93394103c1d622200c63d0ffec3b0c88.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
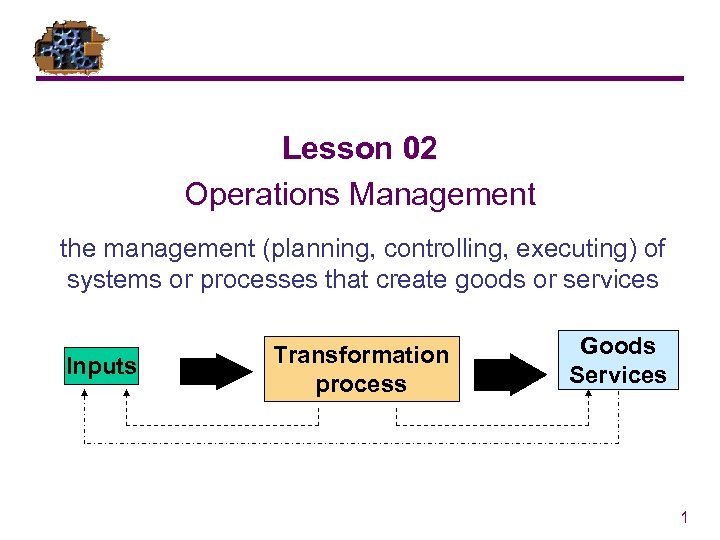 Lesson 02 Operations Management the management (planning, controlling, executing) of systems or processes that create goods or services Inputs Transformation process Goods Services 1
Lesson 02 Operations Management the management (planning, controlling, executing) of systems or processes that create goods or services Inputs Transformation process Goods Services 1
 Goods manufacturing a product (e. g. golf ball, refrigerator, electronic equipment, lawn mowers, pencils, food/cereal, automobiles, tires, etc. ) Characteristics • Physical, durable product • Output can be inventoried • Low customer contact • Long response time • Regional, national or International markets • Large facilities • Capital intensive 2
Goods manufacturing a product (e. g. golf ball, refrigerator, electronic equipment, lawn mowers, pencils, food/cereal, automobiles, tires, etc. ) Characteristics • Physical, durable product • Output can be inventoried • Low customer contact • Long response time • Regional, national or International markets • Large facilities • Capital intensive 2
 Services act oriented (e. g. government, wholesale/retail, financial, healthcare, personal services, business services, education, etc. ) Characteristics • Intangible, perishable product • Output cannot be inventoried • High customer contact • Short response time • Local markets • Small facilities • Labor intensive • Quality not easily 3
Services act oriented (e. g. government, wholesale/retail, financial, healthcare, personal services, business services, education, etc. ) Characteristics • Intangible, perishable product • Output cannot be inventoried • High customer contact • Short response time • Local markets • Small facilities • Labor intensive • Quality not easily 3
 What about Mc. Donald’s? 4
What about Mc. Donald’s? 4
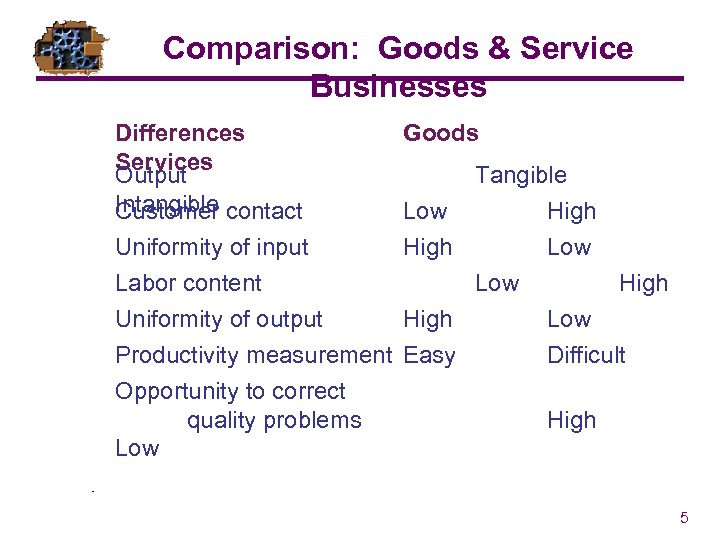 Comparison: Goods & Service Businesses Differences Services Output Intangible contact Customer Uniformity of input Labor content Uniformity of output Productivity measurement Opportunity to correct quality problems Low Goods Tangible Low High Low Easy Difficult High 5
Comparison: Goods & Service Businesses Differences Services Output Intangible contact Customer Uniformity of input Labor content Uniformity of output Productivity measurement Opportunity to correct quality problems Low Goods Tangible Low High Low Easy Difficult High 5
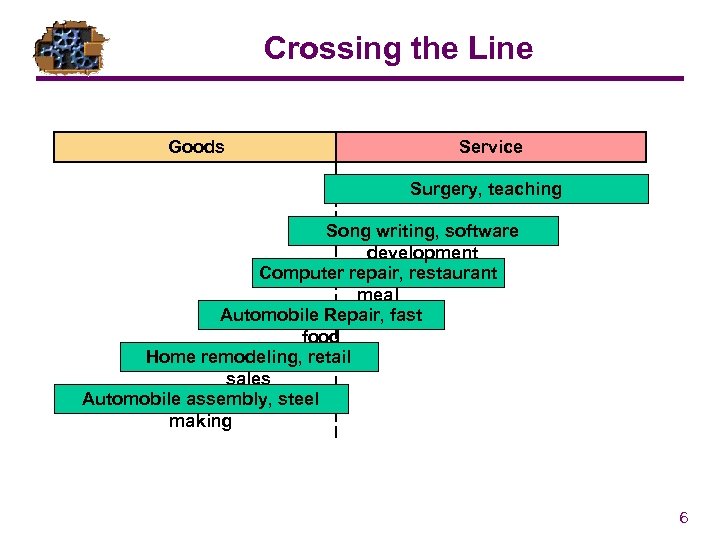 Crossing the Line Goods Service Surgery, teaching Song writing, software development Computer repair, restaurant meal Automobile Repair, fast food Home remodeling, retail sales Automobile assembly, steel making 6
Crossing the Line Goods Service Surgery, teaching Song writing, software development Computer repair, restaurant meal Automobile Repair, fast food Home remodeling, retail sales Automobile assembly, steel making 6
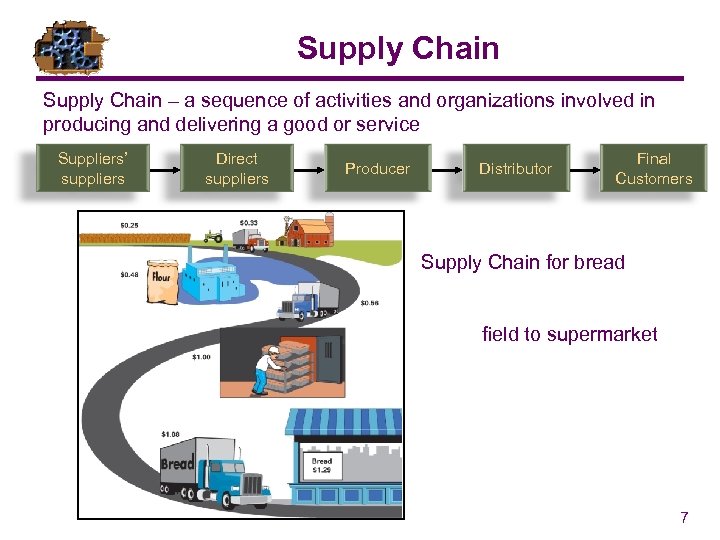 Supply Chain – a sequence of activities and organizations involved in producing and delivering a good or service Suppliers’ suppliers Direct suppliers Producer Distributor Final Customers Supply Chain for bread field to supermarket 7
Supply Chain – a sequence of activities and organizations involved in producing and delivering a good or service Suppliers’ suppliers Direct suppliers Producer Distributor Final Customers Supply Chain for bread field to supermarket 7
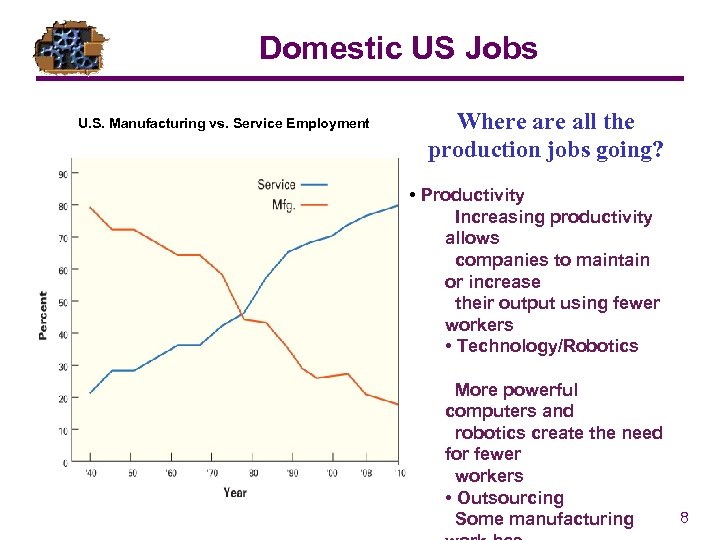 Domestic US Jobs U. S. Manufacturing vs. Service Employment Year Mfg. Service Where all the production jobs going? • Productivity Increasing productivity allows companies to maintain or increase their output using fewer workers • Technology/Robotics 25 75 More powerful computers and robotics create the need for fewer workers • Outsourcing 8 Some manufacturing
Domestic US Jobs U. S. Manufacturing vs. Service Employment Year Mfg. Service Where all the production jobs going? • Productivity Increasing productivity allows companies to maintain or increase their output using fewer workers • Technology/Robotics 25 75 More powerful computers and robotics create the need for fewer workers • Outsourcing 8 Some manufacturing
 So, Why Study OM? Core of all manufacturing business organizations 35% of all jobs are in OM customer service quality assurance production planning and control scheduling inventory management warehouse management Interrelates with all other business organizations 9
So, Why Study OM? Core of all manufacturing business organizations 35% of all jobs are in OM customer service quality assurance production planning and control scheduling inventory management warehouse management Interrelates with all other business organizations 9
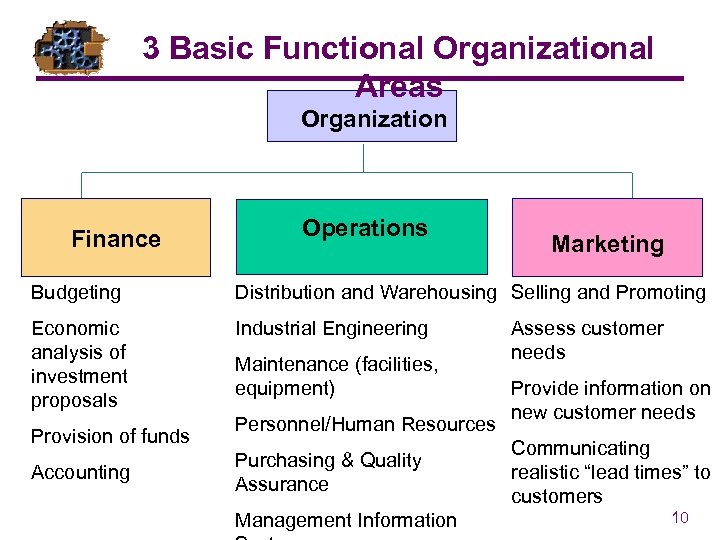 3 Basic Functional Organizational Areas Organization Finance Operations Marketing Budgeting Distribution and Warehousing Selling and Promoting Economic analysis of investment proposals Industrial Engineering Provision of funds Accounting Maintenance (facilities, equipment) Personnel/Human Resources Purchasing & Quality Assurance Management Information Assess customer needs Provide information on new customer needs Communicating realistic “lead times” to customers 10
3 Basic Functional Organizational Areas Organization Finance Operations Marketing Budgeting Distribution and Warehousing Selling and Promoting Economic analysis of investment proposals Industrial Engineering Provision of funds Accounting Maintenance (facilities, equipment) Personnel/Human Resources Purchasing & Quality Assurance Management Information Assess customer needs Provide information on new customer needs Communicating realistic “lead times” to customers 10
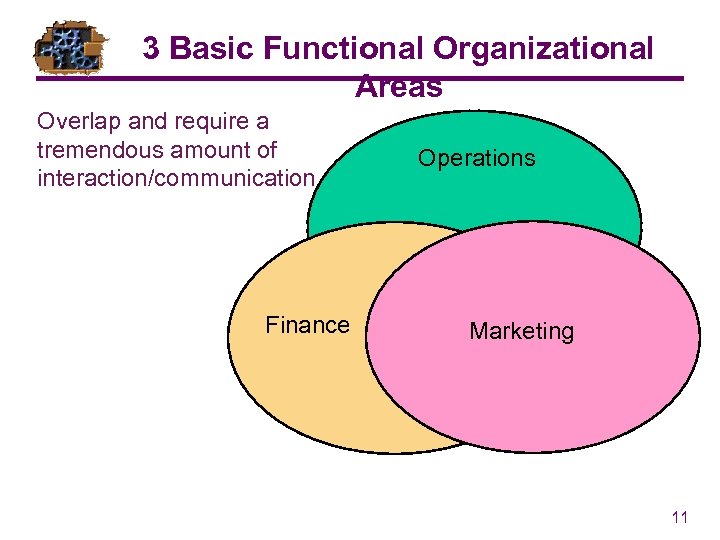 3 Basic Functional Organizational Areas Overlap and require a tremendous amount of interaction/communication Finance Operations Marketing 11
3 Basic Functional Organizational Areas Overlap and require a tremendous amount of interaction/communication Finance Operations Marketing 11
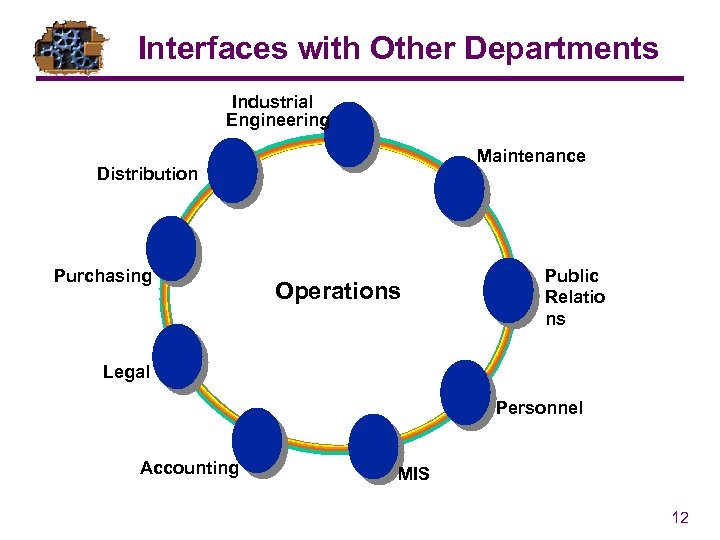 Interfaces with Other Departments Industrial Engineering Maintenance Distribution Purchasing Operations Public Relatio ns Legal Personnel Accounting MIS 12
Interfaces with Other Departments Industrial Engineering Maintenance Distribution Purchasing Operations Public Relatio ns Legal Personnel Accounting MIS 12
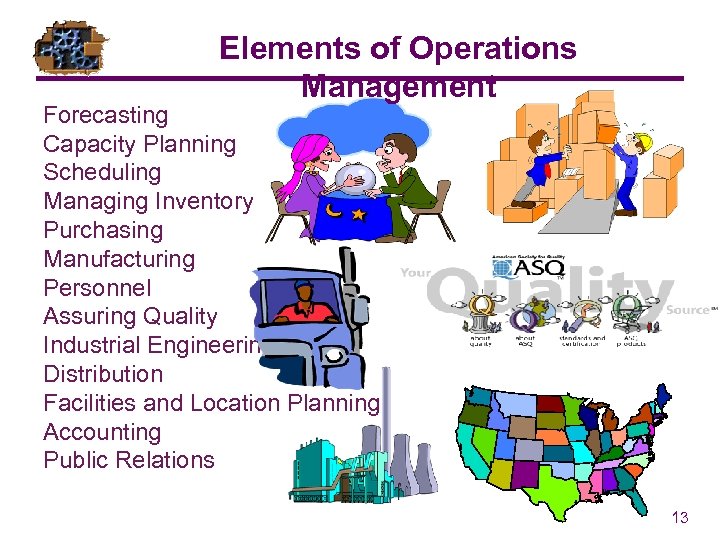 Elements of Operations Management Forecasting Capacity Planning Scheduling Managing Inventory Purchasing Manufacturing Personnel Assuring Quality Industrial Engineering Distribution Facilities and Location Planning Accounting Public Relations 13
Elements of Operations Management Forecasting Capacity Planning Scheduling Managing Inventory Purchasing Manufacturing Personnel Assuring Quality Industrial Engineering Distribution Facilities and Location Planning Accounting Public Relations 13
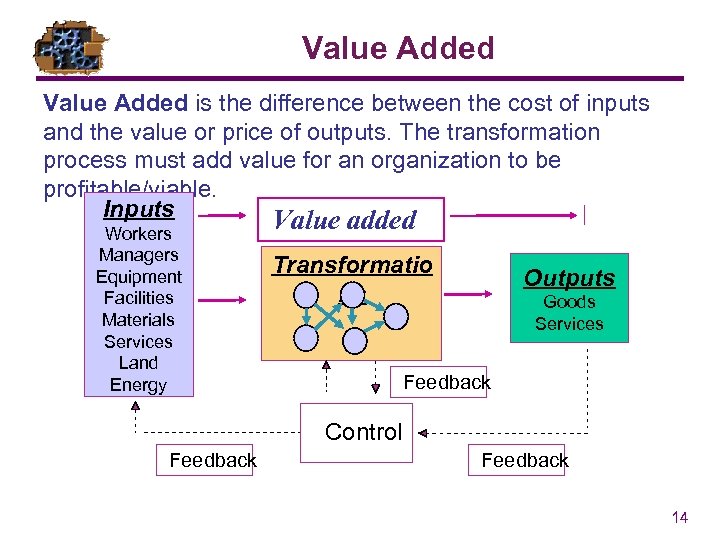 Value Added is the difference between the cost of inputs and the value or price of outputs. The transformation process must add value for an organization to be profitable/viable. Inputs Value added Workers Managers Equipment Facilities Materials Services Land Energy Transformatio ns Outputs Goods Services Feedback Control Feedback 14
Value Added is the difference between the cost of inputs and the value or price of outputs. The transformation process must add value for an organization to be profitable/viable. Inputs Value added Workers Managers Equipment Facilities Materials Services Land Energy Transformatio ns Outputs Goods Services Feedback Control Feedback 14
 Transformations Physical Goods Producing (manufacturing, farming, mining, construction, power generation) Location Transport / Storage (Warehousing, trucking, hotels, airlines) Exchange Retail (Wal-Mart, Dillard's, etc. ) Physiological Healthcare (Hospitals, doctors, dentists) Psychological Entertainment (Films, radio, television, performing arts, recording industry) Informational Communications (Newspapers, radio, telephone, satellites) 15
Transformations Physical Goods Producing (manufacturing, farming, mining, construction, power generation) Location Transport / Storage (Warehousing, trucking, hotels, airlines) Exchange Retail (Wal-Mart, Dillard's, etc. ) Physiological Healthcare (Hospitals, doctors, dentists) Psychological Entertainment (Films, radio, television, performing arts, recording industry) Informational Communications (Newspapers, radio, telephone, satellites) 15
 Value Added The greater the value added the more funds that are available for an organization to invest in research and development new facilities and equipment growth employee programs viability 16
Value Added The greater the value added the more funds that are available for an organization to invest in research and development new facilities and equipment growth employee programs viability 16
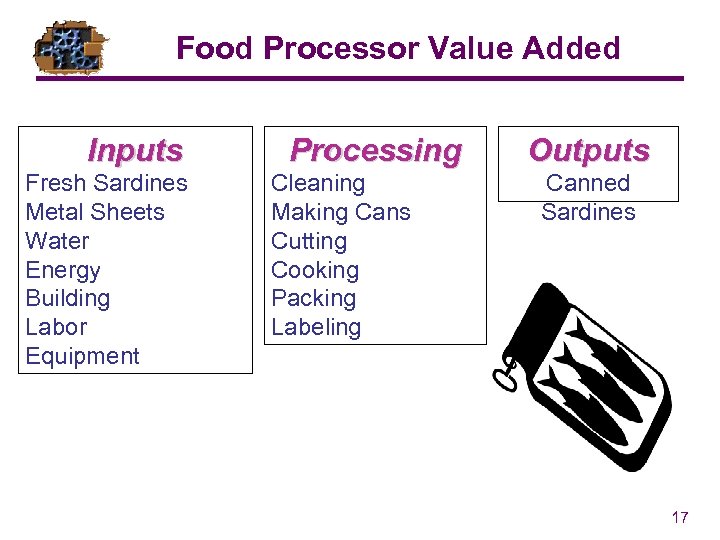 Food Processor Value Added Inputs Fresh Sardines Metal Sheets Water Energy Building Labor Equipment Processing Cleaning Making Cans Cutting Cooking Packing Labeling Outputs Canned Sardines 17
Food Processor Value Added Inputs Fresh Sardines Metal Sheets Water Energy Building Labor Equipment Processing Cleaning Making Cans Cutting Cooking Packing Labeling Outputs Canned Sardines 17
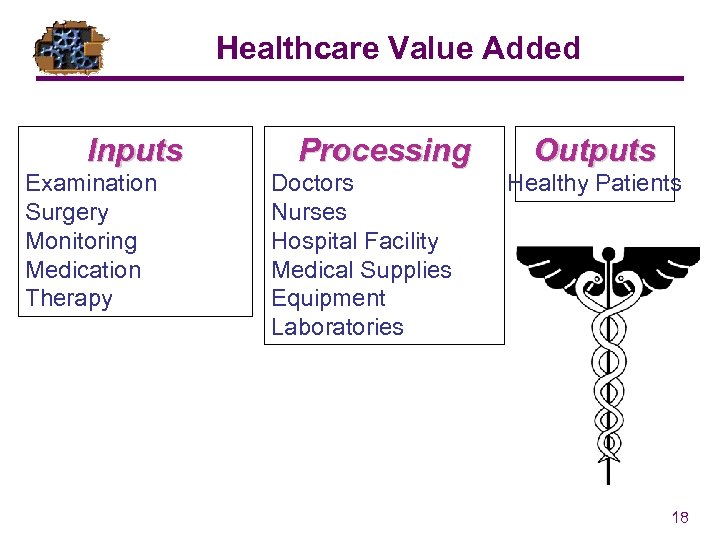 Healthcare Value Added Inputs Examination Surgery Monitoring Medication Therapy Processing Doctors Nurses Hospital Facility Medical Supplies Equipment Laboratories Outputs Healthy Patients 18
Healthcare Value Added Inputs Examination Surgery Monitoring Medication Therapy Processing Doctors Nurses Hospital Facility Medical Supplies Equipment Laboratories Outputs Healthy Patients 18
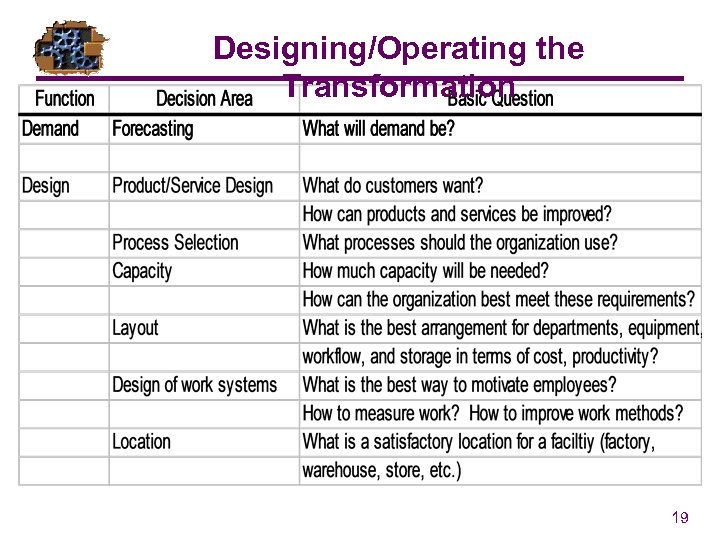 Designing/Operating the Transformation 19
Designing/Operating the Transformation 19
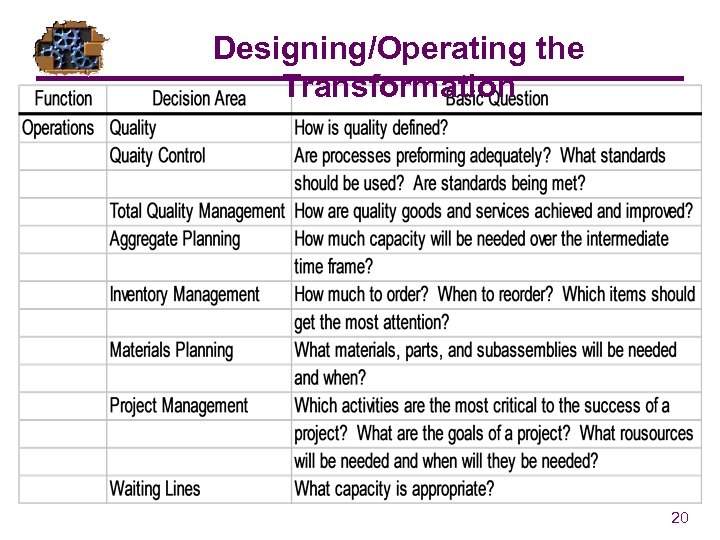 Designing/Operating the Transformation 20
Designing/Operating the Transformation 20
 Role of the Operations Manager The chief role of the operations manager is to be a planner and a decision maker with respect to the previously mentioned areas. Some of the decision making tools at an operations managers disposal will be discussed as part of this course. Listed in the following few slides is an overview of some of the methodologies we will discuss. What - What resources/what amounts When Needed/scheduled/ordered Where - Work to be done How - Designed Who - To do the work 21
Role of the Operations Manager The chief role of the operations manager is to be a planner and a decision maker with respect to the previously mentioned areas. Some of the decision making tools at an operations managers disposal will be discussed as part of this course. Listed in the following few slides is an overview of some of the methodologies we will discuss. What - What resources/what amounts When Needed/scheduled/ordered Where - Work to be done How - Designed Who - To do the work 21
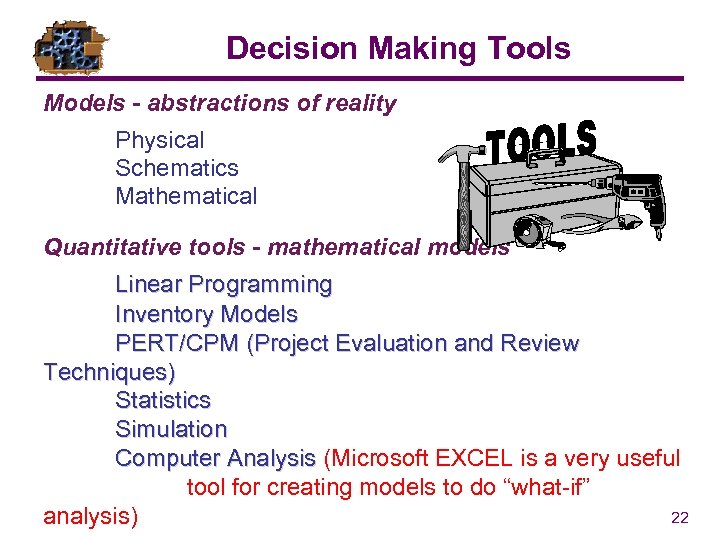 Decision Making Tools Models - abstractions of reality Physical Schematics Mathematical Quantitative tools - mathematical models Linear Programming Inventory Models PERT/CPM (Project Evaluation and Review Techniques) Statistics Simulation Computer Analysis (Microsoft EXCEL is a very useful tool for creating models to do “what-if” 22 analysis)
Decision Making Tools Models - abstractions of reality Physical Schematics Mathematical Quantitative tools - mathematical models Linear Programming Inventory Models PERT/CPM (Project Evaluation and Review Techniques) Statistics Simulation Computer Analysis (Microsoft EXCEL is a very useful tool for creating models to do “what-if” 22 analysis)
 Decision Making Tools Trade-off analysis in Evaluating decisions based on other issues such as financial considerations, company policy, etc. (e. g. considering how much inventory to stock one must consider the financial implications!) Pro-Con analysis Evaluating decisions based on an objective/subjective evaluation of the positive and negative points of the situation under consideration Pro’s Con’s 23
Decision Making Tools Trade-off analysis in Evaluating decisions based on other issues such as financial considerations, company policy, etc. (e. g. considering how much inventory to stock one must consider the financial implications!) Pro-Con analysis Evaluating decisions based on an objective/subjective evaluation of the positive and negative points of the situation under consideration Pro’s Con’s 23
 Decision Making Tools Establish Priorities Prioritize factors which are important to a situation and determine the most important few which most influence the decision Sometimes referred to as the 80/20 rule which basically means that out of all the factors which influence a decision 20% of them will most influence the decision outcome … more commonly known as the Pareto rule. Do not get caught working on problems which are not important … it may show that are not aware of what is most important in your business. 24
Decision Making Tools Establish Priorities Prioritize factors which are important to a situation and determine the most important few which most influence the decision Sometimes referred to as the 80/20 rule which basically means that out of all the factors which influence a decision 20% of them will most influence the decision outcome … more commonly known as the Pareto rule. Do not get caught working on problems which are not important … it may show that are not aware of what is most important in your business. 24
 An Example of Operations Improvement Henry Ford 13 hours to make a car - Can we do it better? Solution Pull chassis down a line with a rope and add parts from strategically placed piles of parts Result 5 hours to make a car Can we do it better (continual improvement)? Result standardization, conveyors, computers, robotics, automation can produce a car in less than an hour 25
An Example of Operations Improvement Henry Ford 13 hours to make a car - Can we do it better? Solution Pull chassis down a line with a rope and add parts from strategically placed piles of parts Result 5 hours to make a car Can we do it better (continual improvement)? Result standardization, conveyors, computers, robotics, automation can produce a car in less than an hour 25
 Recent Trends Influencing OM • Global Marketplace for markets, sourcing, finance • International Trade Agreements (NAFTA, GATT) • Corporate Strategic Planning (integrating OM strategies) • Total Quality Management (TQM) programs • Flexibility in manufacturing methods and lead time reduction (quick delivery allows cost cutting and cost containment for increased leverage against lower cost global competition • Technology (computers, robotics, automation) • Re-engineering - rethink how products are designed and manufactured • Environmental Issues • Corporate downsizing (how to get more done with less because of stock holder pressures and global labor 26 wage pressures
Recent Trends Influencing OM • Global Marketplace for markets, sourcing, finance • International Trade Agreements (NAFTA, GATT) • Corporate Strategic Planning (integrating OM strategies) • Total Quality Management (TQM) programs • Flexibility in manufacturing methods and lead time reduction (quick delivery allows cost cutting and cost containment for increased leverage against lower cost global competition • Technology (computers, robotics, automation) • Re-engineering - rethink how products are designed and manufactured • Environmental Issues • Corporate downsizing (how to get more done with less because of stock holder pressures and global labor 26 wage pressures
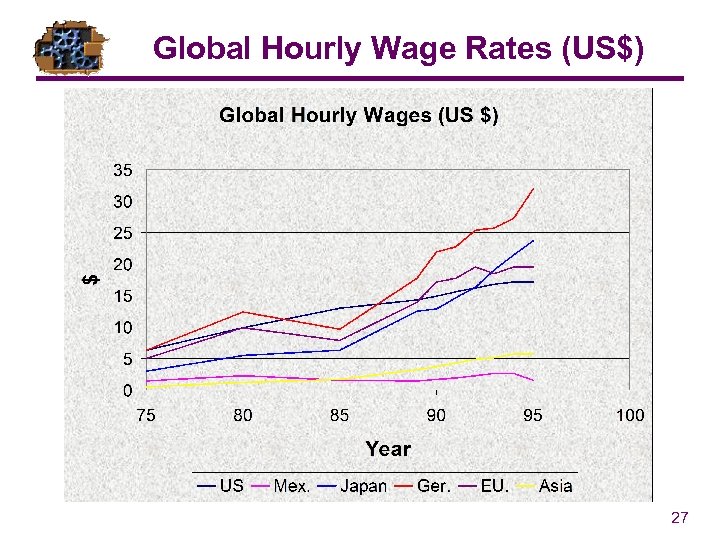 Global Hourly Wage Rates (US$) 27
Global Hourly Wage Rates (US$) 27
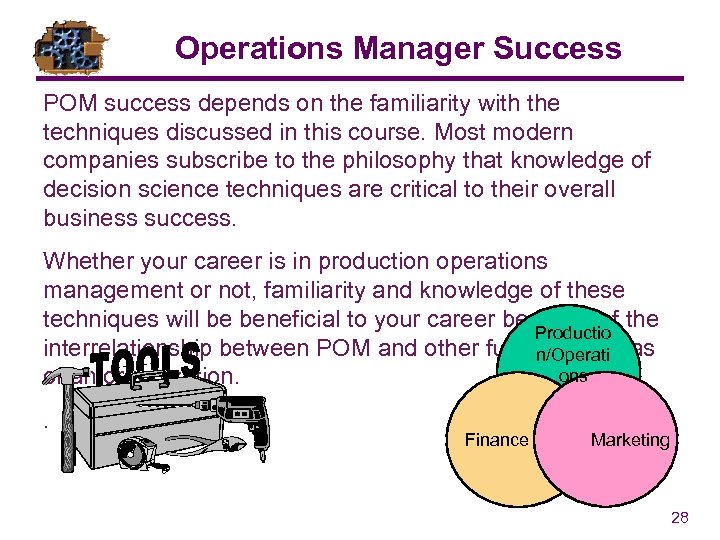 Operations Manager Success POM success depends on the familiarity with the techniques discussed in this course. Most modern companies subscribe to the philosophy that knowledge of decision science techniques are critical to their overall business success. Whether your career is in production operations management or not, familiarity and knowledge of these techniques will be beneficial to your career because of the Productio interrelationship between POM and other functional areas n/Operati ons of an organization. . Finance Marketing 28
Operations Manager Success POM success depends on the familiarity with the techniques discussed in this course. Most modern companies subscribe to the philosophy that knowledge of decision science techniques are critical to their overall business success. Whether your career is in production operations management or not, familiarity and knowledge of these techniques will be beneficial to your career because of the Productio interrelationship between POM and other functional areas n/Operati ons of an organization. . Finance Marketing 28
 Homework Read and understand all material in the chapter. Discussion and Review Questions Recreate and understand all classroom examples Exercises on chapter web page 29
Homework Read and understand all material in the chapter. Discussion and Review Questions Recreate and understand all classroom examples Exercises on chapter web page 29


