fa1b10f230acd14b0fdee29e9ce12b6a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Lesson 1 A Introduction to Computers
Lesson 1 A Introduction to Computers
 Definition of a Computer A computer is an electronic device used to process data, converting the data into information that is useful to people home
Definition of a Computer A computer is an electronic device used to process data, converting the data into information that is useful to people home
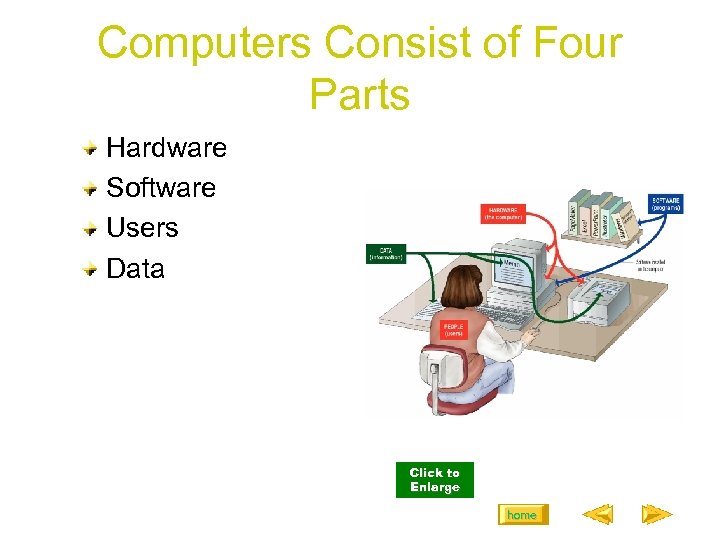 Computers Consist of Four Parts Hardware Software Users Data Click to Enlarge home
Computers Consist of Four Parts Hardware Software Users Data Click to Enlarge home
 Hardware Mechanical devices that make up the computer home
Hardware Mechanical devices that make up the computer home
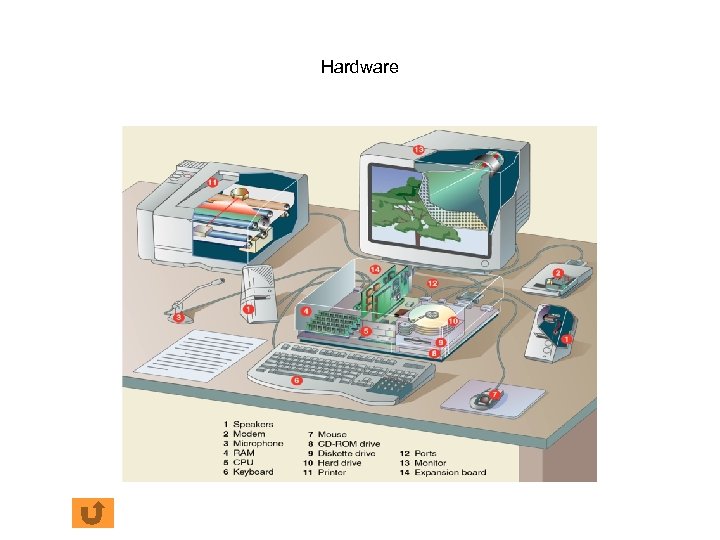 Hardware
Hardware
 Processing The procedure that transforms raw data into useful information is called processing The processor and memory perform this transformation home
Processing The procedure that transforms raw data into useful information is called processing The processor and memory perform this transformation home
 Processor The computer’s brain, which organizes and carries out instructions from either the user or the software home
Processor The computer’s brain, which organizes and carries out instructions from either the user or the software home
 Motherboard Rigid rectangular card containing the circuitry that connects the processor to the other hardware home
Motherboard Rigid rectangular card containing the circuitry that connects the processor to the other hardware home
 Circuit board Motherboard is an example of a circuit board Attached to the motherboard are many smaller circuit boards that house many internal devices home
Circuit board Motherboard is an example of a circuit board Attached to the motherboard are many smaller circuit boards that house many internal devices home
 Central Processing Unit (CPU) Refers to a computer’s processor home
Central Processing Unit (CPU) Refers to a computer’s processor home
 Memory When you launch a program, it is loaded into and run from memory home
Memory When you launch a program, it is loaded into and run from memory home
 Random Access Memory (RAM) Determines a computer’s speed and power home
Random Access Memory (RAM) Determines a computer’s speed and power home
 Memory Measurements Kilobyte (KB) Megabyte (MB) Gigabyte (GB) Terabyte (TB) home
Memory Measurements Kilobyte (KB) Megabyte (MB) Gigabyte (GB) Terabyte (TB) home
 Input Devices Accept data and instructions from the user or from another computer system home
Input Devices Accept data and instructions from the user or from another computer system home
 Most Common Input Devices Keyboard Mouse home
Most Common Input Devices Keyboard Mouse home
 Output Devices Return processed data to the user or to another computer system home
Output Devices Return processed data to the user or to another computer system home
 Most Common Output Devices Monitor Printer home
Most Common Output Devices Monitor Printer home
 Storage Holds data permanently home
Storage Holds data permanently home
 Storage Terms Magnetic disk Read/write heads Disk drive Hard disk or hard drive Diskettes or floppy disks home
Storage Terms Magnetic disk Read/write heads Disk drive Hard disk or hard drive Diskettes or floppy disks home
 Storage Terms Continued CD-ROM drive Compact disks (CDs) Compact Disk-Read-Only Memory (CDROM) CD-Recordable (CD-R) CD-Re. Writable (CD-RW) Digital Video Disk (DVD) home
Storage Terms Continued CD-ROM drive Compact disks (CDs) Compact Disk-Read-Only Memory (CDROM) CD-Recordable (CD-R) CD-Re. Writable (CD-RW) Digital Video Disk (DVD) home
 Software A set of electronic instructions consisting of complex codes, or programs, that make the computer perform tasks home
Software A set of electronic instructions consisting of complex codes, or programs, that make the computer perform tasks home
 Examples of Software System software Application software home
Examples of Software System software Application software home
 Five Computer Categories Supercomputers Mainframe computers Minicomputers Workstations Microcomputers, or personal computers home
Five Computer Categories Supercomputers Mainframe computers Minicomputers Workstations Microcomputers, or personal computers home
 The Internet Started Out As ARPANET In 1969, the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the U. S. Department of Defense created the Internet when it connected the computers at universities and defense contractors. This system was called ARPANET. home
The Internet Started Out As ARPANET In 1969, the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the U. S. Department of Defense created the Internet when it connected the computers at universities and defense contractors. This system was called ARPANET. home
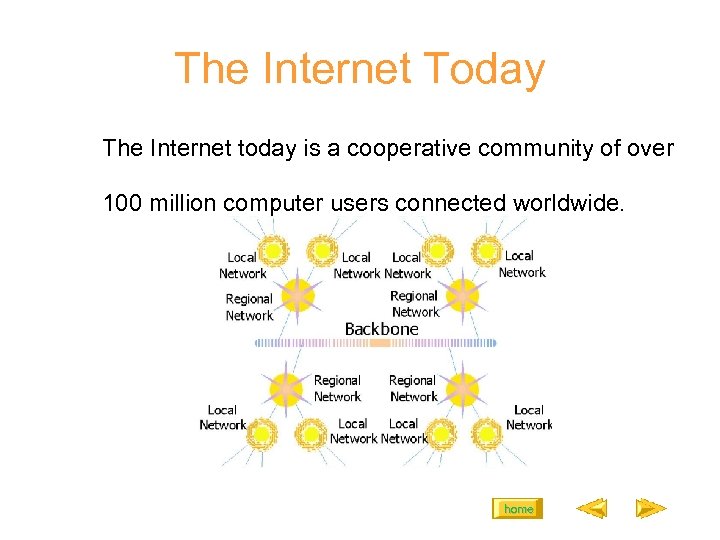 The Internet Today The Internet today is a cooperative community of over 100 million computer users connected worldwide. home
The Internet Today The Internet today is a cooperative community of over 100 million computer users connected worldwide. home
 World Wide Web Accessed through the Internet, the World Wide Web lets users view specially formatted documents home
World Wide Web Accessed through the Internet, the World Wide Web lets users view specially formatted documents home
 Web Browsers A Web browser is computer software that lets you navigate the Web First you connect to the Internet, then you launch the browser, then you view Web pages home
Web Browsers A Web browser is computer software that lets you navigate the Web First you connect to the Internet, then you launch the browser, then you view Web pages home
 URL’s Every Web page has a unique address, called a uniform resource locator, or URL (pronounced as spelled: U-R-L) home
URL’s Every Web page has a unique address, called a uniform resource locator, or URL (pronounced as spelled: U-R-L) home
 Hyperlinks A hyperlink is a part of the Web page that is linked to a URL home
Hyperlinks A hyperlink is a part of the Web page that is linked to a URL home
 Web Search Tools Directories Search Engines Metasearch engines Site-specific search tools home
Web Search Tools Directories Search Engines Metasearch engines Site-specific search tools home
 Lesson 1 A Introduction to Computers and the Internet
Lesson 1 A Introduction to Computers and the Internet


