < 30% Saturated < 10% < 5% PUFA < 10% MUFA < 10% 15% CHO 55% Protein 15% Cholesterol < 300 mg < 200 mg Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 30

Treatment Options • • Diet – Two step approach Drug therapy 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. HMG Co. A Reductase Inhibitors Bile Acid binding Resins Nicotinic Acid Fibric Acid derivatives Probucol Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 31

HMG Co. A Red. Inh. • Called Statins – Atorvastatin, Simvastatin, Lovastatin etc. , • 10 mg of Atorvastatin/Simvastatin OD, up to 40 mg/day • Synthesis of Cholesterol is blocked by inhibiting the enzyme hydroxy-methyl-Glutaryl Coenzyme A reductase • Increase in LDL receptors – traps LDL from plasma • Decrease in LDL by 25 -45%, and VLDL TG by 10 -20% • Increase HDL by 8 -10%, No action on Lp(a) • Free of side effects - < 5%, Rise in Liver enzymes • Rare but serious complication is myopathy –CPK increase • Caution if combined with Gemfibrozil for combined hyperlipids. Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 32

Nicotinic Acid • • Decrease the synthesis of VLDL and LDL in liver 50 – 100 mg t. i. d – increase up to 2 to 5 g/day Do not use sustained release preparation Decreases TG by 25 to 85%, VLDL by 20 -35% Decreases LDL by 10 -15%, may increase HDL? Only agent – lowering Lp(a) by 25% Flushing, pruritus, dry skin – tachycardia and atrial arrythmias – hyper uricemia, peptic ulcer disease, glucose intolerance, hepatic dysfunction • Poor side effect profile is the limitation. • Can be combined with resins, fibrates, statins Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 33

Anion Resins • • Interrupt the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids Increased synthesis of bile acids–cholesterol sequestration Cholestyramine (Questran) 378 g containers or 4 g sachets Colestipol (Colestid) in 300 g or 500 g jars/5 g packs/ 1 g tab Decrease LDL by 20 -30%, Increase HDL and TG Constipation, bloating, nausea, bleeding piles Contra ind. : Biliary obstruction, G. Outlet obst. , Incr. TG Can be combined with Nicotinic acid, Statins Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 34

Fibric Acid derivatives • • Increase LPL activity – Increased hydrolysis of TG Decrease VLDL synthesis, Increase LDL catabolism Only Gemfibrozil is approved – 600 mg b. i. d Decrease TG by 25 -40%, LDL may rise, modest rise HDL Adv. Effects -Incr. Bile lithogenicity, abn. LFT, Myositis Contr. In hepatic or biliary disease, caution in renal failure Increase the anti-coagulant action of Warfarin Can be combined with bile acid binding resins Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 35

Probucol • Probucol (Lorelco) 500 mg b. i. d with food • Third line drug – erratic effect on LDL & decrease of HDL • Lowers Cholesterol and only drug which regresses xanthomas • It is an antioxidant of LDL • Diarrohea, flatulence, nausea, increases QTc • Can be combined with bile acid sequestrating resins Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 36

What is for what • If LDLc is more – Hypercholesterilimia alone – – – Statins 1 st line – Simvastatin – Atorvastatin Statins + Anion resin (Questron)– 2 nd line Or Statins + nicotinc acid – 2 nd line Probucol 3 rd line specially for xanthomas But not Statins + gemfibrozil • If TG alone is elevated – Hypertriglyceridemia – Gemfibrozil – 1 st line – Nicotinic acid with or without Gemfibrozil– 2 nd line • For mixed – combination- Statin+Nicotinic acid Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 37

What’s in a name ? • Statins – Atorvastatin – Storvas, TG-tor, Avastin Simvastatin – Sim, Simvotin • Bile acid sequestering resins – Cholysteramine – Questron – Colistipal – Colestid • Nicotinic Acid – Niasyn • Fibric acid -Gemfibrozil– Lopid, Lipizyl • Probucol – Lorelco Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 38

The Research ADMIT Arterial disease multiple intervention trial (Niacin, Anti-oxidants, vitamins) CHAOS Cambridge heart anti-oxidant study MRC/BHF HPS MRC/BHF heart protection study (anti-oxidants) SU. VI. MAX Supplementation en Vitamines et Mineraux Antioxydants CELL Cost Effectiveness of Lipid Lowering (pravastatin) CIS Coronary Intervention Study (simvastatin) HHS Helsinki Heart Study (Gemfibrozil for TG) SSSS (4 S) Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (Land mark trial Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 39

The Future Research • We do not have yet any drug which increase the HDL • We do not know the precise role of Lp(a) and how to reduce it. • Small LDL needs further evaluation • RCTs to prove that the anti-oxidants have a real role to play both in treatment and in prevention of AVD Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 40
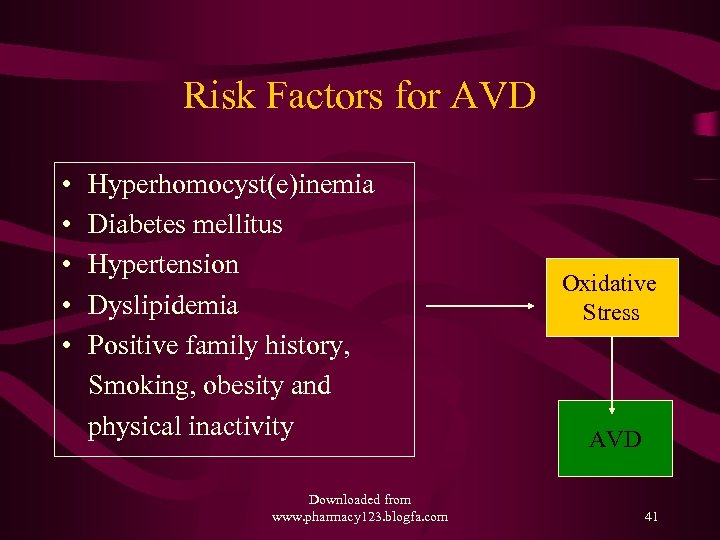
Risk Factors for AVD • • • Hyperhomocyst(e)inemia Diabetes mellitus Hypertension Dyslipidemia Positive family history, Smoking, obesity and physical inactivity Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com Oxidative Stress AVD 41
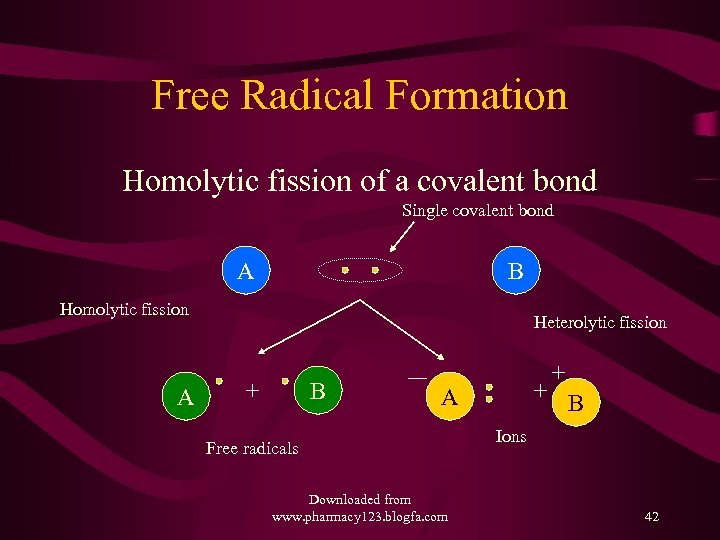
Free Radical Formation Homolytic fission of a covalent bond Single covalent bond A B Homolytic fission Heterolytic fission B A A Free radicals Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com B Ions 42
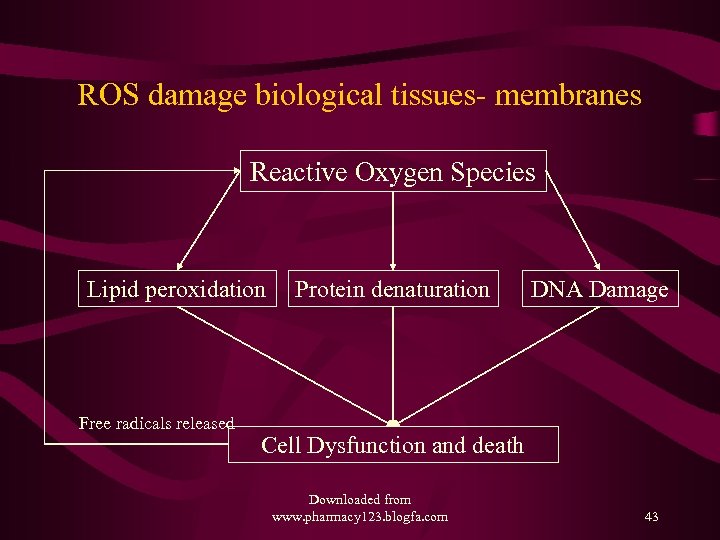
ROS damage biological tissues- membranes Reactive Oxygen Species Lipid peroxidation Free radicals released Protein denaturation DNA Damage Cell Dysfunction and death Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 43

Classification • Preventive antioxidants -Ceruloplasmin, transferrin, lactoferrin • Enzyme antioxidants -Superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase • Scavenging or ‘chain-breaking’ or ‘sacrificial’antioxidants -Vitamins A, C, and E Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 44

ROS and their Antioxidants ROS Antioxidants O 2 Superoxide free radical Superoxide dismutase Vitamin E, -carotene OH Hydroxyl free radical Vitamin C Hydrogen peroxide Glutathione peroxidase Singlet Oxygen Vitamin A, E H 2 O 2 Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 45

Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Free Radicals Superoxide O 2 Hydroxyl OH Non Radicals Hydrogen peroxide H 2 O 2 Singlet oxygen O 2 ROS are highly reactive…. and can damage biological tissues and membranes Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 46
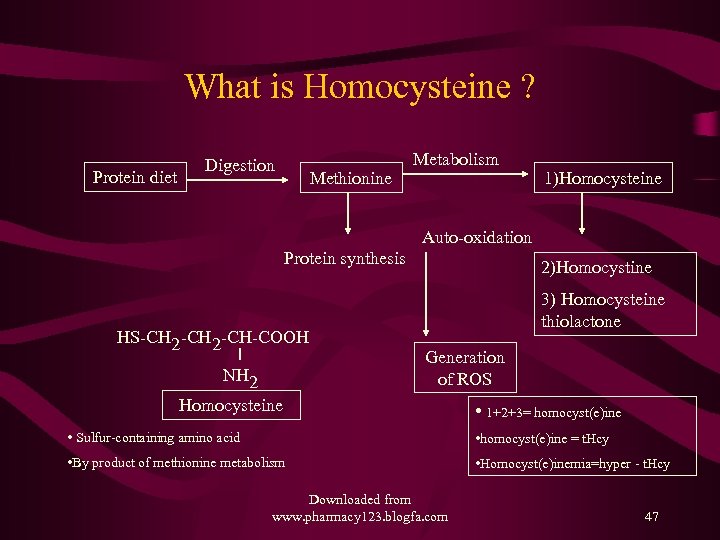
What is Homocysteine ? Protein diet Digestion Methionine Metabolism 1)Homocysteine Auto-oxidation Protein synthesis HS-CH 2 -CH-COOH NH 2 2)Homocystine 3) Homocysteine thiolactone Generation of ROS Homocysteine • 1+2+3= homocyst(e)ine • Sulfur-containing amino acid • homocyst(e)ine = t. Hcy • By product of methionine metabolism • Homocyst(e)inemia=hyper - t. Hcy Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 47
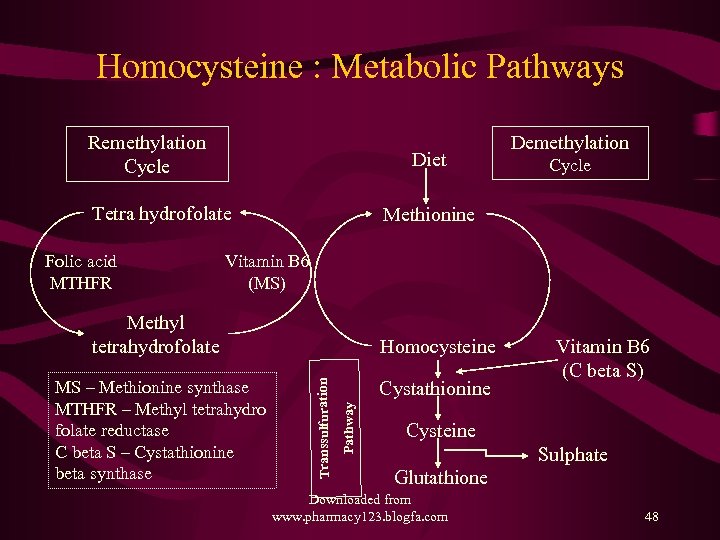
Homocysteine : Metabolic Pathways Remethylation Cycle Diet Tetra hydrofolate Folic acid MTHFR Demethylation Cycle Methionine Vitamin B 6 (MS) Methyl tetrahydrofolate Cystathionine Pathway Transsulfuration MS – Methionine synthase MTHFR – Methyl tetrahydro folate reductase C beta S – Cystathionine beta synthase Homocysteine Vitamin B 6 (C beta S) Cysteine Sulphate Glutathione Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 48
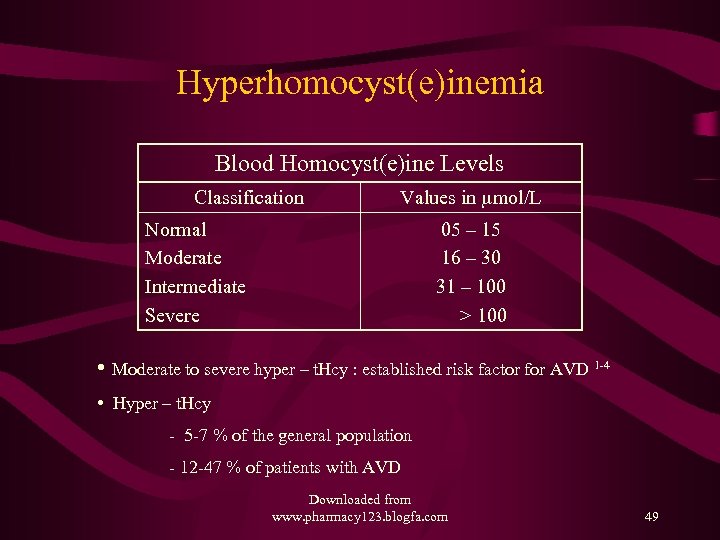
Hyperhomocyst(e)inemia Blood Homocyst(e)ine Levels Classification Values in mmol/L Normal Moderate Intermediate Severe 05 – 15 16 – 30 31 – 100 > 100 • Moderate to severe hyper – t. Hcy : established risk factor for AVD 1 -4 • Hyper – t. Hcy - 5 -7 % of the general population - 12 -47 % of patients with AVD Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 49

Causes of Hyperhomocyst(e)inemia A. Nutritional : Vitamin deficiency Folic Acid Vitamin B 12 Vitamin B 6 B. Genetic : Enzyme Abnormality C. Drugs : Methotrexate, Phenytoin, Theophylline Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 50
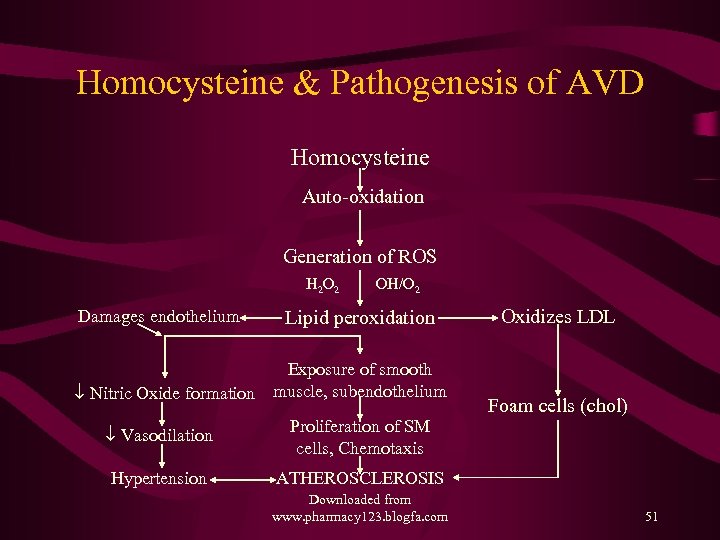
Homocysteine & Pathogenesis of AVD Homocysteine Auto-oxidation Generation of ROS H 2 O 2 Damages endothelium OH/O 2 Lipid peroxidation Exposure of smooth ¯ Nitric Oxide formation muscle, subendothelium ¯ Vasodilation Foam cells (chol) Proliferation of SM cells, Chemotaxis Hypertension Oxidizes LDL ATHEROSCLEROSIS Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 51

New Year Best Wishes We wish you to be blessed always with • BMI of < 25; W/H ratio of 0. 80 • FBG of 60 to 100 • Blood pressure of about 120/80 • LDLc of <100 • TG of <200 • Normal ECG and Treadmill test All these mean a very healthy and Happy HEART Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 52

True ! Eat Drink Indulge Think Be quiet Have high Chol Be high spirited Smoke but not over-eat but not alcohol but not in junk food but not worry but with exercise but not LDL Cholesterol but not be on ‘spirits’ any brand of incense stick, but not cigarettes Downloaded from www. pharmacy 123. blogfa. com 53
f430da0ba023a6c835dc923bbcb25c8d.ppt