4d1d14ddf52ab4dc728120ffbea8f7a2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 84

Lipid Rescue--Its not about the nail? LTC Peter Strube CRNA MSNA APNP ARNP DNAPc Assistant Professor Rosalind Franklin Nurse Anesthesia Program Cell: 608 -469 -1750 pstrube 3000@yahoo. com Email me: I have some great articles for you to read!

Dedicated to: Thomas G Healey, RN, CRNA, MA St Mary’ s University Died January 5, 2014 Navy Corpsman Vietnam

Financial Disclosure There is no financial conflicts with this presentation. Lecturing about a topic does not constitute endorsement of any product. Please take the time to research each topic for more information. Mentioning a product or company does NOT represent endorsement.

Increasing Food Allergy A kiss in 2005—Teen Dies n Peanuts – peanut oil used in Fresenius propoven n n (a propofol product from Europe showing up in hospitals in the U. S. ) http: //www. fda. gov/downloads/Drug. Safety/Dru g. Shortages/UCM 207301. pdf Mehta, 2014. Major finding: No allergic reactions were reported in patients with known food allergies who received propofol prior to undergoing endoscopy. Data source: A review of records from 160 food allergy patients who had endoscopies performed at the Mount Sinai Center for Eosinophilic Disorders from November 2004 to January 2014.

Why bother with the future? n “The future belongs to the unreasonable ones, the ones who look forward not backward, who are certain only of uncertainty, and who have the ability and the confidence to think completely differently. ” n Charles Handy quoting Bernard Shaw n Progressives are main stream only ahead of their time! n The point is not to predict the future but to prepare for it and to shape it

Case Study 26 year old female in labor presents for an elective epidural----Second baby. . Hx of preterm Labor On Fish Oil

Randomized clinical trials of fish oil supplementation in high risk pregnancies. Fish Oil Trials In Pregnancy (FOTIP) Team BJOG. 2000 Mar; 107(3): 382 -95 n To test the postulated preventive effects of dietary n-3 fatty acids on pre-term delivery, intrauterine growth retardation, and pregnancy induced hypertension n 33 -21% reduction in Preterm Labor n WOW… what does this have to do with a epidural…. . We will see

Fish Oil- 3000 mg Omega 3 Fish oil is oil derived from the tissues of oily fish. Fish oils contain the omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), precursors of eicosanoids that are known to reduce inflammation throughout the body, and are thought to have many health benefits. Studies suggest that it is helpful with cardiovascular disease, CAD, Depression, anxiety, increased new born outcomes and many more……. . . Some early studies are looking at using it for depression and suicide prevention… also used for aggressive behavior, alzeimers, Parkinson's and psoriasis. This is to name a few… it is used for a wide array of conditions Bleeding in high doses…greater than 3 grams per day Interacts with some anticoagulation medications and oral contraceptives.

The Ground Rules: n Recognition of Problem: Immediate Medical Management: Treatment: Follow-up, after action review: n Do you know antidotes? n n Interesting thought isn’t it?

History
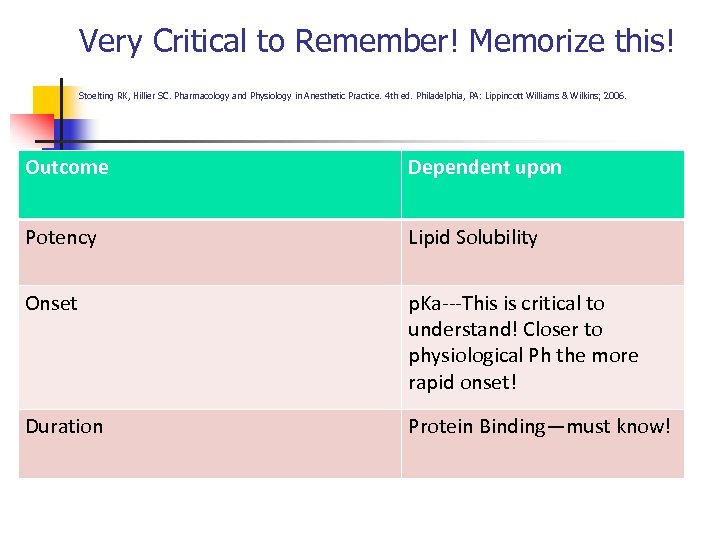
Very Critical to Remember! Memorize this! Stoelting RK, Hillier SC. Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice. 4 th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006. Outcome Dependent upon Potency Lipid Solubility Onset p. Ka---This is critical to understand! Closer to physiological Ph the more rapid onset! Duration Protein Binding—must know!
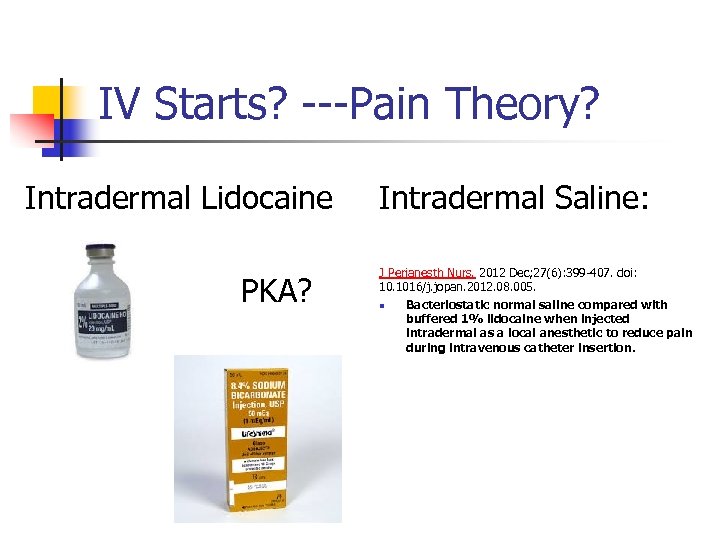
IV Starts? ---Pain Theory? Intradermal Lidocaine PKA? Intradermal Saline: J Perianesth Nurs. 2012 Dec; 27(6): 399 -407. doi: 10. 1016/j. jopan. 2012. 08. 005. n Bacteriostatic normal saline compared with buffered 1% lidocaine when injected intradermal as a local anesthetic to reduce pain during intravenous catheter insertion.

The History n n n First report 1929 – 40 fatalities Risk of modern toxicity first then discussed in 1979 2006/2007 first treatment with Lipids.

Time Line n 1960’s-- Marcaine linked to fetal death with OB use n 1970’s –Marcaine linked to cardiac arrest n 1980’s – cardiac events continue even with introduction Ropivacaine n 1998—magic year…. n 2006 finally hits clinical practice

Toxicity n n n Local anesthetics are amphipathic chemicals, meaning they have affinity for both lipid and water environments. This characteristic allows local anesthetics to cross plasma membrane and intracellular membranes quickly and also to interact with charged targets such as structural or catalytic proteins and signaling systems. Local anesthetics produce a variety of toxic effects in several tissue types, mainly heart, brain and skeletal muscle.

Toxicity The main site of both the clinically desirable and toxic effects of local anesthetics are thought to be exerted at the voltage gated sodium channel, many alternative sites have also been considered recently. Notably, the most potent, toxic local anesthetics, such as bupivacaine, interrupt practically every metabotropic and ionotropic signal transduction scheme that has been studied. Bupivacaine in particular has also been shown to disrupt each of the four components of oxidative phosphorylation: substrate transport, electron transport, proton motive force maintenance and ATP synthesis. An interesting observation that suggests the importance of this effect in bupivacaineinduced toxicity is that the pattern of tissues affected includes those with the highest aerobic demand least tolerance for hypoxia Order of CNS toxicity: Bupivacaine, tetracaine, Etidocaine, lidocaine, mepivacaine and 2 Chloroprocaine.

Rates of Toxicity n 1: 10, 000 epidurals n 1: 1, 000 peripheral blocks n Very unreported in n the non-hospital setting.

Regional: “The majority of women stated that anesthetists were the main, and most reliable, source of their information regarding risks of regional Anaesthesia for caesarean section” Cheng and Cyan Anesthesia Intensive Care- Feb 2007 Stages; First stage pain is from the uterine contraction and dilation of the cervix. Starts at T 11 -12 the moves to T 11 -12 to L 1 The dilation of the cervix plays the key role in pain. Pain is also caused by the uterine contractions and exceeds 25 mm. HG this pain travels via visceral afferent fibers accompanying the sympathetic nerves Second stage: end of first stage to delivery of the baby. Pain is caused by the pain traveling via the pudendal nerves and the distention of the vagina, vulva and perineum trigger the sensation of pain n The onset of perineal pain indicates the beginning of the second stage n T 10 -S 4 n Third stage is Delivery to when the placenta is expelled
Complication rate low for CNRA lumbar epidural injections http: //medicalxpress. com/news/2015 -02 -complication-cnra-lumbar-epidural. html (Health Day)—Complication rates for fluoroscopic-guided lumbar epidural steroid injections (LESIs) performed by certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs) are similar to physician rates cited in the literature, according to a study published online Jan. 27 in the Journal for Healthcare Quality. n n n Donald E. Beissel, D. N. P. , from Southwest Interventional Pain Specialists in Albuquerque, N. M. , conducted a survey of CRNA pain practitioners. He collected data on the number of fluoroscopic-guided LESIs performed and each of 20 complications for a six-month period. Beissel found that participants practiced in urban (23 percent) and rural (77 percent) settings in office/clinic (31 percent), hospital (62 percent), and mixed (7 percent) practices. CRNAs had both master's (62 percent) and doctoral (38 percent) degrees. Experience in performing fluoroscopic-guided LESIs ranged from one to 17 years and 50 to 12, 000 procedures. For each complication, the rate of occurrence was below 1 percent, with the highest rates for bruising and vasovagal reactions. There were no cases of paralysis or death. There was no association between either practice setting or experience level and complication rates. "CRNAs were able to safely and effectively perform fluoroscopic-guided LESIs with complication rates similar to physician rates cited in the literature, " the authors write.

How did we find Lipids? n 1998…… n Rosenblatt 2006; Bupivicaine related cardiac arrest n Litz 2006. IS-Block and Axillary block, pt arrested n More reports followed once this case study was published. n Concept evolved: To create a bank into which LA could be deposited from the cardiac tissue. n Development of first protocols to treat patients. n Interesting outcome included: Reappearance of cardiac collapse and several facilities did not have a second dose of lipids available http: //www. lipidrescue. org

Does your Center have a plan? n Most places do not have a plan to treat. n Academic centers: 59% no plan, but 84% stated they had a CT surgeon within 30 if needed, 74% said the would consider using lipids. n Old days need a CT surgeon for bypass n Now all hospitals can treat. n What is your plan?

The First Steps n Toxicity was the most feared complication of regional anesthesia. n Old and new therapies have combined to reduce risks n Prevention is the key…who helps you with blocks? n Ultrasound!!!!
New Ultrasound? --”Another tool to distinguish us from the CRNA”
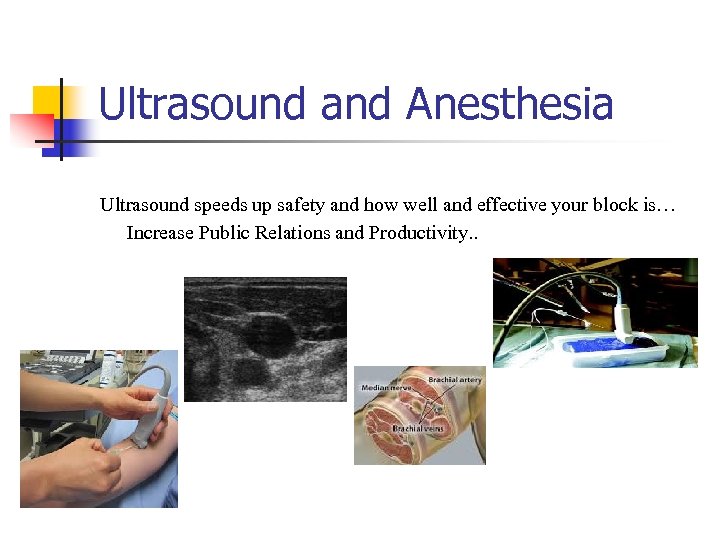
Ultrasound and Anesthesia Ultrasound speeds up safety and how well and effective your block is… Increase Public Relations and Productivity. .
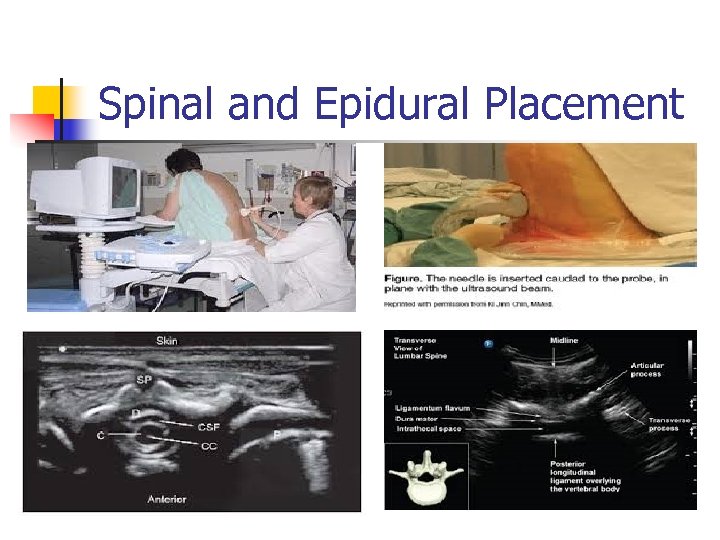
Spinal and Epidural Placement
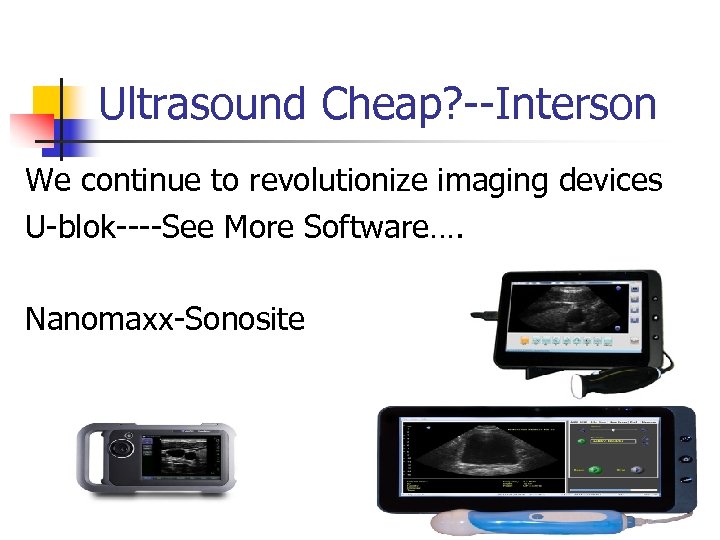
Ultrasound Cheap? --Interson We continue to revolutionize imaging devices U-blok----See More Software…. Nanomaxx-Sonosite

Bupivacaine Toxicity n Blocks Nerve impulses…well isn’t that our goal? Not in the cardiac tissues!!!! n It is more cardiotoxic because it enters sodium channels rapidly and leaves them very slowly n Diffuses during diastole, depresses conduction and inducing reentrant-type ventricular arrhythmias. n n Results in Systolic dysfunction, especially involving right ventricle, which precedes the occurrence of arrhythmias Blocks CNS impulses at lower doses… n Indirect cardiac initially followed by depression and then direct effects: Initial arrhythmias, negative inotropy and chronotropy

Early Identification is the Key Prompt attention to detail……tube the goose…? ? Avoid Benadryl because it works on sodium channels also Hypoventilation………… Expand volume and consider ? ACLS protocols to include all pressers. ?
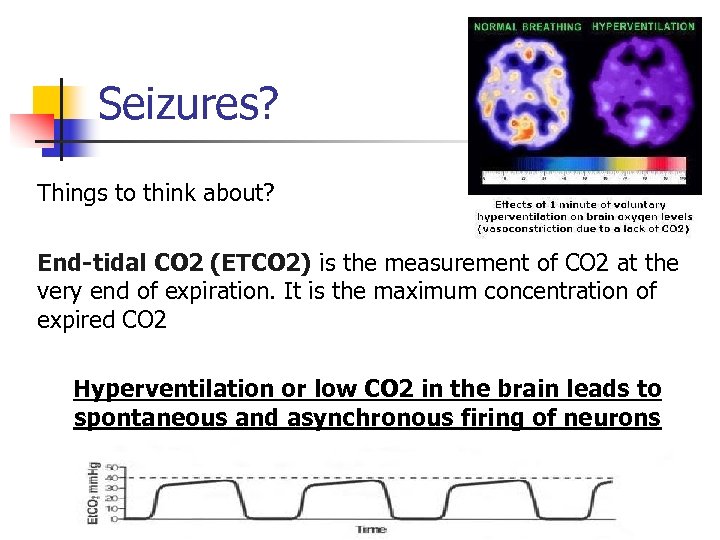
Seizures? Things to think about? End-tidal CO 2 (ETCO 2) is the measurement of CO 2 at the very end of expiration. It is the maximum concentration of expired CO 2 Hyperventilation or low CO 2 in the brain leads to spontaneous and asynchronous firing of neurons

Not Everything is it appears?

Tattoos n n Based on the limited information available it is possible that inserting an epidural or spinal needle through a tattoo could cause long-term problems such as arachnoiditis or a neuropathy secondary to an inflammatory reaction, but we don’t know. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 49: 1057 -1060 (2002) n Professional inks may be made from iron oxides n AANA--2010 n Lumbar Epidural Catheter Placement in the Presence of Low Back Tattoos: A Review of the Safety Concerns n Dawn Welliver, CRNA, MS Mark Welliver, CRNA, DNP Tammy Carroll, CRNA, MSN Peggy James, MD

LAST n Key considerations: n n n Atypical presentations 40% of time Delay of onset: 1 minute with some reports 60 minutes later CV toxicity can occur without CNS toxicity
Lipid Sink n LA love the lipids. . n Bind them with. . . sink n Initial increase in plasma levels n Then Lipids rapidly decrease in serum n It partitions the local away from receptors

A lot of case reports n They all have a single resounding tone with them? n Can you guess what?

Mistakes! n n n n n Intravascular injection Volume: 40 cc 1% Ropivacaine = 400 mg Not aspirating Not assessing for signs of toxicity Giving Lidocaine for ectopy after collapse? Not monitoring patient after IV administration of Bupivacaine Not admitting to problem of toxicity Multiple dosing routes

Mistakes! n n How Many Die From Medical Mistakes in U. S. Hospitals? http: //www. propublica. org/article/how-many-die-from-medicalmistakes-in-us-hospitals

Deaths Per Year! n n 1999, the Institute of Medicine published the famous “To Err Is Human” report, which dropped a bombshell on the medical community by reporting that up to 98, 000 people a year die because of mistakes in hospitals (2014) A study in the current issue of the Journal of Patient Safety that says the numbers may be much higher — between 210, 000 and 440, 000 patients

Lipid Registry 1997 young student accidently overdosed 22 year old instructed to apply 10%lidocaine/10% tetracaine mix prior to hair removal—died.

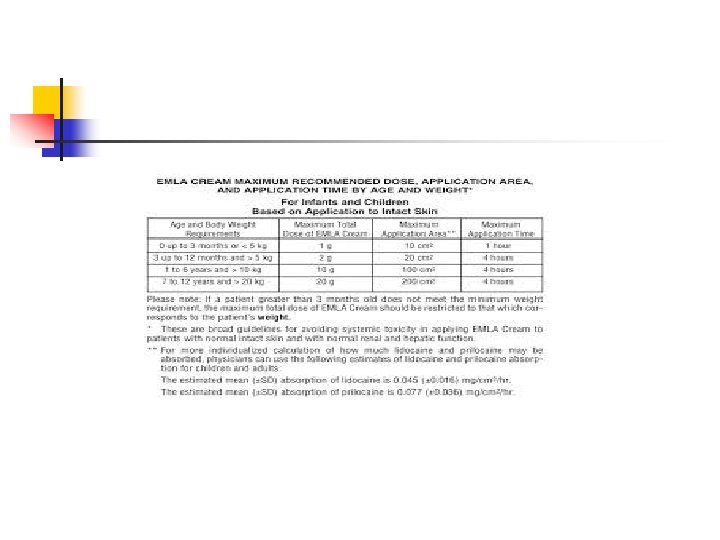
EMLA n n n EMLA = Eutectic (equal) mixture of local anesthetic. 5% Lidocaine and 5% prilocaine Contact time of at least 45 min-1 hour is required under an occlusive dressing. Absorption depends upon contact time, local tissue blood flow, keratin thickness, and total dose. Several types of surgery can be performed with EMLA, including laser removal of port-wine stains, lithotripsy, skin grafting, and circumcision Side effects of EMLA include: skin blanching, edema, erythema. It should not be used on mucous membranes, broken skin, infants less than 1 month old, or patients with methemoglobinemia. Hepatic metabolism of Prilocaine…. Methemoglobinemia… Methemoglobinemia inducing drugs: phenytoin, phenobarbital, acetaminophen, sulfonamides.
Prior to Block • Standard monitoring with audible oxygen saturation tone. n n n n n Oxygen supplementation. Airway Equipment to include suction…… Monitor Patient, before, during and up to 30 minutes post block Slow, incremental injection (5 m. L every 10– 15 seconds). **** Gentle aspiration for blood before injection and every 5 m. L thereafter. ****** Initial injection of local anesthetic test dose containing at least 5– 15 μg epinephrine with observation for heart rate change > 10 beats/min, blood pressure changes > 15 mm. Hg, or lead II T-wave amplitude decrease of 25%. Pretreatment with benzodiazepines to increase the seizure threshold to local anesthetic toxicity. Patient either awake or sedated, but still able to maintain meaningful communication. Resuscitation equipment and medications readily available at all times. If seizures occur, patient care includes airway maintenance, supplemental oxygen, and termination of the seizure with propofol (25– 50 mg) or thiopental (50 mg).

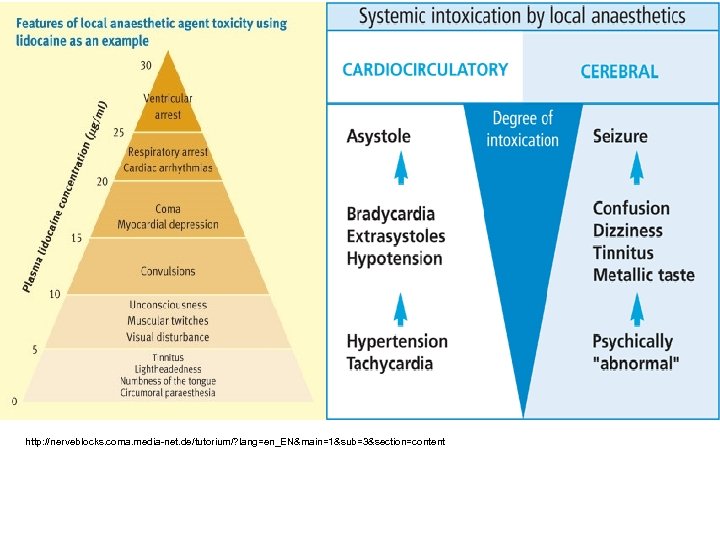
Know Signs: n CNS: excitation, agitation, confusion, twitching, seizures n Depression, sedation, coma, apnea n Metallic taste, circumoral numbness, diplopia, tinnitus, dizzy n Cardiac: initial hyper dynamic, then hypo dynamic

Local Anesthetic Toxicity n n n Systemic toxic effects are related to blood levels and are most commonly seen in the CNS and CV systems CNS: tinnitus, perioral peristhesias, dizziness, lightheadedness progressing to grand mal seizure. (Benzodiazepines and Barbiturates are useful in prevention and treatment of local anesthetic-induced seizures. ) CV: At less than 5 mcg/ml of lidocaine, no symptoms. At 5 -10 mcg/ml there are EKG changes including prolonged PR interval and widened QRS as well as decreased CO and peripheral vasodilation. At > 10 mcg/ml, asystole and circulatory collapse can be seen. n Patients with atypical pseudocholinesterase are more likely to develop toxicity to ester local anesthetics because they cannot metabolize them adequately n Bupivicaine>Etidocaine>Ropivicaine

Local Anesthetic Toxicity n n Bupivicaine dissociates slowly from cardiac sodium channels and has the most persistent depressant effects (most cardiotoxic) Echothiopate (irreversibly), Neostigmine, Pyridostigmine, and Edrophonium can prolong duration of ester local anesthetics Pregnancy, liver disease, neonates, and atypical pseudocholinesterase can prolong ester local anesthetics Volatile anesthetics, propranolol, and cimetidine decrease clearance of amide local anesthetics by inhibiting CP 450
http: //nerveblocks. coma. media-net. de/tutorium/? lang=en_EN&main=1&sub=3§ion=content
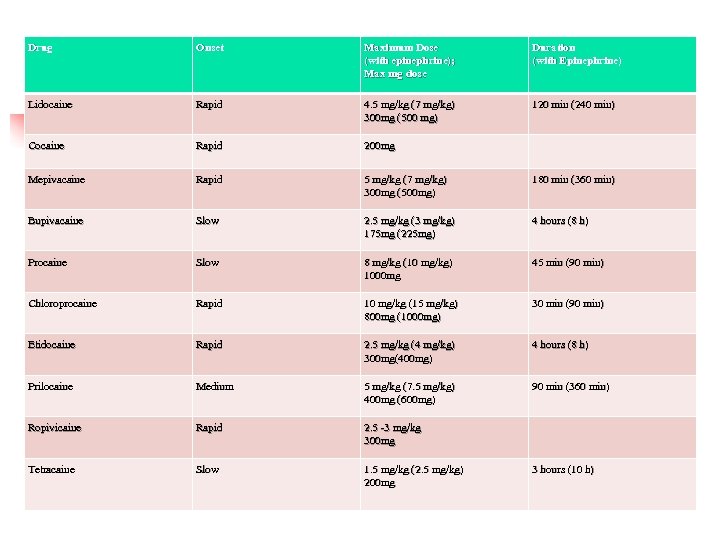
Drug Onset Maximum Dose (with epinephrine); Max mg dose Duration (with Epinephrine) Lidocaine Rapid 4. 5 mg/kg (7 mg/kg) 300 mg (500 mg) 120 min (240 min) Cocaine Rapid 200 mg Mepivacaine Rapid 5 mg/kg (7 mg/kg) 300 mg (500 mg) 180 min (360 min) Bupivacaine Slow 2. 5 mg/kg (3 mg/kg) 175 mg (225 mg) 4 hours (8 h) Procaine Slow 8 mg/kg (10 mg/kg) 1000 mg 45 min (90 min) Chloroprocaine Rapid 10 mg/kg (15 mg/kg) 800 mg (1000 mg) 30 min (90 min) Etidocaine Rapid 2. 5 mg/kg (4 mg/kg) 300 mg(400 mg) 4 hours (8 h) Prilocaine Medium 5 mg/kg (7. 5 mg/kg) 400 mg (600 mg) 90 min (360 min) Ropivicaine Rapid 2. 5 -3 mg/kg 300 mg Tetracaine Slow 1. 5 mg/kg (2. 5 mg/kg) 200 mg 3 hours (10 h)

n You must know your doses…Extrapolation of lab experiments, clinical studies and case reports. n Recommendations from the 1940’s ? ? n Max…. Lidocaine: Chloroprocaine: Tetracaine: Ropivacaine: Procaine: n Trick to calculating the mcg/cc epi? n n n Marcaine 2 -3 mg/kg with or without 4 -7 mg/kg with or without (less IV) 8 -12 mg/kg— 1000 mg max 3 mg/kg— 200 mg max 3 mg/kg— 300 mg max 8 mg/kg – 800 mg max

Initiate Treatment n Some controversy of timing, but based on clinical exam sooner is better. Current Recommendation is SOONER!!!! n Epi may impair treatment, limit epi use less than 1 mcg/kg n Propofol is not a substitute. Will address later n ICU monitoring for 24 -48 hours

Lets recap the highlights Get your pen ready, these are the highlights

LIPID Rescue n n How does this work? School of thought is that LA interfere with fatty acid transport into the mitochondria of the cardiac cells which inhibits the heart from performing oxidative phosphorylation and this is what leads to cardiac dysrhythmias n Most (and current? ? ? ) thought pattern is that LIPIDS act as a SINK n The sink – the lipids provide a alternative binding site for the LA n Cheap and found by accident – when it is cheap what drug company will fund research?

Theories: n n n Positive effect on oxidative metabolism may explain the swift cardiotoxic effect lipid treatment Bupivacaine potentially inhibits fatty acid transport at the inner mitochondrial membrane Lipid could act by countering the brake on the oxidation of the hearts preferred energy source The brand of the lipid emulsion doesn’t influence the outcome—just need lipids. n Basically, we really don’t know!

Test Question? Which Blade is Better? There are 14 main variants of blades, but which one is the best?


LIPID rescue n n n Cardiac toxicity related to the overdose or intravascular injection of local anesthetics has long been a concern of anesthesia Overdose is characterized by seizures, hypotension, atrioventricular conduction delay, idioventricular rhythms, and eventual cardiovascular collapse Think about who is helping you with the block All local anesthetics potentially shorten the myocardial refractory period, Marcaine has the highest affinity for cardiac tissues (cardiac sodium channels) making Marcaine the most likely to participate malignant arrhythmias. Remember B E E R OK B E R

Lipid Rescue n First line of defense is to be conservative!!!! n If the surgeon asks you what the dose is – go under!!—Minimum effective doses should be used n Aspirate prior to injection n Check of HEME n Who is helping you? Incremental dosing…… we need to do it correct n n n Ultrasound!!!!! (Regional, Airway, Venous Arterial, Spinal, Epidural……pneumo? ) Evidence suggests peripheral blocks are performed using significantly larger doses than are necessary

Lipid Rescue n Consider extremes of Age: (4 and under and greater than 70) n History of Cardiac conduction defects n Ischemic heart disease n Renal Dysfunction n Hepatic Dysfunction

Lipid Rescue n Goal is to prevent complications; with proper injection techniques and careful dosing • Remember Madison OB patient a few years ago… The major failure was not identifying the problem n Current treatments ACLS, BYPASS, LIPID rescue n

Lateral—Work Place Bully Definition Bullying is deliberate or intentional behavior using words or actions, intended to cause fear, intimidation or harm. Bullying is a repeated behavior and involves an imbalance of power. The behavior may be motivated by an actual or perceived distinguishing characteristic, such as, but not limited to: age; national origin; race; ethnicity; religion; gender identity; sexual orientation; physical attributes; physical or mental ability or disability; and social, economic or family status. Bullying behavior can be: 1. Physical (e. g. assault, hitting or punching, kicking, theft, threatening behavior) 2. Verbal (e. g. threatening or intimidating language, teasing or name-calling, racist remarks) 3. Indirect (e. g. spreading cruel rumors , intimidation through gestures, social exclusion and sending insulting messages or pictures by mobile phone or using the internet – also known as cyber bullying)

Lateral Violence 57% report verbal abuse 43% experience threatening body language 53% put down by supervisor 40% of abused victims forced to ignore errors or medication errors Shortage can be related to lateral violence


Lipid Rescue n n n 2006 lipid rescue was touted as the new Local Anesthetic toxicity rescue treatment Current suggestion includes LIPID available at all facilities Will we ever know more? Lipids are cheap; drug companies don’t want to pay when there will be little if any profit Mechanism of action: several suggested reasons. Most agree it is a LIPID sink: meaning, lipids reverse local anesthetic cardio toxicity may be increasing cardiac clearance. This nonspecific, observed extraction of local anesthetics from aqueous plasma or cardiac tissue is the lipid sink

First step of resuscitation for lipids rescue!

First Step. . Stay Calm

Lipid Rescue n n n 20% lipid solution 1. 5 ml/kg over 1 minute Follow immediately by a infusion at rate of 0. 25 ml/kg/min (17. 5 ml/min for a 70 kg adult) n n n Repeat dose if no improvement – and double the infusion rate Max of 10 ml/kg? ? ? www. lipidrescue. org n Airway Management TX seizures ACLS------limit epi----Weinberg work! n What about Propofol? (Propofol is 1%) n n



Other Things to Remember! n n Ask the question…. What about other treatments? What did Larry Say?

The Saving Grace! n n n Wellbutrin 7. 95 gms, Lamotrigine 4 grams Wellbutrin 100 mg/TID Lamotrigine 300 mg/QD

Many classes of compounds bind and inhibit Na channels n n n n Local anesthetics General anesthetics Ca channel blockers 2 agonists Tricyclic antidepressants Substance P antagonists Many nerve toxins Benadryl Droperidol ? ?
Harvey M, Cave G. Case report: successful lipid resuscitation in multi-drug overdose with predominant tricyclic antidepressant toxidrome. Int J Emerg Med. 2012 Feb 2; 5(1): 8. [Epub ahead of print] Blaber MS, Khan JN, Brebner JA, Mc. Colm R. J "Lipid Rescue" for Tricyclic Antidepressant Cardiotoxicity. Emerg Med. 2012 Jan 11. [Epub ahead of print] Jakkala-Saibaba R, Morgan PG, Morton GL. Treatment of cocaine overdose with lipid emulsion. Anaesthesia. 2011 Dec; 66(12): 1168 -70. doi: 10. 1111/j. 1365 -2044. 2011. 06895. x. Liang CW, Diamond SJ, Hagg DS. Lipid rescue of massive verapamil overdose: a case report. J Med Case Reports. 2011 Aug 20; 5(1): 399 Jovic-Stosic J, Gligic B, Putic V, Brajkovic G, Spasic R. Severe propranolol and ethanol overdose with wide complex tachycardia treated with intravenous lipid emulsion: a case report. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2011 Jun; 49(5): 426 -30. Shih YH, Chen CH, Wang YM, Liu K. Successful reversal of bupivacaine and lidocaineinduced severe junctional bradycardia by lipid emulsion following infraclavicular brachial plexus block in a uremic patient. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2011 Jun; 49(2): 72 -4.

Droperidol n n n Prophylactic doses (<1 mg) are effective against PONV FDA issued a ‘black box’ warning: n Droperidol may cause death or life-threatening events associated with QT prolongation and torsade's de pointes n Labeling changes based on 100 unique spontaneous cardiovascular adverse events Addition of black box warning has restricted use

Droperidol: The FDA Box Warning n n n n Droperidol has been used for over 40 years Why a problem now? No evidence of adverse events in published trials No published case reports An association does not prove cause and effect If prolonged QTc is an issue then 5 HT 3 antagonists should also carry the same warning At least 3 cases of VT associated with 5 HT 3 administration No “denominator” provided (or available)

Allergic Reactions n n Esters are derivatives of para-aminobenzoic acid. Para-aminobenzoic acid is responsible for most of the allergic phenomenon associated with use of ester local anesthetics. Allergic reactions to amides are extremely rare. Methylparaben (a derivative of para-aminobenzoic acid) found in multi-dose vials may cause some allergic reactions Cross sensitivity to esters and amides does not occur History is key to making the diagnosis. Many local anesthetic preparations often contain epinephrine which causes palpitations that may be reported as an allergy.

Systemic Pharmacologic and Toxicological Effects n Allergic Reactions n n n More common with ester-type local anesthetics. No cross reactivity with amide type. Manifested as contact dermatitis, bronchospasm, hives. Allergic reactions to amide-type local anesthetics is possible but rare. In patients who claim allergy to all local anesthetics, diphenhydramine (1%) has been used as an alternative with some success. Methemoglobinemia (hemoglobin in Fe 3+ oxidation state) n Amide-type agents (lidocaine, prilocaine) n Toxic metabolite (aromatic amine) n Cyanosis (brown blood, blue skin color) n Antidote: methylene blue

Methylene Blue n n This is a age old drug; Traditionally used for Methemoglobinemia and as a tissue marker Recent evidence (mostly in cardiac surgery) shows that it may be a benefit for refractory hypotension Has been used with liver transplant for hypotension Reports of being used for patients on ACE inhibitors for refractory hypotension

Exparel

Posidur n New product just like Exparel n Except Clear…. Could this be trouble?
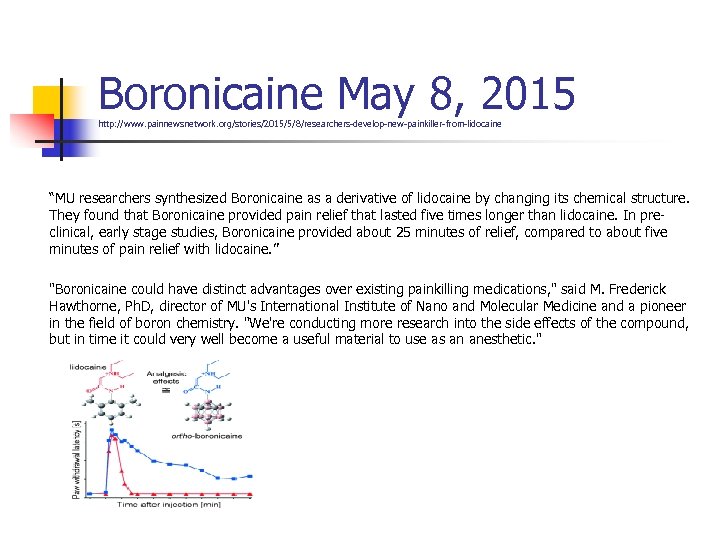
Boronicaine May 8, 2015 http: //www. painnewsnetwork. org/stories/2015/5/8/researchers-develop-new-painkiller-from-lidocaine “MU researchers synthesized Boronicaine as a derivative of lidocaine by changing its chemical structure. They found that Boronicaine provided pain relief that lasted five times longer than lidocaine. In preclinical, early stage studies, Boronicaine provided about 25 minutes of relief, compared to about five minutes of pain relief with lidocaine. ” "Boronicaine could have distinct advantages over existing painkilling medications, " said M. Frederick Hawthorne, Ph. D, director of MU's International Institute of Nano and Molecular Medicine and a pioneer in the field of boron chemistry. "We're conducting more research into the side effects of the compound, but in time it could very well become a useful material to use as an anesthetic. "

The cornea is the clear, dome-shaped outer area of the eye. It lies in front of the colored part of the eye (iris) and the black hole in the iris (pupil). The outermost layer of the eyeball consists of the cornea and the white part of the eye (sclera). A corneal abrasion is basically a superficial cut or scrape on the cornea. A corneal abrasion is not as serious as a corneal ulcer, which is generally deeper and more severe than an abrasion To diagnose a corneal abrasion, a topical anesthetic with a yellow dye called fluorescein is placed into the eye. Under blue cobalt light, the part of the cornea abraded will be stained by the dye and is easily seen by the examiner. The area and depth of the abrasion can be easily seen under a special microscope called a slit lamp biomicroscope. If a microscope is not available, then a blue light called a Burton lamp may be used Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as diclofenac (Voltaren) and ketorolac (Acular) are modestly useful in reducing pain from corneal abrasions If antibiotics are used, ointment (e. g. , bacitracin [AK-Tracin], erythromycin, gentamycin [Garamycin]) is more lubricating than drops and is considered first-line treatment. In patients who wear contact lenses, an antipseudomonal antibiotic (e. g. , ciprofloxacin [Ciloxan], gentamycin, ofloxacin [Ocuflox]) should be used, and contact lens use should be discontinued. Clinical trial data are lacking, but it is recommended that contact lenses be avoided until the abrasion is healed and the antibiotic course completed. Proparacaine: DO NOT USE TETRACAINE Dry Eyes? Where do you put your pulse ox?

Things to never forget! n Remember that local anesthetic toxicity is additive, i. e. , there is no advantage to mixing drugs in combination thinking that you will lessen the likelihood of toxicity. n n Additive effect: 50% Lidocaine+50% dose Marcaine = 100% of toxic effects Know all routes and duration of actions!

Have you thought about all the locations of local? n What could we have missed?
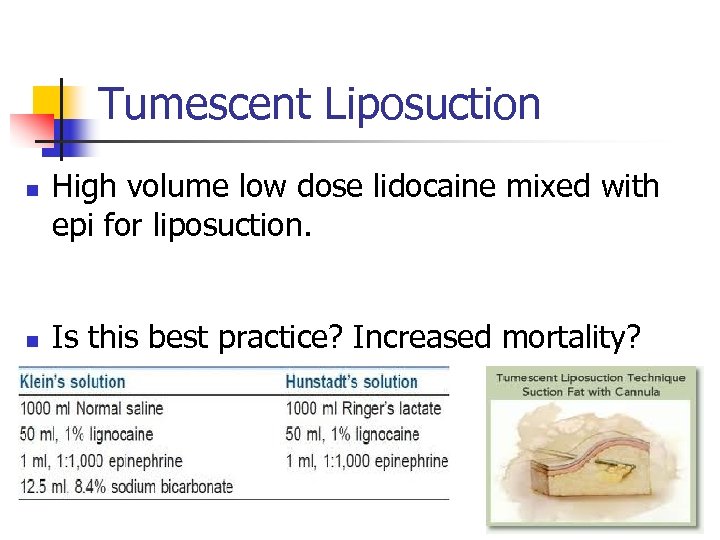
Tumescent Liposuction n n High volume low dose lidocaine mixed with epi for liposuction. Is this best practice? Increased mortality?

Can I be excused? … my brain is full !
Thanks, Peter: pstrube 3000@yahoo. com
4d1d14ddf52ab4dc728120ffbea8f7a2.ppt