61b699182fb8d41691bcd877ebcc4c3a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 89
 Life Course Health Development: A Transformative Framework To Improve Children’s Health Neal Halfon, MD, MPH UCLA Schools of Public Health, Medicine, Public Affairs UCLA Center for Healthier Children, Families and Communities National Center for Infancy & Early Childhood Health Policy MCHB-AIM Child & Adolescent Policy Support Center City. Mat. CH ’ 08, Albuquerque September 21, 2008 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Life Course Health Development: A Transformative Framework To Improve Children’s Health Neal Halfon, MD, MPH UCLA Schools of Public Health, Medicine, Public Affairs UCLA Center for Healthier Children, Families and Communities National Center for Infancy & Early Childhood Health Policy MCHB-AIM Child & Adolescent Policy Support Center City. Mat. CH ’ 08, Albuquerque September 21, 2008 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Goals of this Presentation n To review the evidence, importance and potential impact of the developmental origins of health and disease n To consider the strategic role that the emerging Life Course Health Development approach can play in Advancing a progression Health Policy Agenda n Enabling significant Health Systems Reform in the US n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Goals of this Presentation n To review the evidence, importance and potential impact of the developmental origins of health and disease n To consider the strategic role that the emerging Life Course Health Development approach can play in Advancing a progression Health Policy Agenda n Enabling significant Health Systems Reform in the US n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Take home Points: Power of LCHD n n Life Course Health Development (LCHD) is different than a life course approach LCHD –integrating framework n n n Connecting the disparate parts of MCH Connecting MCH to rest of health and human development Leverages MCH and Positions and Prioritizes MCH policy Provides a new Operating Logic for Transforming the Health System Powerful analytic model for solving MCH problems Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Take home Points: Power of LCHD n n Life Course Health Development (LCHD) is different than a life course approach LCHD –integrating framework n n n Connecting the disparate parts of MCH Connecting MCH to rest of health and human development Leverages MCH and Positions and Prioritizes MCH policy Provides a new Operating Logic for Transforming the Health System Powerful analytic model for solving MCH problems Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 From Lifespan to LCHD Lifespan models – connect the dots- linking early life to later life n Life stage models – periods of psychological development n Life-course models – are concerned with patterns and pathways that connect the dots between early and later life n Life Course Health Development modelsn Connect the dots n Describe the pathways or heath trajectories n Address the mechanisms that determine or influence health trajectories n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
From Lifespan to LCHD Lifespan models – connect the dots- linking early life to later life n Life stage models – periods of psychological development n Life-course models – are concerned with patterns and pathways that connect the dots between early and later life n Life Course Health Development modelsn Connect the dots n Describe the pathways or heath trajectories n Address the mechanisms that determine or influence health trajectories n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 LCHD Where We Have Been Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
LCHD Where We Have Been Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
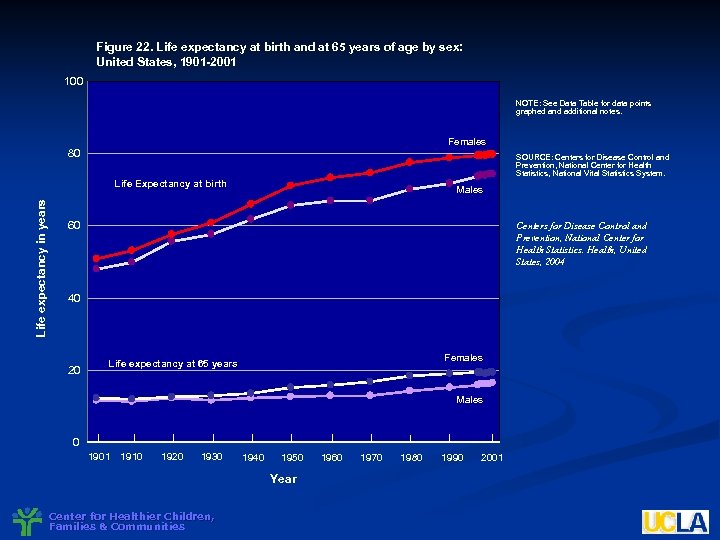 Figure 22. Life expectancy at birth and at 65 years of age by sex: United States, 1901 -2001 100 NOTE: See Data Table for data points graphed and additional notes. Females 80 SOURCE: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. Life expectancy in years Life Expectancy at birth Males 60 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2004 40 20 Females Life expectancy at 65 years Males 0 1901 1910 1920 1930 1940 1950 Year Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities 1960 1970 1980 1990 2001
Figure 22. Life expectancy at birth and at 65 years of age by sex: United States, 1901 -2001 100 NOTE: See Data Table for data points graphed and additional notes. Females 80 SOURCE: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System. Life expectancy in years Life Expectancy at birth Males 60 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2004 40 20 Females Life expectancy at 65 years Males 0 1901 1910 1920 1930 1940 1950 Year Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities 1960 1970 1980 1990 2001
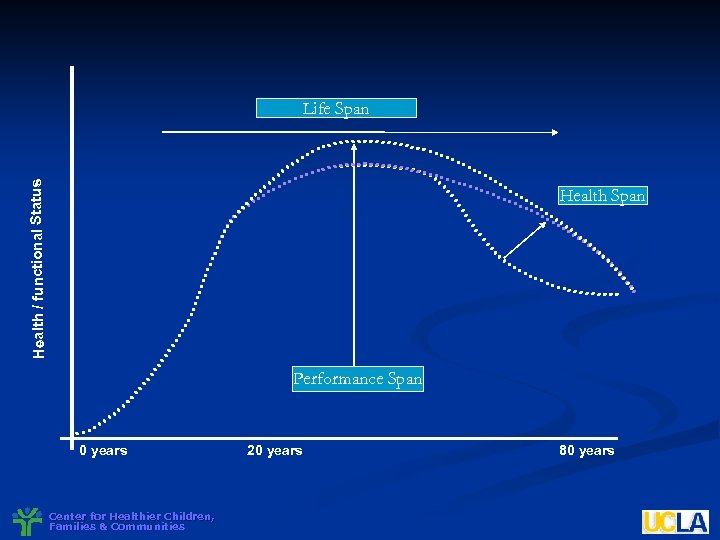 Health / functional Status Life Span Health Span Performance Span 0 years Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities 20 years 80 years
Health / functional Status Life Span Health Span Performance Span 0 years Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities 20 years 80 years
 Social/Nutritional/Epidemiological/ Developmental Shift n Social Conditions dramatically changes over this time period n n n Nature, Array, and Prevalence of Risk, Protective and Health Promoting factors Nutritional Conditions change- high sugar, high fat diets Types, prevalence, distribution of acute and chronic disease changes dramatically Developmental expectancies change Capacity of Medical Care to intervene, modify risk and treat disease Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Social/Nutritional/Epidemiological/ Developmental Shift n Social Conditions dramatically changes over this time period n n n Nature, Array, and Prevalence of Risk, Protective and Health Promoting factors Nutritional Conditions change- high sugar, high fat diets Types, prevalence, distribution of acute and chronic disease changes dramatically Developmental expectancies change Capacity of Medical Care to intervene, modify risk and treat disease Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
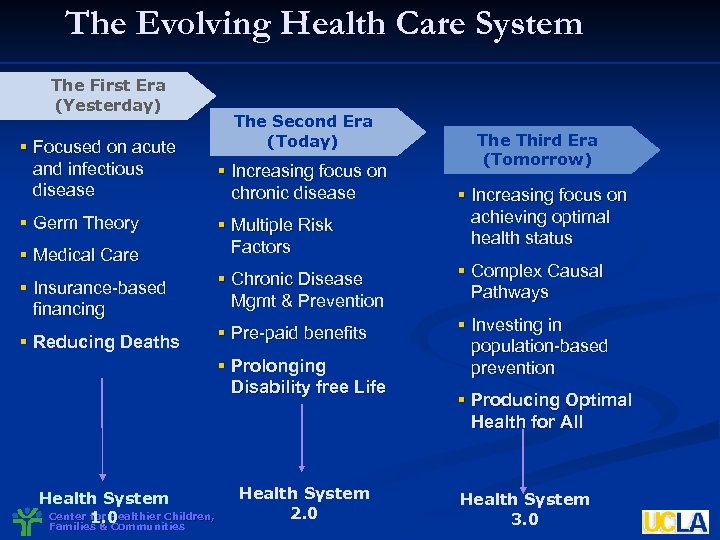 The Evolving Health Care System The First Era (Yesterday) § Focused on acute and infectious disease The Second Era (Today) § Increasing focus on chronic disease Third Era (Tomorrow) § Medical Care § Multiple Risk Factors § Increasing focus on achieving optimal health status § Insurance-based financing § Chronic Disease Mgmt & Prevention § Complex Causal Pathways § Reducing Deaths § Pre-paid benefits § Investing in population-based prevention § Germ Theory § Prolonging Disability free Life Health System Center for Healthier Children, 1. 0 Families & Communities Health System 2. 0 § Producing Optimal Health for All Health System 3. 0
The Evolving Health Care System The First Era (Yesterday) § Focused on acute and infectious disease The Second Era (Today) § Increasing focus on chronic disease Third Era (Tomorrow) § Medical Care § Multiple Risk Factors § Increasing focus on achieving optimal health status § Insurance-based financing § Chronic Disease Mgmt & Prevention § Complex Causal Pathways § Reducing Deaths § Pre-paid benefits § Investing in population-based prevention § Germ Theory § Prolonging Disability free Life Health System Center for Healthier Children, 1. 0 Families & Communities Health System 2. 0 § Producing Optimal Health for All Health System 3. 0
 2004 National Research Council and Institute of Medicine Report Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
2004 National Research Council and Institute of Medicine Report Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 IOM/NRC Definition of Children’s Health (2004) “Children’s health is the extent to which individual children or groups of children are able or enabled to (a) develop and realize their potential, (b) satisfy their needs, and (c) develop the capacities that allow them to interact successfully with their biological, physical, and social environments. ” From Children’s Health, the Nation’s Wealth, National Academies Press, 2004. Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
IOM/NRC Definition of Children’s Health (2004) “Children’s health is the extent to which individual children or groups of children are able or enabled to (a) develop and realize their potential, (b) satisfy their needs, and (c) develop the capacities that allow them to interact successfully with their biological, physical, and social environments. ” From Children’s Health, the Nation’s Wealth, National Academies Press, 2004. Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 LCHD Defines Health as a developmental process n Builds upon Ecological and Transactional models of Life Span Development n Utilizes a rapidly Expanding Evidence Base n Life Course Chronic Disease Epidemiology n Neurobiology n Early Intervention Research n Economics of Human Capital Formation n Gene-Environment/ Social Epidemiology n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
LCHD Defines Health as a developmental process n Builds upon Ecological and Transactional models of Life Span Development n Utilizes a rapidly Expanding Evidence Base n Life Course Chronic Disease Epidemiology n Neurobiology n Early Intervention Research n Economics of Human Capital Formation n Gene-Environment/ Social Epidemiology n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Health as a Developmental Process n Health is a developmental process Health develops across the life course n Health development can be represented by health trajectories n Critical/ Sensitive periods n Gene - Environment – Interaction have different impacts during different periods n Macro and Micro pathways delineate how toxic environments and risky families get under the skin n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Health as a Developmental Process n Health is a developmental process Health develops across the life course n Health development can be represented by health trajectories n Critical/ Sensitive periods n Gene - Environment – Interaction have different impacts during different periods n Macro and Micro pathways delineate how toxic environments and risky families get under the skin n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
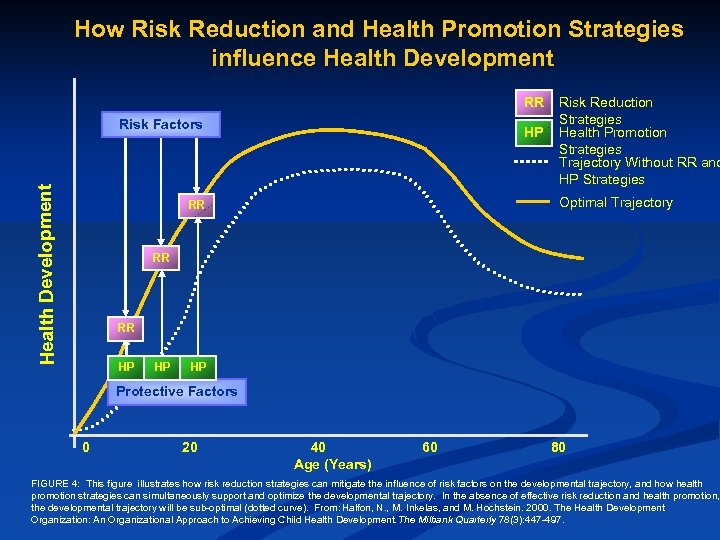 How Risk Reduction and Health Promotion Strategies influence Health Development RR Health Development Risk Factors HP Risk Reduction Strategies Health Promotion Strategies Trajectory Without RR and HP Strategies Optimal Trajectory RR RR RR HP HP HP Protective Factors 0 20 40 Age (Years) 60 80 FIGURE 4: This figure illustrates how risk reduction strategies can mitigate the influence of risk factors on the developmental trajectory, and how health promotion strategies can simultaneously support and optimize the developmental trajectory. In the absence of effective risk reduction and health promotion, the developmental trajectory will be sub-optimal (dotted curve). From: Halfon, N. , M. Inkelas, and M. Hochstein. 2000. The Health Development Organization: An Organizational Approach to Achieving Child Health Development. The Milbank Quarterly 78(3): 447 -497.
How Risk Reduction and Health Promotion Strategies influence Health Development RR Health Development Risk Factors HP Risk Reduction Strategies Health Promotion Strategies Trajectory Without RR and HP Strategies Optimal Trajectory RR RR RR HP HP HP Protective Factors 0 20 40 Age (Years) 60 80 FIGURE 4: This figure illustrates how risk reduction strategies can mitigate the influence of risk factors on the developmental trajectory, and how health promotion strategies can simultaneously support and optimize the developmental trajectory. In the absence of effective risk reduction and health promotion, the developmental trajectory will be sub-optimal (dotted curve). From: Halfon, N. , M. Inkelas, and M. Hochstein. 2000. The Health Development Organization: An Organizational Approach to Achieving Child Health Development. The Milbank Quarterly 78(3): 447 -497.
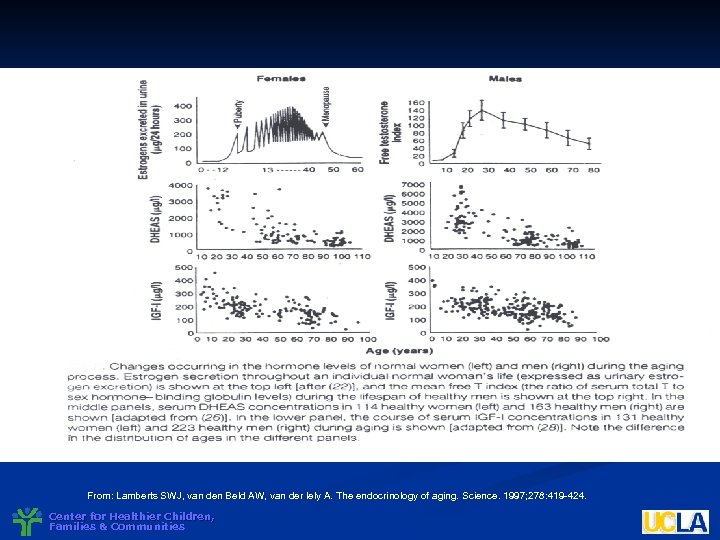 Fig. From: Lamberts SWJ, van den Beld AW, van der lely A. The endocrinology of aging. Science. 1997; 278: 419 -424. Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Fig. From: Lamberts SWJ, van den Beld AW, van der lely A. The endocrinology of aging. Science. 1997; 278: 419 -424. Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
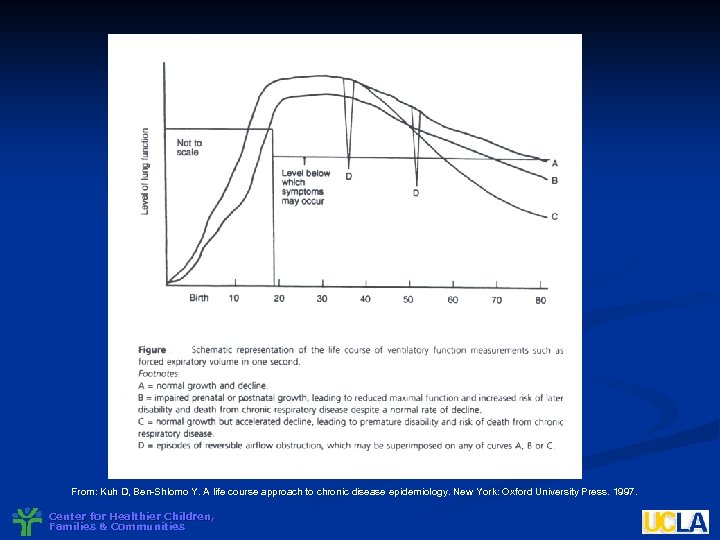 From: Kuh D, Ben-Shlomo Y. A life course approach to chronic disease epidemiology. New York: Oxford University Press. 1997. Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
From: Kuh D, Ben-Shlomo Y. A life course approach to chronic disease epidemiology. New York: Oxford University Press. 1997. Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
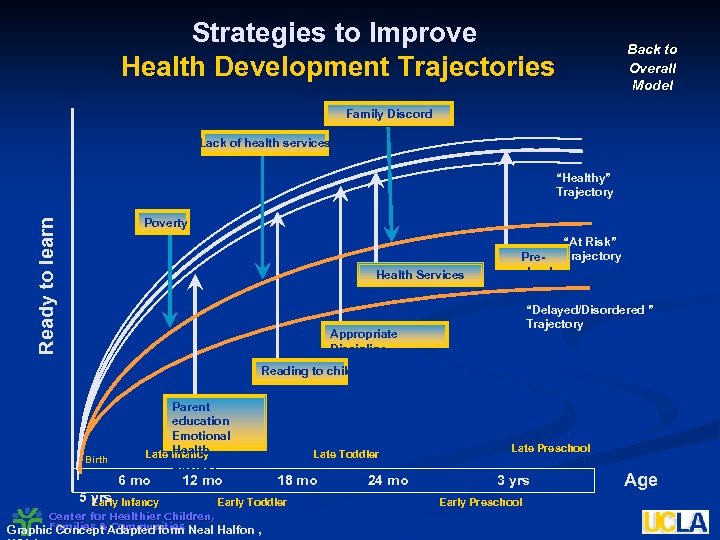 Strategies to Improve Health Development Trajectories Back to Overall Model Family Discord Lack of health services “Healthy” Trajectory Ready to learn Poverty Health Services Preschool “At Risk” Trajectory “Delayed/Disordered ” Trajectory Appropriate Discipline Reading to child Birth Parent education Emotional Health Late Infancy Literacy 6 mo 12 mo 5 yrs Infancy Early Center for Healthier Children, Late Toddler 18 mo Early Toddler Families & Communities Graphic Concept Adapted form Neal Halfon , 24 mo Late Preschool 3 yrs Early Preschool Age
Strategies to Improve Health Development Trajectories Back to Overall Model Family Discord Lack of health services “Healthy” Trajectory Ready to learn Poverty Health Services Preschool “At Risk” Trajectory “Delayed/Disordered ” Trajectory Appropriate Discipline Reading to child Birth Parent education Emotional Health Late Infancy Literacy 6 mo 12 mo 5 yrs Infancy Early Center for Healthier Children, Late Toddler 18 mo Early Toddler Families & Communities Graphic Concept Adapted form Neal Halfon , 24 mo Late Preschool 3 yrs Early Preschool Age
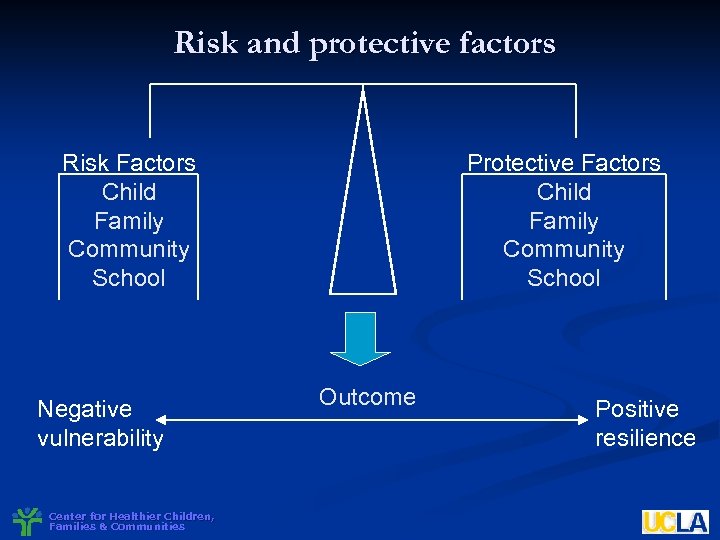 Risk and protective factors Risk Factors Child Family Community School Negative vulnerability Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Protective Factors Child Family Community School Outcome Positive resilience
Risk and protective factors Risk Factors Child Family Community School Negative vulnerability Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Protective Factors Child Family Community School Outcome Positive resilience
 LCHD Connecting the Dots Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
LCHD Connecting the Dots Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
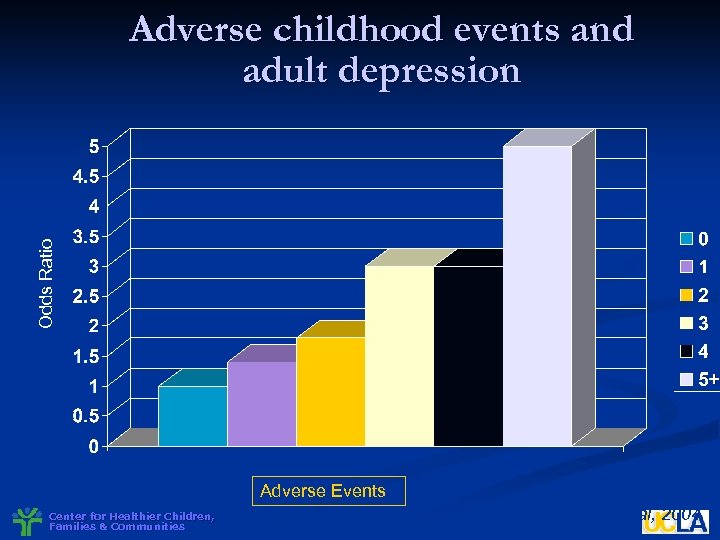 Odds Ratio Adverse childhood events and adult depression Adverse Events Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Chapman et al, 2004
Odds Ratio Adverse childhood events and adult depression Adverse Events Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Chapman et al, 2004
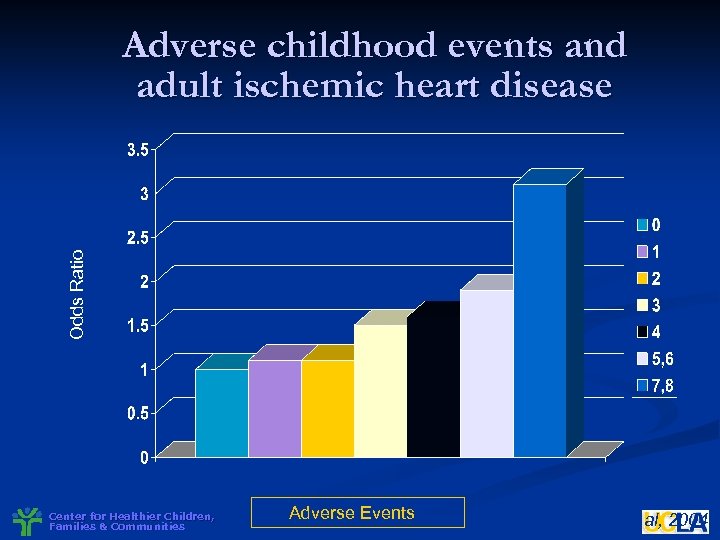 Odds Ratio Adverse childhood events and adult ischemic heart disease Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Adverse Events Dong et al, 2004
Odds Ratio Adverse childhood events and adult ischemic heart disease Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Adverse Events Dong et al, 2004
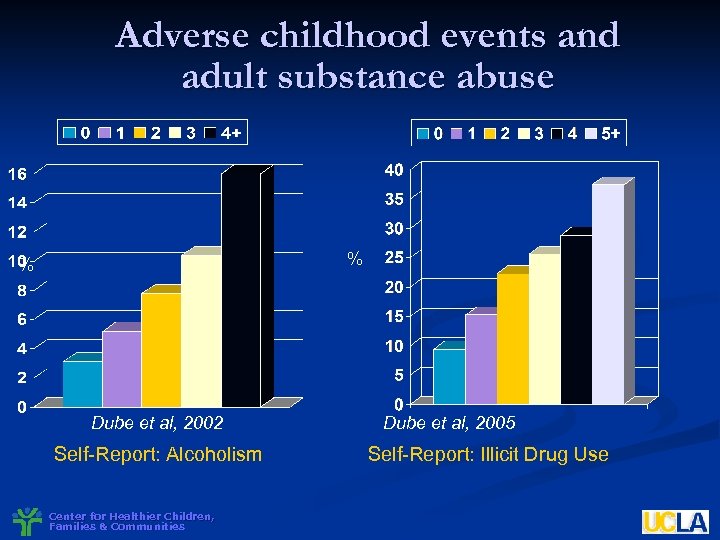 Adverse childhood events and adult substance abuse % % Dube et al, 2002 Self-Report: Alcoholism Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Dube et al, 2005 Self-Report: Illicit Drug Use
Adverse childhood events and adult substance abuse % % Dube et al, 2002 Self-Report: Alcoholism Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Dube et al, 2005 Self-Report: Illicit Drug Use
 LCHD Actionable Mechanisms for Intervention Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
LCHD Actionable Mechanisms for Intervention Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Cumulative, Programming and Pathway Mechanisms Influence LCHD n Three basic mechanisms influence LCHD n n n Cumulative - additive effect of multiple risks and protective factors, weathering Programming - time specific influence of stimulus or insult during a critical or sensitive period on selection, adaptation, compensatory processes Pathways-chains of (eco-culturally constructed) linked exposures that create a constrained conduit of geneenvironment transactions Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Cumulative, Programming and Pathway Mechanisms Influence LCHD n Three basic mechanisms influence LCHD n n n Cumulative - additive effect of multiple risks and protective factors, weathering Programming - time specific influence of stimulus or insult during a critical or sensitive period on selection, adaptation, compensatory processes Pathways-chains of (eco-culturally constructed) linked exposures that create a constrained conduit of geneenvironment transactions Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
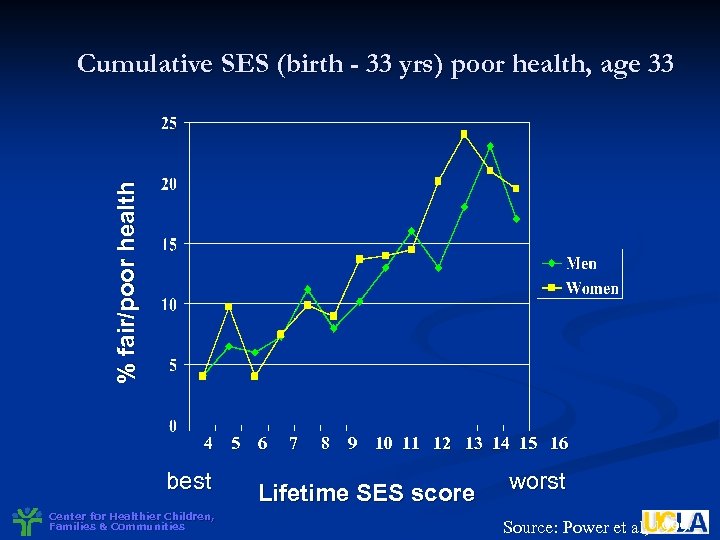 % fair/poor health Cumulative SES (birth - 33 yrs) poor health, age 33 4 5 6 best Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Lifetime SES score worst Source: Power et al, 1999
% fair/poor health Cumulative SES (birth - 33 yrs) poor health, age 33 4 5 6 best Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Lifetime SES score worst Source: Power et al, 1999
 LCHD Programming Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
LCHD Programming Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
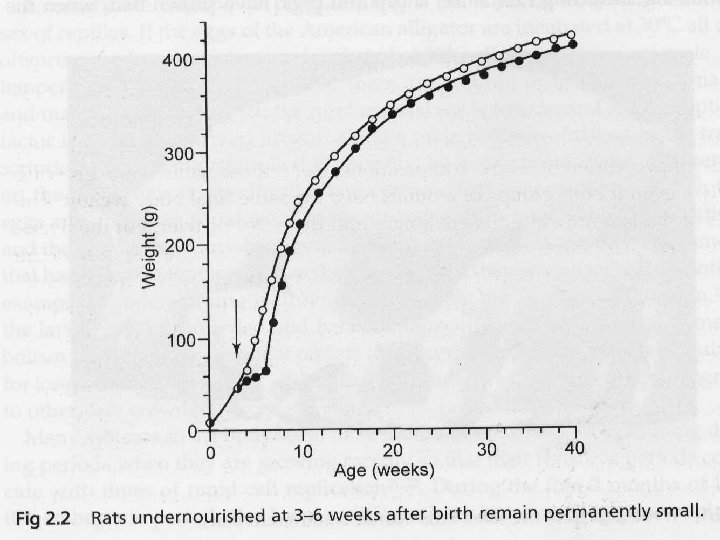 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
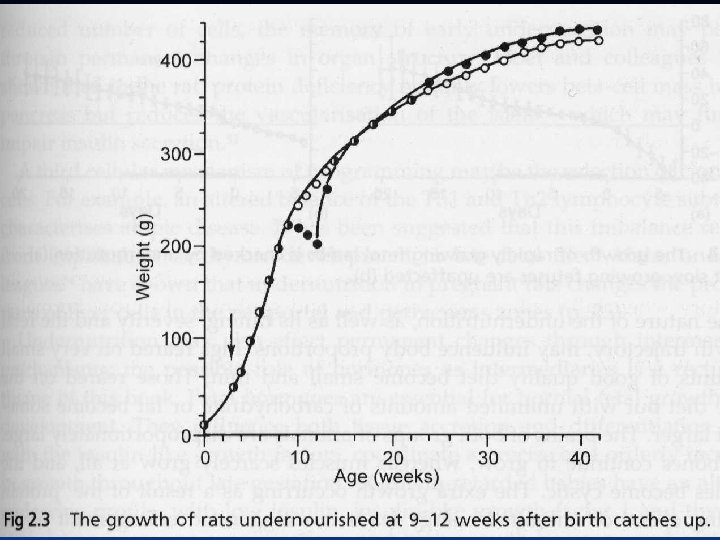 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Life Course Chronic Disease Epidemiology: Barker Hypothesis Affiliation: MRC Environmental epidemiology unit in South Hampton n Design: Historical Cohort n Key Finding: Fetal growth and development, and other factors, in first year(s) of life related to cardiovascular and other chronic disease in the fifth and sixth decade n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Life Course Chronic Disease Epidemiology: Barker Hypothesis Affiliation: MRC Environmental epidemiology unit in South Hampton n Design: Historical Cohort n Key Finding: Fetal growth and development, and other factors, in first year(s) of life related to cardiovascular and other chronic disease in the fifth and sixth decade n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
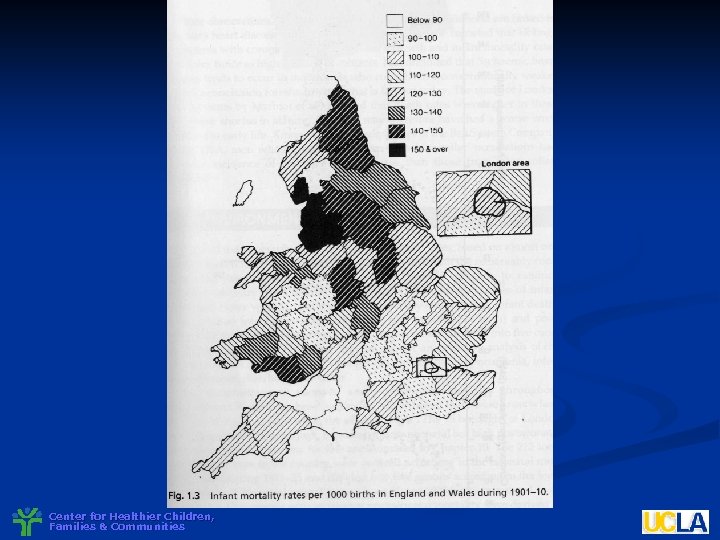 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
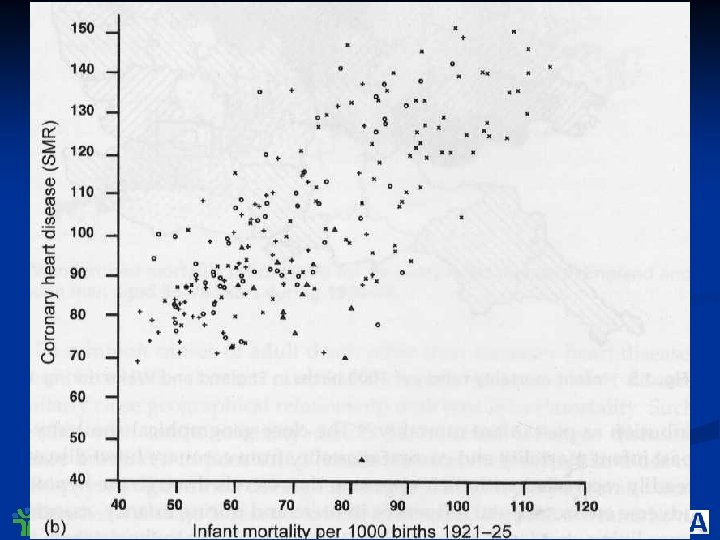 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
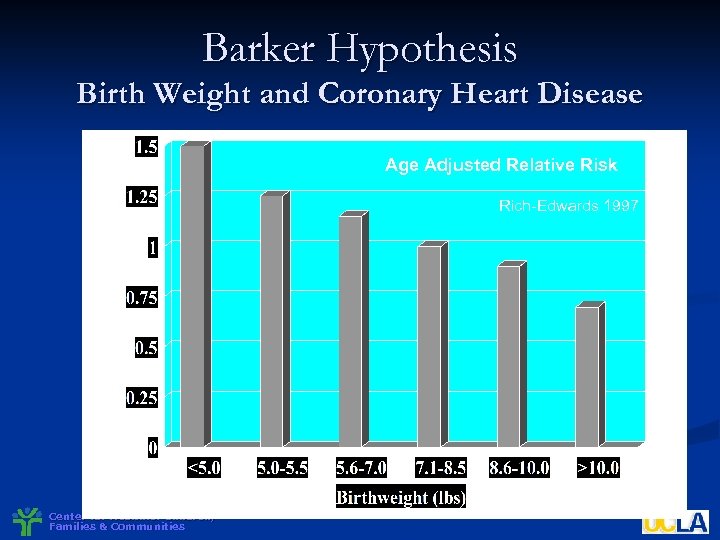 Barker Hypothesis Birth Weight and Coronary Heart Disease Age Adjusted Relative Risk Rich-Edwards 1997 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Barker Hypothesis Birth Weight and Coronary Heart Disease Age Adjusted Relative Risk Rich-Edwards 1997 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
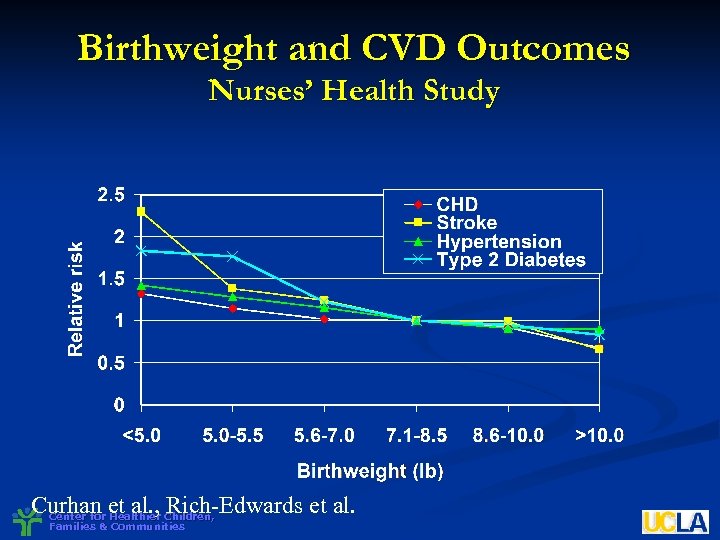 Birthweight and CVD Outcomes Nurses’ Health Study Curhan et al. , Children, Rich-Edwards et al. Center for Healthier Families & Communities
Birthweight and CVD Outcomes Nurses’ Health Study Curhan et al. , Children, Rich-Edwards et al. Center for Healthier Families & Communities
 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
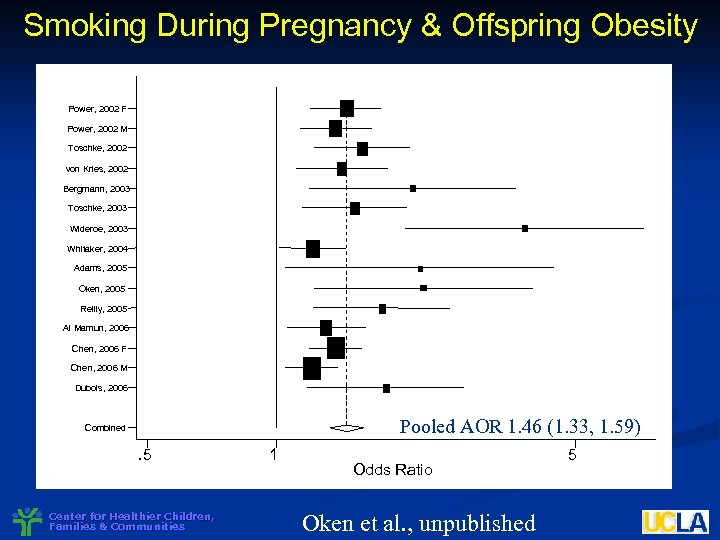 Smoking During Pregnancy & Offspring Obesity Power, 2002 F Power, 2002 M Toschke, 2002 von Kries, 2002 Bergmann, 2003 Toschke, 2003 Wideroe, 2003 Whitaker, 2004 Adams, 2005 Oken, 2005 Reilly, 2005 Al Mamun, 2006 Chen, 2006 F Chen, 2006 M Dubois, 2006 Pooled AOR 1. 46 (1. 33, 1. 59) Combined . 5 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities 1 Odds Ratio Oken et al. , unpublished 5
Smoking During Pregnancy & Offspring Obesity Power, 2002 F Power, 2002 M Toschke, 2002 von Kries, 2002 Bergmann, 2003 Toschke, 2003 Wideroe, 2003 Whitaker, 2004 Adams, 2005 Oken, 2005 Reilly, 2005 Al Mamun, 2006 Chen, 2006 F Chen, 2006 M Dubois, 2006 Pooled AOR 1. 46 (1. 33, 1. 59) Combined . 5 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities 1 Odds Ratio Oken et al. , unpublished 5
 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
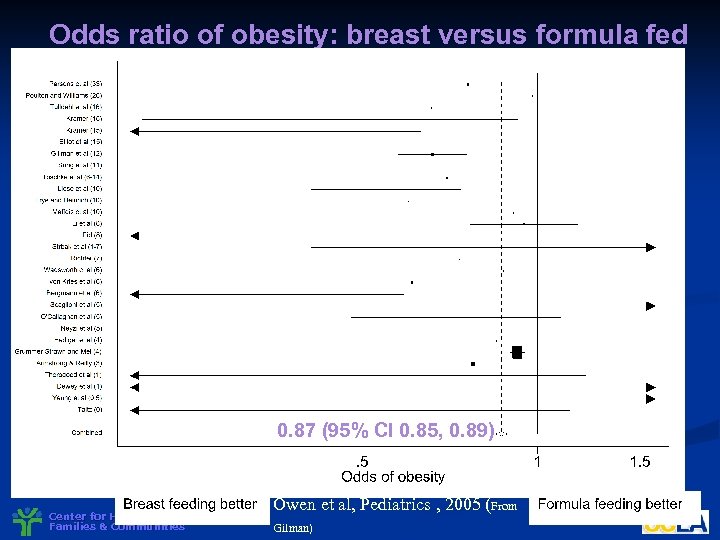 Odds ratio of obesity: breast versus formula fed 0. 87 (95% CI 0. 85, 0. 89) Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Owen et al, Pediatrics , 2005 (From Gilman)
Odds ratio of obesity: breast versus formula fed 0. 87 (95% CI 0. 85, 0. 89) Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Owen et al, Pediatrics , 2005 (From Gilman)
 LCHD Programming leads to Latent Effects Long time horizons between exposure and outcomes Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
LCHD Programming leads to Latent Effects Long time horizons between exposure and outcomes Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Cumulative, Programming and Pathway Mechanisms Influence LCHD n Three basic mechanisms influence LCHD n n n Cumulative - additive effect of multiple risks and protective factors, weathering Programming - time specific influence of stimulus or insult during a critical or sensitive period on selection, adaptation, compensatory processes Pathways- chains of (eco-culturally constructed) linked exposures that create a constrained conduit of geneenvironment transactions Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Cumulative, Programming and Pathway Mechanisms Influence LCHD n Three basic mechanisms influence LCHD n n n Cumulative - additive effect of multiple risks and protective factors, weathering Programming - time specific influence of stimulus or insult during a critical or sensitive period on selection, adaptation, compensatory processes Pathways- chains of (eco-culturally constructed) linked exposures that create a constrained conduit of geneenvironment transactions Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
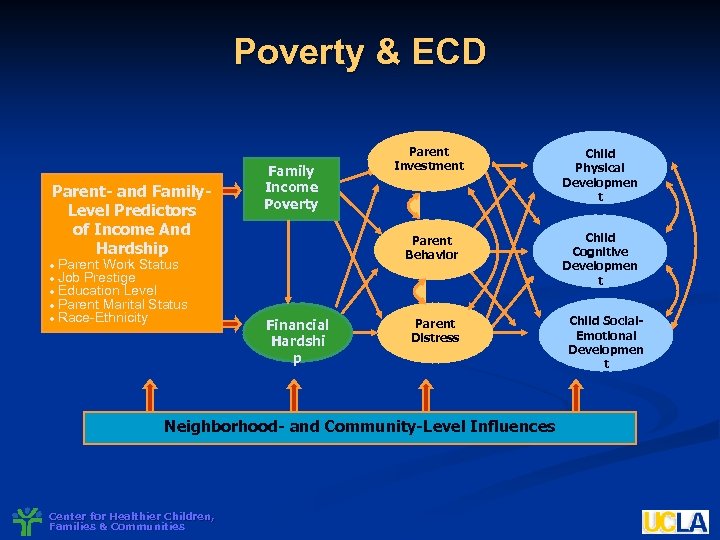 Poverty & ECD Parent- and Family. Level Predictors of Income And Hardship Parent Work Status Job Prestige Education Level Parent Marital Status Race-Ethnicity Financial Hardshi p Child Physical Developmen t Parent Behavior Family Income Poverty Parent Investment Child Cognitive Developmen t Parent Distress Neighborhood- and Community-Level Influences Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Child Social. Emotional Developmen t
Poverty & ECD Parent- and Family. Level Predictors of Income And Hardship Parent Work Status Job Prestige Education Level Parent Marital Status Race-Ethnicity Financial Hardshi p Child Physical Developmen t Parent Behavior Family Income Poverty Parent Investment Child Cognitive Developmen t Parent Distress Neighborhood- and Community-Level Influences Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Child Social. Emotional Developmen t
 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
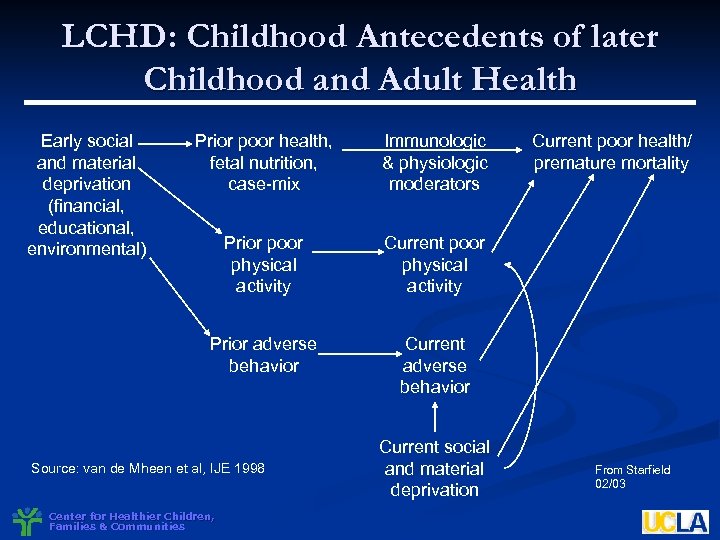 LCHD: Childhood Antecedents of later Childhood and Adult Health Early social and material deprivation (financial, educational, environmental) Prior poor health, fetal nutrition, case-mix Immunologic & physiologic moderators Prior poor physical activity Current poor physical activity Prior adverse behavior Current adverse behavior Source: van de Mheen et al, IJE 1998 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Current social and material deprivation Current poor health/ premature mortality From Starfield 02/03
LCHD: Childhood Antecedents of later Childhood and Adult Health Early social and material deprivation (financial, educational, environmental) Prior poor health, fetal nutrition, case-mix Immunologic & physiologic moderators Prior poor physical activity Current poor physical activity Prior adverse behavior Current adverse behavior Source: van de Mheen et al, IJE 1998 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Current social and material deprivation Current poor health/ premature mortality From Starfield 02/03
 LCHD: New Approaches to Old Problems Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
LCHD: New Approaches to Old Problems Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 How are LCHD concepts being used n Health System Reform (US) n n Aday’s Reinventing Public Health Breslow’s 3 rd Era of Health and Health Care Snyderman’s Future Medical/Health System analysis Health System Reform ( Intl) n n n UK – Acheson Report, Sure Start, Health Development Agency Canada –CIAR, Major Measurement Strategy focused on curve shifting across the life course WHO- ECD initiative, Commission on Social Determinants of Health Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
How are LCHD concepts being used n Health System Reform (US) n n Aday’s Reinventing Public Health Breslow’s 3 rd Era of Health and Health Care Snyderman’s Future Medical/Health System analysis Health System Reform ( Intl) n n n UK – Acheson Report, Sure Start, Health Development Agency Canada –CIAR, Major Measurement Strategy focused on curve shifting across the life course WHO- ECD initiative, Commission on Social Determinants of Health Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
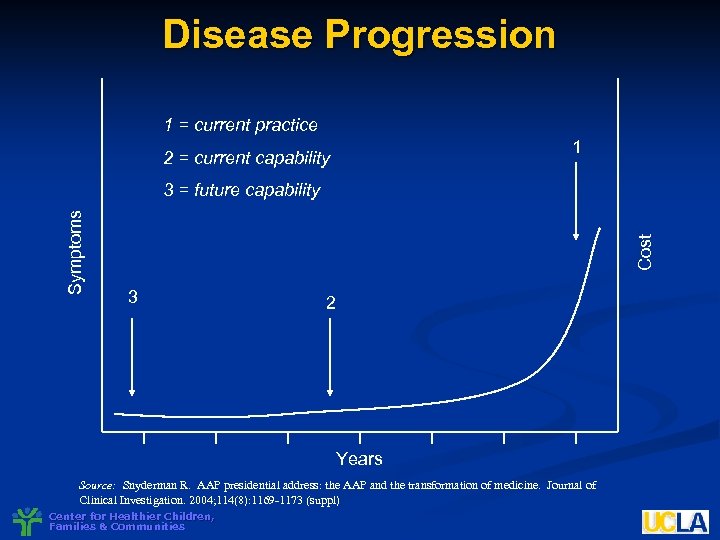 Disease Progression 1 = current practice 1 2 = current capability Cost Symptoms 3 = future capability 3 2 Years Source: Snyderman R. AAP presidential address: the AAP and the transformation of medicine. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2004; 114(8): 1169 -1173 (suppl) Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Disease Progression 1 = current practice 1 2 = current capability Cost Symptoms 3 = future capability 3 2 Years Source: Snyderman R. AAP presidential address: the AAP and the transformation of medicine. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2004; 114(8): 1169 -1173 (suppl) Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
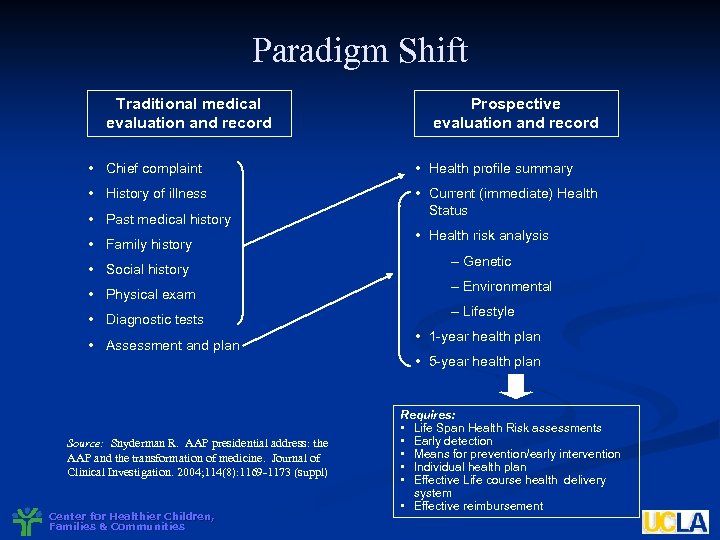 Paradigm Shift Traditional medical evaluation and record Prospective evaluation and record • Chief complaint • Health profile summary • History of illness • Current (immediate) Health Status • Past medical history • Family history • Social history • Physical exam • Diagnostic tests • Assessment and plan • Health risk analysis – Genetic – Environmental – Lifestyle • 1 -year health plan • 5 -year health plan Source: Snyderman R. AAP presidential address: the AAP and the transformation of medicine. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2004; 114(8): 1169 -1173 (suppl) Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Requires: • Life Span Health Risk assessments • Early detection • Means for prevention/early intervention • Individual health plan • Effective Life course health delivery system • Effective reimbursement
Paradigm Shift Traditional medical evaluation and record Prospective evaluation and record • Chief complaint • Health profile summary • History of illness • Current (immediate) Health Status • Past medical history • Family history • Social history • Physical exam • Diagnostic tests • Assessment and plan • Health risk analysis – Genetic – Environmental – Lifestyle • 1 -year health plan • 5 -year health plan Source: Snyderman R. AAP presidential address: the AAP and the transformation of medicine. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2004; 114(8): 1169 -1173 (suppl) Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Requires: • Life Span Health Risk assessments • Early detection • Means for prevention/early intervention • Individual health plan • Effective Life course health delivery system • Effective reimbursement
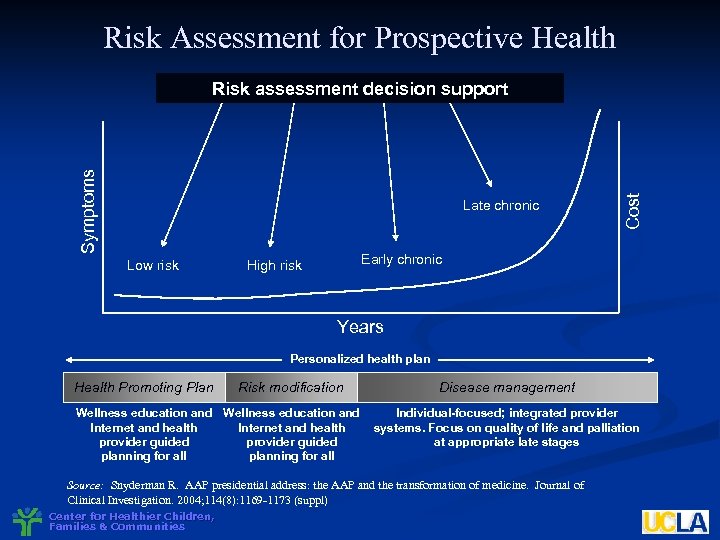 Risk Assessment for Prospective Health Late chronic Low risk Cost Symptoms Risk assessment decision support Early chronic High risk Years Personalized health plan Health Promoting Plan Risk modification Wellness education and Internet and health provider guided planning for all Disease management Individual-focused; integrated provider systems. Focus on quality of life and palliation at appropriate late stages Source: Snyderman R. AAP presidential address: the AAP and the transformation of medicine. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2004; 114(8): 1169 -1173 (suppl) Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Risk Assessment for Prospective Health Late chronic Low risk Cost Symptoms Risk assessment decision support Early chronic High risk Years Personalized health plan Health Promoting Plan Risk modification Wellness education and Internet and health provider guided planning for all Disease management Individual-focused; integrated provider systems. Focus on quality of life and palliation at appropriate late stages Source: Snyderman R. AAP presidential address: the AAP and the transformation of medicine. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2004; 114(8): 1169 -1173 (suppl) Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
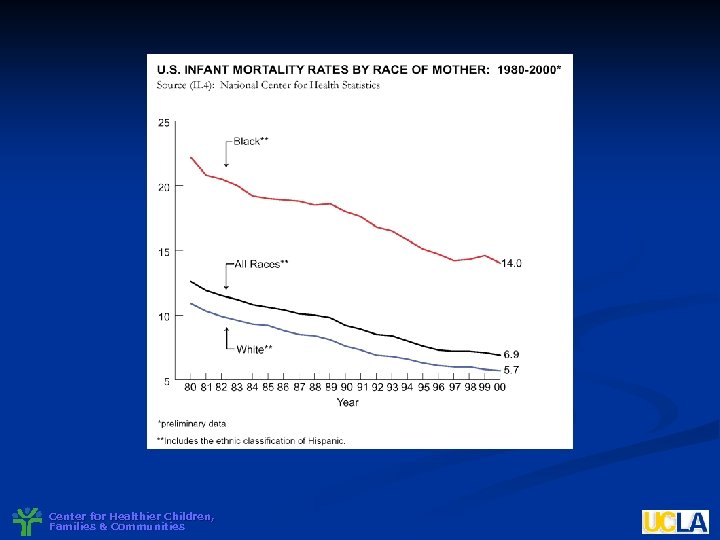 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
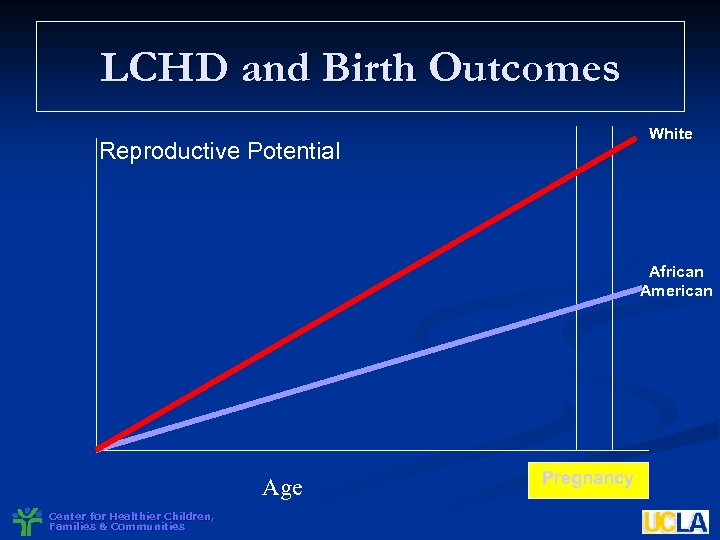 LCHD and Birth Outcomes White Reproductive Potential African American Age Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Pregnancy
LCHD and Birth Outcomes White Reproductive Potential African American Age Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Pregnancy
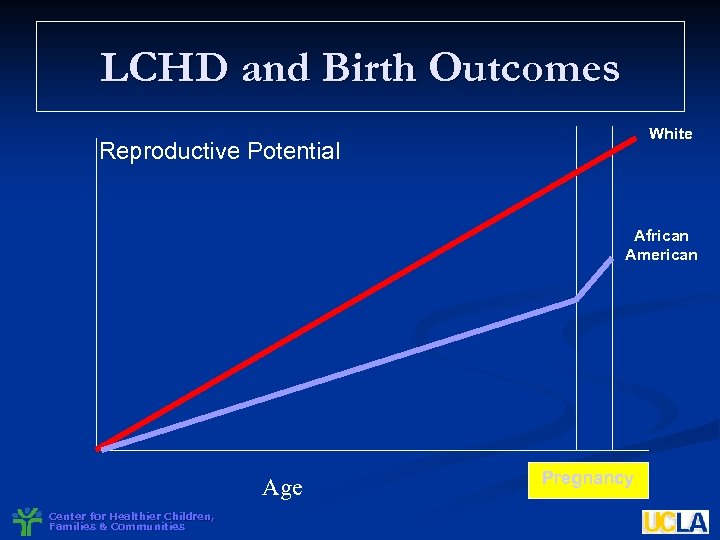 LCHD and Birth Outcomes White Reproductive Potential African American Age Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Pregnancy
LCHD and Birth Outcomes White Reproductive Potential African American Age Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Pregnancy
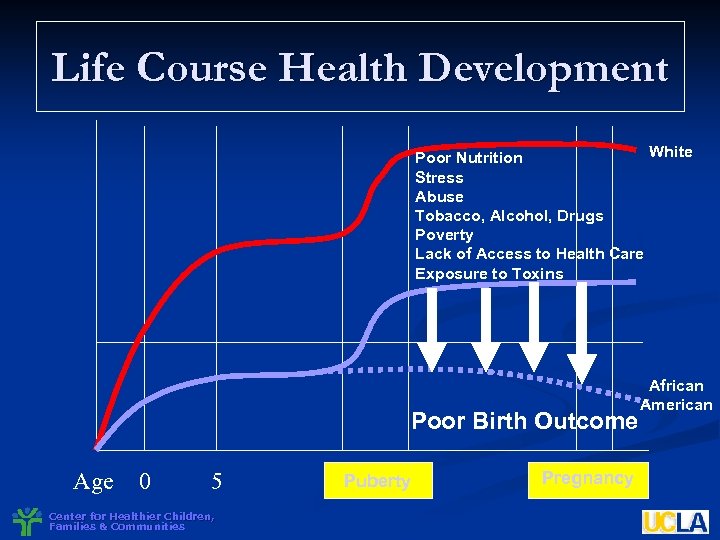 Life Course Health Development White Poor Nutrition Stress Abuse Tobacco, Alcohol, Drugs Poverty Lack of Access to Health Care Exposure to Toxins Poor Birth Outcome Age 0 5 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Puberty Pregnancy African American
Life Course Health Development White Poor Nutrition Stress Abuse Tobacco, Alcohol, Drugs Poverty Lack of Access to Health Care Exposure to Toxins Poor Birth Outcome Age 0 5 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Puberty Pregnancy African American
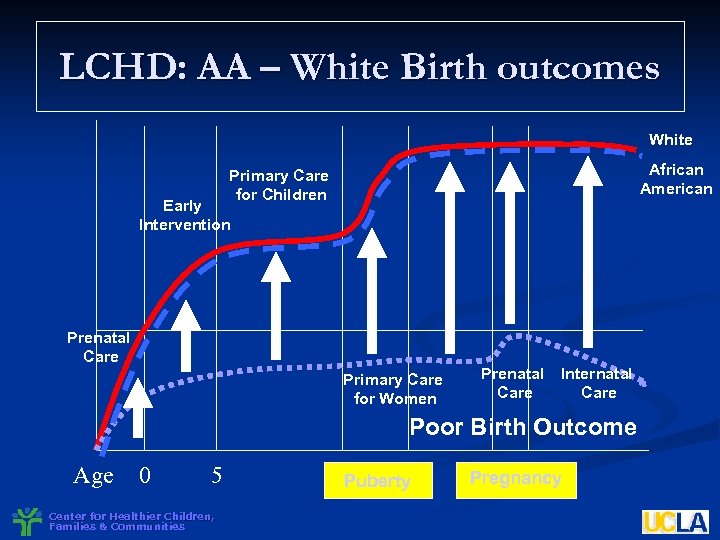 LCHD: AA – White Birth outcomes White African American Primary Care for Children Early Intervention Prenatal Care Primary Care for Women Prenatal Care Internatal Care Poor Birth Outcome Age 0 5 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Puberty Pregnancy
LCHD: AA – White Birth outcomes White African American Primary Care for Children Early Intervention Prenatal Care Primary Care for Women Prenatal Care Internatal Care Poor Birth Outcome Age 0 5 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Puberty Pregnancy
 LCHD Framework: Service Delivery System Applications Health Services Moving from health maintenance to health development organizations n Integration strategies for newly engineered health systems n n Vertical – Primary, Secondary, Tertiary n Horizontal – Biological, Behavioral, Social, Env. n Longitudinal – Life-course/Lifespan Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
LCHD Framework: Service Delivery System Applications Health Services Moving from health maintenance to health development organizations n Integration strategies for newly engineered health systems n n Vertical – Primary, Secondary, Tertiary n Horizontal – Biological, Behavioral, Social, Env. n Longitudinal – Life-course/Lifespan Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
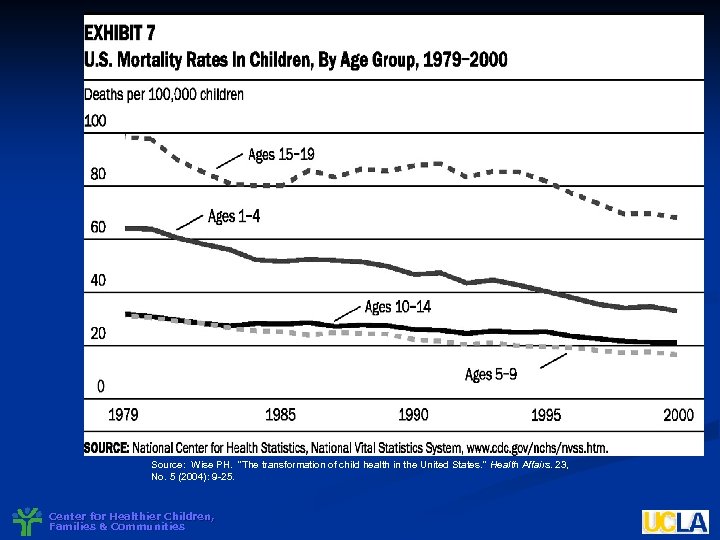 Source: Wise PH. “The transformation of child health in the United States. ” Health Affairs. 23, No. 5 (2004): 9 -25. Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Source: Wise PH. “The transformation of child health in the United States. ” Health Affairs. 23, No. 5 (2004): 9 -25. Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
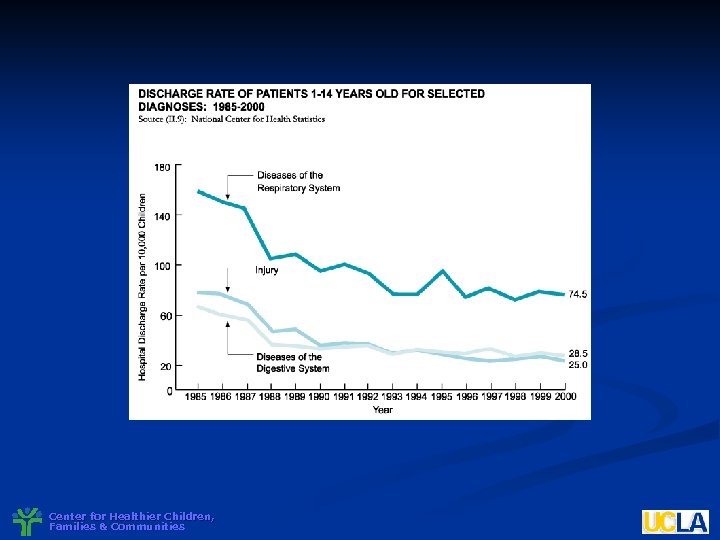
 Changing Pattern of Childhood Morbidity Increase in chronic health problems (10 -14%) n Greater recognition of mental health problems (15 -20%) n Greater appreciation of role and impact of developmental health problems – learning, language (10 -17%) n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Changing Pattern of Childhood Morbidity Increase in chronic health problems (10 -14%) n Greater recognition of mental health problems (15 -20%) n Greater appreciation of role and impact of developmental health problems – learning, language (10 -17%) n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Children & Youth at Risk 4 -6% Severe Disabilities 12 -16% Special Health Care Needs 30 -40% Behavioral, Mental Health Learning Problems 50 -60% Good Enough Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities What % are thriving ? 30% ? 40% ? 50% ?
Children & Youth at Risk 4 -6% Severe Disabilities 12 -16% Special Health Care Needs 30 -40% Behavioral, Mental Health Learning Problems 50 -60% Good Enough Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities What % are thriving ? 30% ? 40% ? 50% ?
 How well is the 2. 0 Child Health System Performing? Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
How well is the 2. 0 Child Health System Performing? Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 The existing child health service system n n n n Demand greater than services available Families have complex needs - often beyond capability of any single service Difficulty accessing services Socio-economic gradient of access Focus on treatment rather than prevention/early intervention Episodic contact Poor quality of Well Child Care Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
The existing child health service system n n n n Demand greater than services available Families have complex needs - often beyond capability of any single service Difficulty accessing services Socio-economic gradient of access Focus on treatment rather than prevention/early intervention Episodic contact Poor quality of Well Child Care Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 The existing child health service system n n n Fragmented service delivery n Different sectors (health, public health, population health, civic) n Different funding streams n Different cultures Lack of co-ordination Narrow programmatic criteria for eligibility Variable understanding of child health issues Local community generally has limited accountability or responsibility Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
The existing child health service system n n n Fragmented service delivery n Different sectors (health, public health, population health, civic) n Different funding streams n Different cultures Lack of co-ordination Narrow programmatic criteria for eligibility Variable understanding of child health issues Local community generally has limited accountability or responsibility Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 How do we get the health system that children need? Incremental vs. Transformational Reforms Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
How do we get the health system that children need? Incremental vs. Transformational Reforms Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Transforming the Child Health System: New Paradigm vs. Old System Child health system was designed for the first era of health care ( acute, infectious disease model) n It was upgraded a bit for the 2 nd era, with more regionalization, chronic disease care n Ill equipped for this new era n Under-performing n Facing many new challenges n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Transforming the Child Health System: New Paradigm vs. Old System Child health system was designed for the first era of health care ( acute, infectious disease model) n It was upgraded a bit for the 2 nd era, with more regionalization, chronic disease care n Ill equipped for this new era n Under-performing n Facing many new challenges n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Child Health 3. 0 : the New & Improved approach n n n Integrated and comprehensive approach - broadbanding of services to achieve curve shifting outcomes Greater flexibility of services and improved coordination at local community level Increased community and consumer participation Prevention, health promotion, early intervention, developmental optimization focus Focus on outcomes through improved systems performance Innovative funding and accountability arrangements Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Child Health 3. 0 : the New & Improved approach n n n Integrated and comprehensive approach - broadbanding of services to achieve curve shifting outcomes Greater flexibility of services and improved coordination at local community level Increased community and consumer participation Prevention, health promotion, early intervention, developmental optimization focus Focus on outcomes through improved systems performance Innovative funding and accountability arrangements Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
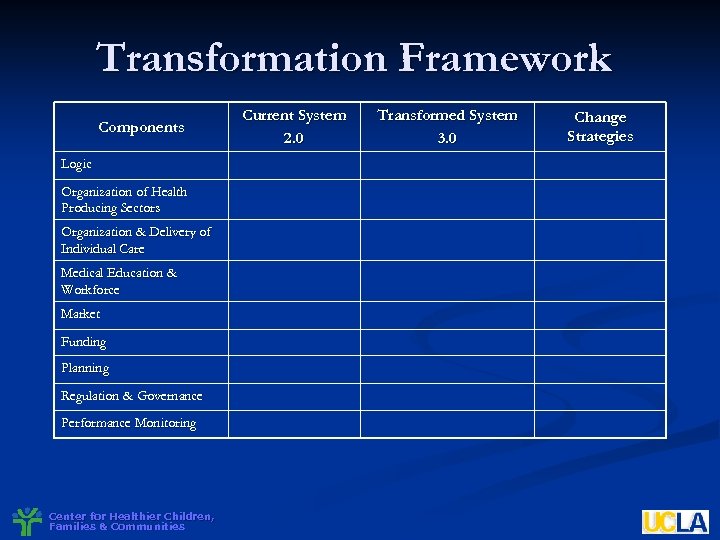 Transformation Framework Components Logic Organization of Health Producing Sectors Organization & Delivery of Individual Care Medical Education & Workforce Market Funding Planning Regulation & Governance Performance Monitoring Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Current System 2. 0 Transformed System 3. 0 Change Strategies
Transformation Framework Components Logic Organization of Health Producing Sectors Organization & Delivery of Individual Care Medical Education & Workforce Market Funding Planning Regulation & Governance Performance Monitoring Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Current System 2. 0 Transformed System 3. 0 Change Strategies
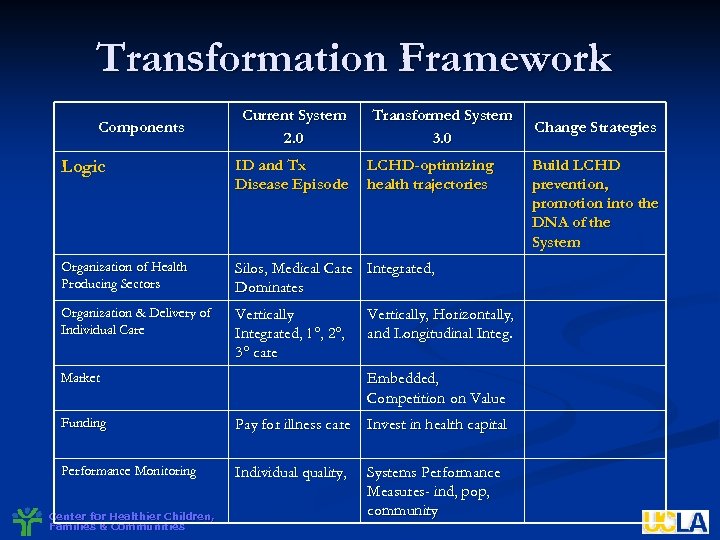 Transformation Framework Components Current System 2. 0 Transformed System 3. 0 Logic ID and Tx Disease Episode Organization of Health Producing Sectors Silos, Medical Care Integrated, Dominates Organization & Delivery of Individual Care Vertically Integrated, 1°, 2°, 3° care Market LCHD-optimizing health trajectories Vertically, Horizontally, and Longitudinal Integ. Embedded, Competition on Value Funding Pay for illness care Invest in health capital Performance Monitoring Individual quality, Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Systems Performance Measures- ind, pop, community Change Strategies Build LCHD prevention, promotion into the DNA of the System
Transformation Framework Components Current System 2. 0 Transformed System 3. 0 Logic ID and Tx Disease Episode Organization of Health Producing Sectors Silos, Medical Care Integrated, Dominates Organization & Delivery of Individual Care Vertically Integrated, 1°, 2°, 3° care Market LCHD-optimizing health trajectories Vertically, Horizontally, and Longitudinal Integ. Embedded, Competition on Value Funding Pay for illness care Invest in health capital Performance Monitoring Individual quality, Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Systems Performance Measures- ind, pop, community Change Strategies Build LCHD prevention, promotion into the DNA of the System
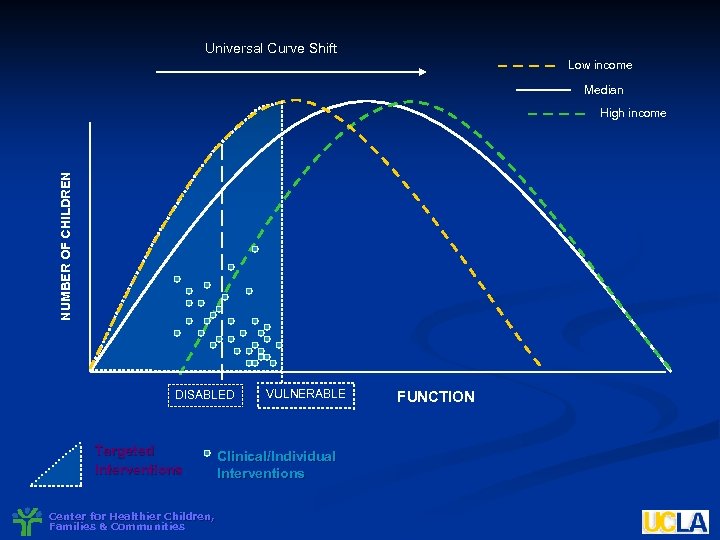 Universal Curve Shift Low income Median NUMBER OF CHILDREN High income DISABLED Targeted Interventions Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities VULNERABLE Clinical/Individual Interventions FUNCTION
Universal Curve Shift Low income Median NUMBER OF CHILDREN High income DISABLED Targeted Interventions Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities VULNERABLE Clinical/Individual Interventions FUNCTION
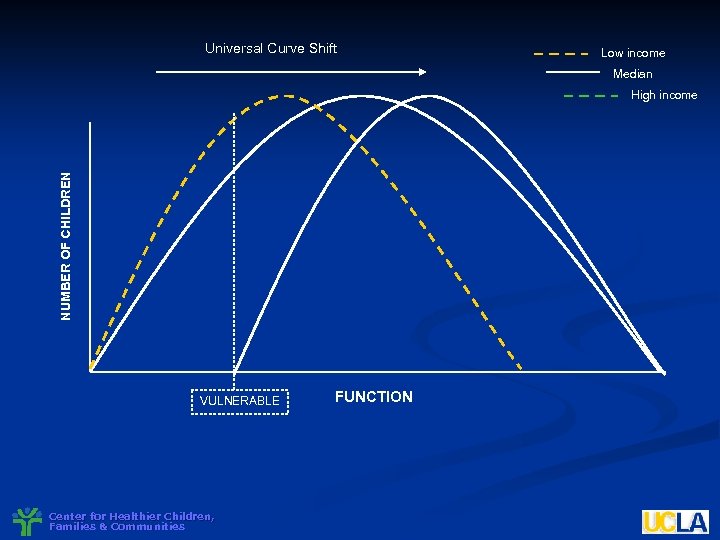 Universal Curve Shift Low income Median NUMBER OF CHILDREN High income VULNERABLE Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities FUNCTION
Universal Curve Shift Low income Median NUMBER OF CHILDREN High income VULNERABLE Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities FUNCTION
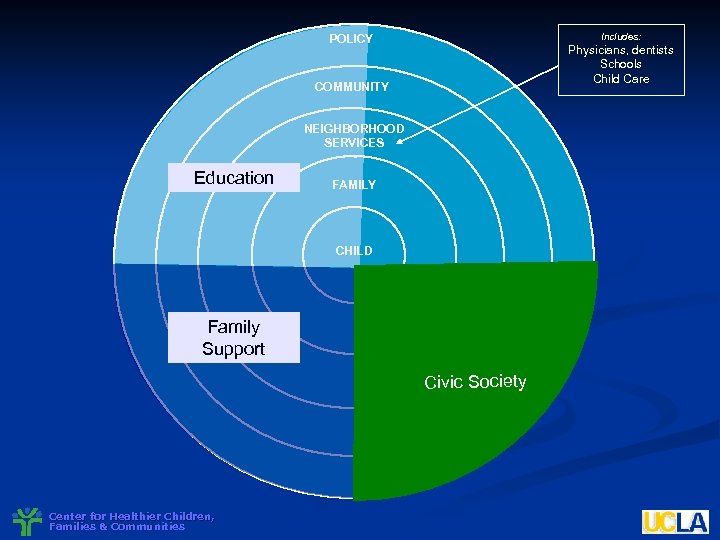 Includes: POLICY Physicians, dentists Schools Child Care COMMUNITY NEIGHBORHOOD SERVICES Education FAMILY CHILD Family Support Clinical/Individual Child Health Targeted Universal Civic Society Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Includes: POLICY Physicians, dentists Schools Child Care COMMUNITY NEIGHBORHOOD SERVICES Education FAMILY CHILD Family Support Clinical/Individual Child Health Targeted Universal Civic Society Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
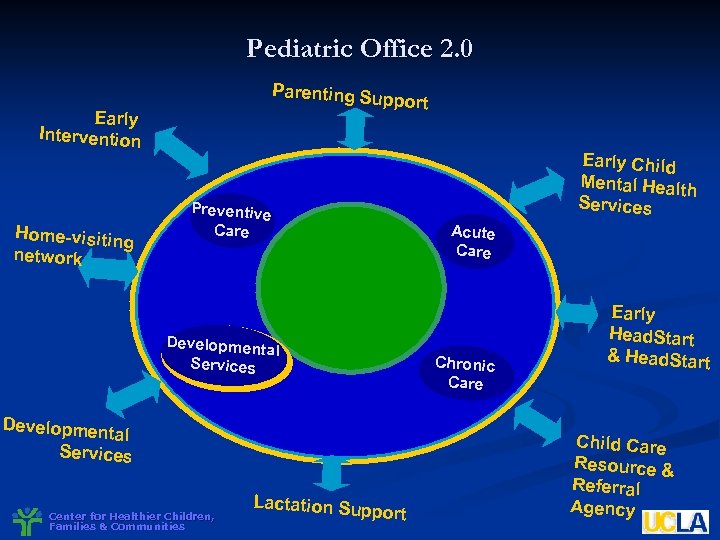 Pediatric Office 2. 0 Parenting Su pport Early Intervention Home-visitin g network Early Child Mental Healt h Services Preventive Care Acute Care Developmen tal Services Chronic Care Developmen tal Services Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Lactation Su pport Early Head. Start & Head. Start Child Care Resource & Referral Agency
Pediatric Office 2. 0 Parenting Su pport Early Intervention Home-visitin g network Early Child Mental Healt h Services Preventive Care Acute Care Developmen tal Services Chronic Care Developmen tal Services Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Lactation Su pport Early Head. Start & Head. Start Child Care Resource & Referral Agency
 18 month visit n Pediatric Care 2. 0 n C. D – Disability n Screen 4 -6 % w/ disability Screening tools & Pathway Pediatric Office connected to Regional Center n n n Pediatric Care 3. 0 n n Optimize Developmental Health I. D 30 -40% developmental risk Screening tools & Pathway Pediatric Office connected: n n n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities n Child care Many other programs Coordination Regional center ++
18 month visit n Pediatric Care 2. 0 n C. D – Disability n Screen 4 -6 % w/ disability Screening tools & Pathway Pediatric Office connected to Regional Center n n n Pediatric Care 3. 0 n n Optimize Developmental Health I. D 30 -40% developmental risk Screening tools & Pathway Pediatric Office connected: n n n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities n Child care Many other programs Coordination Regional center ++
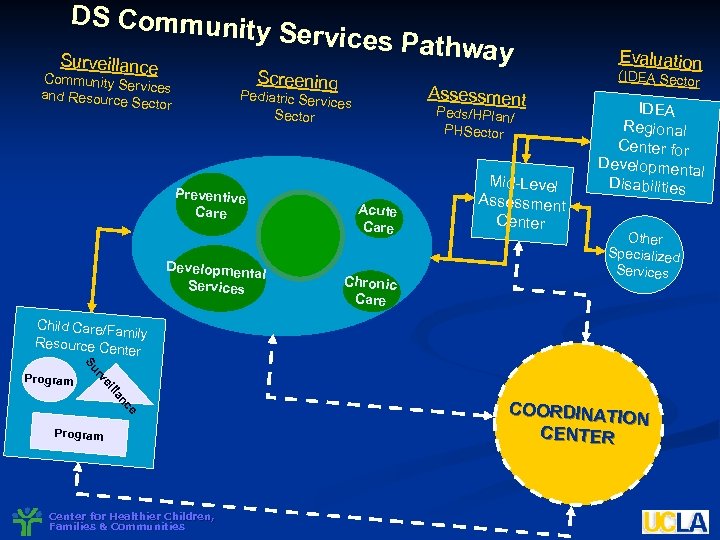 DS Commun ity Services P athway Surveillance Screening Community S ervices and Resource Sector Assessment Pediatric Serv ices Sector Preventive Care Developmen tal Services Peds/HPlan/ PHSector Acute Care Chronic Care Mid-Level Assessment Center Evaluation (IDEA Sector IDEA Regional Center for Developmenta l Disabilities Other Specialized Services Child Care/Fa mily Resource Cen ter Su ll ei rv Program ce an Program Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities COORDINAT ION CENTER
DS Commun ity Services P athway Surveillance Screening Community S ervices and Resource Sector Assessment Pediatric Serv ices Sector Preventive Care Developmen tal Services Peds/HPlan/ PHSector Acute Care Chronic Care Mid-Level Assessment Center Evaluation (IDEA Sector IDEA Regional Center for Developmenta l Disabilities Other Specialized Services Child Care/Fa mily Resource Cen ter Su ll ei rv Program ce an Program Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities COORDINAT ION CENTER
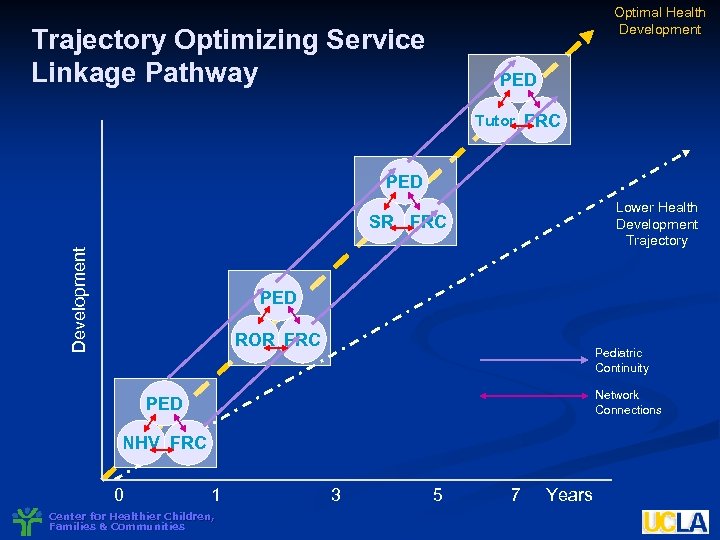 Optimal Health Development Trajectory Optimizing Service Linkage Pathway PED Tutor FRC PED Lower Health Development Trajectory Development SR FRC PED ROR FRC Pediatric Continuity Network Connections PED NHV FRC 0 1 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities 3 5 7 Years
Optimal Health Development Trajectory Optimizing Service Linkage Pathway PED Tutor FRC PED Lower Health Development Trajectory Development SR FRC PED ROR FRC Pediatric Continuity Network Connections PED NHV FRC 0 1 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities 3 5 7 Years
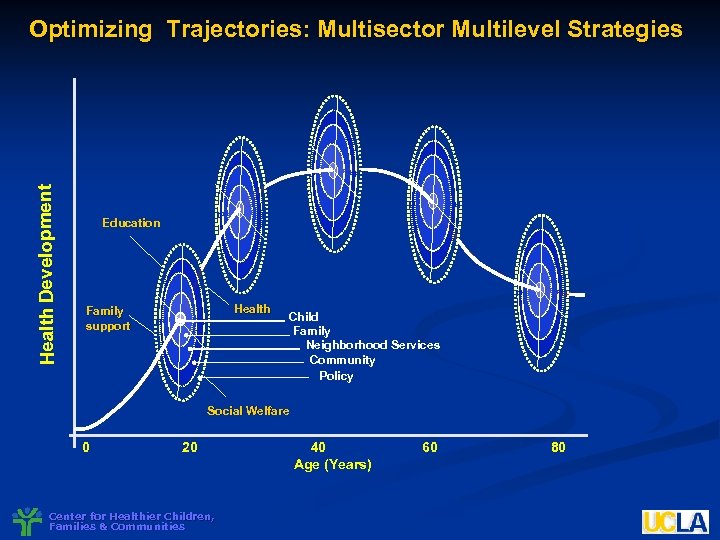 Health Development Optimizing Trajectories: Multisector Multilevel Strategies Education Health Family support Child Family Neighborhood Services Community Policy Social Welfare 0 20 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities 40 Age (Years) 60 80
Health Development Optimizing Trajectories: Multisector Multilevel Strategies Education Health Family support Child Family Neighborhood Services Community Policy Social Welfare 0 20 Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities 40 Age (Years) 60 80
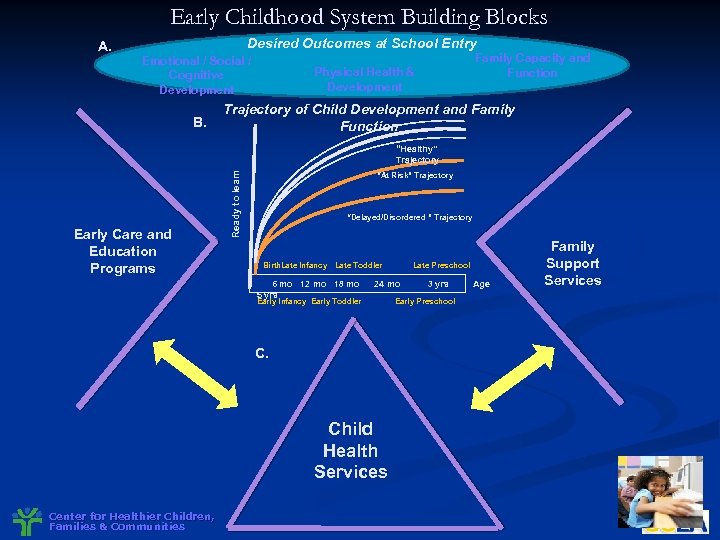 Early Childhood System Building Blocks A. Desired Outcomes at School Entry Emotional / Social / Cognitive Development B. Family Capacity and Function Physical Health & Development Trajectory of Child Development and Family Function Early Care and Education Programs Ready to learn “Healthy” Trajectory “At Risk” Trajectory “Delayed/Disordered ” Trajectory Birth. Late Infancy Late Toddler 6 mo 12 mo 18 mo 5 yrs 24 mo Early Infancy Early Toddler C. Child Health Services Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Late Preschool 3 yrs Early Preschool Age Family Support Services
Early Childhood System Building Blocks A. Desired Outcomes at School Entry Emotional / Social / Cognitive Development B. Family Capacity and Function Physical Health & Development Trajectory of Child Development and Family Function Early Care and Education Programs Ready to learn “Healthy” Trajectory “At Risk” Trajectory “Delayed/Disordered ” Trajectory Birth. Late Infancy Late Toddler 6 mo 12 mo 18 mo 5 yrs 24 mo Early Infancy Early Toddler C. Child Health Services Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Late Preschool 3 yrs Early Preschool Age Family Support Services
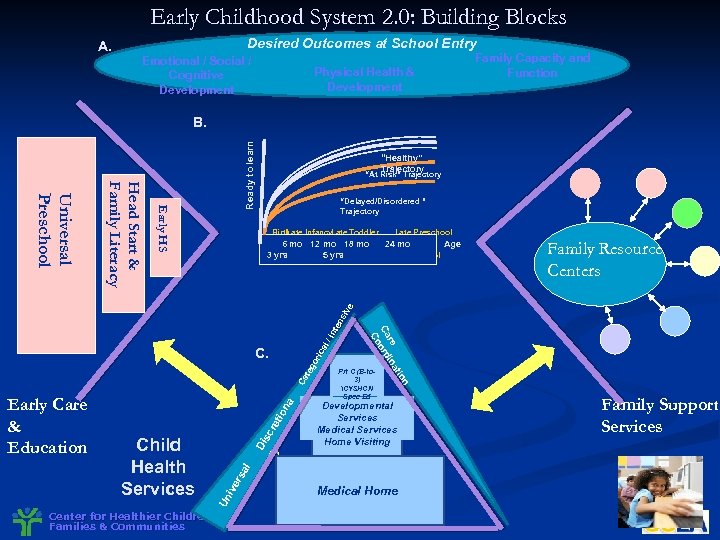 Early Childhood System 2. 0: Building Blocks A. Desired Outcomes at School Entry Emotional / Social / Cognitive Development Family Capacity and Function Physical Health & Development Early HS “Healthy” Trajectory “At Risk” Trajectory “Delayed/Disordered ” Trajectory Birth Late Infancy Late Toddler 6 mo 12 mo 18 mo Early Toddler 3 yrs Infancy 5 yrs Late Preschool 24 mo Early Preschool Age Family Resource Centers Int ica l/ Ca a ion Di ry scre t al rs ive Un Child Health Services Developmental Services Medical Services Home Visiting Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Medical Home n Early Care & Education Prt C (B-to 3) CYSHCN Spec Ed tio teg or C. re ina Ca ord Co en siv e Head Start & Family Literacy Universal Preschool Ready to learn B. Family Support Services
Early Childhood System 2. 0: Building Blocks A. Desired Outcomes at School Entry Emotional / Social / Cognitive Development Family Capacity and Function Physical Health & Development Early HS “Healthy” Trajectory “At Risk” Trajectory “Delayed/Disordered ” Trajectory Birth Late Infancy Late Toddler 6 mo 12 mo 18 mo Early Toddler 3 yrs Infancy 5 yrs Late Preschool 24 mo Early Preschool Age Family Resource Centers Int ica l/ Ca a ion Di ry scre t al rs ive Un Child Health Services Developmental Services Medical Services Home Visiting Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Medical Home n Early Care & Education Prt C (B-to 3) CYSHCN Spec Ed tio teg or C. re ina Ca ord Co en siv e Head Start & Family Literacy Universal Preschool Ready to learn B. Family Support Services
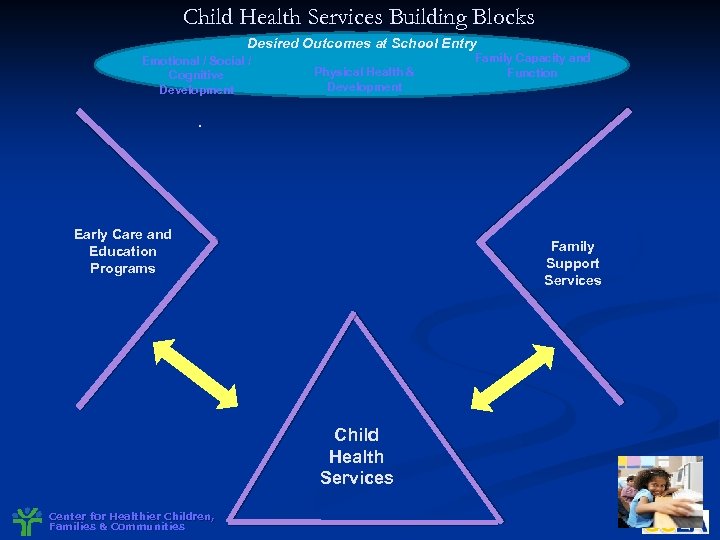 Child Health Services Building Blocks Desired Outcomes at School Entry Emotional / Social / Cognitive Development Physical Health & Development Family Capacity and Function . Early Care and Education Programs Family Support Services Child Health Services Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Child Health Services Building Blocks Desired Outcomes at School Entry Emotional / Social / Cognitive Development Physical Health & Development Family Capacity and Function . Early Care and Education Programs Family Support Services Child Health Services Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
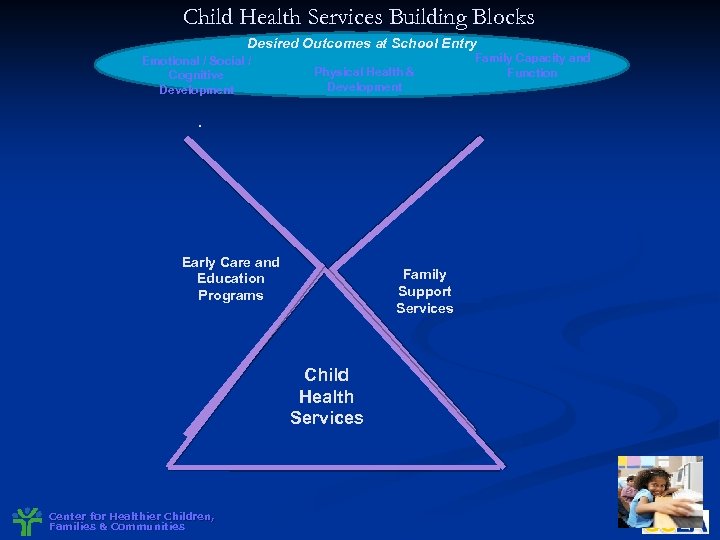 Child Health Services Building Blocks Desired Outcomes at School Entry Emotional / Social / Cognitive Development Physical Health & Development . Early Care and Education Programs Family Support Services Child Health Services Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Family Capacity and Function
Child Health Services Building Blocks Desired Outcomes at School Entry Emotional / Social / Cognitive Development Physical Health & Development . Early Care and Education Programs Family Support Services Child Health Services Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Family Capacity and Function
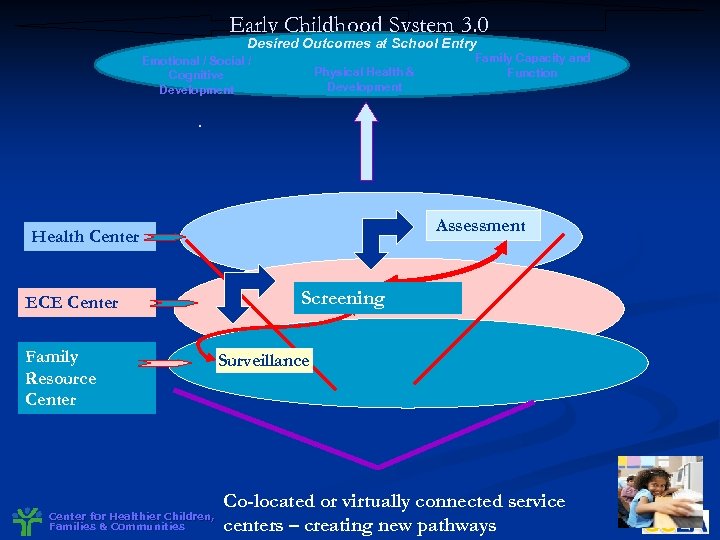 Early Childhood System 3. 0 Desired Outcomes at School Entry Emotional / Social / Cognitive Development Physical Health & Development Family Capacity and Function . Assessment Health Center ECE Center Family Resource Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Screening Surveillance Co-located or virtually connected service centers – creating new pathways
Early Childhood System 3. 0 Desired Outcomes at School Entry Emotional / Social / Cognitive Development Physical Health & Development Family Capacity and Function . Assessment Health Center ECE Center Family Resource Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities Screening Surveillance Co-located or virtually connected service centers – creating new pathways
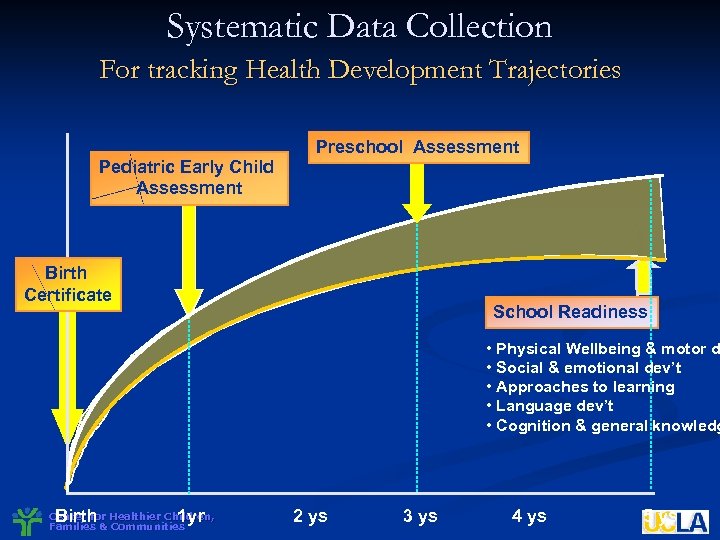 Systematic Data Collection For tracking Health Development Trajectories Pediatric Early Child Assessment Preschool Assessment Birth Certificate School Readiness • Physical Wellbeing & motor d • Social & emotional dev’t • Approaches to learning • Language dev’t • Cognition & general knowledg Birth 1 yr Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities 2 ys 3 ys 4 ys 5 ys
Systematic Data Collection For tracking Health Development Trajectories Pediatric Early Child Assessment Preschool Assessment Birth Certificate School Readiness • Physical Wellbeing & motor d • Social & emotional dev’t • Approaches to learning • Language dev’t • Cognition & general knowledg Birth 1 yr Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities 2 ys 3 ys 4 ys 5 ys
 What does LCHD New Synthesis Provide to the Discourse on Health System Reform? Big Idea – Forward looking n Integrative Framework n n Connect up an increasingly balkanized field Reframe for health system reform goals n Positions child/MCH in Vanguard of New Era in Health and Health Care Reform n New Rational for current and future activities n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
What does LCHD New Synthesis Provide to the Discourse on Health System Reform? Big Idea – Forward looking n Integrative Framework n n Connect up an increasingly balkanized field Reframe for health system reform goals n Positions child/MCH in Vanguard of New Era in Health and Health Care Reform n New Rational for current and future activities n Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 Take home Points: Power of LCHD n n Life Course Health Development (LCHD) is different than a life course approach LCHD –integrating framework n n n Connecting the disparate parts of MCH Connecting MCH to rest of health and human development Leverages MCH and Positions and Prioritizes MCH policy Provides a new Operating Logic for Transforming the Health System Powerful analytic model for solving MCH problems Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
Take home Points: Power of LCHD n n Life Course Health Development (LCHD) is different than a life course approach LCHD –integrating framework n n n Connecting the disparate parts of MCH Connecting MCH to rest of health and human development Leverages MCH and Positions and Prioritizes MCH policy Provides a new Operating Logic for Transforming the Health System Powerful analytic model for solving MCH problems Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 LCHD Framework: Think Different! n n n Developmentally - in order to optimize outcomes Population and upstream determinants of the outcomes that we want to achieve How to shift population risk curves and not just work at the individual level How to use alignment, connection, networking strategies to join up people, sectors, systems into a more functional approach - open source for a flatter health policy world How to change the culture of the system we work in To frame health in terms of its life long impacts Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
LCHD Framework: Think Different! n n n Developmentally - in order to optimize outcomes Population and upstream determinants of the outcomes that we want to achieve How to shift population risk curves and not just work at the individual level How to use alignment, connection, networking strategies to join up people, sectors, systems into a more functional approach - open source for a flatter health policy world How to change the culture of the system we work in To frame health in terms of its life long impacts Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
 UCLA Center for Healthier Children, Families and Communities & National Center for Infancy and Early Childhood Health Policy AIM-MCHB Child and Adolescent Policy Support Center Http. //healthychild. ucla. edu Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities
UCLA Center for Healthier Children, Families and Communities & National Center for Infancy and Early Childhood Health Policy AIM-MCHB Child and Adolescent Policy Support Center Http. //healthychild. ucla. edu Center for Healthier Children, Families & Communities


