08c4768a90a8978ea4a64df2a0f2e1b0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Lesson Four Data Privacy and Encryption Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Lesson Four Data Privacy and Encryption Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Lesson Objectives • Define the term cryptology and discuss the types and applications of cryptology. • Identify the components of a cryptography systems. • Identify and discuss common approaches to cryptography. • Compare and contrast symmetric and asymmetric encryption. • Define the term digital signature and explain its function. • Define the term Public-Key Infrastructure and explains it uses. • List the most common secure applications and explain there function. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Lesson Objectives • Define the term cryptology and discuss the types and applications of cryptology. • Identify the components of a cryptography systems. • Identify and discuss common approaches to cryptography. • Compare and contrast symmetric and asymmetric encryption. • Define the term digital signature and explain its function. • Define the term Public-Key Infrastructure and explains it uses. • List the most common secure applications and explain there function. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Protecting Your Personal Information • Every day you share personal information about yourself with others • It is so routine that you may not even realize you are doing it Ø write a check at the grocery store, Ø charge tickets to a ball game, Ø rent a car, Ø mail your tax returns, Ø buy a gift online, Ø call home on your cell phone, Ø schedule a doctors appointment Ø or apply for a credit card. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Protecting Your Personal Information • Every day you share personal information about yourself with others • It is so routine that you may not even realize you are doing it Ø write a check at the grocery store, Ø charge tickets to a ball game, Ø rent a car, Ø mail your tax returns, Ø buy a gift online, Ø call home on your cell phone, Ø schedule a doctors appointment Ø or apply for a credit card. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Protecting Your Personal Information Each transaction requires you to share personal information: Øyour bank and credit card account numbers Øyour income Øyour Social Security number (SSN) Øor your name Øaddress and phone numbers Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Protecting Your Personal Information Each transaction requires you to share personal information: Øyour bank and credit card account numbers Øyour income Øyour Social Security number (SSN) Øor your name Øaddress and phone numbers Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 What happened with my personal information? ØIts important to find out what happens to the personal information you and your children provide to companies, marketers and government agencies. ØThese organizations may use your information simply to process your order; to tell you about products, services, or promotions; or to share with others. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
What happened with my personal information? ØIts important to find out what happens to the personal information you and your children provide to companies, marketers and government agencies. ØThese organizations may use your information simply to process your order; to tell you about products, services, or promotions; or to share with others. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Identity Theft – Fastest Growing Crime ØIdentity thieves, who want your information to commit fraud ØIdentity theft is the fastest-growing white-collar crime in America ØOccurs when someone steals your personal identifying information to vopen new charge accounts, vorder merchandise vor borrow money ØConsumers targeted by identity thieves usually don’t know they’ve been victimized. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Identity Theft – Fastest Growing Crime ØIdentity thieves, who want your information to commit fraud ØIdentity theft is the fastest-growing white-collar crime in America ØOccurs when someone steals your personal identifying information to vopen new charge accounts, vorder merchandise vor borrow money ØConsumers targeted by identity thieves usually don’t know they’ve been victimized. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 FTC Tips to Avoid Identity Theft ØBefore you reveal any personally identifying information, find out how it will be used and whether it will be shared with others ØRead the privacy policy on any website directed to you or your children ØMinimize the identification information and the number of cards you carry to what you’ll actually need Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
FTC Tips to Avoid Identity Theft ØBefore you reveal any personally identifying information, find out how it will be used and whether it will be shared with others ØRead the privacy policy on any website directed to you or your children ØMinimize the identification information and the number of cards you carry to what you’ll actually need Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 FTC Tips to Avoid Identity Theft ØDon’t put all your identifying information in one holder in your purse, briefcase, wallet or backpack ØKeep items with personal information in a safe place ØProtect yourself against dumpster diving ØUse a secure browser when shopping online to guard ØEmploy encryption when transferring sensitive or confidential data Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
FTC Tips to Avoid Identity Theft ØDon’t put all your identifying information in one holder in your purse, briefcase, wallet or backpack ØKeep items with personal information in a safe place ØProtect yourself against dumpster diving ØUse a secure browser when shopping online to guard ØEmploy encryption when transferring sensitive or confidential data Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
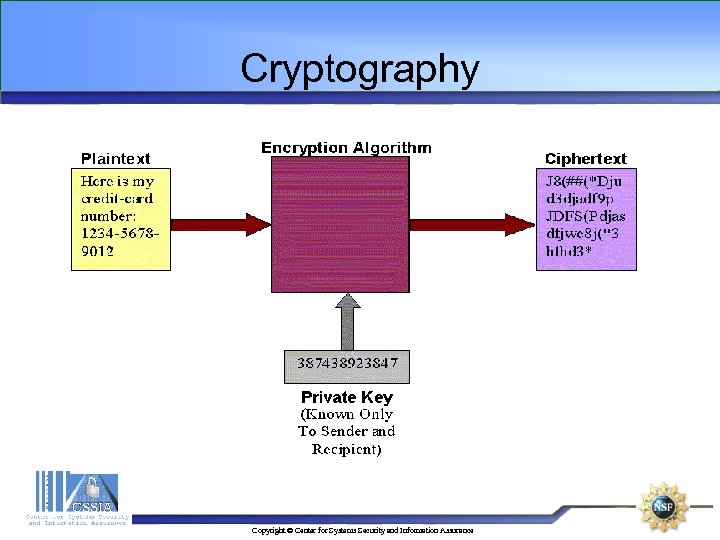
 Cryptography • Cryptography The art and science of keeping information secure from unintended audiences, of encrypting it • Cryptanalysis The art and science of breaking encoded data • Cryptology The branch of mathematics encompassing both cryptography and cryptanalysis • Cryptography Plays a crucial role in the transfer of confidential information across local networks and the Internet Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Cryptography • Cryptography The art and science of keeping information secure from unintended audiences, of encrypting it • Cryptanalysis The art and science of breaking encoded data • Cryptology The branch of mathematics encompassing both cryptography and cryptanalysis • Cryptography Plays a crucial role in the transfer of confidential information across local networks and the Internet Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Cryptography Components • Encryption Algorithm A set of mathematically expressed processes for encrypting information • Ciphertext Encrypted text • Plaintext What you have before encryption, and ciphertext is the encrypted result • Key Information used to change the operations performed in crypto-equipment for the purpose of encrypting or decrypting electronic signals. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Cryptography Components • Encryption Algorithm A set of mathematically expressed processes for encrypting information • Ciphertext Encrypted text • Plaintext What you have before encryption, and ciphertext is the encrypted result • Key Information used to change the operations performed in crypto-equipment for the purpose of encrypting or decrypting electronic signals. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Cryptography Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Cryptography Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Applying Cryptography • Encrypts data residing on storage devices or traveling through communication channels to ensure that any illegal access is not successful • Secures the process of authenticating different parties attempting any function on the system • Presents a party wishing be granted certain functionality on the system a way to prove that they indeed who they say they are • Ensures that credentials are only used by their rightful owner Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Applying Cryptography • Encrypts data residing on storage devices or traveling through communication channels to ensure that any illegal access is not successful • Secures the process of authenticating different parties attempting any function on the system • Presents a party wishing be granted certain functionality on the system a way to prove that they indeed who they say they are • Ensures that credentials are only used by their rightful owner Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Principles of Modern Cryptography • Emphasis that security should not depend on the secrecy of the encryption method (or algorithm), only the secrecy of the keys • Revelation of the secret keys must not occur when plaintext and ciphertext are compared, and no person should have knowledge of the key • Execution of today's algorithms are by computers or specialized hardware devices, and in most cases are implemented in computer software Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Principles of Modern Cryptography • Emphasis that security should not depend on the secrecy of the encryption method (or algorithm), only the secrecy of the keys • Revelation of the secret keys must not occur when plaintext and ciphertext are compared, and no person should have knowledge of the key • Execution of today's algorithms are by computers or specialized hardware devices, and in most cases are implemented in computer software Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
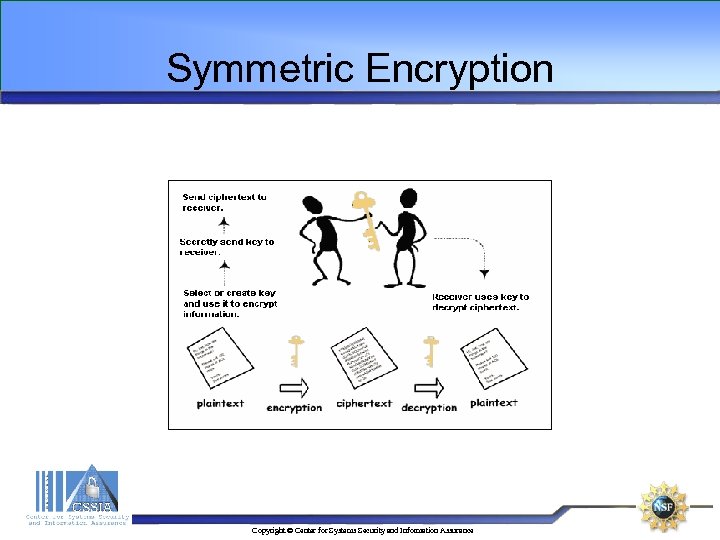
 Symmetric Encryption • The message can be encrypted and decrypted using the same key • Symmetric encryption is faster compared to asymmetric encryption • Both the sender and the recipient must have an access to (same) encryption key (a disadvantage) • Secure distribution of the (encryption) key between the parties is required • The most commonly used symmetric encryption method is Data Encryption Standard Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Symmetric Encryption • The message can be encrypted and decrypted using the same key • Symmetric encryption is faster compared to asymmetric encryption • Both the sender and the recipient must have an access to (same) encryption key (a disadvantage) • Secure distribution of the (encryption) key between the parties is required • The most commonly used symmetric encryption method is Data Encryption Standard Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Symmetric Encryption Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Symmetric Encryption Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
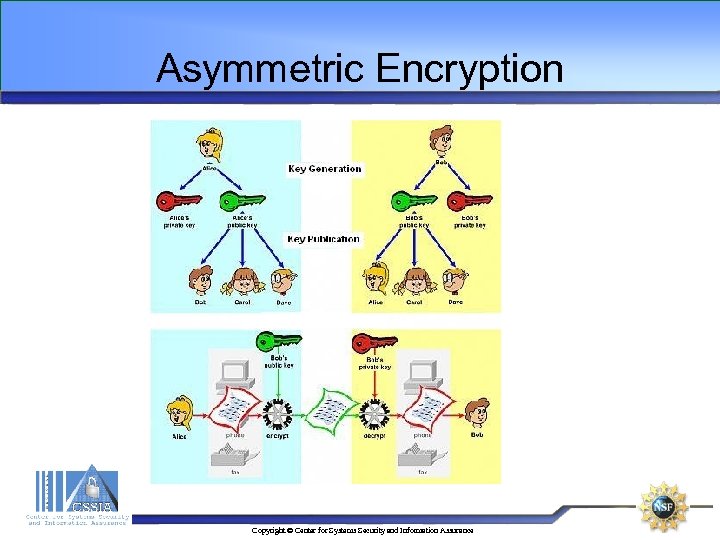
 Asymmetric Encryption • Based on the usage of key pairs • Exchangeable keys • The recipient's private key is only in the recipient's possession, no third party is able to decrypt the message encrypted with the recipient's public key • Management of keys is a big advantage • Time-consuming • Referred to as public key encryption. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Asymmetric Encryption • Based on the usage of key pairs • Exchangeable keys • The recipient's private key is only in the recipient's possession, no third party is able to decrypt the message encrypted with the recipient's public key • Management of keys is a big advantage • Time-consuming • Referred to as public key encryption. Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Asymmetric Encryption Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Asymmetric Encryption Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
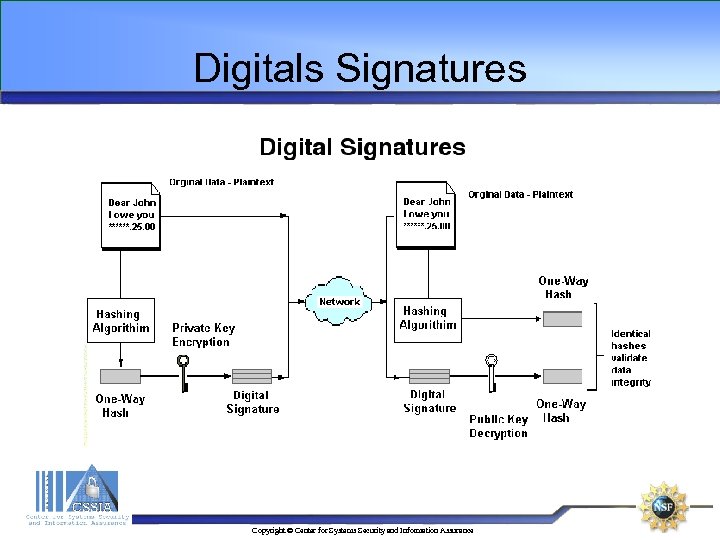
 Digitals Signatures Extra data is appended to a message which identifies and authenticates the sender and message data using publickey encryption Ø The sender uses a one-way hash function to generate a hash-code of about 32 bits from the message data Ø The sender then encrypts the hash-code with his private key Ø The receiver re-computes the hash-code from the data and decrypts the received hash with the sender's public key Ø If the two hash-codes are equal, the receiver can be sure that data has not been corrupted and that it came from the given sender Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Digitals Signatures Extra data is appended to a message which identifies and authenticates the sender and message data using publickey encryption Ø The sender uses a one-way hash function to generate a hash-code of about 32 bits from the message data Ø The sender then encrypts the hash-code with his private key Ø The receiver re-computes the hash-code from the data and decrypts the received hash with the sender's public key Ø If the two hash-codes are equal, the receiver can be sure that data has not been corrupted and that it came from the given sender Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Digitals Signatures Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Digitals Signatures Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 RSA • A public key cipher which can be used both for encrypting messages and making digital signatures • The company RSA Data Security Inc. takes its name from this algorithm, and has acquired the rights to the patents which cover it Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
RSA • A public key cipher which can be used both for encrypting messages and making digital signatures • The company RSA Data Security Inc. takes its name from this algorithm, and has acquired the rights to the patents which cover it Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Public-key Infrastructure (PKI) • Combine software, encryption technologies, and services to enable enterprises to protect the security of their communications and business transactions on the Internet • Integrate digital certificates, public-key cryptography, and certificate authorities into a total, enterprise-wide network security architecture Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Public-key Infrastructure (PKI) • Combine software, encryption technologies, and services to enable enterprises to protect the security of their communications and business transactions on the Internet • Integrate digital certificates, public-key cryptography, and certificate authorities into a total, enterprise-wide network security architecture Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Virtual Private Network (VPNs) • Connect a group of two or more computer systems to a private network with limited public-network access, that communicates securely over a public network, such as the internet • Include encryption, authentication of remote users or hosts, and mechanisms for hiding or masking information about private network topology from potential attackers on the public network Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Virtual Private Network (VPNs) • Connect a group of two or more computer systems to a private network with limited public-network access, that communicates securely over a public network, such as the internet • Include encryption, authentication of remote users or hosts, and mechanisms for hiding or masking information about private network topology from potential attackers on the public network Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Secure Application Protocols • Secure/MIME (S/MIME) A version of the MIME protocol that supports encryption of messages. S/MIME is based on RSA's public-key encryption technology • Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) A standard that will enable secure credit card transactions on the Internet • Secure Shell (SSH) A program to log into another computer over a network, to execute commands in a remote machine, and to move files from one machine to another Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Secure Application Protocols • Secure/MIME (S/MIME) A version of the MIME protocol that supports encryption of messages. S/MIME is based on RSA's public-key encryption technology • Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) A standard that will enable secure credit card transactions on the Internet • Secure Shell (SSH) A program to log into another computer over a network, to execute commands in a remote machine, and to move files from one machine to another Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Secure Application Protocols • SHTTP An extension to the HTTP protocol to support sending data securely over the World Wide Web • IP Security (IPSec) A set of protocols developed by the IETF to support secure exchange of packets at the IP layer Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Secure Application Protocols • SHTTP An extension to the HTTP protocol to support sending data securely over the World Wide Web • IP Security (IPSec) A set of protocols developed by the IETF to support secure exchange of packets at the IP layer Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Exercise 4. 1 Using PGP Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Exercise 4. 1 Using PGP Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Exercise 4. 2 Using Token Generator Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Exercise 4. 2 Using Token Generator Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Exercise 4. 3 VPN Demonstration Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Exercise 4. 3 VPN Demonstration Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Exercise 4. 4 Using SHTTP Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Exercise 4. 4 Using SHTTP Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Exercise 4. 5 Viewing a Digital Certificate Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Exercise 4. 5 Viewing a Digital Certificate Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
 Exercise 4. 6 Protecting Word Documents Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance
Exercise 4. 6 Protecting Word Documents Copyright © Center for Systems Security and Information Assurance


