548909a79ba1f30a87ac2513762e81f3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Integrating an imaging biobank in a BBMRI biobank Bernard Gibaud Medi. CIS, LTSI, U 1099 Inserm Faculté de médecine, Rennes bernard. gibaud@univ-rennes 1. fr
Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Overview • Imaging biobanks – Origin of the concept – Imaging biobanks in the IA context • Synergy with biobanks • From concept to implementation – Collaboration ESR / BBMRI-ERIC • Perspectives / Conclusion
Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Origin of the concept • 2014: Working group on Imaging Biobanks (E. Neri) • Extracts from the ESR Mission statement – « to promote the development of imaging biobanks and intelligent tools for the analysis and processing of biomarkers » – « to stimulate the link between imaging biobanks and traditional biobanks through the development of standards » – « to monitor the existing imaging biobanks in Europe, to promote the federation of such imaging biobanks, and to elaborate a white paper on imaging biobanks»

Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Imaging biobanks 2015: Paper prepared by the ESR Working Group on Imaging Biobanks
Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Imaging biobank • Definition: – « organised databases of medical images, and associated imaging biomarkers (radiology and beyond), shared among multiple researchers, linked to other repositories » [Mission statement of ESR WG on imaging biobanks]
Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Imaging biobanks in the AI context • In the past, image analysis methods were – designed by humans, based on assumptions on what could be detectable in the image data • Then, the evolution consisted – for humans to select multiple features (cf radiomics) – and let the computer assess their relevance from large learning data sets • Now, especially with Deep learning, the general trend is – to let the computer choose the relevant image features à Consequence: Imaging Data has become a key resource for developing AIbased methods, by providing large annotated datasets
Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Imaging data • Acquired images (i. e. acquired on humans, animals, or specimen from these organisms) • Derived data, generated through automated data processing – Images, e. g. denoised images, corrected of bias distorsion, template-resampled images, statistical maps, etc. – ROI, e. g. binary masks (segmentation results), graphs (e. g. contours, tractography, 3 D surfaces 3 D as meshes) – Measurements made from image data (imaging biomarkers) • Metadata – Descriptive metadata – Provenance metadata (acquisition protocols, image processing protocols) – Contextual metadata (other data concerning the subject, e. g. histopathology, clinical data, omics data)
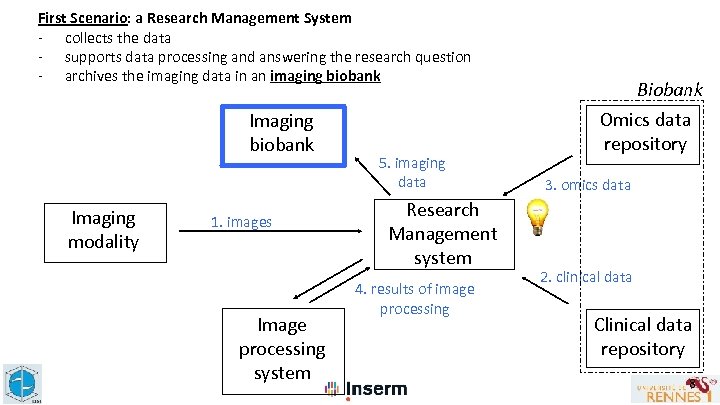
First Scenario: a Research Management System - collects the data - supports data processing and answering the research question - archives the imaging data in an imaging biobank Imaging modality 1. images Image processing system 5. imaging data Research Management system 4. results of image processing Biobank Omics data repository 3. omics data 2. clinical data Clinical data repository 8
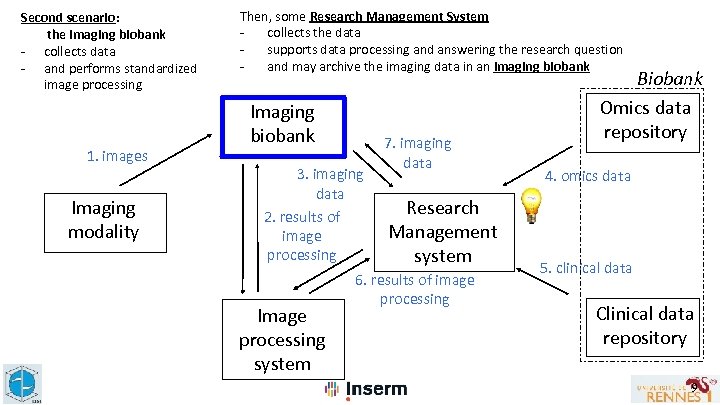
Second scenario: the Imaging biobank - collects data - and performs standardized image processing 1. images Imaging modality Then, some Research Management System collects the data supports data processing and answering the research question and may archive the imaging data in an imaging biobank Imaging biobank 3. imaging data 2. results of image processing Image processing system 7. imaging data Research Management system 6. results of image processing Biobank Omics data repository 4. omics data 5. clinical data Clinical data repository 9
Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna From concept to implementation • Collaboration between ESR and BBMRI-ERIC – Started in 2015 – MIABIS* – DICOM Working Group – Describing image collections in the BBMRI-ERIC DIRECTORY * Minimum Information About BIobank data Sharing
Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna BBMRI-ERIC Directory • A resource allowing to describe biobanks and the collections of specimen that they hold • Based on the MIABIS model • Three basic levels – Biobanks: institutional envelopes – Collections: contain information on samples and data – Networks: can be seen as a federation of biobanks • Contact persons defined at either of these 3 levels

Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Image collections in the BBMRI-ERIC Directory • Image collections are collections – Analogy between • samples taken from donors and • images taken from patients – No reason to describe patients in a different way (demographic data, disease data etc. ) • Inherit most of the characteristics of collections

Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Attributes describing collections id country biobank collection name acronym description bioresource_reference parent_collection network type data_categories order_of_magnitude size timestamp standards id_card contact_information head_firstname head_lastname head_role contact_priority latitude longitude donor_data sex diagnosis_available age_low age_high age_unit imaging_data body_part_examined imaging_modality image_dataset_type sample_data materials storage_temperatures access_policy sample_access_fee sample_access_joint_project sample_access_description sample_access_uri data_access_fee data_access_joint_project data_access_description data_access_uri image_access_fee image_joint_projects image_access_description image_access_uri collaboration_commercial collaboration_non_for_profit sample_mgmt sample_processing_sop sample_transport_sop sample_storage_sop data_mgmt data_processing_sop data_transport_sop data_storage_sop

Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Notion of sub-collection • Possibility to define sub-collections – e. g. focusing on the imaging part of an existing collection – or on a specific pathology • Enabling a more fine-grained description – of the subjects involved (number, age, gender) – imaging modalities available – or specifying a specific contact person
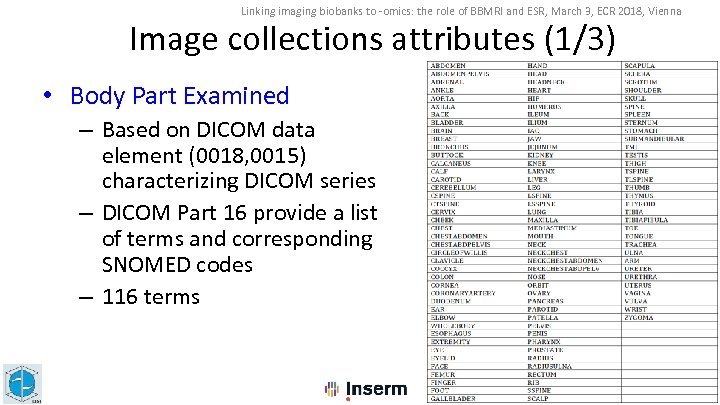
Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Image collections attributes (1/3) • Body Part Examined – Based on DICOM data element (0018, 0015) characterizing DICOM series – DICOM Part 16 provide a list of terms and corresponding SNOMED codes – 116 terms
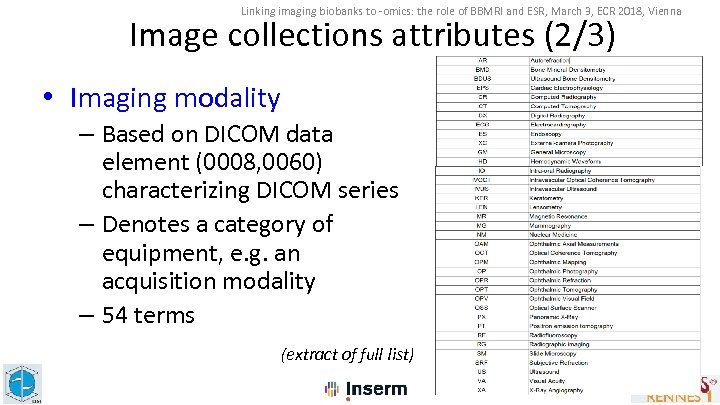
Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Image collections attributes (2/3) • Imaging modality – Based on DICOM data element (0008, 0060) characterizing DICOM series – Denotes a category of equipment, e. g. an acquisition modality – 54 terms (extract of full list) 16
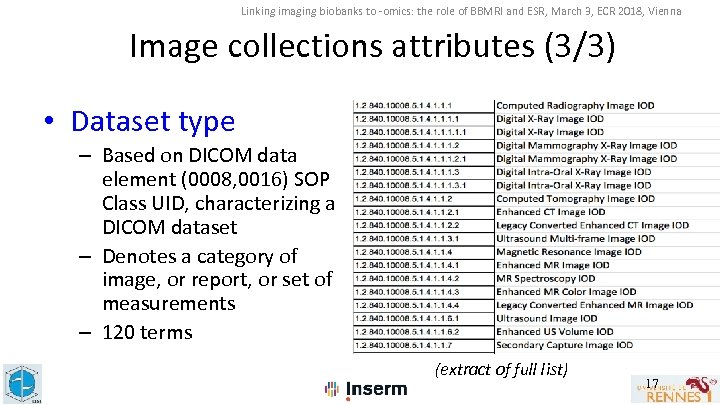
Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Image collections attributes (3/3) • Dataset type – Based on DICOM data element (0008, 0016) SOP Class UID, characterizing a DICOM dataset – Denotes a category of image, or report, or set of measurements – 120 terms (extract of full list) 17
Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Populating the BBMRI-ERIC directory with descriptions of image collections • Several groups developing imaging biobanks answered positively – – – Daniele Regge, Italy Emanuele Neri, Italy Daniel Bos, Aad van der Lugt, Netherlands Michel Dojat, France Luis Marti Bonmati, Spain
Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Management of image collections in the BBMRI-ERIC Directory • Two main situations occurred 1. 2. Descriptions of the collections already available from National BBMRI nodes in their national directories (this was the case for Netherlands) Descriptions of the collections not available from National BBMRI nodes, e. g. related biobanks were imaging biobanks (Italy, France), or located in countries that are not part of BBMRI-ERIC, yet (e. g. Spain)

Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Image collections currently listed • • • NL: Rotterdam study (population) – MR, CT, US – NL: The Maastricht Study (population) – MR, US – NL: SMART (arterial) – MR, US – NL: Nijmegen Brain Imaging Genetics (BIG) – MR NL: Generation R (population) – MR – NL: NELSON: Lung cancer screening – CT – NL: Depression and Anxiety – MR – NL: Leiden Longevity Study – MR, CT – NL: PROSPER: Pravastatin and risk of vasc diseases – MR • • • IT: Multiparam MR of prostate – MR IT: Rectal Cancer – MR SP: Endometrial cancer – MR – SP: Gliobastoma – MR– SP: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis– MR – FR: Grapheme-color synesthesia - MR FR: Oxy. TC: Cranial trauma - MR FR: Co. A: Brain functional Healthy subjects - MR FR: AGIR-PARK: Parkinson - MR
Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Perspectives • To extend the descriptions of image collections – especially imaging sub-modalities (especially in MR) • To describe imaging data available in image collections and especially imaging biomarkers • Strategy – To reuse/extend the MIABIS/ OMIABIS models – To reuse existing terminology/ontology (e. g. DICOM, Rad. Lex) – To collaborate closely with people developing imaging biobanks, especially in the context of large population studies
SF 10: Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications, March 2, ECR 2018, Vienna Conclusion / Summary • Imaging biobanks will play a key role in the development of AI-based methods in medical imaging – by providing annotated data – for learning, performance assessment, and comparison of methods • This data must be linked to other related data (e. g. histopathology, omics) managed in biobanks • Collaboration between ESR and BBMRI-ERIC is essential in this context

Linking imaging biobanks to -omics: the role of BBMRI and ESR, March 3, ECR 2018, Vienna Acknowledgements • To all the members of the MIABIS-DICOM WG • Special thanks to – Daniele Regge, Emanuele Neri, Luis Marti Bonmati, Angel Alberich-Bayarri, Michel Dojat, Daniel Bos, Aad van der Lugt, Matthias Günther – David van Enckevort, Petr Holub
548909a79ba1f30a87ac2513762e81f3.ppt