26a84c9fe3183afd300583a0f41ae654.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71
 Life After the War • With a partner you need to outline the first 2 sections of Chapter 9 – take detailed notes. • Then come up with 8 ideas, events, people, etc. that should absolutely be know within each section (8 per section so 16 total). – explain why in 2 -3 sentences for each of these ideas, events, people, etc. how they are absolutely important within these sections.
Life After the War • With a partner you need to outline the first 2 sections of Chapter 9 – take detailed notes. • Then come up with 8 ideas, events, people, etc. that should absolutely be know within each section (8 per section so 16 total). – explain why in 2 -3 sentences for each of these ideas, events, people, etc. how they are absolutely important within these sections.

 Warm Up #1 • List 5 things that you could not live without. Then choose one and explain why.
Warm Up #1 • List 5 things that you could not live without. Then choose one and explain why.
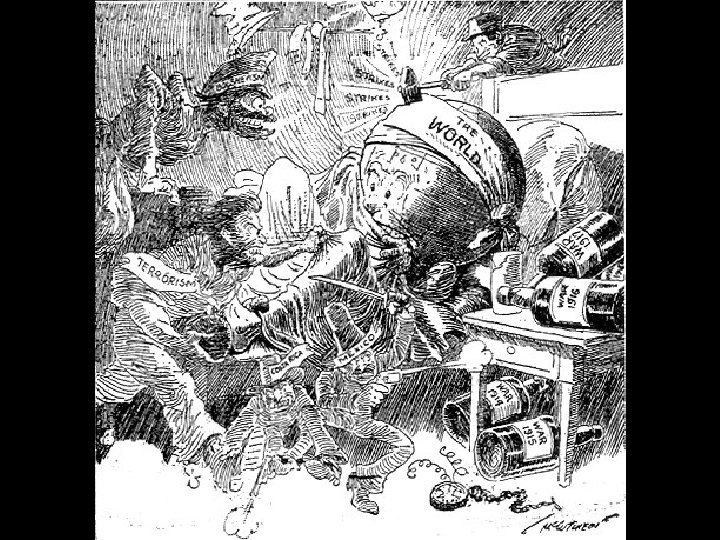

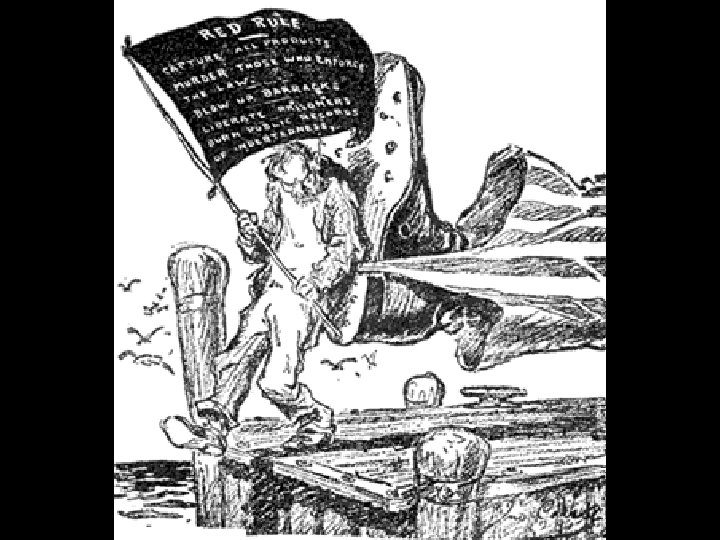
 “Red Scare” -- Anti. Bolshevism “Put Them Out & Keep Them Out” – Philadelphia Inquirer
“Red Scare” -- Anti. Bolshevism “Put Them Out & Keep Them Out” – Philadelphia Inquirer









 The Booming Economy • Between 1922 and 1929 the annual Gross National Product of the USA increased by 40%. The average income per head increased by 27%.
The Booming Economy • Between 1922 and 1929 the annual Gross National Product of the USA increased by 40%. The average income per head increased by 27%.
 • Consumer boom – growth of personal possessions (c. f. Woolworths, hire purchase, commercial travellers). • Synthetics – the invention of bakelite (the first plastic), cellophane and nylon - and chemicals.
• Consumer boom – growth of personal possessions (c. f. Woolworths, hire purchase, commercial travellers). • Synthetics – the invention of bakelite (the first plastic), cellophane and nylon - and chemicals.
 The Macy’s Parade ( Thanksgiving Day 1924 )
The Macy’s Parade ( Thanksgiving Day 1924 )

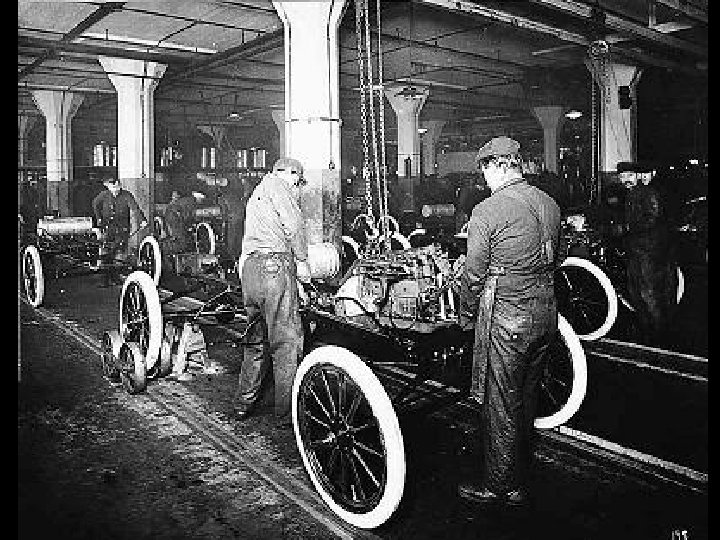
 • Innovation in production methods, especially in the motor industry (by 1925 Ford were producing a car every 10 seconds); this pushed down prices and made goods more accessible for ordinary people (the ‘Tin Lizzie’ cost $850 in 1910, only $295 in 1920). • Upsurge in car ownership – esp. the Ford Model T; 15 million had been produced
• Innovation in production methods, especially in the motor industry (by 1925 Ford were producing a car every 10 seconds); this pushed down prices and made goods more accessible for ordinary people (the ‘Tin Lizzie’ cost $850 in 1910, only $295 in 1920). • Upsurge in car ownership – esp. the Ford Model T; 15 million had been produced
 Henry Ford
Henry Ford


 • Consumer durables/electrical goods – fridges, washing machines, dishwashers, vacuum cleaners, record players. • Communications revolution – number of telephone doubled/ number of radios increased from 60, 000 to 10 million.
• Consumer durables/electrical goods – fridges, washing machines, dishwashers, vacuum cleaners, record players. • Communications revolution – number of telephone doubled/ number of radios increased from 60, 000 to 10 million.


 • Entertainment industry – Hollywood, Charlie Chaplin, the ‘talkies’ and cinemas, jazz clubs and speakeasies. • Stock market – Wall Street boomed (a 'bull' market) with many people buying shares to make a profit. Many new businesses were 'floated' on the stock market.
• Entertainment industry – Hollywood, Charlie Chaplin, the ‘talkies’ and cinemas, jazz clubs and speakeasies. • Stock market – Wall Street boomed (a 'bull' market) with many people buying shares to make a profit. Many new businesses were 'floated' on the stock market.
 Skyscrapers, highways and urban development.
Skyscrapers, highways and urban development.

 Warm Up #2 • What was the “Red Scare” and why did so many Americans fear communism? Explain
Warm Up #2 • What was the “Red Scare” and why did so many Americans fear communism? Explain
 Harding vs. Coolidge (Skip) • Compare these two presidents by creating a chart that list each presidents positive and negative impacts on the White House and Nation. After listing the two presidents impacts you’ll need to choose one and tell which was a better president for the United States. Use examples to explain why one was better than the other.
Harding vs. Coolidge (Skip) • Compare these two presidents by creating a chart that list each presidents positive and negative impacts on the White House and Nation. After listing the two presidents impacts you’ll need to choose one and tell which was a better president for the United States. Use examples to explain why one was better than the other.
 Harding vs. Coolidge (Skip) Positive: Negative: The better president between Harding and Coolidge was …. because. .
Harding vs. Coolidge (Skip) Positive: Negative: The better president between Harding and Coolidge was …. because. .
 American Life in the “Roaring Twenties” • • Revival of Antiforeignism The Reconstituted Ku Klux Klan The Wets Versus the Drys New Goals for Women
American Life in the “Roaring Twenties” • • Revival of Antiforeignism The Reconstituted Ku Klux Klan The Wets Versus the Drys New Goals for Women

 Chapter 9 & 10 1) Red Scare 2) Labor Strife & Limiting Immigration 3) The New Economic Era 4) Harding and Coolidge Presidency 5) Lingering Effects of WWI 6) Women’s New Role in Society 7) Prohibition 8) Urbanization & Conflicts Over Values 9) Great Migration & Life in Harlem 10) Harlem Renaissance 11) Change in Entertainment in the 1920’s 12) Era of Hero’s & the Arts of 1920’s
Chapter 9 & 10 1) Red Scare 2) Labor Strife & Limiting Immigration 3) The New Economic Era 4) Harding and Coolidge Presidency 5) Lingering Effects of WWI 6) Women’s New Role in Society 7) Prohibition 8) Urbanization & Conflicts Over Values 9) Great Migration & Life in Harlem 10) Harlem Renaissance 11) Change in Entertainment in the 1920’s 12) Era of Hero’s & the Arts of 1920’s

 Warm Up #3 • What was American life like during the “Roaring Twenties? ” Make sure to give multiple examples and analyze how these examples were similar, different, or the same.
Warm Up #3 • What was American life like during the “Roaring Twenties? ” Make sure to give multiple examples and analyze how these examples were similar, different, or the same.
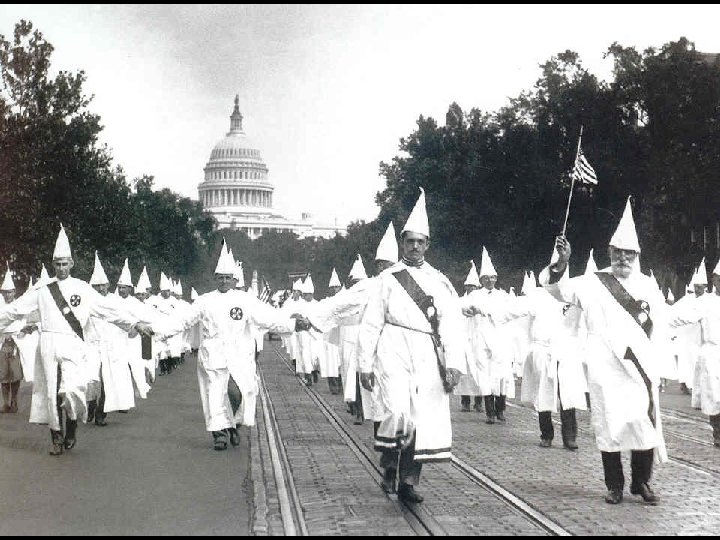
 The Reconstituted Ku Klux Klan
The Reconstituted Ku Klux Klan


 “The prestige of government has undoubtedly been lowered considerably by the Prohibition law. For nothing is more destructive of respect for the government and the law of the land than passing laws which cannot be enforced. ” Albert Einstein, “My First Impression of the U. S. A. , ” 1921
“The prestige of government has undoubtedly been lowered considerably by the Prohibition law. For nothing is more destructive of respect for the government and the law of the land than passing laws which cannot be enforced. ” Albert Einstein, “My First Impression of the U. S. A. , ” 1921
 Temperance • Over abuse of alcohol was found to expand into prostitution, gambling, and narcotics. This led to the 18 th amendment. The amendment banned the manufacture and sale of any alcoholic beverage. The Congress approved of this for it wanted to maintain a sober workforce during World War I.
Temperance • Over abuse of alcohol was found to expand into prostitution, gambling, and narcotics. This led to the 18 th amendment. The amendment banned the manufacture and sale of any alcoholic beverage. The Congress approved of this for it wanted to maintain a sober workforce during World War I.
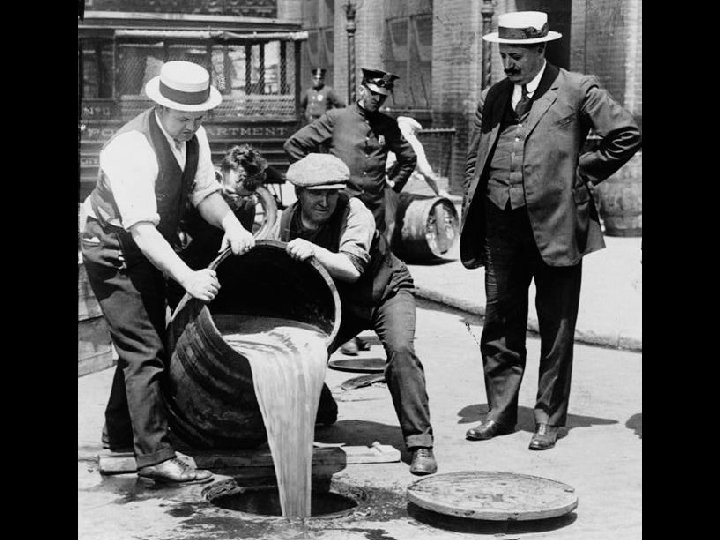



 • The Prohibition Amendment was ignored since the majority of Americans drank alcoholic beverages. However, since no one wanted to get caught, covert organizations were made. Among these were the Speakeasies. The Speakeasies were bars and clubs that sold bootleg alcohol illegally. Bootleg alcohol is smuggled and was mainly smuggled from Canada and made by the citizens.
• The Prohibition Amendment was ignored since the majority of Americans drank alcoholic beverages. However, since no one wanted to get caught, covert organizations were made. Among these were the Speakeasies. The Speakeasies were bars and clubs that sold bootleg alcohol illegally. Bootleg alcohol is smuggled and was mainly smuggled from Canada and made by the citizens.
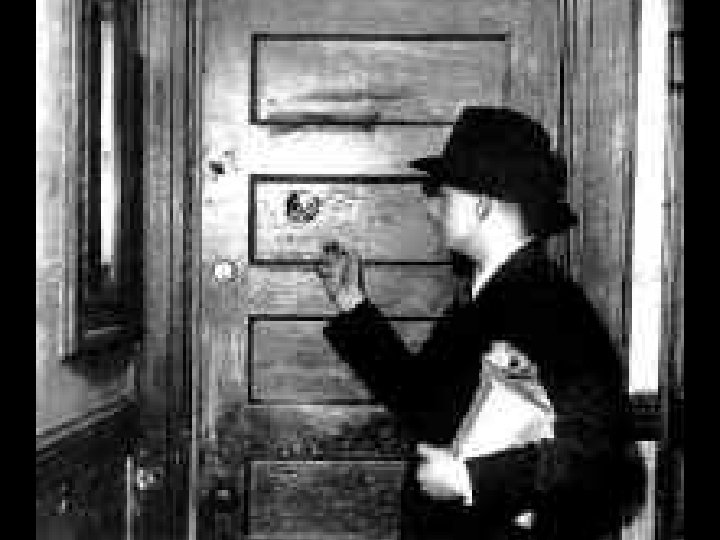
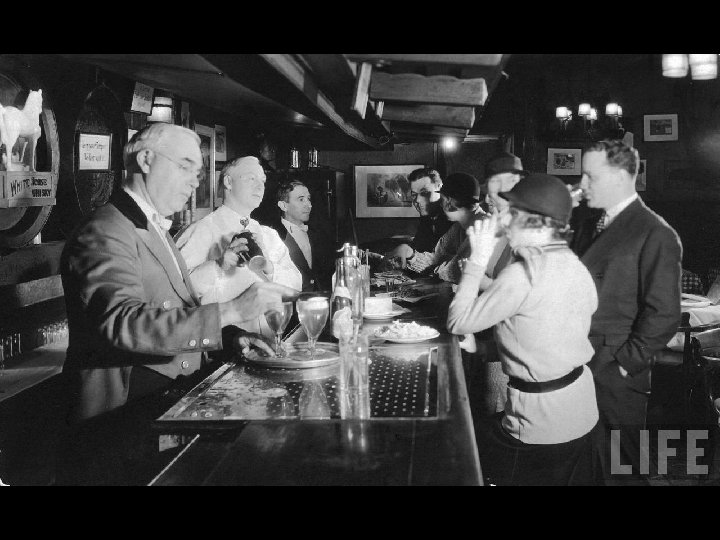



 • In this bootlegging industry, Al Capone was one of the main figures. He headed a Chicago bootlegging ring. Capone led a crime syndicate dedicated to smuggling and bootlegging alcohol and other illegal crimes during this era. Republicans and southern Democrats supported prohibition, and urban Democrats wanted it repealed. The increasing unpopularity of prohibition and the Great Depression led to the 21 st amendment, which repealed the 18 th prohibition amendment.
• In this bootlegging industry, Al Capone was one of the main figures. He headed a Chicago bootlegging ring. Capone led a crime syndicate dedicated to smuggling and bootlegging alcohol and other illegal crimes during this era. Republicans and southern Democrats supported prohibition, and urban Democrats wanted it repealed. The increasing unpopularity of prohibition and the Great Depression led to the 21 st amendment, which repealed the 18 th prohibition amendment.



 Flappers
Flappers
 • Flapper in the 1920 s was a term applied to a "new breed" of young Western women who wore short skirts, bobbed their hair, listened to jazz, and flaunted their disdain for what was then considered acceptable behavior. Flappers were seen as brash for wearing excessive makeup, drinking, treating sex in a casual manner, smoking, driving automobiles and otherwise flouting social and sexual norms.
• Flapper in the 1920 s was a term applied to a "new breed" of young Western women who wore short skirts, bobbed their hair, listened to jazz, and flaunted their disdain for what was then considered acceptable behavior. Flappers were seen as brash for wearing excessive makeup, drinking, treating sex in a casual manner, smoking, driving automobiles and otherwise flouting social and sexual norms.
 Scopes Trial • http: //www. schoo ltube. com/video/ 8 e 2 edc 48907 c 73 4 d 8 c 37/
Scopes Trial • http: //www. schoo ltube. com/video/ 8 e 2 edc 48907 c 73 4 d 8 c 37/

 The Jazz Age was an effect of the Harlem Renaissance. This was an era of written and artistic creativity among African-Americans after World War I that lasted until the middle of the 1930’s Depression. The migration of African-Americans to northern cities contributed to the rise of the Harlem Renaissance. Between 1919 and 1926, many African. Americans left their rural southern homes and moved to urban areas like New York City, Chicago, and Washington D. C. This migration was one of the factors that contributed to artistic style change and success of African. American artists. The Harlem Renaissance was first known as the New Negro Movement that had first started as a series of literary discussions in Greenwich Village and Harlem. This movement brought unparalleled creative activity in literature (especially in poems, plays, dramas, and essays), art and music. It also allowed the redefinition of African-American heritage.
The Jazz Age was an effect of the Harlem Renaissance. This was an era of written and artistic creativity among African-Americans after World War I that lasted until the middle of the 1930’s Depression. The migration of African-Americans to northern cities contributed to the rise of the Harlem Renaissance. Between 1919 and 1926, many African. Americans left their rural southern homes and moved to urban areas like New York City, Chicago, and Washington D. C. This migration was one of the factors that contributed to artistic style change and success of African. American artists. The Harlem Renaissance was first known as the New Negro Movement that had first started as a series of literary discussions in Greenwich Village and Harlem. This movement brought unparalleled creative activity in literature (especially in poems, plays, dramas, and essays), art and music. It also allowed the redefinition of African-American heritage.


![Pictured here are Langston Hughes [far left] with [left to right: ] Charles S. Pictured here are Langston Hughes [far left] with [left to right: ] Charles S.](https://present5.com/presentation/26a84c9fe3183afd300583a0f41ae654/image-62.jpg) Pictured here are Langston Hughes [far left] with [left to right: ] Charles S. Johnson, E. Franklin Frazier, Rudolph Fisher and Hubert T. Delaney
Pictured here are Langston Hughes [far left] with [left to right: ] Charles S. Johnson, E. Franklin Frazier, Rudolph Fisher and Hubert T. Delaney
 Jazz Music
Jazz Music
 Popular Sports • The 1920 s allowed for an enthusiasm in professional sports. Many different types of sports became popular during this time period, therefore giving this period another name: “Golden Age of Sports”. Baseball, football, boxing, horse racing, and tennis are some sports that rose in popularity. Influential athletes from this era include Babe Ruth and Jack Dempsey. • Babe Ruth, a baseball player, was considered a role model. He didn’t mind if people knew about his alcohol drinking or cigar smoking. Jack Dempsey
Popular Sports • The 1920 s allowed for an enthusiasm in professional sports. Many different types of sports became popular during this time period, therefore giving this period another name: “Golden Age of Sports”. Baseball, football, boxing, horse racing, and tennis are some sports that rose in popularity. Influential athletes from this era include Babe Ruth and Jack Dempsey. • Babe Ruth, a baseball player, was considered a role model. He didn’t mind if people knew about his alcohol drinking or cigar smoking. Jack Dempsey
 Dempsey Ruth
Dempsey Ruth
 Marcus Garvey “Liberate the minds of men and ultimately you will liberate the bodies of men. ” “A people without the knowledge of their past history, origin and culture is like a tree without roots. ” • http: //tcooo. podomatic. com/entry/2010 -05 -27 T 13_26_4707_00
Marcus Garvey “Liberate the minds of men and ultimately you will liberate the bodies of men. ” “A people without the knowledge of their past history, origin and culture is like a tree without roots. ” • http: //tcooo. podomatic. com/entry/2010 -05 -27 T 13_26_4707_00

 Warm Up #4 • What role did “Flappers” have on changing the social norms and roles for women in society? Make sure to give clear examples and explain your answer!
Warm Up #4 • What role did “Flappers” have on changing the social norms and roles for women in society? Make sure to give clear examples and explain your answer!
 Presentations • 1920’s (Roaring Twenties) Individual Research Project – Share who your individual is and make it clear on how your individual had an impact or made a major contribution to the time frame. – Think of your presentation as a trailer to a blockbuster movie, but in your trailer you ruin the ending by sharing all the important information. • Do not read directly from your papers!
Presentations • 1920’s (Roaring Twenties) Individual Research Project – Share who your individual is and make it clear on how your individual had an impact or made a major contribution to the time frame. – Think of your presentation as a trailer to a blockbuster movie, but in your trailer you ruin the ending by sharing all the important information. • Do not read directly from your papers!

 Warm Up #5 • What impact did Prohibition have on the American society and economy? Make sure to give clear examples and explain your answer!
Warm Up #5 • What impact did Prohibition have on the American society and economy? Make sure to give clear examples and explain your answer!


