cb2ba597c66b99533de1673decc7ca33.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Lesson One Basic Information Security and Data Assurance Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Lesson Objectives • Provide the NSTISSC definition for information security. • Explain the term security and identify the multiple layers of organizational security. • Identify and describe the critical characteristics of information. • Match key terms in the field of information assurance with corresponding definitions. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
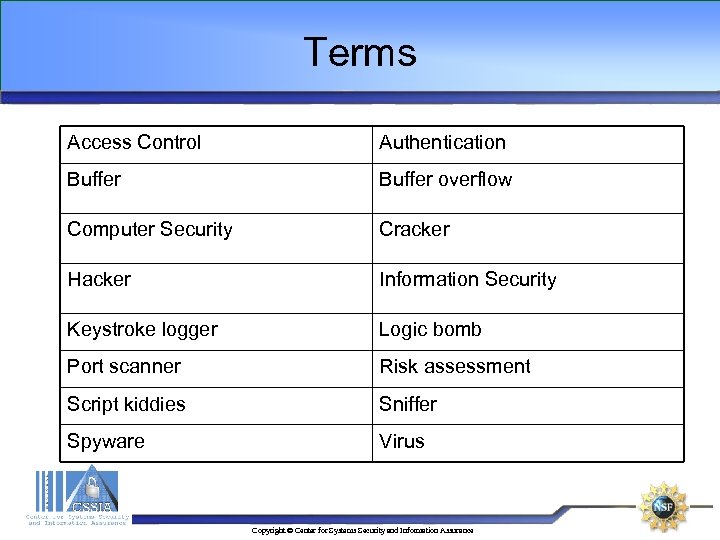
Terms Access Control Authentication Buffer overflow Computer Security Cracker Hacker Information Security Keystroke logger Logic bomb Port scanner Risk assessment Script kiddies Sniffer Spyware Virus Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

What is Security • “The quality or state of being secure – to be free from danger” • Be free from adversaries or danger Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

NSTISSC Definition of Information Security • Information Security is the protection of information and systems and hardware that use, store, and transmit that information. • Information security encompasses those steps that are taken to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data or resources. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

What is Information Security & Data Assurance • Information security according to the text is the process of protecting a computer from harmful attacks. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
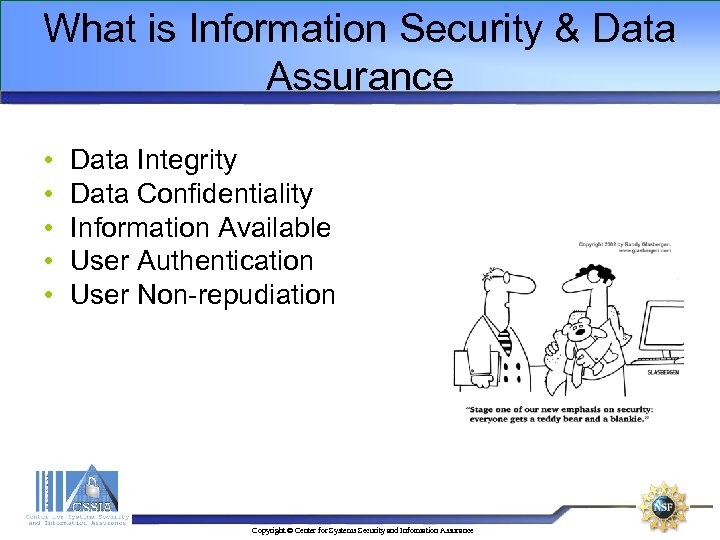
What is Information Security & Data Assurance • • • Data Integrity Data Confidentiality Information Available User Authentication User Non-repudiation Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

ABC of Information Security Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

What is Information Integrity? • Provides confidence that data has not been modified by accident or design • Refers to the validity of data • Can be compromised in a number of ways: Ø Human errors when data is entered or deleted Ø Errors that occur when data is transmitted from one computer to another Ø Software bugs or viruses Ø Hardware malfunctions, such as disk crashes Ø Natural disasters, such as fires and floods Ø Intentionally by hackers or other people. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
What is Information Confidentially? • Confidentiality of data means that no one who does not have authority to access the data has done so. • Eliminating the unauthorized disclosure of information Ø Human errors when data is entered Ø Errors that occur when data is transmitted Software Spyware Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

What is Information Availability? • An area that is sometimes overlooked by information security programs is data availability • Data and computing resources need to be available to accomplish the organizations mission • Many modern attacks affect the availability of data (Ping Attacks, Do. S, Viruses) Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Data Availability Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
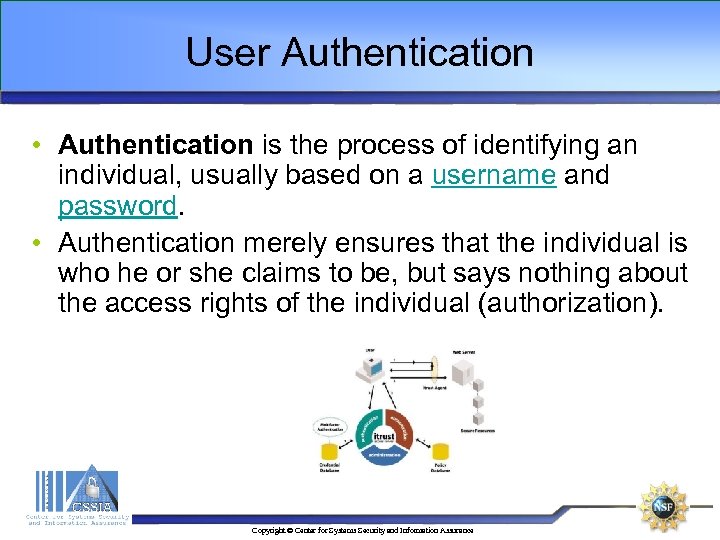
User Authentication • Authentication is the process of identifying an individual, usually based on a username and password. • Authentication merely ensures that the individual is who he or she claims to be, but says nothing about the access rights of the individual (authorization). Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
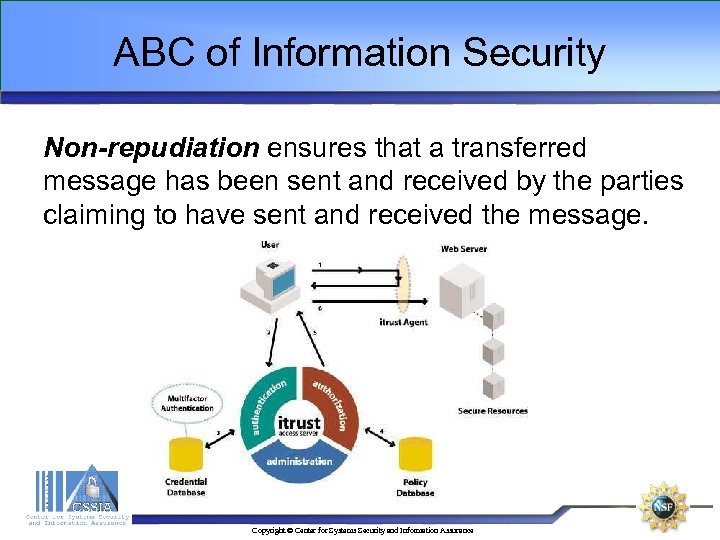
ABC of Information Security Non-repudiation ensures that a transferred message has been sent and received by the parties claiming to have sent and received the message. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Why information Security Is Important There a variety of reasons why information security is so important to both businesses and individuals. • Prevent Data Theft • Protect Intellectual Property • Thwart Identity Theft • Avoid Legal Consequences • Maintain Productivity • Foil Cyberterrorism Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
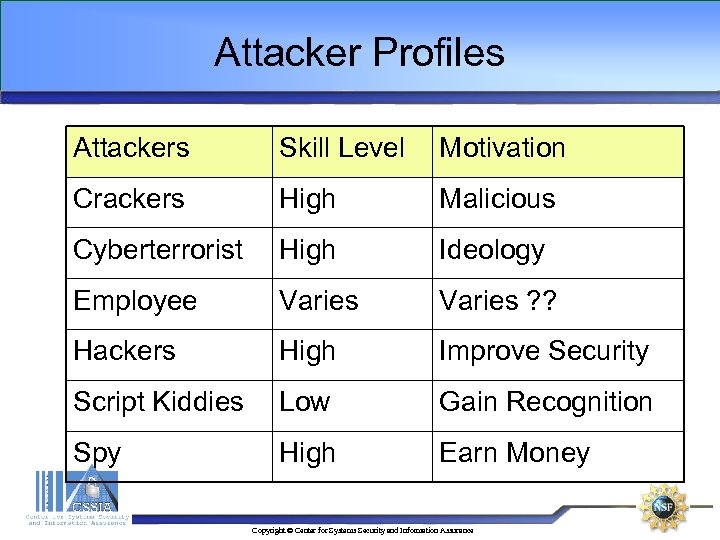
Attacker Profiles Attackers Skill Level Motivation Crackers High Malicious Cyberterrorist High Ideology Employee Varies ? ? Hackers High Improve Security Script Kiddies Low Gain Recognition Spy High Earn Money Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
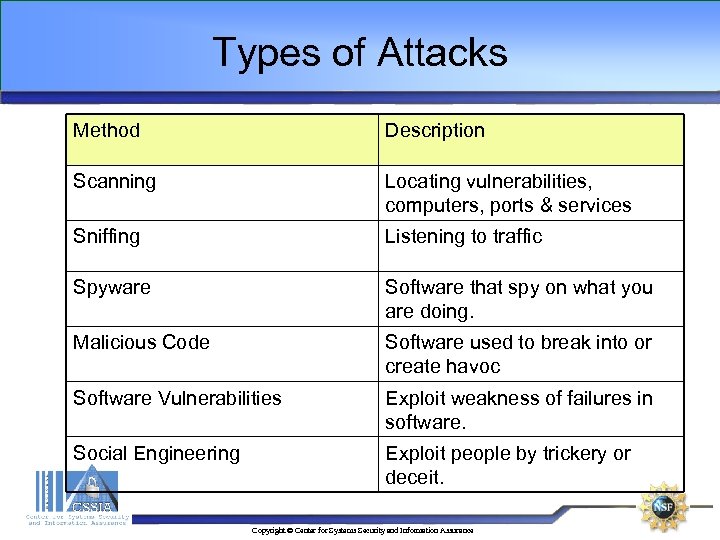
Types of Attacks Method Description Scanning Locating vulnerabilities, computers, ports & services Sniffing Listening to traffic Spyware Software that spy on what you are doing. Malicious Code Software used to break into or create havoc Software Vulnerabilities Exploit weakness of failures in software. Social Engineering Exploit people by trickery or deceit. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Threats • • Gain unauthorized access to systems or information in order to commit fraud, network intrusion, industrial espionage, identity theft, or simply to disrupt the system or network Typical targets include telephone and cable companies, answering services, financial institutions, fortune 500 corporations, military and government agencies, and healthcare organizations. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Types of Sensitive Information • • • Contract information Legal cases Personnel files Patient records Credit or financial records • Treatment or therapy records • Arrest/crime • Trade secrets, recipes and formulas • Patent Applications Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Layers of Organizational Security • Personal Security Individuals or groups granted access to resources • Information Security Protection of organizational information • Operational Security Protection of a process or series of activities • Communication Security Protecting an organization’s communication media Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Layers of Organizational Security • Network Security Protection of organizations network components, connections and content • Physical Security Protection of physical objects and properties Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Major Components This class is not an all inclusive guide to corporate information security. Information security consists of four major components: Ø Culture Ø Processes Ø Policies Ø Technologies Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Who is Susceptible? • • • Understand all organization experience situations that increase the risk of information security issues: Termination of a disgruntled employee that holds a grudge Electronic transactions occur Sensitive or personal information is handled A highly competitive business climate Individuals that lack security awareness and best practices Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Weakest Link • Information Security’s weakest link is people. • Comp. TIA the “Computing Technology Industry Association” identifies that nearly two-thirds of reported security breaches are primarily the result of human error. • Information security is a distributed responsibility and is very important to the survival of any business. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Social Engineering • Using psychological methods (ranging from friendliness to assumed identities) to gain access to a system or location • Targets are normally common workers including: Ø Ø Receptionists Telephone Operators Admin Assistants Security Guards Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Social Engineering • Most people are trusting and helpful. • People looking to acquire information they wouldn’t normally have access to will attempt to exploit this natural behavior using Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Key To Information Security • Never give your passwords to anyone. • Never use email to send confidential or sensitive information (passwords, SSN, or CC numbers). • Always log off of your applications when done. • Keep the area where your computer is located secure (locks). • Keep your anti-virus software files up-to-date. • Utilize "Windows Update" frequently for critical/security updates when using Internet Explorer. • Be cautious of unknown attachments and emails. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Key To Information Security • • • Verify and report all virus warnings. Remember you are responsible for all actions originating from your computer and/or your user account. Become familiarize with your organization’s Acceptable Use Policy. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Case Study 1 • Files containing several month’s worth of budget negotiation documentation were lost in a computer virus attack. • Computer viruses are programs that can enter a computer system without the user’s knowledge and damage the information contained on floppy and hard disk drives. • The loss of data resulted in over 2, 000 hours of labor costing over $200, 000. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Case Study 2 Important legislative briefing lost when the corporate attorney’s laptop computer is stolen. • The company lost thousands in labor, cost fines, and judicial delays. • Resulted in the organization losing opportunity for geographic expansion and growth in market share. • Resulted in loss of jobs and promotions for persons involved. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Case Study 3 • • Personal password and username emailed to scrupulous cyber criminal Resulted in identify theft, financial lose and personal embarrassment Expensive attorney fees, court cost and reapplication for all credit accounts Affected personal credit rating Resulted in the cancellation of vacations and important personal purchases Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Case Study 4 • A system administrator accidentally stumbles upon child pornography while backing up his supervisor’s workstation. • He is not sure whether to continue the backup or stop and call someone. He decides to ignore the incident. Three weeks later the local FBI computer crimes division present an order to seize all the systems in the branch office. What is the technicians legal liability? Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Exercise One • Use the internet to find as much information about your partner as possible. Specifically try to find phone number and address. A map to their house would be useful. (Page 29) Try the following websites: • searchsystems. net • Brbpub. com/pubrecsites. asp • Willyancey. com • Indorrgs. virginia. edu/portico • www. thechampion. org Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance

Exercise Two • • • America Community College is a mid-size college in Indiana. The director of Information Technology suddenly quit. Before leaving he sent you and your team to security awareness training. Because the college is so heavily dependant on computers and technology the college vice president ask you and your team to propose a comprehensive security plan to address the most common types of attacks and threats. You and your team need to develop a 10 minute presentation for the college board and president to communicate threat and need for the college to finance and implement a comprehensive security plan. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
cb2ba597c66b99533de1673decc7ca33.ppt