лекция 4 лесные ресурсы.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Лесные ресурсы Лекция 4
Лесные ресурсы Лекция 4
 A forest is an area with a high density of trees.
A forest is an area with a high density of trees.
 q. Forests cover approximately 9. 4% of the Earth's surface (or 30% of total land area), though they once covered much more (about 50% of total land area). q. Forests functions are: habitats for organisms, hydrologic flow modulator, and soil conservers, constituting one of the most important aspects of the biosphere.
q. Forests cover approximately 9. 4% of the Earth's surface (or 30% of total land area), though they once covered much more (about 50% of total land area). q. Forests functions are: habitats for organisms, hydrologic flow modulator, and soil conservers, constituting one of the most important aspects of the biosphere.
 Лесные ресурсы: древесные и не древесные
Лесные ресурсы: древесные и не древесные
 Forests produce all the following products: • Ink • Cosmetics • Camphor • Essential Oils • Soap, Chewing Gum • Timber, Wood, Paper, Food, • Herbal Medicines, Plastic • Balsam, Sausage casing, Flowers • Tannin and Cinnamon, Rubber and Gums • Adhesive, Compost, Decorations • Bark products, Fuel – firewood, Paint • Medicine, Charcoal, Disinfectant, Sandalwood • Turpentine, Varnish, Wax, Cellulose, Honey, Cellophane.
Forests produce all the following products: • Ink • Cosmetics • Camphor • Essential Oils • Soap, Chewing Gum • Timber, Wood, Paper, Food, • Herbal Medicines, Plastic • Balsam, Sausage casing, Flowers • Tannin and Cinnamon, Rubber and Gums • Adhesive, Compost, Decorations • Bark products, Fuel – firewood, Paint • Medicine, Charcoal, Disinfectant, Sandalwood • Turpentine, Varnish, Wax, Cellulose, Honey, Cellophane.
 Forests • Forests can be found in all regions capable of sustaining tree growth, at altitudes up to the tree line , except where natural fire frequency or other disturbance is too high, or where the environment has been altered by human activity.
Forests • Forests can be found in all regions capable of sustaining tree growth, at altitudes up to the tree line , except where natural fire frequency or other disturbance is too high, or where the environment has been altered by human activity.
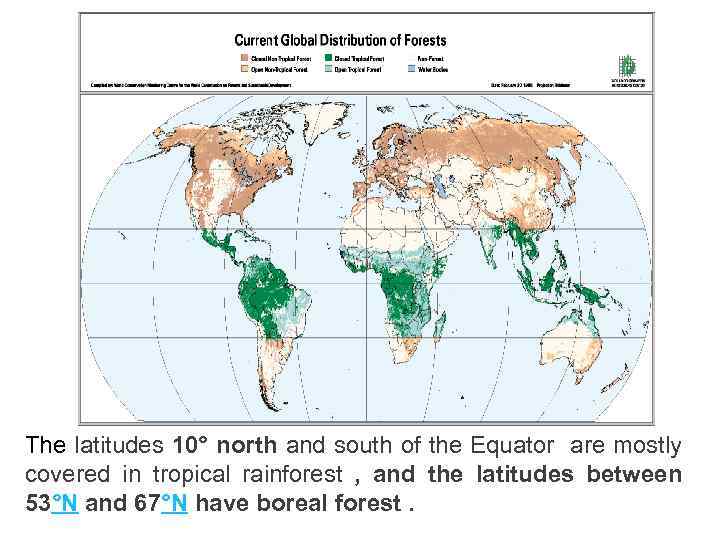 The latitudes 10° north and south of the Equator are mostly covered in tropical rainforest , and the latitudes between 53°N and 67°N have boreal forest.
The latitudes 10° north and south of the Equator are mostly covered in tropical rainforest , and the latitudes between 53°N and 67°N have boreal forest.
 Лесные ресурсывозобновляемые!!!
Лесные ресурсывозобновляемые!!!
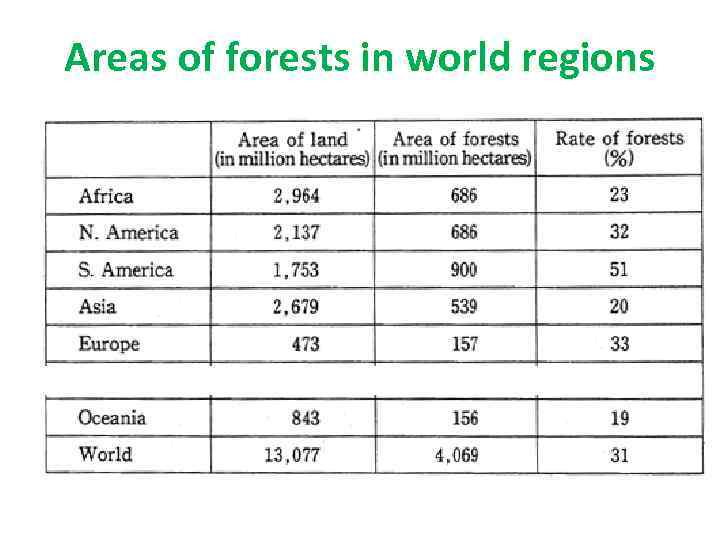 Areas of forests in world regions
Areas of forests in world regions
 Classification • Boreal forests occupy the subarctic zone and are generally evergreen and coniferous. • Temperate zones support both broadleaf deciduous forests (e. g. , temperate deciduous forest ) and evergreen coniferous forests (e. g. , temperate coniferous forests and temperate rainforest ). Warm temperate zones support broadleaf evergreen forests. • Tropical and subtropical forests include tropical and subtropical dry forests, tropical and subtropical moist forests, and tropical and subtropical coniferous forests.
Classification • Boreal forests occupy the subarctic zone and are generally evergreen and coniferous. • Temperate zones support both broadleaf deciduous forests (e. g. , temperate deciduous forest ) and evergreen coniferous forests (e. g. , temperate coniferous forests and temperate rainforest ). Warm temperate zones support broadleaf evergreen forests. • Tropical and subtropical forests include tropical and subtropical dry forests, tropical and subtropical moist forests, and tropical and subtropical coniferous forests.
 • forest resources in Japan
• forest resources in Japan
 • Наличие ландшафтных парков и садов является важной предпосылкой развития туризма
• Наличие ландшафтных парков и садов является важной предпосылкой развития туризма

 Япония
Япония
 The share of forested area to total area (%) in North-East Asia • • • Russian Far East – 41 -45 % Japan – 62 -65% North-East China – 41 -45 % Mongolia – 9 % North Korea – 62 -65 % Republic of Korea – 62 -65 % Source: Natural resources use of the Russian Far East and Northeast Asia : potential for integration and sustainable development , Vladivostok-Khabarovsk, 2005.
The share of forested area to total area (%) in North-East Asia • • • Russian Far East – 41 -45 % Japan – 62 -65% North-East China – 41 -45 % Mongolia – 9 % North Korea – 62 -65 % Republic of Korea – 62 -65 % Source: Natural resources use of the Russian Far East and Northeast Asia : potential for integration and sustainable development , Vladivostok-Khabarovsk, 2005.
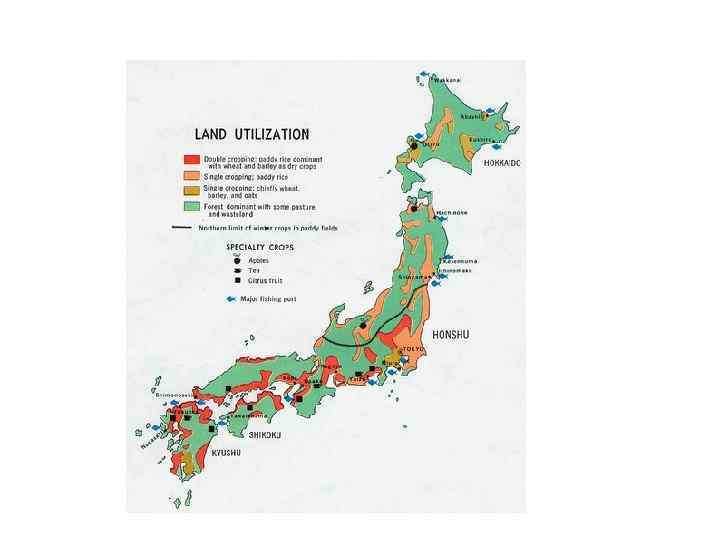
 Forest resources in Japan • Forests cover two thirds of Japan's land area, and generally tree growth is favoured by the temperate climate, abundant rainfall, and fertile soils. • For centuries forests have served the Japanese people in many ways. • Over the years, management has been in reasonably good accord with natural and social conditions, but recently many problems have arisen -for example, conflicts among land uses and a decline in forest industry.
Forest resources in Japan • Forests cover two thirds of Japan's land area, and generally tree growth is favoured by the temperate climate, abundant rainfall, and fertile soils. • For centuries forests have served the Japanese people in many ways. • Over the years, management has been in reasonably good accord with natural and social conditions, but recently many problems have arisen -for example, conflicts among land uses and a decline in forest industry.
 Canada
Canada
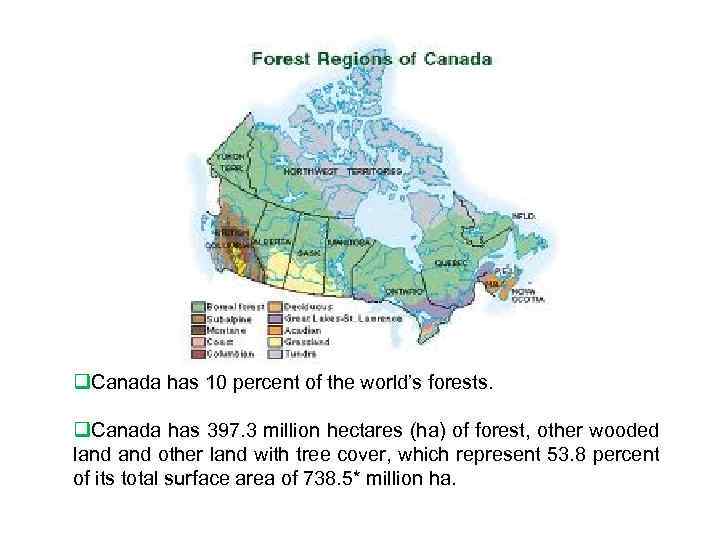 q. Canada has 10 percent of the world’s forests. q. Canada has 397. 3 million hectares (ha) of forest, other wooded land other land with tree cover, which represent 53. 8 percent of its total surface area of 738. 5* million ha.
q. Canada has 10 percent of the world’s forests. q. Canada has 397. 3 million hectares (ha) of forest, other wooded land other land with tree cover, which represent 53. 8 percent of its total surface area of 738. 5* million ha.
 Canada q In Canada, the predominant tree species on forest land are spruce (53. 2 percent), poplar (11. 6 percent) and pine (9. 3 percent). q Canada harvested 162. 8 million cubic metres (m 3) of roundwood. q Annually, less that 1 percent of Canada’s forests are harvested; q A total of 18. 6 million ha were affected by insect defoliation in 2007; 1. 7 million ha were lost due to forest fires in 2008. q Revenues from the sale of timber from provincial and territorial crown lands were estimated to be $1. 3 billion in 2007.
Canada q In Canada, the predominant tree species on forest land are spruce (53. 2 percent), poplar (11. 6 percent) and pine (9. 3 percent). q Canada harvested 162. 8 million cubic metres (m 3) of roundwood. q Annually, less that 1 percent of Canada’s forests are harvested; q A total of 18. 6 million ha were affected by insect defoliation in 2007; 1. 7 million ha were lost due to forest fires in 2008. q Revenues from the sale of timber from provincial and territorial crown lands were estimated to be $1. 3 billion in 2007.
 Canada q National Economic Importance The forest sector’s contribution to the Canadian economy (GDP) in 2008 constant dollars was $23. 8 billion, or 1. 9 percent, in 2008. q In 2008, the sector provided direct employment for 231 500 people, representing 1. 6 percent of total employment in Canada: wood industries, for 110 300 people; paper and allied industries, for 73 600 people; logging, for 34 000 people; and forestry services, for 13 600 people. Employment is spread across Canada but is primarily in Quebec (72 600 people), British Columbia (58 400 people) and Ontario (53 600 people). q Wages and salaries for direct employment were $11. 5 billion in 2007. q Revenue from manufactured goods was $68. 5 billion in 2007.
Canada q National Economic Importance The forest sector’s contribution to the Canadian economy (GDP) in 2008 constant dollars was $23. 8 billion, or 1. 9 percent, in 2008. q In 2008, the sector provided direct employment for 231 500 people, representing 1. 6 percent of total employment in Canada: wood industries, for 110 300 people; paper and allied industries, for 73 600 people; logging, for 34 000 people; and forestry services, for 13 600 people. Employment is spread across Canada but is primarily in Quebec (72 600 people), British Columbia (58 400 people) and Ontario (53 600 people). q Wages and salaries for direct employment were $11. 5 billion in 2007. q Revenue from manufactured goods was $68. 5 billion in 2007.
 q Canada International Importance In 2008, Canada was the world’s largest forest-product exporter (10. 6 percent). Forest products were a major contributor to Canada’s surplus balance of trade in 2008 ($20. 1 billion). The total value of Canadian forest-product domestic exports decreased by 10. 4 percent in 2008 to $30. 1 billion. British Columbia accounted for $9. 9 billion (29. 4 percent); Quebec, $9. 2 billion (27. 4 percent); Ontario, $5. 3 billion ( 15. 8 percent); and other provinces and territories, $9. 2 billion (27. 4)
q Canada International Importance In 2008, Canada was the world’s largest forest-product exporter (10. 6 percent). Forest products were a major contributor to Canada’s surplus balance of trade in 2008 ($20. 1 billion). The total value of Canadian forest-product domestic exports decreased by 10. 4 percent in 2008 to $30. 1 billion. British Columbia accounted for $9. 9 billion (29. 4 percent); Quebec, $9. 2 billion (27. 4 percent); Ontario, $5. 3 billion ( 15. 8 percent); and other provinces and territories, $9. 2 billion (27. 4)
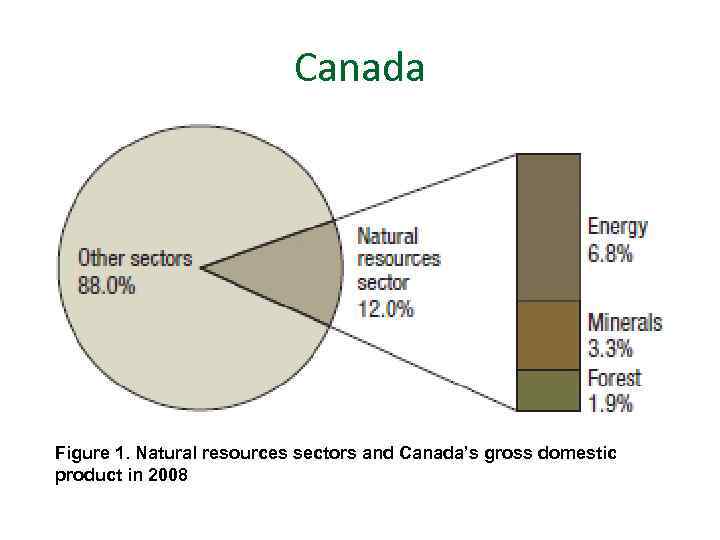 Canada Figure 1. Natural resources sectors and Canada’s gross domestic product in 2008
Canada Figure 1. Natural resources sectors and Canada’s gross domestic product in 2008
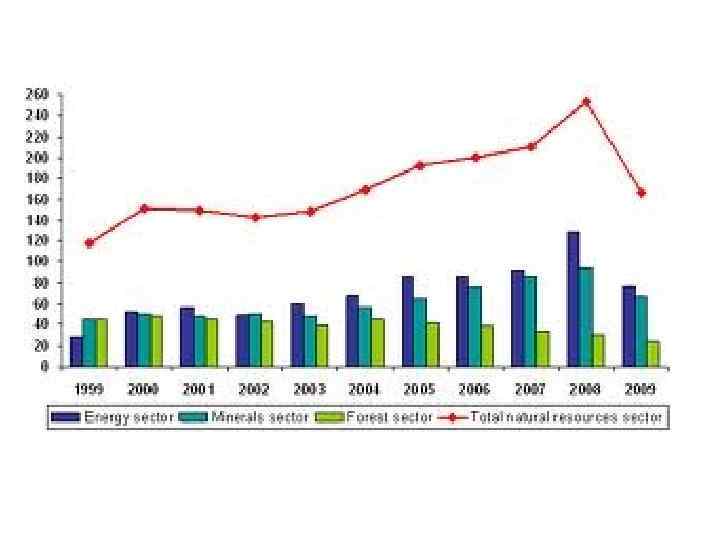
 Canada q. Canada has the largest area of certified forest in the world – more than 145 million ha. Approximately 40 percent of the world’s certified forest area is in Canada. q. Approximately 8 percent of Canada’s forest area is protected by legislation. By law, all forests harvested (less than 1 percent annually) on Canada’s public land must be successfully regenerated.
Canada q. Canada has the largest area of certified forest in the world – more than 145 million ha. Approximately 40 percent of the world’s certified forest area is in Canada. q. Approximately 8 percent of Canada’s forest area is protected by legislation. By law, all forests harvested (less than 1 percent annually) on Canada’s public land must be successfully regenerated.
 Russian Federation is powerful forest country. The forested area occupies 764 million ha. (which is about 22 % of world forests), and the total wood stock is more than 20% of the whole stock in the world. Just for comparison, the next largest forest countries own: Brazil – 16%, Canada – 7% and US – 6% of the world’s forest cover.
Russian Federation is powerful forest country. The forested area occupies 764 million ha. (which is about 22 % of world forests), and the total wood stock is more than 20% of the whole stock in the world. Just for comparison, the next largest forest countries own: Brazil – 16%, Canada – 7% and US – 6% of the world’s forest cover.
 Forest resources of East Siberian and Far Eastern regions • East Siberian and Far Eastern regions contain 71. 4 % of Russian forests and 62. 8% of total Russian wood stock
Forest resources of East Siberian and Far Eastern regions • East Siberian and Far Eastern regions contain 71. 4 % of Russian forests and 62. 8% of total Russian wood stock
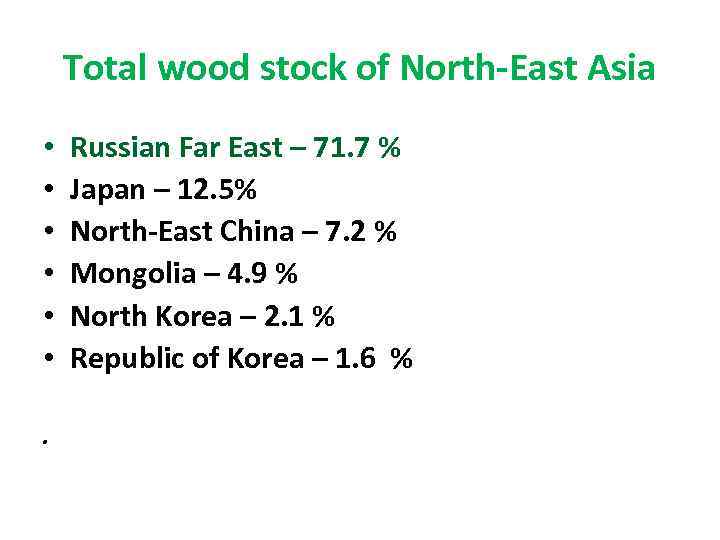 Total wood stock of North-East Asia • • • . Russian Far East – 71. 7 % Japan – 12. 5% North-East China – 7. 2 % Mongolia – 4. 9 % North Korea – 2. 1 % Republic of Korea – 1. 6 %
Total wood stock of North-East Asia • • • . Russian Far East – 71. 7 % Japan – 12. 5% North-East China – 7. 2 % Mongolia – 4. 9 % North Korea – 2. 1 % Republic of Korea – 1. 6 %
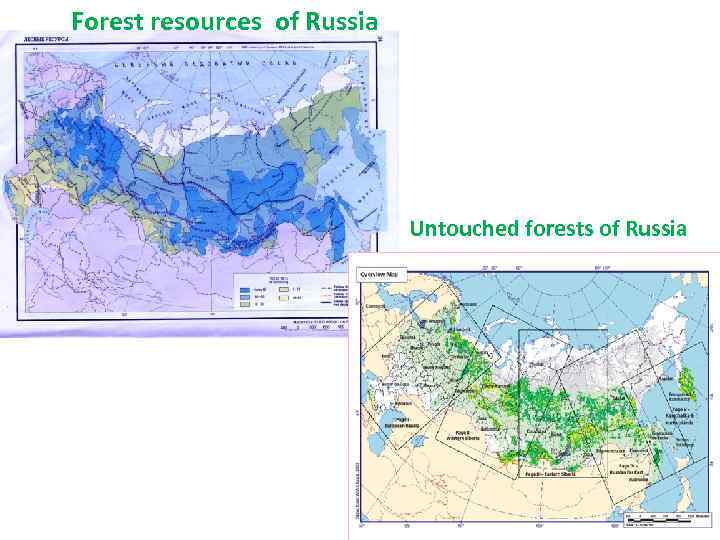 Forest resources of Russia Untouched forests of Russia
Forest resources of Russia Untouched forests of Russia
 General background information on the current status of the sector The forest sector of the Russian economy has been traditionally subdivided into two groups: 1) The forest industrial complex (FIC) combines logging, pulping and wood processing industries. FIC was involved in the process of destatization and privatization (95 % – under private, stock or mixed forms of property). 2) Forestry is represented by a system of state management of the lands of the forest fund of Russia. Forestry remained in the state sector converting from an economic entity into a state management body. 32
General background information on the current status of the sector The forest sector of the Russian economy has been traditionally subdivided into two groups: 1) The forest industrial complex (FIC) combines logging, pulping and wood processing industries. FIC was involved in the process of destatization and privatization (95 % – under private, stock or mixed forms of property). 2) Forestry is represented by a system of state management of the lands of the forest fund of Russia. Forestry remained in the state sector converting from an economic entity into a state management body. 32
 Russian forests • Russian forests have the great ecological and biospheric importance, and the wood industry plays a certain role in Russian economy. • The wood industrial sector (WIS) may be characterized by followings: the total wood production is about 4. 5% of GDP; currency gain from export made is about 4. 4% of total export value.
Russian forests • Russian forests have the great ecological and biospheric importance, and the wood industry plays a certain role in Russian economy. • The wood industrial sector (WIS) may be characterized by followings: the total wood production is about 4. 5% of GDP; currency gain from export made is about 4. 4% of total export value.
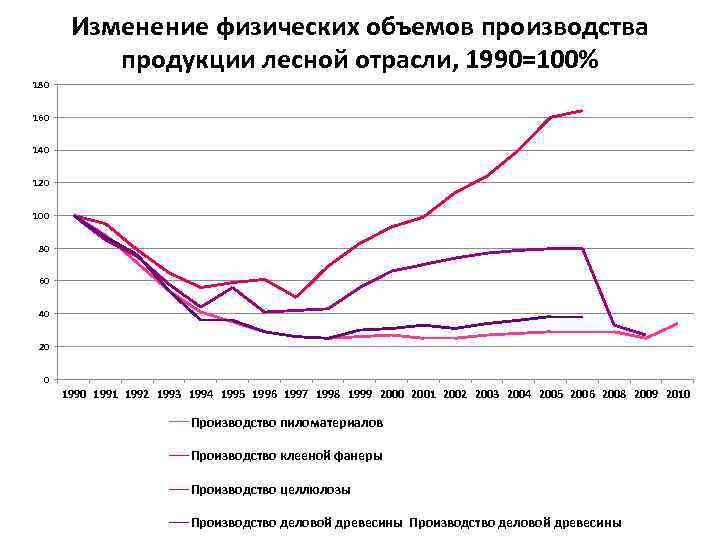 Изменение физических объемов производства продукции лесной отрасли, 1990=100% 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2008 2009 2010 Производство пиломатериалов Производство клееной фанеры Производство целлюлозы Производство деловой древесины
Изменение физических объемов производства продукции лесной отрасли, 1990=100% 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2008 2009 2010 Производство пиломатериалов Производство клееной фанеры Производство целлюлозы Производство деловой древесины
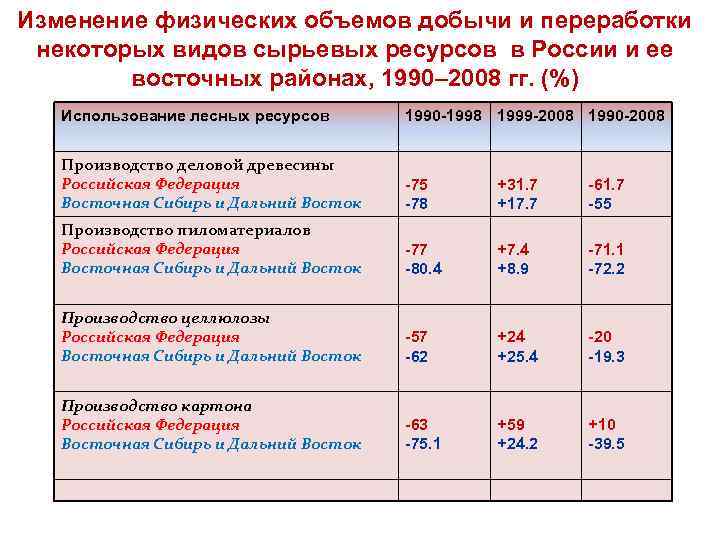 Изменение физических объемов добычи и переработки некоторых видов сырьевых ресурсов в России и ее восточных районах, 1990– 2008 гг. (%) Использование лесных ресурсов 1990 -1998 1999 -2008 1990 -2008 Производство деловой древесины Российская Федерация Восточная Сибирь и Дальний Восток -75 -78 +31. 7 +17. 7 -61. 7 -55 Производство пиломатериалов Российская Федерация Восточная Сибирь и Дальний Восток -77 -80. 4 +7. 4 +8. 9 -71. 1 -72. 2 Производство целлюлозы Российская Федерация Восточная Сибирь и Дальний Восток -57 -62 +24 +25. 4 -20 -19. 3 Производство картона Российская Федерация Восточная Сибирь и Дальний Восток -63 -75. 1 +59 +24. 2 +10 -39. 5 Federation (1990 -2006), %
Изменение физических объемов добычи и переработки некоторых видов сырьевых ресурсов в России и ее восточных районах, 1990– 2008 гг. (%) Использование лесных ресурсов 1990 -1998 1999 -2008 1990 -2008 Производство деловой древесины Российская Федерация Восточная Сибирь и Дальний Восток -75 -78 +31. 7 +17. 7 -61. 7 -55 Производство пиломатериалов Российская Федерация Восточная Сибирь и Дальний Восток -77 -80. 4 +7. 4 +8. 9 -71. 1 -72. 2 Производство целлюлозы Российская Федерация Восточная Сибирь и Дальний Восток -57 -62 +24 +25. 4 -20 -19. 3 Производство картона Российская Федерация Восточная Сибирь и Дальний Восток -63 -75. 1 +59 +24. 2 +10 -39. 5 Federation (1990 -2006), %
 Положительное влияние q. Региональный экономический рост и локальный q. Стимулирует развитие других отраслей q. Занятость населения q. Природоохранные и рекреационные функции
Положительное влияние q. Региональный экономический рост и локальный q. Стимулирует развитие других отраслей q. Занятость населения q. Природоохранные и рекреационные функции
 Проблемы
Проблемы
 Проблемы • Perfection and practical application of criteria and indicators of sustainable forest management. • Current state of forest's resources of Russia, including environmental functions of forests • Problems of protection of forests against natural disasters and illegal cuttings • Problems of forest management for conservation of biological diversity 02. 2018 38
Проблемы • Perfection and practical application of criteria and indicators of sustainable forest management. • Current state of forest's resources of Russia, including environmental functions of forests • Problems of protection of forests against natural disasters and illegal cuttings • Problems of forest management for conservation of biological diversity 02. 2018 38
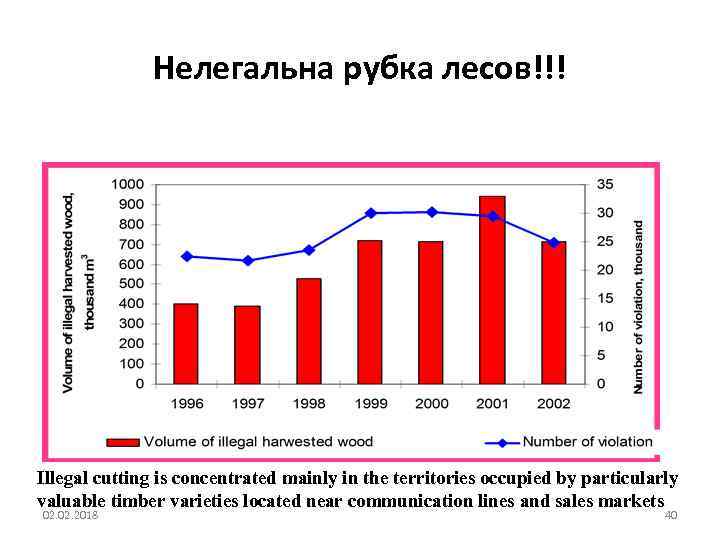 Нелегальна рубка лесов!!! Illegal cutting is concentrated mainly in the territories occupied by particularly valuable timber varieties located near communication lines and sales markets 02. 2018 40
Нелегальна рубка лесов!!! Illegal cutting is concentrated mainly in the territories occupied by particularly valuable timber varieties located near communication lines and sales markets 02. 2018 40



