ee65b93d36905bdfc8144c082bbb10d7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Linnfall Consulting The electricity market in Great Britain: the pool, NETA and EMR Linnfall Consulting November 2013
Structure of this presentation Introduction 2 The pool NETA EMR Linnfall Consulting
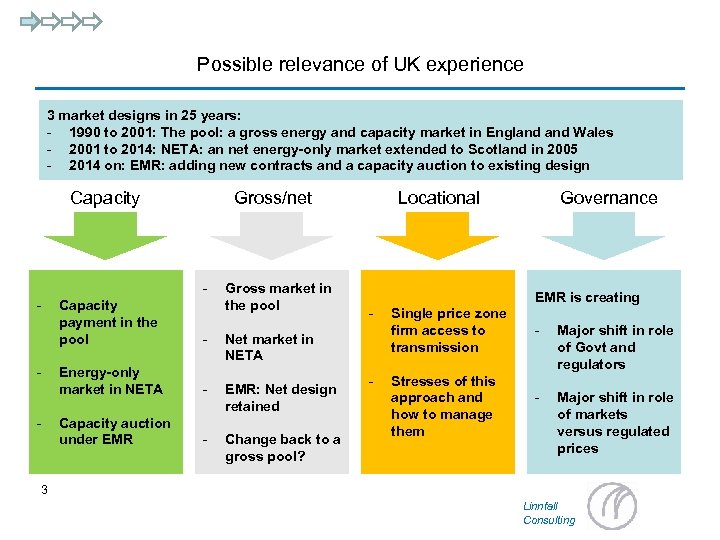
Possible relevance of UK experience 3 market designs in 25 years: - 1990 to 2001: The pool: a gross energy and capacity market in England Wales - 2001 to 2014: NETA: an net energy-only market extended to Scotland in 2005 - 2014 on: EMR: adding new contracts and a capacity auction to existing design Capacity Gross/net - Gross market in the pool Capacity payment in the pool EMR: Net design retained Capacity auction under EMR - - Change back to a gross pool? Governance EMR is creating Net market in NETA Energy-only market in NETA - - Locational - - Single price zone firm access to transmission Stresses of this approach and how to manage them - Major shift in role of Govt and regulators - Major shift in role of markets versus regulated prices 3 Linnfall Consulting
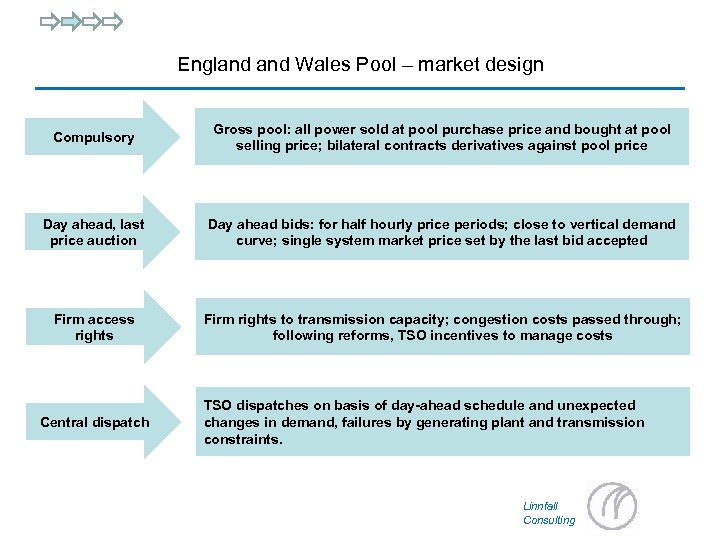
England Wales Pool – market design Compulsory Gross pool: all power sold at pool purchase price and bought at pool selling price; bilateral contracts derivatives against pool price Day ahead, last price auction Day ahead bids: for half hourly price periods; close to vertical demand curve; single system market price set by the last bid accepted Firm access rights Firm rights to transmission capacity; congestion costs passed through; following reforms, TSO incentives to manage costs Central dispatch TSO dispatches on basis of day-ahead schedule and unexpected changes in demand, failures by generating plant and transmission constraints. Linnfall Consulting
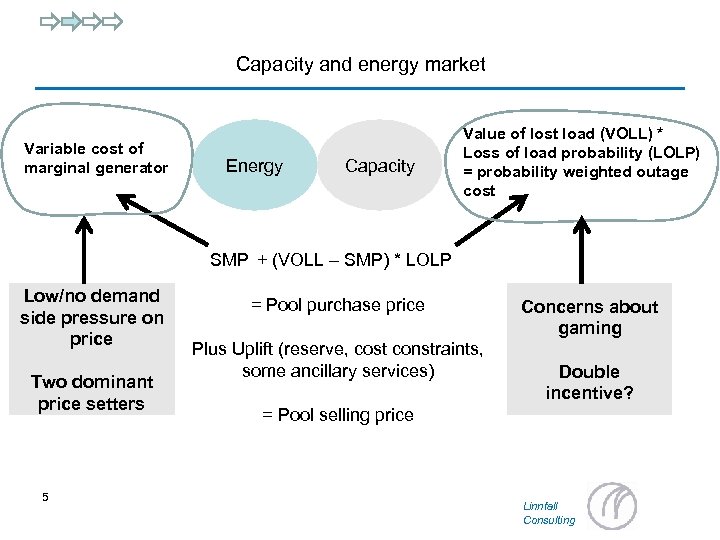
Capacity and energy market Variable cost of marginal generator Energy Capacity Value of lost load (VOLL) * Loss of load probability (LOLP) = probability weighted outage cost SMP + (VOLL – SMP) * LOLP Low/no demand side pressure on price Two dominant price setters 5 = Pool purchase price Plus Uplift (reserve, cost constraints, some ancillary services) Concerns about gaming Double incentive? = Pool selling price Linnfall Consulting
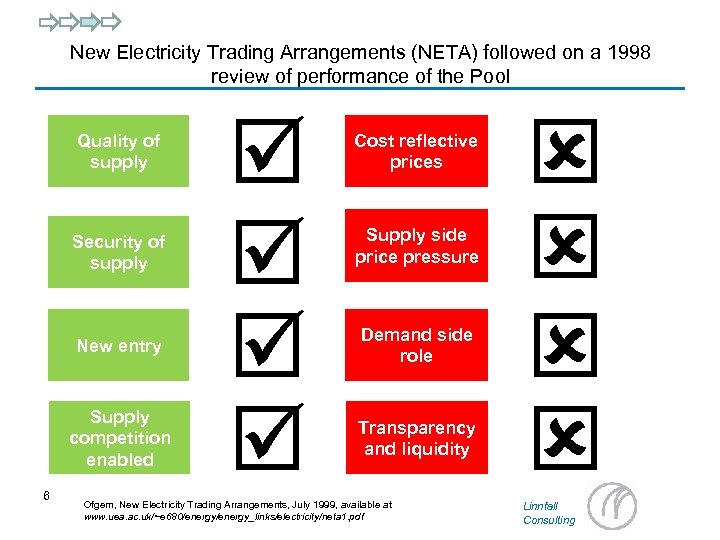
New Electricity Trading Arrangements (NETA) followed on a 1998 review of performance of the Pool Quality of supply Security of supply New entry Supply competition enabled 6 Cost reflective prices Supply side price pressure Demand side role Transparency and liquidity Ofgem, New Electricity Trading Arrangements, July 1999, available at www. uea. ac. uk/~e 680/energy_links/electricity/neta 1. pdf Linnfall Consulting
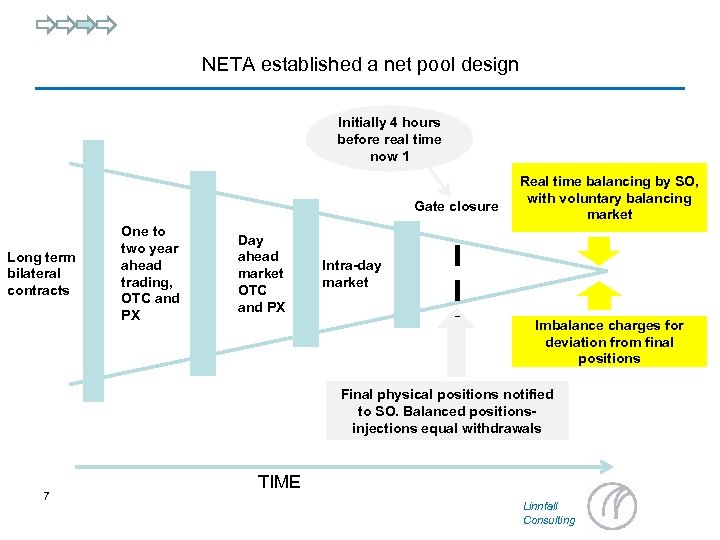
NETA established a net pool design Initially 4 hours before real time now 1 Gate closure Long term bilateral contracts One to two year ahead trading, OTC and PX Day ahead market OTC and PX Real time balancing by SO, with voluntary balancing market Intra-day market Imbalance charges for deviation from final positions Final physical positions notified to SO. Balanced positionsinjections equal withdrawals 7 TIME Linnfall Consulting
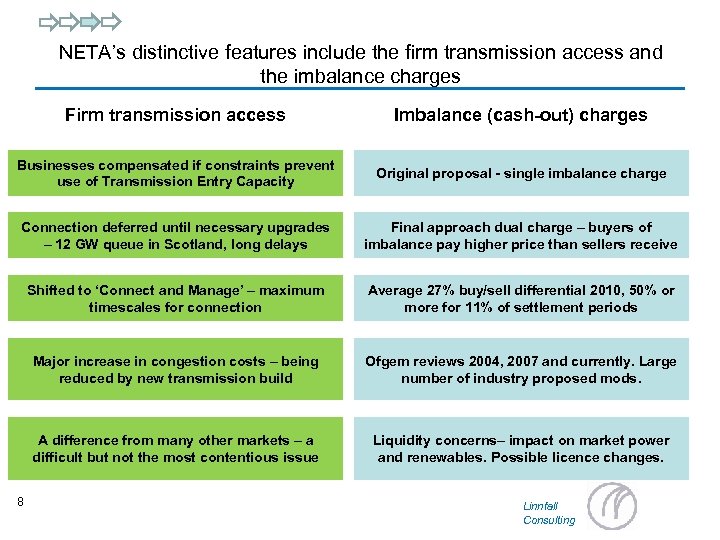
NETA’s distinctive features include the firm transmission access and the imbalance charges Firm transmission access Imbalance (cash-out) charges Businesses compensated if constraints prevent use of Transmission Entry Capacity Original proposal - single imbalance charge Connection deferred until necessary upgrades – 12 GW queue in Scotland, long delays Final approach dual charge – buyers of imbalance pay higher price than sellers receive Shifted to ‘Connect and Manage’ – maximum timescales for connection Average 27% buy/sell differential 2010, 50% or more for 11% of settlement periods Major increase in congestion costs – being reduced by new transmission build Ofgem reviews 2004, 2007 and currently. Large number of industry proposed mods. A difference from many other markets – a difficult but not the most contentious issue Liquidity concerns– impact on market power and renewables. Possible licence changes. 8 Linnfall Consulting
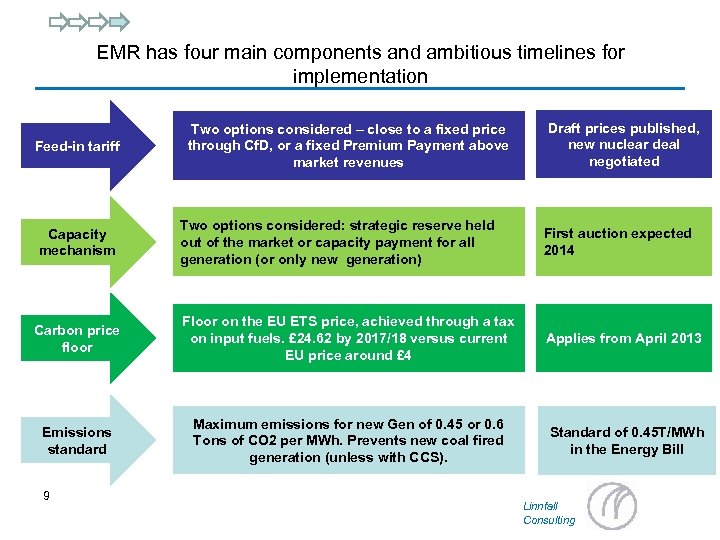
EMR has four main components and ambitious timelines for implementation Feed-in tariff Two options considered – close to a fixed price through Cf. D, or a fixed Premium Payment above market revenues Draft prices published, new nuclear deal negotiated Two options considered: strategic reserve held out of the market or capacity payment for all generation (or only new generation) First auction expected 2014 Carbon price floor Floor on the EU ETS price, achieved through a tax on input fuels. £ 24. 62 by 2017/18 versus current EU price around £ 4 Applies from April 2013 Emissions standard Maximum emissions for new Gen of 0. 45 or 0. 6 Tons of CO 2 per MWh. Prevents new coal fired generation (unless with CCS). Standard of 0. 45 T/MWh in the Energy Bill Capacity mechanism 9 Linnfall Consulting
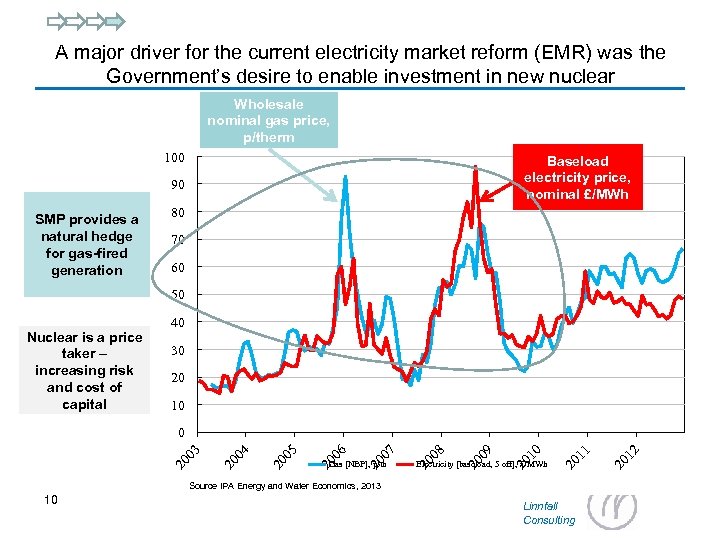
A major driver for the current electricity market reform (EMR) was the Government’s desire to enable investment in new nuclear Wholesale nominal gas price, p/therm 100 Baseload electricity price, nominal £/MWh 90 SMP provides a natural hedge for gas-fired generation 80 70 60 50 Nuclear is a price taker – increasing risk and cost of capital 40 30 20 10 Source IPA Energy and Water Economics, 2013 10 Linnfall Consulting 20 12 Electricity [baseload, 5 off], £/MWh 20 11 20 10 20 09 Gas [NBP], p/th 20 08 20 07 20 06 20 05 20 04 20 03 0
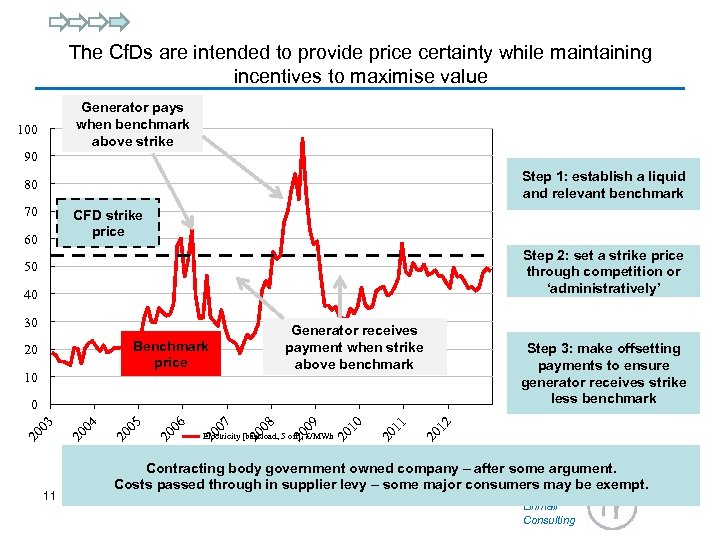
The Cf. Ds are intended to provide price certainty while maintaining incentives to maximise value Generator pays when benchmark above strike 100 90 Step 1: establish a liquid and relevant benchmark 80 70 CFD strike price 60 Step 2: set a strike price through competition or ‘administratively’ 50 40 30 Generator receives payment when strike above benchmark Benchmark price 20 10 11 20 12 Electricity [baseload, 5 off], £/MWh 20 11 20 10 20 09 20 08 20 07 20 06 20 05 20 04 20 03 0 Step 3: make offsetting payments to ensure generator receives strike less benchmark Contracting body government owned company – after some argument. Costs passed through in supplier levy – some major consumers may be exempt. Linnfall Consulting
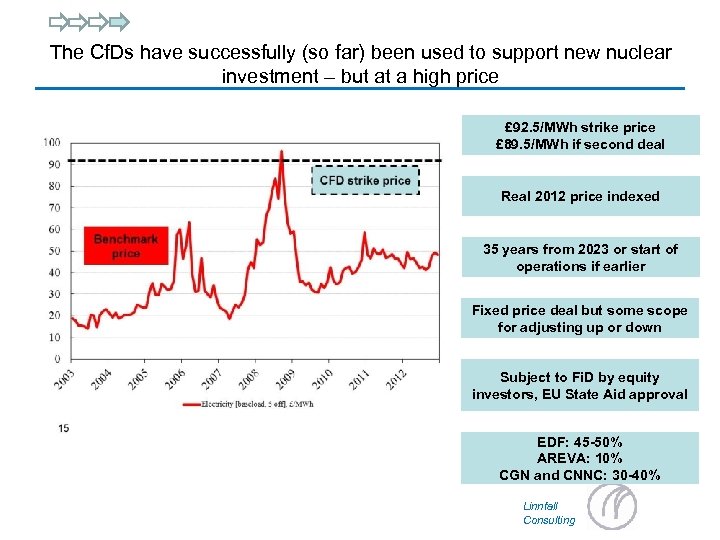
The Cf. Ds have successfully (so far) been used to support new nuclear investment – but at a high price £ 92. 5/MWh strike price £ 89. 5/MWh if second deal Real 2012 price indexed 35 years from 2023 or start of operations if earlier Fixed price deal but some scope for adjusting up or down Subject to Fi. D by equity investors, EU State Aid approval EDF: 45 -50% AREVA: 10% CGN and CNNC: 30 -40% Linnfall Consulting
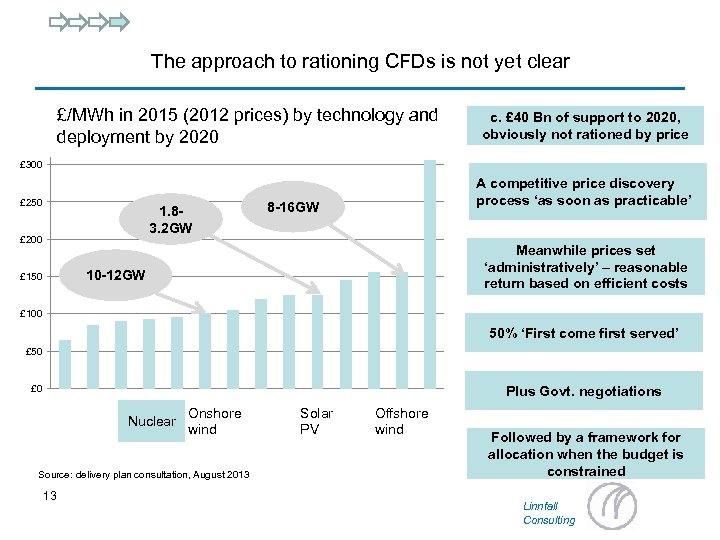
The approach to rationing CFDs is not yet clear £/MWh in 2015 (2012 prices) by technology and deployment by 2020 c. £ 40 Bn of support to 2020, obviously not rationed by price £ 300 £ 250 1. 83. 2 GW £ 200 A competitive price discovery process ‘as soon as practicable’ 8 -16 GW Meanwhile prices set ‘administratively’ – reasonable return based on efficient costs 10 -12 GW £ 150 £ 100 50% ‘First come first served’ £ 50 Plus Govt. negotiations £ 0 Nuclear Onshore wind Source: delivery plan consultation, August 2013 13 Solar PV Offshore wind Followed by a framework for allocation when the budget is constrained Linnfall Consulting
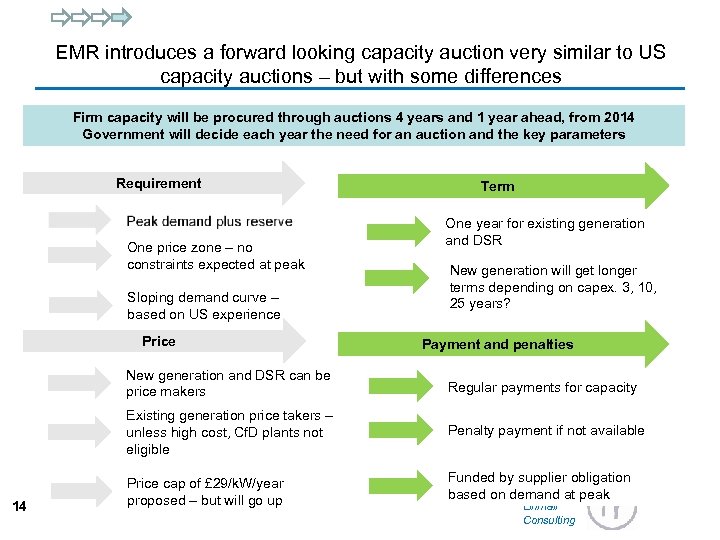
EMR introduces a forward looking capacity auction very similar to US capacity auctions – but with some differences Firm capacity will be procured through auctions 4 years and 1 year ahead, from 2014 Government will decide each year the need for an auction and the key parameters Requirement One price zone – no constraints expected at peak Sloping demand curve – based on US experience Price Term One year for existing generation and DSR New generation will get longer terms depending on capex. 3, 10, 25 years? Payment and penalties New generation and DSR can be price makers Existing generation price takers – unless high cost, Cf. D plants not eligible 14 Regular payments for capacity Penalty payment if not available Price cap of £ 29/k. W/year proposed – but will go up Funded by supplier obligation based on demand at peak Linnfall Consulting
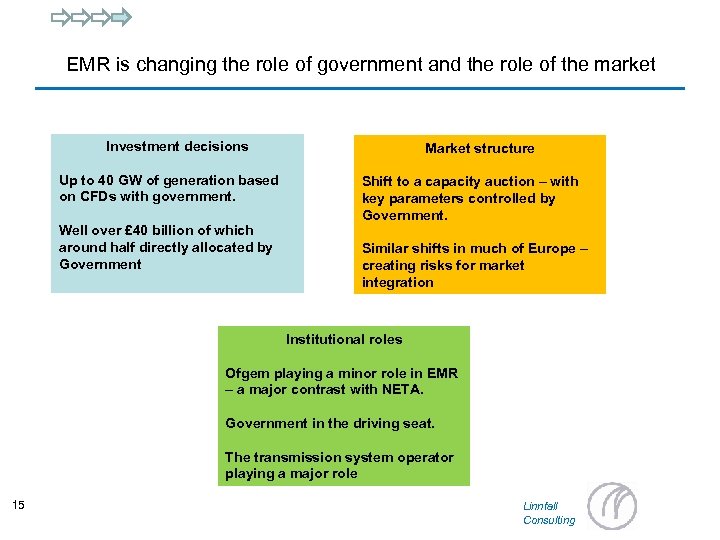
EMR is changing the role of government and the role of the market Investment decisions Up to 40 GW of generation based on CFDs with government. Well over £ 40 billion of which around half directly allocated by Government Market structure Shift to a capacity auction – with key parameters controlled by Government. Similar shifts in much of Europe – creating risks for market integration Institutional roles Ofgem playing a minor role in EMR – a major contrast with NETA. Government in the driving seat. The transmission system operator playing a major role 15 Linnfall Consulting

And if you want more details on EMR…. The proposals for implementing EMR, updated on 24 October, are at https: //www. gov. uk/government/consultations/proposals-for-implementation-of-electricity-marketreform – – – – 16 – The Electricity Market Reform: consultation on proposals for implementation The Contracts for Difference (Allocation) regulations 2014 The Contracts for Difference (Supplier Obligation) Regulations The Electricity Capacity (Payment) Regulations 2014 The Electricity Capacity Regulations 2014 Capacity market rules: consultation draft Modifications to National Grid Licence: special condition N of NGET transmission licence Annex B: background on supporting and transitional policy arrangements Impact assessment: measures to address potential conflicts of interest arising in relation to the choice of National Grid as the delivery body Impact assessment: contracts for difference Annex D: eligibility crtiteria Impact assessment: supplier obligation, contracts for difference Impact assessment: capacity market Impact of EMR on interconnection Capacity market gaming and consistency assessment Linnfall Consulting
ee65b93d36905bdfc8144c082bbb10d7.ppt