70f9e3873e2e2d2eb2a6f55accaf79bc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 LIGO Status Report LIGO ESF Exploratory Workshop Perugia, Italy September 21 st – 23 rd, 2005 LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z Guido Mueller University of Florida For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration
LIGO Status Report LIGO ESF Exploratory Workshop Perugia, Italy September 21 st – 23 rd, 2005 LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z Guido Mueller University of Florida For the LIGO Scientific Collaboration
 Table of Content § Layout § Seismic Isolation » Suspension system » HEPI § Interferometer » Wavefront Sensor » Thermal Correction System (TCS) » Laser situation § Science Output » Sensitivities/Papers at different Science Runs § S 5 -Plans LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 2
Table of Content § Layout § Seismic Isolation » Suspension system » HEPI § Interferometer » Wavefront Sensor » Thermal Correction System (TCS) » Laser situation § Science Output » Sensitivities/Papers at different Science Runs § S 5 -Plans LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 2
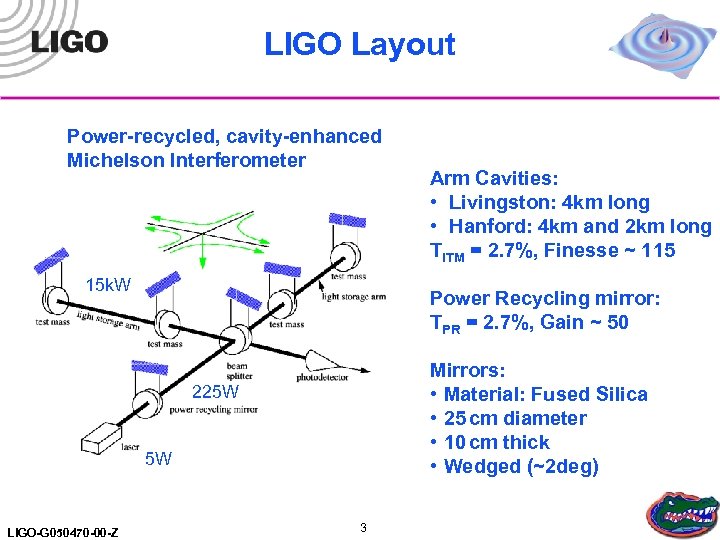 LIGO Layout Power-recycled, cavity-enhanced Michelson Interferometer 15 k. W Power Recycling mirror: TPR = 2. 7%, Gain ~ 50 Mirrors: • Material: Fused Silica • 25 cm diameter • 10 cm thick • Wedged (~2 deg) 225 W 5 W LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z Arm Cavities: • Livingston: 4 km long • Hanford: 4 km and 2 km long TITM = 2. 7%, Finesse ~ 115 3
LIGO Layout Power-recycled, cavity-enhanced Michelson Interferometer 15 k. W Power Recycling mirror: TPR = 2. 7%, Gain ~ 50 Mirrors: • Material: Fused Silica • 25 cm diameter • 10 cm thick • Wedged (~2 deg) 225 W 5 W LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z Arm Cavities: • Livingston: 4 km long • Hanford: 4 km and 2 km long TITM = 2. 7%, Finesse ~ 115 3
 Seismic Isolation Optics suspension: § Single steel wire pendulum LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 4
Seismic Isolation Optics suspension: § Single steel wire pendulum LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 4
 Seismic Isolation Optics suspension: § Single steel wire pendulum » Normal modes: – – – Pendulum: ~0. 74 Hz Yaw mode: ~0. 5 Hz Pitch mode: ~0. 6 Hz Roll mode: ~18 Hz Violin mode: ~345 Hz § Coil-magnet actuation » Magnet on optic » Coil on support frame » Includes shadow sensor LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 5
Seismic Isolation Optics suspension: § Single steel wire pendulum » Normal modes: – – – Pendulum: ~0. 74 Hz Yaw mode: ~0. 5 Hz Pitch mode: ~0. 6 Hz Roll mode: ~18 Hz Violin mode: ~345 Hz § Coil-magnet actuation » Magnet on optic » Coil on support frame » Includes shadow sensor LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 5
 Seismic Isolation Optics suspension: § Single steel wire pendulum » Normal modes: – – – Pendulum: ~0. 74 Hz Yaw mode: ~0. 5 Hz Pitch mode: ~0. 6 Hz Roll mode: ~18 Hz Violin mode: ~340 Hz § Coil-magnet actuation » Magnet on optic » Coil on support frame » Includes shadow sensor LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 6
Seismic Isolation Optics suspension: § Single steel wire pendulum » Normal modes: – – – Pendulum: ~0. 74 Hz Yaw mode: ~0. 5 Hz Pitch mode: ~0. 6 Hz Roll mode: ~18 Hz Violin mode: ~340 Hz § Coil-magnet actuation » Magnet on optic » Coil on support frame » Includes shadow sensor LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 6
 Seismic Isolation § Vibration Isolation System: » 4 layer passive isolation stack LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 7
Seismic Isolation § Vibration Isolation System: » 4 layer passive isolation stack LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 7
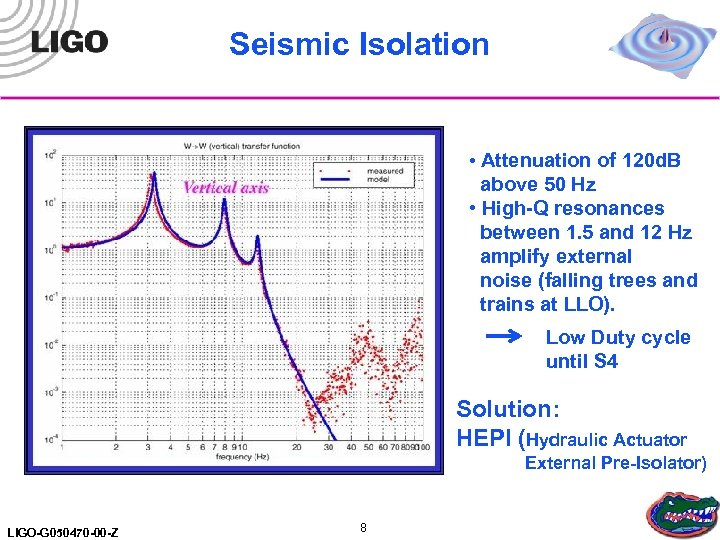 Seismic Isolation • Attenuation of 120 d. B above 50 Hz • High-Q resonances between 1. 5 and 12 Hz amplify external noise (falling trees and trains at LLO). Low Duty cycle until S 4 Solution: HEPI (Hydraulic Actuator External Pre-Isolator) LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 8
Seismic Isolation • Attenuation of 120 d. B above 50 Hz • High-Q resonances between 1. 5 and 12 Hz amplify external noise (falling trees and trains at LLO). Low Duty cycle until S 4 Solution: HEPI (Hydraulic Actuator External Pre-Isolator) LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 8
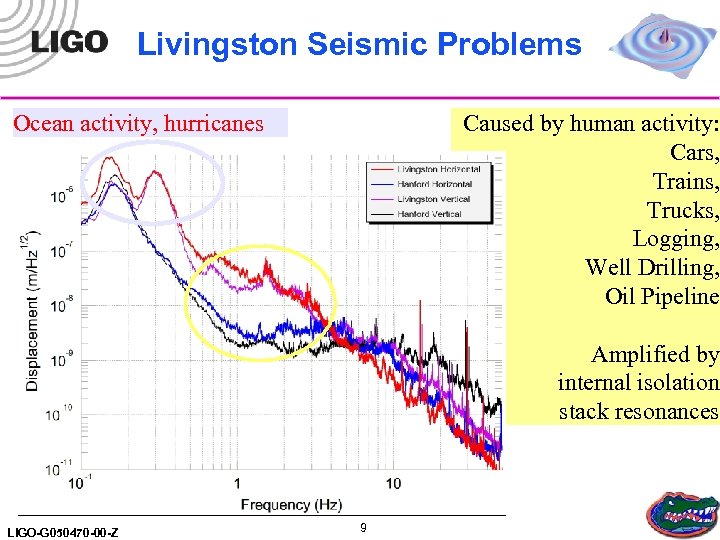 Livingston Seismic Problems Caused by human activity: Cars, Trains, Trucks, Logging, Well Drilling, Oil Pipeline Ocean activity, hurricanes Amplified by internal isolation stack resonances 9 LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 9
Livingston Seismic Problems Caused by human activity: Cars, Trains, Trucks, Logging, Well Drilling, Oil Pipeline Ocean activity, hurricanes Amplified by internal isolation stack resonances 9 LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 9
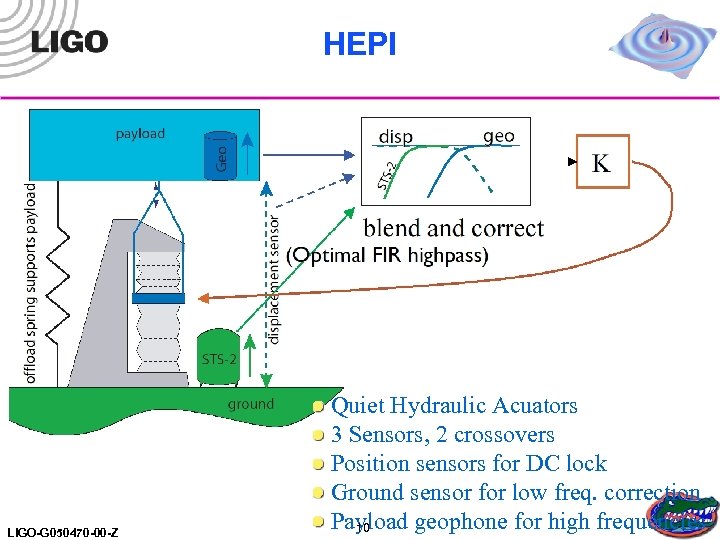 HEPI LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z Quiet Hydraulic Acuators 3 Sensors, 2 crossovers Position sensors for DC lock Ground sensor for low freq. correction Payload geophone for high frequencies 10
HEPI LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z Quiet Hydraulic Acuators 3 Sensors, 2 crossovers Position sensors for DC lock Ground sensor for low freq. correction Payload geophone for high frequencies 10
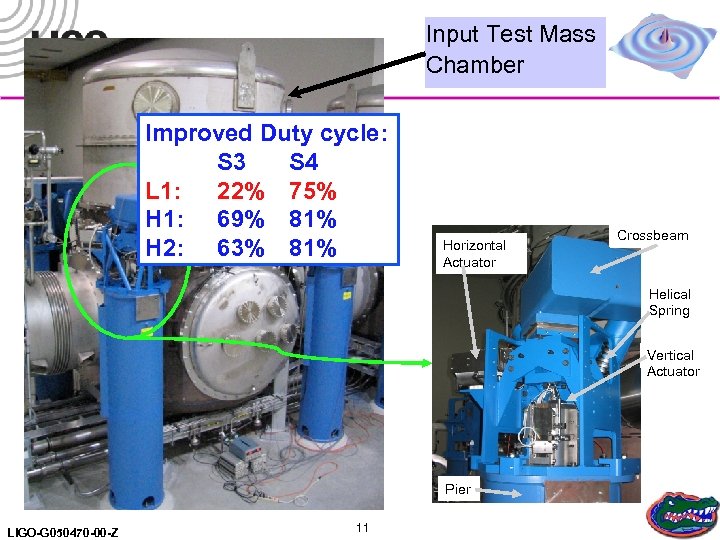 Input Test Mass Chamber Improved Duty cycle: S 3 S 4 L 1: 22% 75% H 1: 69% 81% H 2: 63% 81% Horizontal Actuator Crossbeam Helical Spring Vertical Actuator Pier LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 11
Input Test Mass Chamber Improved Duty cycle: S 3 S 4 L 1: 22% 75% H 1: 69% 81% H 2: 63% 81% Horizontal Actuator Crossbeam Helical Spring Vertical Actuator Pier LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 11
 Wavefront Sensing § System measures & controls mirror (core optic) pitch & yaw angles » Complication: each sensor is sensitive to alignment of multiple mirrors » Before and during S 4, the servo bandwidths was very low » Current status: Mixing of control signals is carefully tuned to decouple the WFS channels from each other » Increased gain and bandwidth (2 -4 Hz for ITM and ETM) ØMain benefit: reduces the orthogonal phase signal at the anti-symmetric port (ASI), allowing higher power operation LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 12
Wavefront Sensing § System measures & controls mirror (core optic) pitch & yaw angles » Complication: each sensor is sensitive to alignment of multiple mirrors » Before and during S 4, the servo bandwidths was very low » Current status: Mixing of control signals is carefully tuned to decouple the WFS channels from each other » Increased gain and bandwidth (2 -4 Hz for ITM and ETM) ØMain benefit: reduces the orthogonal phase signal at the anti-symmetric port (ASI), allowing higher power operation LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 12
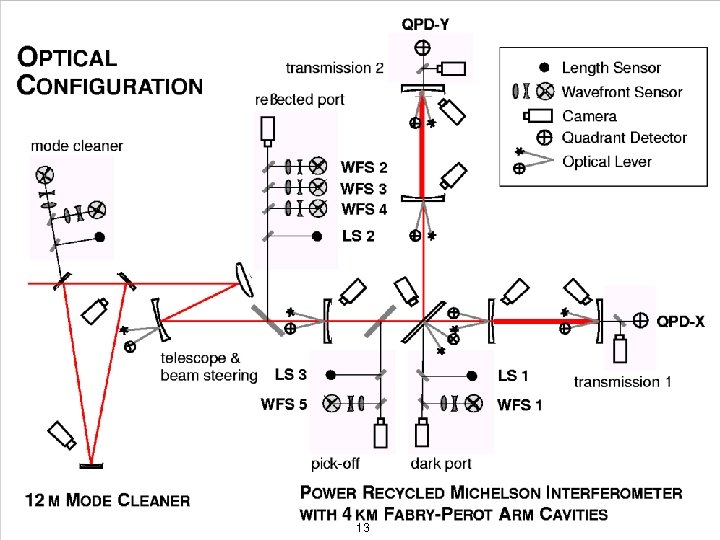 LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 13
LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 13
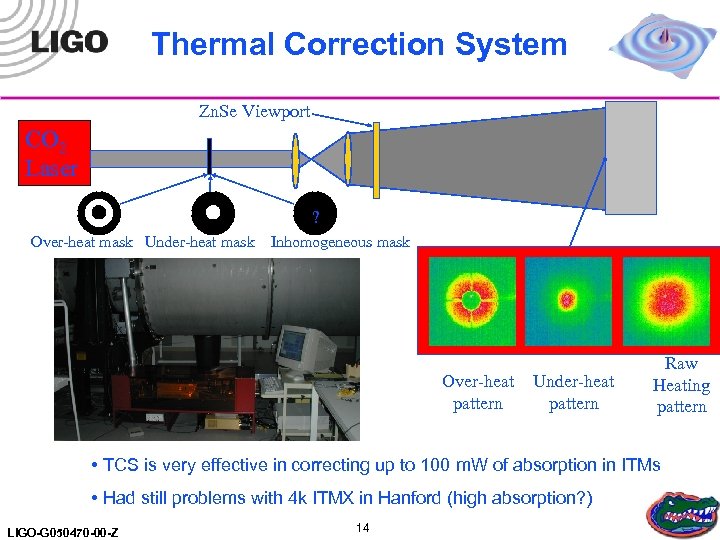 Thermal Correction System Zn. Se Viewport CO 2 Laser ? Over-heat mask Under-heat mask Inhomogeneous mask Over-heat pattern Under-heat pattern Raw Heating pattern • TCS is very effective in correcting up to 100 m. W of absorption in ITMs • Had still problems with 4 k ITMX in Hanford (high absorption? ) LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 14
Thermal Correction System Zn. Se Viewport CO 2 Laser ? Over-heat mask Under-heat mask Inhomogeneous mask Over-heat pattern Under-heat pattern Raw Heating pattern • TCS is very effective in correcting up to 100 m. W of absorption in ITMs • Had still problems with 4 k ITMX in Hanford (high absorption? ) LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 14
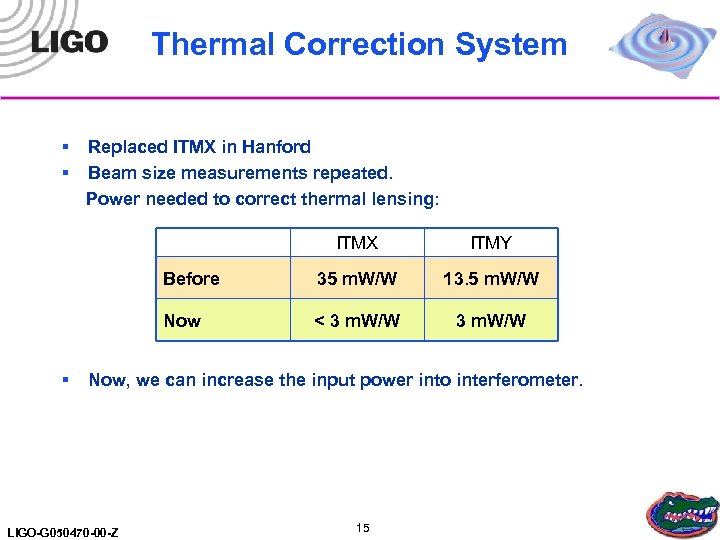 Thermal Correction System § § Replaced ITMX in Hanford Beam size measurements repeated. Power needed to correct thermal lensing: ITMX Before 35 m. W/W 13. 5 m. W/W Now § ITMY < 3 m. W/W Now, we can increase the input power into interferometer. LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 15
Thermal Correction System § § Replaced ITMX in Hanford Beam size measurements repeated. Power needed to correct thermal lensing: ITMX Before 35 m. W/W 13. 5 m. W/W Now § ITMY < 3 m. W/W Now, we can increase the input power into interferometer. LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 15
 Laser Situation Hanford: H 1: § Laser replaced in April 2004 § Power output: 11 W (without any degradation since April 04) H 2: § Original laser, running since October 1998 § Replaced Master laser early this year § Power output: 7 W (scheduled for replacement soon) L 1: LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 16
Laser Situation Hanford: H 1: § Laser replaced in April 2004 § Power output: 11 W (without any degradation since April 04) H 2: § Original laser, running since October 1998 § Replaced Master laser early this year § Power output: 7 W (scheduled for replacement soon) L 1: LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 16
 Hardware Status Summary: § Seismic Isolation now active (HEPI) » Improved duty cycle § Wavefront Sensors tuned and activated » Larger bandwidth in control loops » Enables higher power operation § Thermal Correction System installed and “dirty” mirror replaced » Enables higher power operation LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 17
Hardware Status Summary: § Seismic Isolation now active (HEPI) » Improved duty cycle § Wavefront Sensors tuned and activated » Larger bandwidth in control loops » Enables higher power operation § Thermal Correction System installed and “dirty” mirror replaced » Enables higher power operation LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 17
 Data Runs S 1 run: 17 days (August / September 2002) S 2 run: 59 days (February—April 2003) S 3 run: 70 days (October 2003 – January 2004) S 4 run: 50 days (February – March 2005) LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 18
Data Runs S 1 run: 17 days (August / September 2002) S 2 run: 59 days (February—April 2003) S 3 run: 70 days (October 2003 – January 2004) S 4 run: 50 days (February – March 2005) LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 18
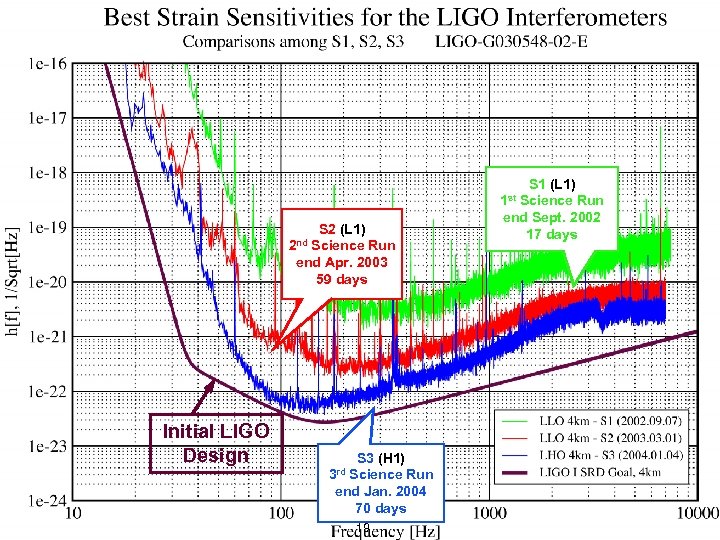 Sensitivities S 1 (L 1) Science Run end Sept. 2002 17 days 1 st S 2 (L 1) Science Run end Apr. 2003 59 days 2 nd Initial LIGO Design S 3 (H 1) Science Run end Jan. 2004 70 days 3 rd LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 19
Sensitivities S 1 (L 1) Science Run end Sept. 2002 17 days 1 st S 2 (L 1) Science Run end Apr. 2003 59 days 2 nd Initial LIGO Design S 3 (H 1) Science Run end Jan. 2004 70 days 3 rd LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 19
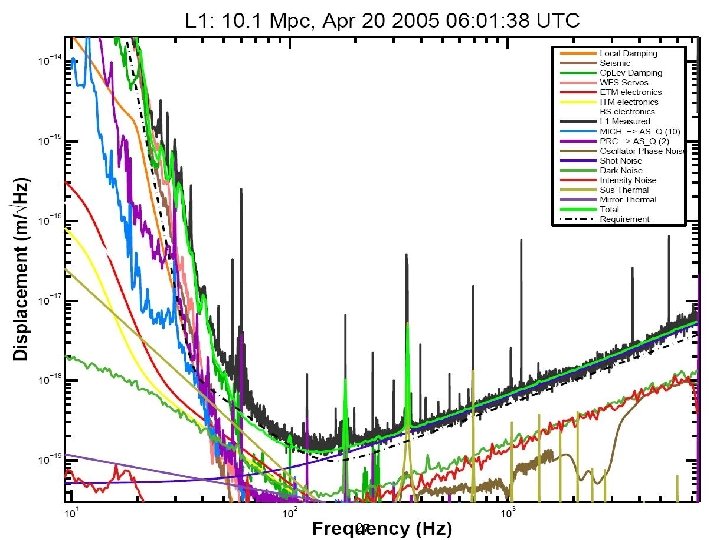
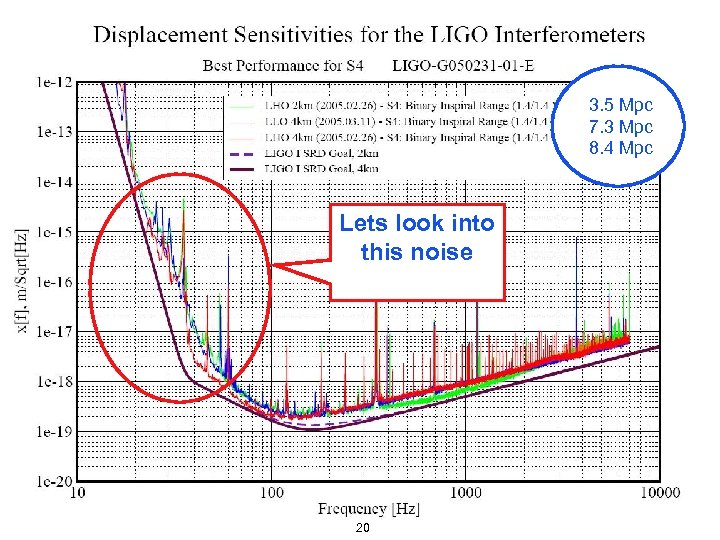 3. 5 Mpc 7. 3 Mpc 8. 4 Mpc Lets look into this noise LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 20
3. 5 Mpc 7. 3 Mpc 8. 4 Mpc Lets look into this noise LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 20
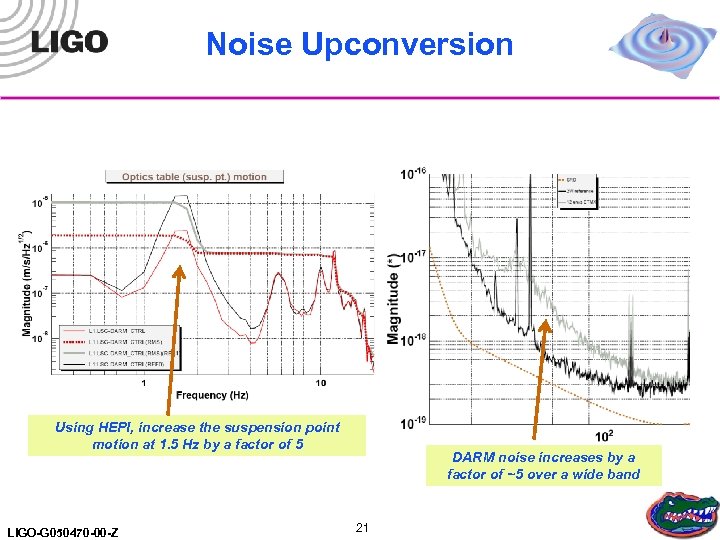 Noise Upconversion Using HEPI, increase the suspension point motion at 1. 5 Hz by a factor of 5 LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z DARM noise increases by a factor of ~5 over a wide band 21
Noise Upconversion Using HEPI, increase the suspension point motion at 1. 5 Hz by a factor of 5 LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z DARM noise increases by a factor of ~5 over a wide band 21
 Data Analysis § Binary systems » Neutron star – Neutron star » Black hole – Black hole § Periodic Sources » Rotating pulsars § “Burst” Sources » Supernovae » Gamma ray bursters » ? ? ? § Stochastic » Big Bang Background » Cosmic Strings LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z BANG! 22
Data Analysis § Binary systems » Neutron star – Neutron star » Black hole – Black hole § Periodic Sources » Rotating pulsars § “Burst” Sources » Supernovae » Gamma ray bursters » ? ? ? § Stochastic » Big Bang Background » Cosmic Strings LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z BANG! 22
 Science § S 1: Aug. 23 – Sep. 9 2002, 17 days » Setting upper limits on the strength of periodic gravitational waves from PSR J 1939+2134 using the first science data from the GEO 600 and LIGO detectors, Phys. Rev. D 69: 082004 (2004). » First upper limits from LIGO on gravitational wave bursts, Phys. Rev. D 69: 102001 (2004). » Analysis of LIGO data for gravitational waves from binary neutron stars, Phys. Rev. D 69: 122001 (2004). » Analysis of first LIGO science data for stochastic gravitational waves, Phys. Rev. D 69: 122004 (2004). LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 23
Science § S 1: Aug. 23 – Sep. 9 2002, 17 days » Setting upper limits on the strength of periodic gravitational waves from PSR J 1939+2134 using the first science data from the GEO 600 and LIGO detectors, Phys. Rev. D 69: 082004 (2004). » First upper limits from LIGO on gravitational wave bursts, Phys. Rev. D 69: 102001 (2004). » Analysis of LIGO data for gravitational waves from binary neutron stars, Phys. Rev. D 69: 122001 (2004). » Analysis of first LIGO science data for stochastic gravitational waves, Phys. Rev. D 69: 122004 (2004). LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 23
 Science § S 2 Feb. 14 – Apr. 14, 2003, 59 days » Limits on gravitational-wave emission from selected pulsars using LIGO data, Phys. Rev. Lett 94: 181103 (2004). » Search for gravitational waves associated with the gamma ray burst GRB 030329 using the LIGO detectors, Phys. Rev. D, Vol. 72, 042002 (2005) » Search for gravitational waves from galactic and extra-galactic binary neutron stars, gr-qc 0505041 (2005) » Search for Gravitational Waves from Primordial Black Hole Binary Coalescences in the Galactic Halo, gr-qc 0505042 (2005) » Upper limits from the LIGO and TAMA detectors on the rate of gravitational-wave bursts, gr-qc 0507081 » Upper limits on gravitational wave bursts in LIGO’s second science run, gr-qc 0505029 (2005) § S 3: October 31, 2003 – January 9, 2004, 70 days § S 4: February 2, 2005 – March 23, 2005, 50 days LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 24
Science § S 2 Feb. 14 – Apr. 14, 2003, 59 days » Limits on gravitational-wave emission from selected pulsars using LIGO data, Phys. Rev. Lett 94: 181103 (2004). » Search for gravitational waves associated with the gamma ray burst GRB 030329 using the LIGO detectors, Phys. Rev. D, Vol. 72, 042002 (2005) » Search for gravitational waves from galactic and extra-galactic binary neutron stars, gr-qc 0505041 (2005) » Search for Gravitational Waves from Primordial Black Hole Binary Coalescences in the Galactic Halo, gr-qc 0505042 (2005) » Upper limits from the LIGO and TAMA detectors on the rate of gravitational-wave bursts, gr-qc 0507081 » Upper limits on gravitational wave bursts in LIGO’s second science run, gr-qc 0505029 (2005) § S 3: October 31, 2003 – January 9, 2004, 70 days § S 4: February 2, 2005 – March 23, 2005, 50 days LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 24
 S 5 -Run § S 5 goal: » one year’s data of coincident operation at the science goal sensitivity § Current Plan (LSC meeting in August) » Staggered start to S 5 » L 1 was expected to start with S 5 on Oct 21 » Expect Hurricane related delays: – LLO is intact, up, and running – No Hotels for visiting scientists and local stuff has some problems at their homes (power outages, flooding, school closings, etc. ) » H 2 start Nov 4 » H 1 schedule still uncertain—recovery from Test Mass replacement § Performance goals for S 5 » H 1, L 1 over 10 Mpc inspiral range, H 2 over 5 Mpc » Overall “Science content” ~ 100 times S 4 LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 25
S 5 -Run § S 5 goal: » one year’s data of coincident operation at the science goal sensitivity § Current Plan (LSC meeting in August) » Staggered start to S 5 » L 1 was expected to start with S 5 on Oct 21 » Expect Hurricane related delays: – LLO is intact, up, and running – No Hotels for visiting scientists and local stuff has some problems at their homes (power outages, flooding, school closings, etc. ) » H 2 start Nov 4 » H 1 schedule still uncertain—recovery from Test Mass replacement § Performance goals for S 5 » H 1, L 1 over 10 Mpc inspiral range, H 2 over 5 Mpc » Overall “Science content” ~ 100 times S 4 LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 25
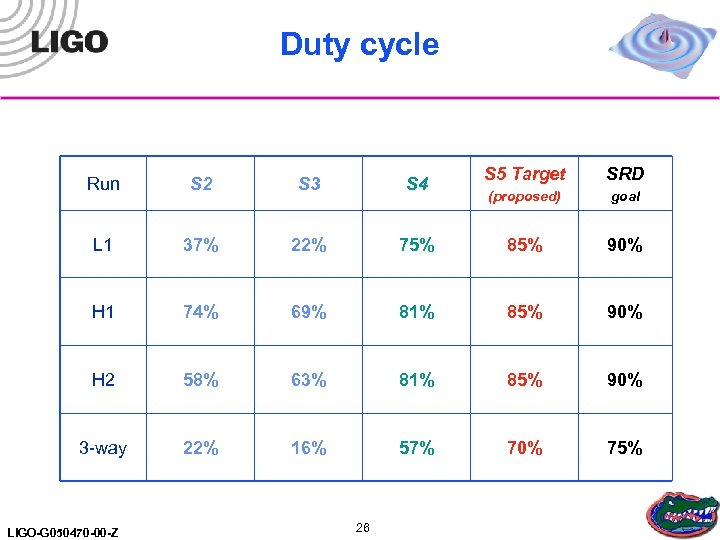 Duty cycle S 5 Target SRD (proposed) goal 75% 85% 90% 69% 81% 85% 90% 58% 63% 81% 85% 90% 22% 16% 57% 70% 75% Run S 2 S 3 S 4 L 1 37% 22% H 1 74% H 2 3 -way LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 26
Duty cycle S 5 Target SRD (proposed) goal 75% 85% 90% 69% 81% 85% 90% 58% 63% 81% 85% 90% 22% 16% 57% 70% 75% Run S 2 S 3 S 4 L 1 37% 22% H 1 74% H 2 3 -way LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 26
 LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 27
LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 27
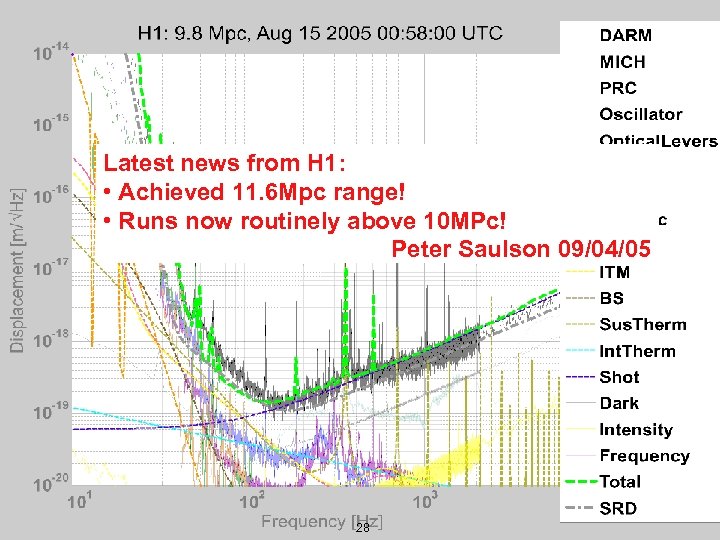 Latest news from H 1: • Achieved 11. 6 Mpc range! • Runs now routinely above 10 MPc! Peter Saulson 09/04/05 LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 28
Latest news from H 1: • Achieved 11. 6 Mpc range! • Runs now routinely above 10 MPc! Peter Saulson 09/04/05 LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 28
 LIGO Science Collaboration A family photo LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 29
LIGO Science Collaboration A family photo LIGO-G 050470 -00 -Z 29


