b4a63617a2c6787693d160264d309afd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Lessons from implementations of Basel II and for Solvency II Workshop Sydney 2006, Manley Beach gerhard. stahl@bafin. de and stefan. jaschke@bafin. de Sydney December 11, 2006 Seite 1

Agenda Part 0: Who is QRM & cross-sectoral overview Part 1: Market risk models for the trading book of banks Part 2: Credit risk models at banks Part 3: Operational risk models at banks Part 4: Market risk models at investment funds Part 5: Holistic models at insurers (Solvency II) Part 6: Economic capital and use test Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Seite 2

Lessons from implementations of Basel I & II and for Solvency II Who is QRM & cross-sectoral overview Sydney December 11, 2006 Seite 3

Ba. Fin as the German financial regulator As from Ba. Fin’s mission statement: • Preserve stability of the German financial system • Maintain confidence of investors and consumers • Safeguard fair behaviour of market participants Ba. Fin approach: • Integrated supervision (banking, insurance, financial services) • Risk identification and risk limitation • Prevention before punishment • Principle based (not rule based) regulation Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Seite 4

QRM experiences from banks, funds & insurers Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Seite 5

QRM: RISQUE is our Business • Regulation • Inspections • Supervision • Quantitative Methods • Uniformly across the whole financial market • Excellence Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Seite 6

Responsibilities of Q RM • On-site inspections for market risk models, IRBA, IRB, Op. Risk, …, Solvency II, …. • Principal work for any type of risk model • Research • special audits according to § 44 banking act • international groups as far as risk models are in focus • representing the Ba. Fin in international groups (Basel, . . ) Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Seite 7

Regulatory Activities – Memberships in Working Groups • AIG validation subgroup • CEBS validation subgroup • RTF on concentration risk ü ü • RTF intersection of market and credit risk • Co-chairing BCBS working group on liquidity risk • national IRBA Working Group (Ba. Fin + Bundesbank) • national Op. Risk Working Group (Ba. Fin + Bundesbank) • Ba. Fin Working Group on the relation between Solvency II and Basel II Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Seite 8
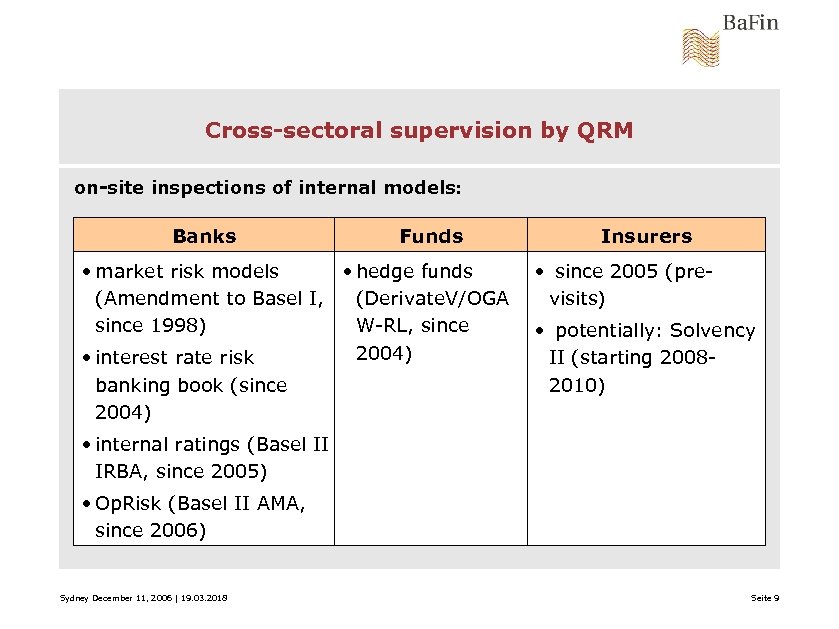
Cross-sectoral supervision by QRM on-site inspections of internal models: Banks Funds • market risk models • hedge funds (Amendment to Basel I, (Derivate. V/OGA since 1998) W-RL, since 2004) • interest rate risk banking book (since 2004) Insurers • since 2005 (previsits) • potentially: Solvency II (starting 20082010) • internal ratings (Basel II IRBA, since 2005) • Op. Risk (Basel II AMA, since 2006) Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Seite 9

Internal Model (IM) Auditing Background • Regulation in Germany was almost juridical, typically offsite supervision, before 1997 • Development of auditing expertise at Ba. Fin and Deutsche Bundesbank since 1996 • Institutions may use suitable internal risk models for determining the capital charges or partial capital charges for the market risk since 1997, provided that Ba. Fin has confirmed their suitability in writing upon the institution's request (“Principle I concerning the capital of institutions” ) Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Seite 10

We are living in a risk society - Lessons from IM for Basel II • Stochastic modelling and regulation • Non-linear instruments, complex hedging strategies • Large-scale forecasting models with thousands of variables • Portfolio view of risk • Are multivariate non-linear stochastic models complex? • No! – the complexity comes from the interdisciplinary use of Va. R-Models • The risk management process itself is a tool to reduce complexity Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Seite 11
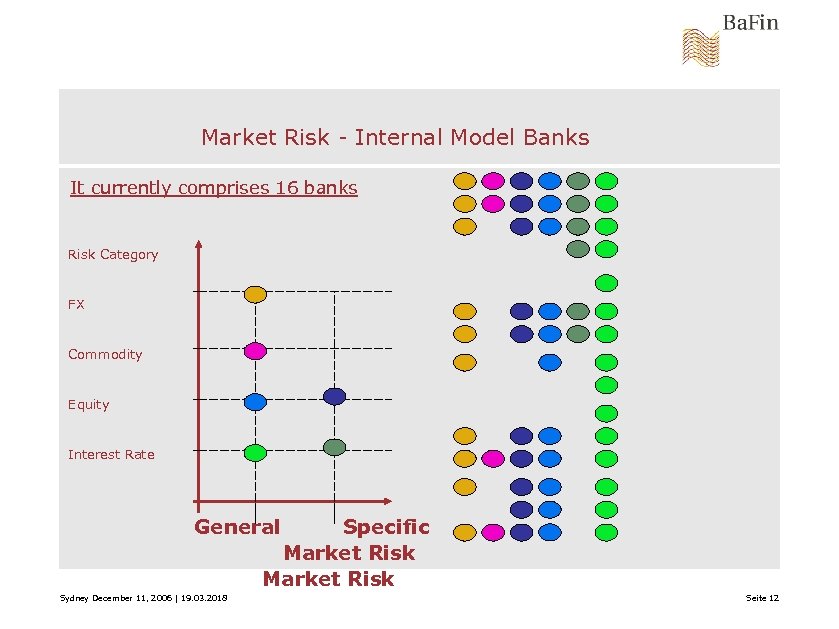
Market Risk - Internal Model Banks It currently comprises 16 banks Risk Category FX Commodity Equity Interest Rate General Specific Market Risk Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Seite 12
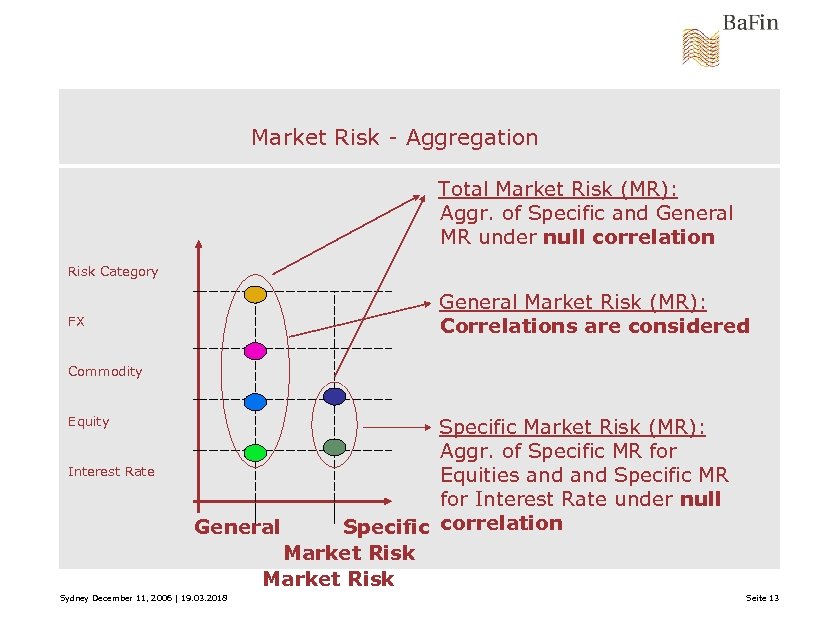
Market Risk - Aggregation Total Market Risk (MR): Aggr. of Specific and General MR under null correlation Risk Category General Market Risk (MR): Correlations are considered FX Commodity Equity Interest Rate Specific Market Risk (MR): Aggr. of Specific MR for Equities and Specific MR for Interest Rate under null General Specific correlation Market Risk Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Seite 13
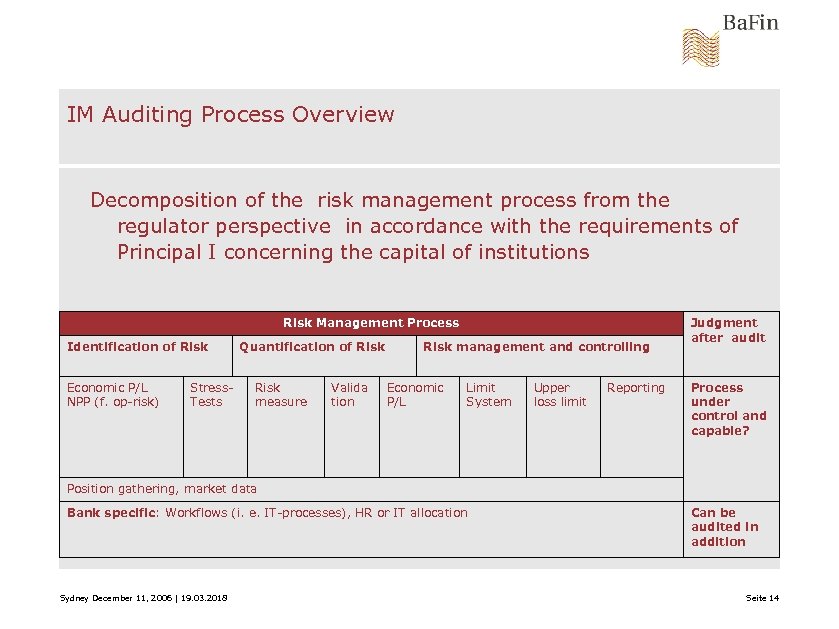
IM Auditing Process Overview Decomposition of the risk management process from the regulator perspective in accordance with the requirements of Principal I concerning the capital of institutions Risk Management Process Identification of Risk Economic P/L NPP (f. op-risk) Stress. Tests Quantification of Risk measure Valida tion Risk management and controlling Economic P/L Limit System Upper loss limit Reporting Judgment after audit Process under control and capable? Position gathering, market data Bank specific: Workflows (i. e. IT-processes), HR or IT allocation Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Can be audited in addition Seite 14
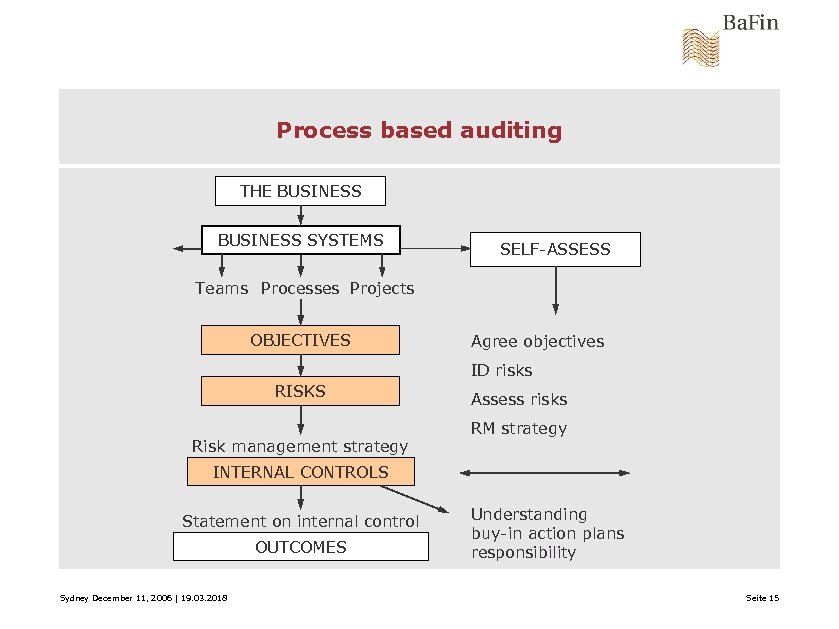
Process based auditing THE BUSINESS SYSTEMS SELF-ASSESS Teams Processes Projects OBJECTIVES Agree objectives ID risks RISKS Risk management strategy Assess risks RM strategy INTERNAL CONTROLS Statement on internal control OUTCOMES Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Understanding buy-in action plans responsibility Seite 15

The Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA) Definition “Internal auditing is an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organisation‘s operations. It helps an organisation accomplish its objectives by bringing a systematic, disciplined approach to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management, control and governance process” Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Seite 16
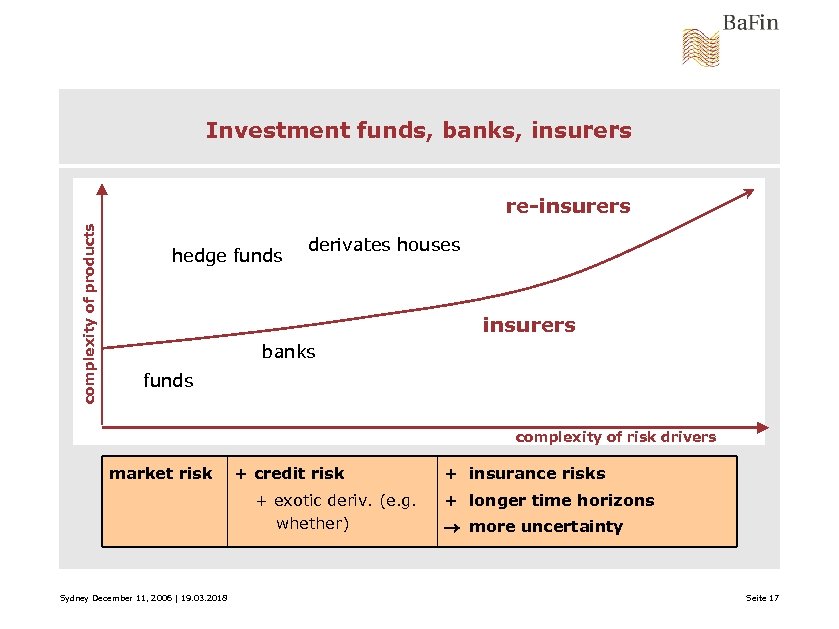
Investment funds, banks, insurers complexity of products re-insurers hedge funds derivates houses insurers banks funds complexity of risk drivers market risk + credit risk + exotic deriv. (e. g. whether) Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 + insurance risks + longer time horizons more uncertainty Seite 17
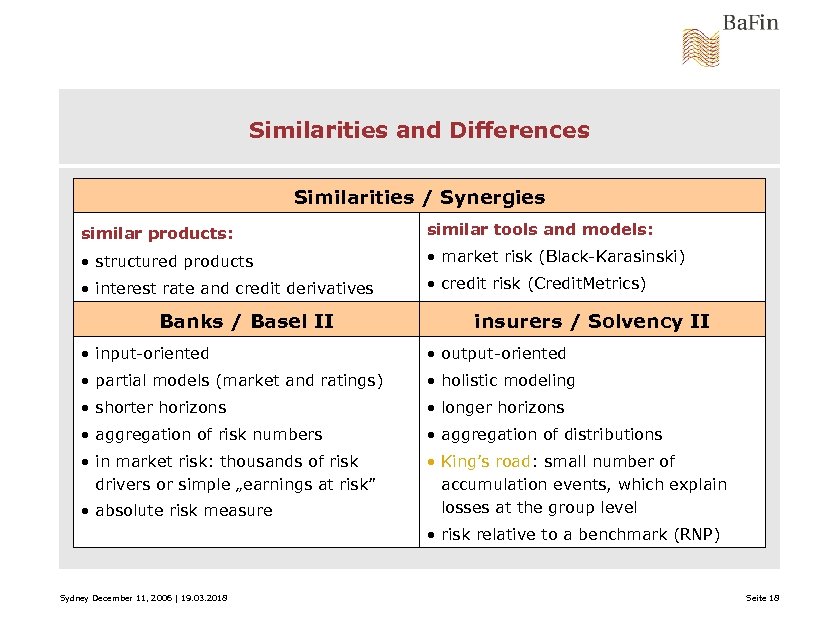
Similarities and Differences Similarities / Synergies similar products: similar tools and models: • structured products • market risk (Black-Karasinski) • interest rate and credit derivatives • credit risk (Credit. Metrics) Banks / Basel II insurers / Solvency II • input-oriented • output-oriented • partial models (market and ratings) • holistic modeling • shorter horizons • longer horizons • aggregation of risk numbers • aggregation of distributions • in market risk: thousands of risk drivers or simple „earnings at risk” • King’s road: small number of accumulation events, which explain losses at the group level • absolute risk measure • risk relative to a benchmark (RNP) Sydney December 11, 2006 | 19. 03. 2018 Seite 18
b4a63617a2c6787693d160264d309afd.ppt