24a308e8289d42cac1c0c45ef4e9fe48.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Lighting and Full-Duplex Communicatio using Optical LED technology Dr. Fernando EE 8114 Charles Lim Nov. 24, 2003
Lighting and Full-Duplex Communicatio using Optical LED technology Dr. Fernando EE 8114 Charles Lim Nov. 24, 2003
 The LED Advantage Consumes only one fourth or less power than incandescent bulbs. n 25, 000 to 50, 000 continuous hours of life n No RF EMI n Very secure compared to RF n Robust compared to other lighting devices n High data rate capability n
The LED Advantage Consumes only one fourth or less power than incandescent bulbs. n 25, 000 to 50, 000 continuous hours of life n No RF EMI n Very secure compared to RF n Robust compared to other lighting devices n High data rate capability n
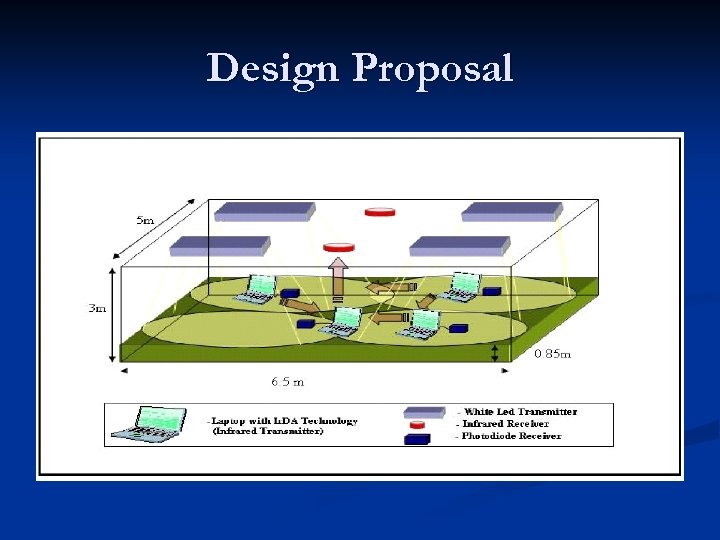 Design Proposal
Design Proposal
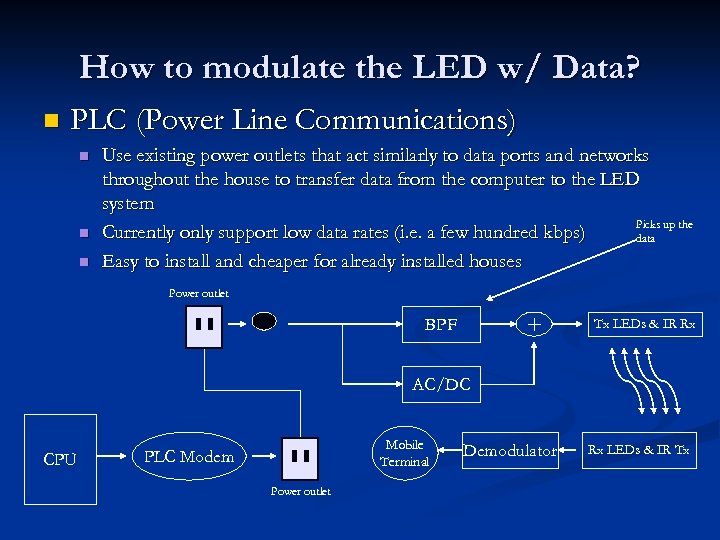 How to modulate the LED w/ Data? n PLC (Power Line Communications) n n n Use existing power outlets that act similarly to data ports and networks throughout the house to transfer data from the computer to the LED system Picks up the Currently only support low data rates (i. e. a few hundred kbps) data Easy to install and cheaper for already installed houses Power outlet BPF Tx LEDs & IR Rx AC/DC CPU Mobile Terminal PLC Modem Power outlet Demodulator Rx LEDs & IR Tx
How to modulate the LED w/ Data? n PLC (Power Line Communications) n n n Use existing power outlets that act similarly to data ports and networks throughout the house to transfer data from the computer to the LED system Picks up the Currently only support low data rates (i. e. a few hundred kbps) data Easy to install and cheaper for already installed houses Power outlet BPF Tx LEDs & IR Rx AC/DC CPU Mobile Terminal PLC Modem Power outlet Demodulator Rx LEDs & IR Tx
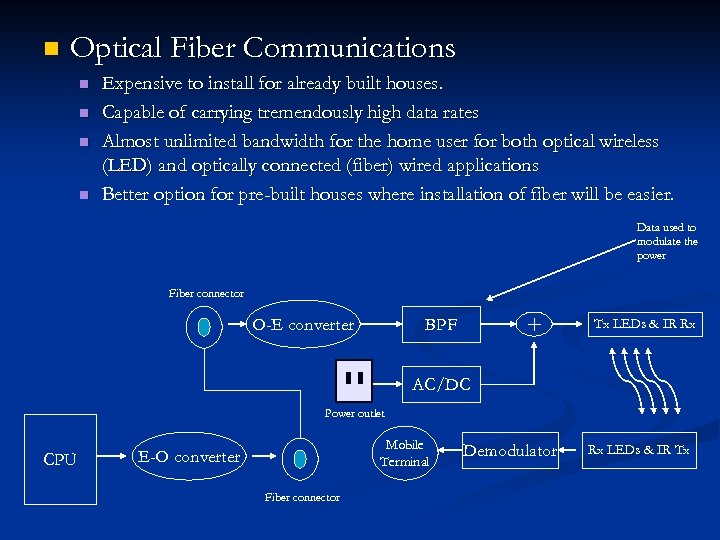 n Optical Fiber Communications n n Expensive to install for already built houses. Capable of carrying tremendously high data rates Almost unlimited bandwidth for the home user for both optical wireless (LED) and optically connected (fiber) wired applications Better option for pre-built houses where installation of fiber will be easier. Data used to modulate the power Fiber connector BPF O-E converter Tx LEDs & IR Rx AC/DC Power outlet CPU Mobile Terminal E-O converter Fiber connector Demodulator Rx LEDs & IR Tx
n Optical Fiber Communications n n Expensive to install for already built houses. Capable of carrying tremendously high data rates Almost unlimited bandwidth for the home user for both optical wireless (LED) and optically connected (fiber) wired applications Better option for pre-built houses where installation of fiber will be easier. Data used to modulate the power Fiber connector BPF O-E converter Tx LEDs & IR Rx AC/DC Power outlet CPU Mobile Terminal E-O converter Fiber connector Demodulator Rx LEDs & IR Tx
 Factors affecting LED systems Thermal Temperature n Packaging Type and System Integration n Multi-path Dispersion n Reflectivity of the Room n Downlink/Uplink Data rate n LED Power n Need for Channel Equalizer n
Factors affecting LED systems Thermal Temperature n Packaging Type and System Integration n Multi-path Dispersion n Reflectivity of the Room n Downlink/Uplink Data rate n LED Power n Need for Channel Equalizer n
 n Thermal Management n n n Packaging Type n n n For LEDs to achieve long lifetimes in the range of 25, 000 to 50, 000 hours, the temperature of the junction must be under 75°C. Also, once the junction temperature reaches over 125°C, problems with LEDs become a lot more common. Current packages have 300°C. If assume room temperature 25°C, then minimum package thermal resistance is 50°C. System Integration n n Unlike incandescent bulbs, LEDs do not radiate wasted heat away from the part. It requires the device be properly cooled. Design and installation of not only LEDs but the cooling system is critical as well for LED systems.
n Thermal Management n n n Packaging Type n n n For LEDs to achieve long lifetimes in the range of 25, 000 to 50, 000 hours, the temperature of the junction must be under 75°C. Also, once the junction temperature reaches over 125°C, problems with LEDs become a lot more common. Current packages have 300°C. If assume room temperature 25°C, then minimum package thermal resistance is 50°C. System Integration n n Unlike incandescent bulbs, LEDs do not radiate wasted heat away from the part. It requires the device be properly cooled. Design and installation of not only LEDs but the cooling system is critical as well for LED systems.
 n Multi-Path Dispersion n n n Reflectivity of the room n n n Main issue in optical wireless technology Due to the large amount of lighting LEDs Minimal interference from the white LEDs and IR LED due to spectral separation Photodiodes also has spectral separation to minimize interference IR and LED Tx linewidth chosen such that minimal interference with photodiodes. Higher reflectivity means more dispersion Depends on color and reflectivity of materials inside room Downlink/Uplink data rate n n n Receiver and LED system circuitry determined by the downlink bandwidth Downlink easier to design, larger power from lighting LEDs Uplink data rate cannot be very high due to limited IR power Uplink bandwidth restriction determined by IR transmitter and receiver design. Higher data rates = Higher Cost
n Multi-Path Dispersion n n n Reflectivity of the room n n n Main issue in optical wireless technology Due to the large amount of lighting LEDs Minimal interference from the white LEDs and IR LED due to spectral separation Photodiodes also has spectral separation to minimize interference IR and LED Tx linewidth chosen such that minimal interference with photodiodes. Higher reflectivity means more dispersion Depends on color and reflectivity of materials inside room Downlink/Uplink data rate n n n Receiver and LED system circuitry determined by the downlink bandwidth Downlink easier to design, larger power from lighting LEDs Uplink data rate cannot be very high due to limited IR power Uplink bandwidth restriction determined by IR transmitter and receiver design. Higher data rates = Higher Cost
 n LED Power n n n Higher Power allows for faster data rates Limitations in power output design due to government restrictions Channel Equalizer n n n n To achieve better data rates and reliability a dynamic channel equalizer is required. Use LMS digital signal processing algorithm LMS block is right after modulator and demodulator for both IR and light LEDs Dynamically adjust downlink/uplink bit rates depending on current room BER Increases reliability of system Mobility is increased Higher Efficiency
n LED Power n n n Higher Power allows for faster data rates Limitations in power output design due to government restrictions Channel Equalizer n n n n To achieve better data rates and reliability a dynamic channel equalizer is required. Use LMS digital signal processing algorithm LMS block is right after modulator and demodulator for both IR and light LEDs Dynamically adjust downlink/uplink bit rates depending on current room BER Increases reliability of system Mobility is increased Higher Efficiency
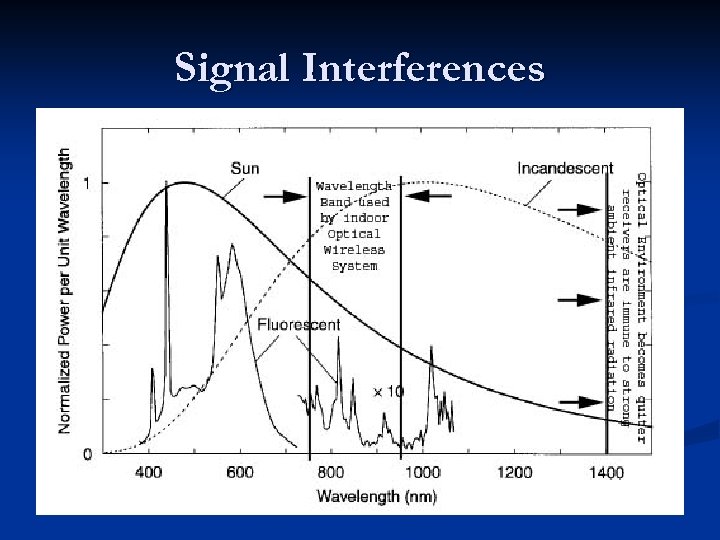 Signal Interferences
Signal Interferences
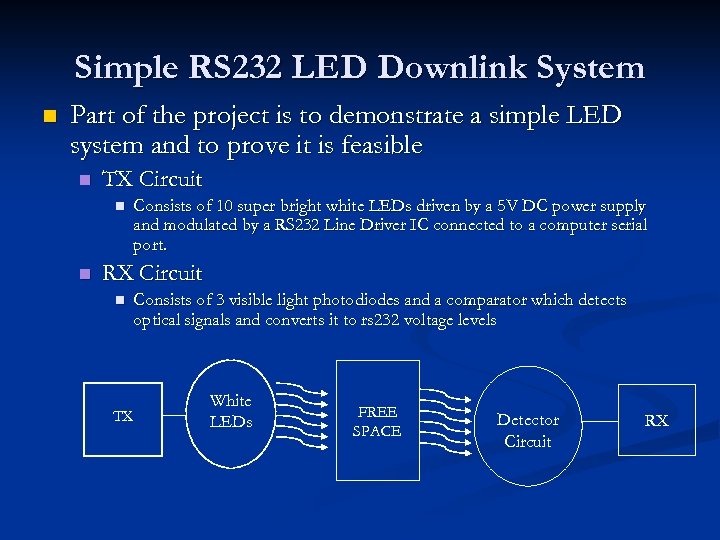 Simple RS 232 LED Downlink System n Part of the project is to demonstrate a simple LED system and to prove it is feasible n TX Circuit n n Consists of 10 super bright white LEDs driven by a 5 V DC power supply and modulated by a RS 232 Line Driver IC connected to a computer serial port. RX Circuit n Consists of 3 visible light photodiodes and a comparator which detects optical signals and converts it to rs 232 voltage levels TX White LEDs FREE SPACE Detector Circuit RX
Simple RS 232 LED Downlink System n Part of the project is to demonstrate a simple LED system and to prove it is feasible n TX Circuit n n Consists of 10 super bright white LEDs driven by a 5 V DC power supply and modulated by a RS 232 Line Driver IC connected to a computer serial port. RX Circuit n Consists of 3 visible light photodiodes and a comparator which detects optical signals and converts it to rs 232 voltage levels TX White LEDs FREE SPACE Detector Circuit RX
 Conclusion n n This project achieves Lighting and communication using Optical wireless communication. Through more research and design, optical wireless communications will eventually achieve: n n n Reliable high data rate transfers No RF interference Mobility and security Minimal multi-path distortion Higher power efficiency, lower transmit and receive power Integrating Lighting and communication for home
Conclusion n n This project achieves Lighting and communication using Optical wireless communication. Through more research and design, optical wireless communications will eventually achieve: n n n Reliable high data rate transfers No RF interference Mobility and security Minimal multi-path distortion Higher power efficiency, lower transmit and receive power Integrating Lighting and communication for home
 Conclusion…… Future of Wireless communication ……….
Conclusion…… Future of Wireless communication ……….
![References n [1] Balasingam, Charles Lim, Gajendran Wignarajah, Jeyacanthan Nesarajah, Sarmila Selvaratnam, “Lighting and References n [1] Balasingam, Charles Lim, Gajendran Wignarajah, Jeyacanthan Nesarajah, Sarmila Selvaratnam, “Lighting and](https://present5.com/presentation/24a308e8289d42cac1c0c45ef4e9fe48/image-14.jpg) References n [1] Balasingam, Charles Lim, Gajendran Wignarajah, Jeyacanthan Nesarajah, Sarmila Selvaratnam, “Lighting and Communication from the same source”, 2003 ICUE (International Conference for Upcoming Engineers) n [2] Toshihiko Komine, Masao Nakagawa, “Integrated system of white LED visiblelight communication and power-line communication”, 2002 IEEE n [3] Yuichi Tanaka, Shinichirou Haruyama, Masao Nakagawa, “Wireless Optical Transmissions with white colored LED for Wireless Home Links” , 2000 IEEE n [4] Tsunemasa Taguchi, Yamaguchi University, “Light Gets Solid”, OE Magazine, The Monthly Publication of SPIE October 2003 n [5] Srinath Aanegola, Jim Petroski, Emil Radkov, GELcore LLC, “Let There Be Light”, OE Magazine, The Monthly Publication of SPIE October 2003
References n [1] Balasingam, Charles Lim, Gajendran Wignarajah, Jeyacanthan Nesarajah, Sarmila Selvaratnam, “Lighting and Communication from the same source”, 2003 ICUE (International Conference for Upcoming Engineers) n [2] Toshihiko Komine, Masao Nakagawa, “Integrated system of white LED visiblelight communication and power-line communication”, 2002 IEEE n [3] Yuichi Tanaka, Shinichirou Haruyama, Masao Nakagawa, “Wireless Optical Transmissions with white colored LED for Wireless Home Links” , 2000 IEEE n [4] Tsunemasa Taguchi, Yamaguchi University, “Light Gets Solid”, OE Magazine, The Monthly Publication of SPIE October 2003 n [5] Srinath Aanegola, Jim Petroski, Emil Radkov, GELcore LLC, “Let There Be Light”, OE Magazine, The Monthly Publication of SPIE October 2003


