93e279876f73b97b76154bc945511681.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 LEGISLATIVE COMMITTEE STRUCTURE AND PROCESS Presentation for 2006 Airtap Fall Forum Amy Vennewitz Metropolitan Council
LEGISLATIVE COMMITTEE STRUCTURE AND PROCESS Presentation for 2006 Airtap Fall Forum Amy Vennewitz Metropolitan Council
 Legislative Work Can be Exciting!!
Legislative Work Can be Exciting!!
 Current Political Structure n Governor n n Senate n n n Governor Tim Pawlenty, Republican 67 Total Members, 4 -year terms DFL Majority, 38 members Republican Minority, 29 members Majority Leader Senator Dean Johnson House n n 134 Total Members, 2 -year terms Republican Majority, 68 members DFL Minority, 66 members Speaker of the House Representative Steve Sviggum
Current Political Structure n Governor n n Senate n n n Governor Tim Pawlenty, Republican 67 Total Members, 4 -year terms DFL Majority, 38 members Republican Minority, 29 members Majority Leader Senator Dean Johnson House n n 134 Total Members, 2 -year terms Republican Majority, 68 members DFL Minority, 66 members Speaker of the House Representative Steve Sviggum
 After November 7? ? n November 7 – Election day n Governor and all members of Senate and House standing for election n 30 of 201 Legislators (15%) Retiring n Potential incumbent losses n Landscape could remain same or have large changes
After November 7? ? n November 7 – Election day n Governor and all members of Senate and House standing for election n 30 of 201 Legislators (15%) Retiring n Potential incumbent losses n Landscape could remain same or have large changes
 Activity Starts Immediately n Governor makes key agency appointments n reviews/selects budget initiatives n n House and Senate elect caucus leadership n establish new legislative committee structure n appoint committee chairs & members n membership proportionally balanced n
Activity Starts Immediately n Governor makes key agency appointments n reviews/selects budget initiatives n n House and Senate elect caucus leadership n establish new legislative committee structure n appoint committee chairs & members n membership proportionally balanced n
 Legislative Committees n Policy Committees Policy committees for major topic areas, i. e. education, environment, transportation n Hear all bills in topic area n Pass bills to other policy committees, budget committees (divisions) or to floor n n Budget Committees or Divisions Also for major topic areas n Hear only bills with “fiscal impact” n Pass bills to Finance and Tax committees n
Legislative Committees n Policy Committees Policy committees for major topic areas, i. e. education, environment, transportation n Hear all bills in topic area n Pass bills to other policy committees, budget committees (divisions) or to floor n n Budget Committees or Divisions Also for major topic areas n Hear only bills with “fiscal impact” n Pass bills to Finance and Tax committees n
 Legislative Committees Cont. n Finance and Tax Committees Chaired by senior legislators n In Senate, Finance hears spending bills, Taxes hears revenue raising bills n In House, Ways and Means committee hears both finance and tax bills n n Rules Committees Chaired by majority leaders in Senate & House n Hear bills that have not met “rules” n
Legislative Committees Cont. n Finance and Tax Committees Chaired by senior legislators n In Senate, Finance hears spending bills, Taxes hears revenue raising bills n In House, Ways and Means committee hears both finance and tax bills n n Rules Committees Chaired by majority leaders in Senate & House n Hear bills that have not met “rules” n
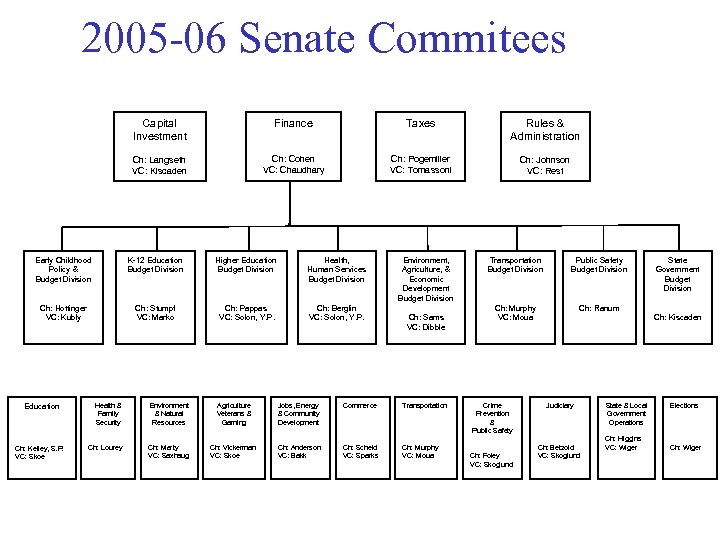 2005 -06 Senate Commitees Capital Investment Finance Taxes Rules & Administration Ch: Langseth VC: Kiscaden Ch: Cohen VC: Chaudhary Ch: Pogemiller VC: Tomassoni Ch: Johnson VC: Rest Early Childhood Policy & Budget Division K-12 Education Budget Division Higher Education Budget Division Health, Human Services Budget Division Ch: Hottinger VC: Kubly Ch: Stumpf VC: Marko Ch: Pappas VC: Solon, Y. P. Ch: Berglin VC: Solon, Y. P. Education Ch: Kelley, S. P. VC: Skoe Environment, Agriculture, & Economic Development Budget Division Ch: Sams VC: Dibble Health & Family Security Environment & Natural Resources Agriculture Veterans & Gaming Jobs, Energy & Community Development Commerce Transportation Ch: Lourey Ch: Marty VC: Saxhaug Ch: Vickerman VC: Skoe Ch: Anderson VC: Bakk Ch: Scheid VC: Sparks Ch: Murphy VC: Moua Transportation Budget Division Public Safety Budget Division Ch: Murphy VC: Moua Ch: Ranum Crime Prevention & Public Safety Ch: Foley VC: Skoglund State Government Budget Division Ch: Kiscaden Judiciary Ch: Betzold VC: Skoglund State & Local Government Operations Ch: Higgins VC: Wiger Elections Ch: Wiger
2005 -06 Senate Commitees Capital Investment Finance Taxes Rules & Administration Ch: Langseth VC: Kiscaden Ch: Cohen VC: Chaudhary Ch: Pogemiller VC: Tomassoni Ch: Johnson VC: Rest Early Childhood Policy & Budget Division K-12 Education Budget Division Higher Education Budget Division Health, Human Services Budget Division Ch: Hottinger VC: Kubly Ch: Stumpf VC: Marko Ch: Pappas VC: Solon, Y. P. Ch: Berglin VC: Solon, Y. P. Education Ch: Kelley, S. P. VC: Skoe Environment, Agriculture, & Economic Development Budget Division Ch: Sams VC: Dibble Health & Family Security Environment & Natural Resources Agriculture Veterans & Gaming Jobs, Energy & Community Development Commerce Transportation Ch: Lourey Ch: Marty VC: Saxhaug Ch: Vickerman VC: Skoe Ch: Anderson VC: Bakk Ch: Scheid VC: Sparks Ch: Murphy VC: Moua Transportation Budget Division Public Safety Budget Division Ch: Murphy VC: Moua Ch: Ranum Crime Prevention & Public Safety Ch: Foley VC: Skoglund State Government Budget Division Ch: Kiscaden Judiciary Ch: Betzold VC: Skoglund State & Local Government Operations Ch: Higgins VC: Wiger Elections Ch: Wiger
 20005 -06 House Committees Capital Investment Ways and Means Taxes Ch: Dorman Ch: Knoblach Rules & Legislative Administration Ch: Krinkie Ch: Paulson Jobs and Economic Opportunity Policy and Finance Education Finance Higher Education Finance Health Policy and Finance Agriculture, Environment and Natural Resources Finance Transportation Finance Public Safety Policy and Finance State Government Finance Ch: Sykora Ch: Nornes Ch: Bradley Ch: Ozment Ch: Holberg Ch: Smith Ch: Seifert Ch: Gunther Education Policy & Reform Ch: Buesgens Environment & Natural Resources Ch: Hackbarth Agriculture & Rural Development Ch: Davids: Local Government Ch: Olson Commerce & Financial Institutions Transportation Ch: Wilkins Ch: Erhardt Regulated Industires Ch: Westrom Ethics Ch: Erickson Government Operations & Veterans Affairs Civil Law & Elections Ch: Tingelstad Ch: Johnson
20005 -06 House Committees Capital Investment Ways and Means Taxes Ch: Dorman Ch: Knoblach Rules & Legislative Administration Ch: Krinkie Ch: Paulson Jobs and Economic Opportunity Policy and Finance Education Finance Higher Education Finance Health Policy and Finance Agriculture, Environment and Natural Resources Finance Transportation Finance Public Safety Policy and Finance State Government Finance Ch: Sykora Ch: Nornes Ch: Bradley Ch: Ozment Ch: Holberg Ch: Smith Ch: Seifert Ch: Gunther Education Policy & Reform Ch: Buesgens Environment & Natural Resources Ch: Hackbarth Agriculture & Rural Development Ch: Davids: Local Government Ch: Olson Commerce & Financial Institutions Transportation Ch: Wilkins Ch: Erhardt Regulated Industires Ch: Westrom Ethics Ch: Erickson Government Operations & Veterans Affairs Civil Law & Elections Ch: Tingelstad Ch: Johnson
 Committee Structure Chair – Member of majority party, some seniority, interest/expertise in subject n Committee staff n committee secretary & administrator, work directly for chair n non-partisan professional staff, policy analysts, counsel, fiscal analysts, work for all legislators n majority & minority partisan staff, hired by caucuses, work for legislators in their respective caucus n
Committee Structure Chair – Member of majority party, some seniority, interest/expertise in subject n Committee staff n committee secretary & administrator, work directly for chair n non-partisan professional staff, policy analysts, counsel, fiscal analysts, work for all legislators n majority & minority partisan staff, hired by caucuses, work for legislators in their respective caucus n
 Typical Committees with Jurisdiction over Airport Issues n Transportation Policy n n n Subcommittee on aviation in both Senate & House Airport operations, noise issues Transportation Finance Mn. DOT Office of Aeronautics, State Airport Fund n State and Local Government Operations (Senate) and Local Government (House) n Land use, noise, MAC governance issues n n Legislative Commission on Metropolitan Governance (joint Senate/House) n Metropolitan Council governance and budget
Typical Committees with Jurisdiction over Airport Issues n Transportation Policy n n n Subcommittee on aviation in both Senate & House Airport operations, noise issues Transportation Finance Mn. DOT Office of Aeronautics, State Airport Fund n State and Local Government Operations (Senate) and Local Government (House) n Land use, noise, MAC governance issues n n Legislative Commission on Metropolitan Governance (joint Senate/House) n Metropolitan Council governance and budget
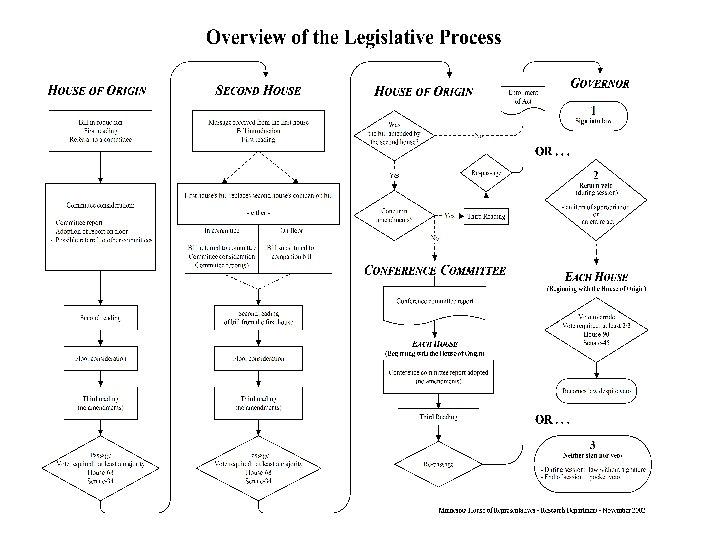
 Basic Bill Flow n Idea generation n n Legislator requests a bill draft n n n Individuals & constituents, legislators, professional group/associations, Governor and agencies Senate & House professional staff or Revisor of Statutes drafts bill Finds author in “other” house & co-authors Companion (identical) bills introduced in both houses First reading on floor Bill is referred to Committee n In Senate President refers, in House Speaker refers
Basic Bill Flow n Idea generation n n Legislator requests a bill draft n n n Individuals & constituents, legislators, professional group/associations, Governor and agencies Senate & House professional staff or Revisor of Statutes drafts bill Finds author in “other” house & co-authors Companion (identical) bills introduced in both houses First reading on floor Bill is referred to Committee n In Senate President refers, in House Speaker refers
 Committee Actions on Bills n Committee Options Hear, amend, pass the bill n Hear the bill, vote it down n Hear the bill, put in into another bill n Don’t hear the bill n Committee reports the bill to the floor or another committee n Budget or fiscal bills must go to a finance or tax committee n
Committee Actions on Bills n Committee Options Hear, amend, pass the bill n Hear the bill, vote it down n Hear the bill, put in into another bill n Don’t hear the bill n Committee reports the bill to the floor or another committee n Budget or fiscal bills must go to a finance or tax committee n
 Floor Actions on Bills n Bill is reported to floor, second reading n Individual bill or omnibus bill Bill is debated, amended on floor n Third reading (no amendments) n Bill passes (fails) and is transmitted to “other” house n Other house passes identical bill or amends bill n (substitutes language) Bill sent to Governor (if identical) n Conference Committee (if amended) n
Floor Actions on Bills n Bill is reported to floor, second reading n Individual bill or omnibus bill Bill is debated, amended on floor n Third reading (no amendments) n Bill passes (fails) and is transmitted to “other” house n Other house passes identical bill or amends bill n (substitutes language) Bill sent to Governor (if identical) n Conference Committee (if amended) n
 Conference Committee Actions Equal # of Senators and Representatives (typically 3 -5) n Staff prepares side-by-side comparisons n Committee recommends final bill content n Majority of members from each house must agree on final content n Each house must adopt committee report n Pass final bill without amendment n
Conference Committee Actions Equal # of Senators and Representatives (typically 3 -5) n Staff prepares side-by-side comparisons n Committee recommends final bill content n Majority of members from each house must agree on final content n Each house must adopt committee report n Pass final bill without amendment n
 Governor’s Actions Bill presented to Governor n 3 days to: (if session has ended, 10 days) n Sign n Allow to become law without signature n Veto n n Veto override requires 2/3 vote 90 votes in House n 45 votes in Senate n
Governor’s Actions Bill presented to Governor n 3 days to: (if session has ended, 10 days) n Sign n Allow to become law without signature n Veto n n Veto override requires 2/3 vote 90 votes in House n 45 votes in Senate n
 Biennial Legislative Timeline n Odd-year session Pass 2 -year biennial budget n Starts very early January n Required to end first Mon. after 3 rd Sat. in May n n Even-year session Pass bonding bill authorizing capital projects n Starts late February – March n Total biennial legislative days limited to 120 n State revenue forecasts n n February and November
Biennial Legislative Timeline n Odd-year session Pass 2 -year biennial budget n Starts very early January n Required to end first Mon. after 3 rd Sat. in May n n Even-year session Pass bonding bill authorizing capital projects n Starts late February – March n Total biennial legislative days limited to 120 n State revenue forecasts n n February and November
 Advocacy – Where to have Impact n Direct contact with Legislators Get sponsorship of requested legislation n Explain issues one-on-one n n Contact staff Input on bill drafting, other issues n Assistance on process n n Testify at Committee Hearings n n Provide expertise, information Get membership, others to contact
Advocacy – Where to have Impact n Direct contact with Legislators Get sponsorship of requested legislation n Explain issues one-on-one n n Contact staff Input on bill drafting, other issues n Assistance on process n n Testify at Committee Hearings n n Provide expertise, information Get membership, others to contact


