78af6f3d9dd2b996a02a451be279e129.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53

LEGISLATIVE BRANCH • • Organization Powers of Congress Representation How a Bill becomes a Law
• • • • • • Sessions Special sessions joint session Organization of Congress House of Representatives (Ho. R) Ho. R qualifications Congressional Districts Census Constituents Gerrymander Senate Qualifications Membership privileges Majority party Minority party Congressional leadership Whip Speaker of the House Senate Leadership President Pro Temp Standing Committees Sub-Committees Select Committee • • • • • Joint committees Conference committees Powers of Congress Enumerated Powers Legislative Powers Taxes and Spending Revenue Bills Appropriations Bills Gibbons v. Ogden Implied powers Mc. Culloch v. Maryland Non-legislative Powers denied to Congress Writ of habeas corpus Bills of attainder Ex post facto laws Casework Pork-barrel projects Bills • Private • Public • Ho. R • Senate • House Rules Committee • Committee Action • Christmas Tree Bills • Ho. R • Senators • Filibuster • Cloture • Presidential Action • Congressional Override • Checks and Balances

ORGANIZATION OF CONGRESS • Each term of Congress begins on January 3 (typically) of odd-numbered years and last for two years o 114 th term, 2 nd session • Each term equals two sessions (meetings) that typically lasts from Jan. until Nov. /Dec.

ORGANIZATION OF CONGRESS • Congress may also meet during special sessions to address issues in a time of crisis (current economic bailout) • A joint session is when the House of Representatives and Senate meet together (State of the Union address)

ORGANIZATION OF CONGRESS • Bicameral (2 chamber legislature) o House of Representativeslower house o Senate- Upper house o Based on English Parliament

HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES • 435 voting members • Based on state population (bigger the state, the more reps. ) • 3 Non-voting members. Guam, Virgin Islands, Puerto Rico (defense & economic issues)
HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES • QUALIFICATIONS 25 years old Legal U. S. resident for at least 7 years o Resident of state representing for 1 year o o Lynn Westmoreland U. S. Congressman
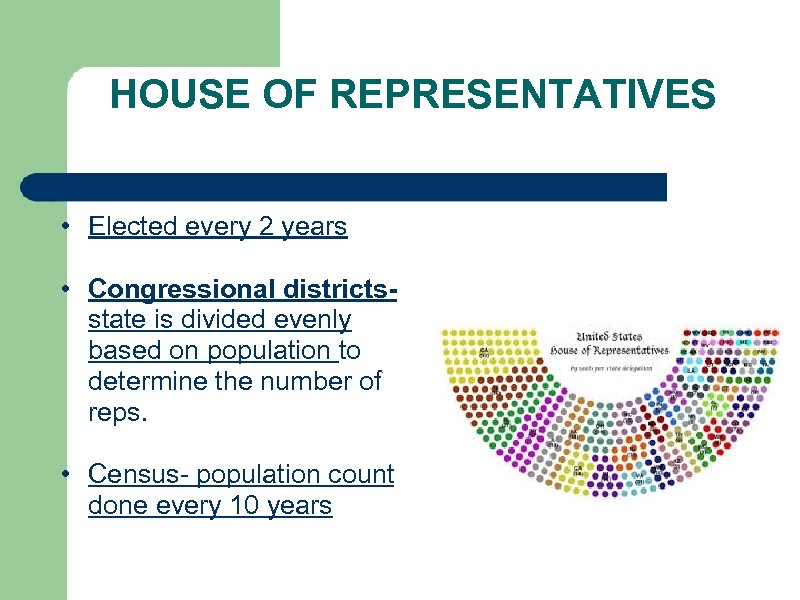
HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES • Elected every 2 years • Congressional districtsstate is divided evenly based on population to determine the number of reps. • Census- population count done every 10 years


HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES • Constituents- people represented in congressional districts
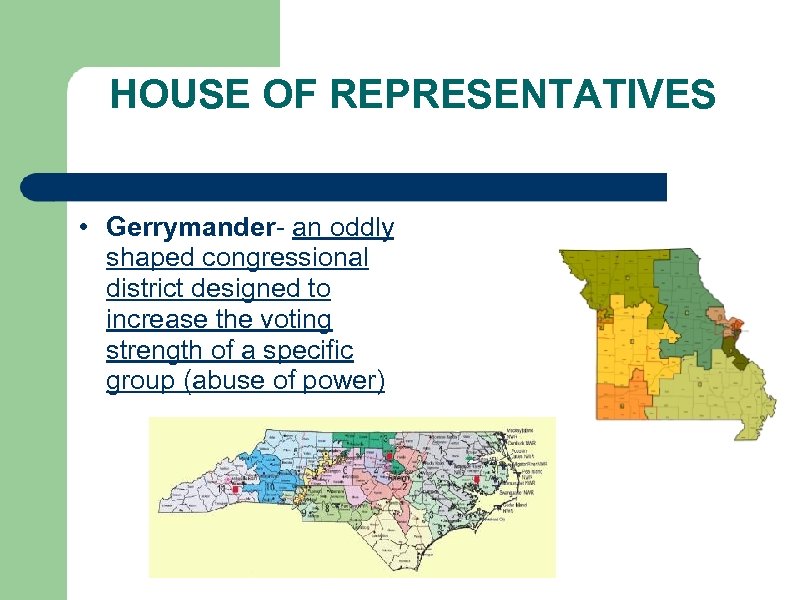
HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES • Gerrymander- an oddly shaped congressional district designed to increase the voting strength of a specific group (abuse of power)
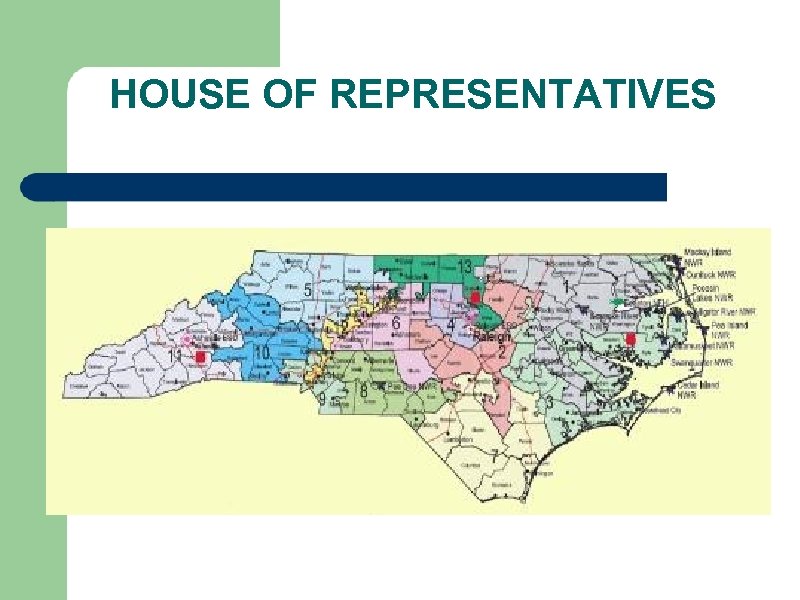
HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES

SENATE • 100 members (2 from each state) • Elected every 6 years • 1/3 of Senate is elected every 2 years to ensure stable leadership

SENATE • QUALIFICATIONS 30 years old Legal U. S. resident for at least 9 years o Resident of state representing for at least 1 year o o John “Johnny” Isakson (R) David Perdue (R)

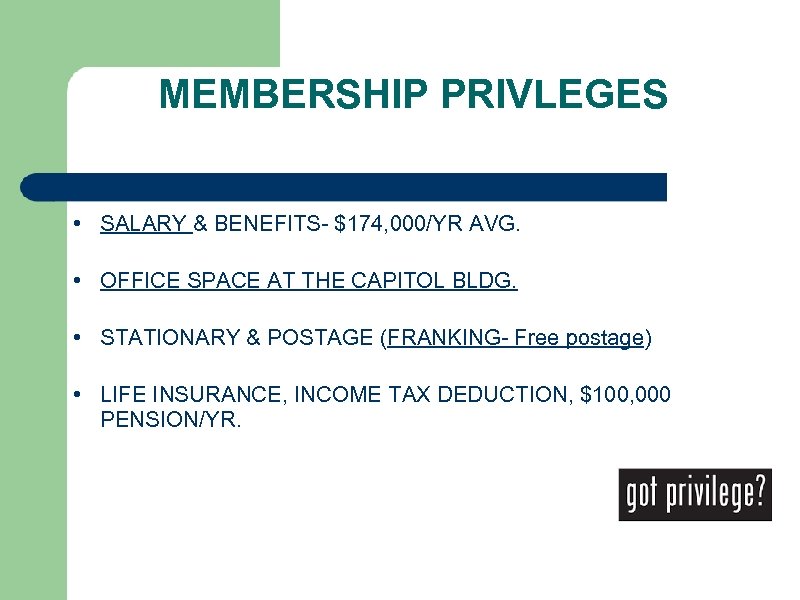
MEMBERSHIP PRIVLEGES • SALARY & BENEFITS- $174, 000/YR AVG. • OFFICE SPACE AT THE CAPITOL BLDG. • STATIONARY & POSTAGE (FRANKING- Free postage) • LIFE INSURANCE, INCOME TAX DEDUCTION, $100, 000 PENSION/YR.

MEMBERSHIP PRIVLEGES • FREE FROM ARREST DURING SESSION (EXCEPT TREASON, FELONY) • CAN’T BE SUED FOR WHAT IS SAID IN SESSION (SLANDER) • CENSURE- VOTE OF FORMAL DISAPPROVAL OF A MEMBER’S ACTIONS
CONGRESSIONAL LEADERS • Majority Party- 51% or more is of one political party o Decides who gets to serve on specific committees/issues decided o Kevin Mc. Carthy (R) is current HOR Majority Leader o Mitch Mc. Connell (R) is current Senate Majority Leader
CONGRESSIONAL LEADERS • Minority Party- less than 50% is of one political party o Nancy Pelosi(D) is current HOR Minority Leader o Harry Reid(D) is current Senate Minority Leader
CONGRESSIONAL LEADERSHIP Majority leader is floor leader in HOR • Leads monthly/bi-monthly meetings • Encourages party members to vote

CONGRESSIONAL LEADERSHIP Whip- assistant floor leader • Enforces rules of floor • Applies pressure to vote with party • Both parties have whips in both HOR & Senate

SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE- Paul Ryan (R-WI) • Leader of HOR • Chosen by members of majority party • Influential & experienced • Steers legislation through HOR bill process • Oversees HOR debates/floor activities/speakers • 3 rd in line for the Presidency Paul Ryan- WI (R)

SENATE LEADERSHIP • Vice President is leader of Senate (Joe Biden- D) • ONLY votes in case of a tie • Rarely attends sessions

SENATE LEADERSHIP • President Pro Tempore (“for the time being”)presides over the Senate in the VP’s absence • Orrin Hatch (D-WV) • Runs daily operations

COMMITTEES • Standing committees-permanent committees that continue their work from session to session (education, social security, taxes, welfare, healthcare) • Sub-committees-smaller part of standing committees; these are used to specify the work of Congress even more

COMMITTEES • Select committees-created to do a special job for a limited period (poverty, war on drugs, 9/11 Commission, economic bailout) • Joint committees-a meeting of committees from both houses of Congress • Conference committees-used to maintain the integrity of a bill; can be both standing and select

POWERS OF CONGRESS LEGISLATIVE POWERS • Article I of the Constitution outlines the major powers of the Leg. Branch

POWERS OF CONGRESS LEGISLATIVE POWERS o o o Enumerated Powers-powers listed in the Constitution Primary job is to make laws Clauses 1 -17 in Article I of the Constitution (expressed powers)
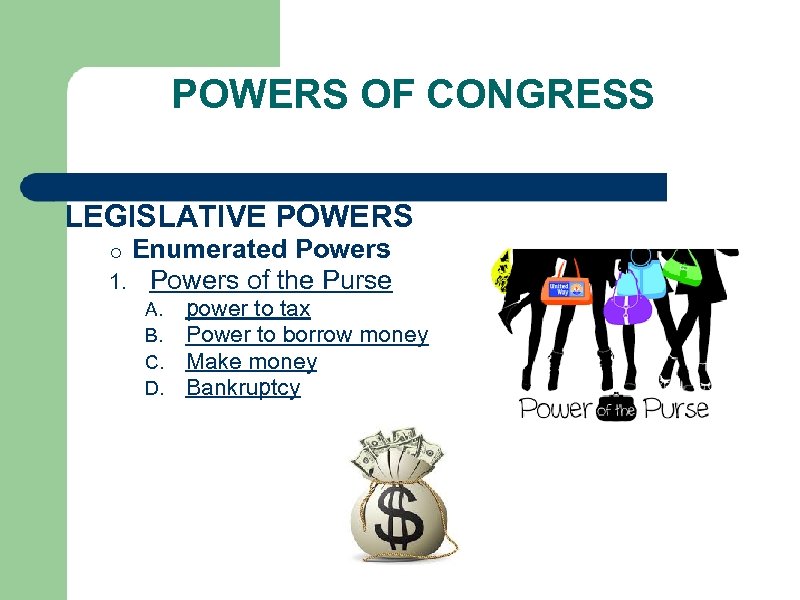
POWERS OF CONGRESS LEGISLATIVE POWERS o Enumerated Powers 1. Powers of the Purse A. power to tax B. Power to borrow money C. Make money D. Bankruptcy
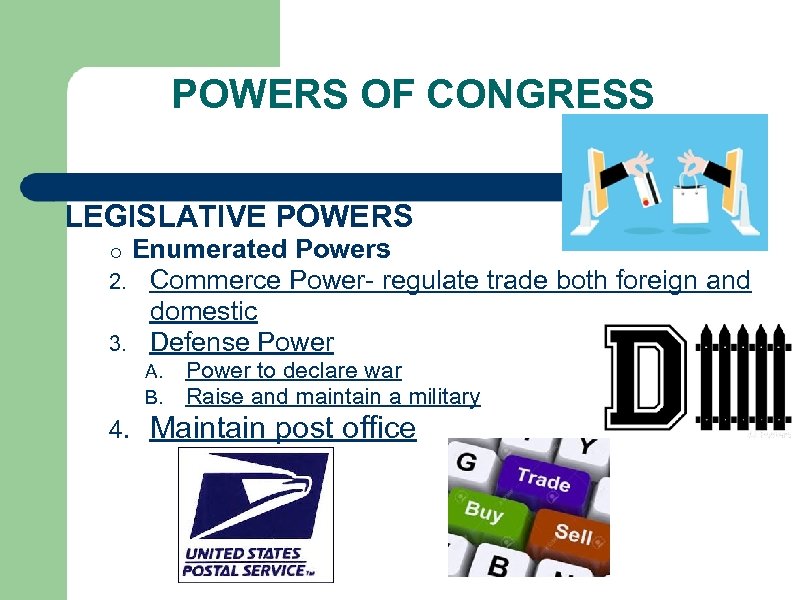
POWERS OF CONGRESS LEGISLATIVE POWERS o Enumerated Powers 2. Commerce Power- regulate domestic 3. Defense Power A. B. 4. Power to declare war Raise and maintain a military Maintain post office trade both foreign and

POWERS OF CONGRESS LEGISLATIVE POWERS o Enumerated Powers 5. Copyrights and patents 6. Naturalization a. Immigration b. Citizenship 7. Establish Courts 8. Laws about election

POWERS OF CONGRESS TAXES & SPENDING (expressed power) All tax bills and other measures to raise money must start in the HOR • Revenue bills-create projects and establish how much money needed • Appropriations bills-how to provide the money for each project (lump sum or payments)

POWERS OF CONGRESS REGULATING COMMERCE & FOREIGN RELATIONS • Regulates foreign & interstate trade • Power to declare war • Create, maintain, oversee army, navy, nat’l guard • Senate approval of all treaties w/ foreign nations

POWERS OF CONGRESS LEGISLATIVE POWERS Gibbons v. Ogden - Upheld that the Legislative Branch has the power to regulate trade from state to state

POWERS OF CONGRESS LEGISLATIVE POWERS o Clause 18 of the Constitution outlines Congress’s implied powers (powers not stated specifically in the Constitution) § AKA “Necessary and Proper” clause or Elastic Clause § Turn to page 134 in textbook

POWERS OF CONGRESS LEGISLATIVE POWERS • Mc. Culloch v. Maryland- addressed the problem of whether or not Congress could use the Necessary and Proper Clause to make a bank • Allows Congress to make laws with implied powers

POWERS OF CONGRESS NON-LEGISLATIVE POWERS (for both houses) • • Propose Amendments Conduct investigations • • Congressional oversight-members of Congress watching the Executive Branch’s actions Confirm the VP in the event of a vacancy

POWERS OF CONGRESS NON-LEGISLATIVE POWERS (HOR) • HOR has sole power of Impeachment- formal accusation of misconduct while in office HOR majority vote to bring to trial; Senate serves as jury and 2/3 majority vote will remove a person from office • Election of President o In case of a tie in a Presidential election, the HOR has the power to choose the President

POWERS OF CONGRESS NON-LEGISLATIVE POWERS (Senate) • Approves appointments to the executive and judicial branches

POWERS DENIED TO CONGRESS CANNOT: • suspend the writ of habeas corpus (court order that requires police to bring a prisoner to court to explain why they are holding the person) • passing bills of attainder (laws that punish a person without a jury trial) • pass ex post facto laws (laws that make an act a crime after the act has been committed)
3 MAJOR DUTIES OF CONGRESS • Lawmaking • Casework-the work that members of Congress do to help the people they represent (constituents) with a problem • Helping the District or State o Pork-barrel projects-government projects and grants that primarily benefit the home district or state (brings in $$)

HOW A BILL BECOMES A LAW • ANYONE can propose or write a bill! Private bills-concern individual people or places EX. Immigration Public bills-apply to the whole nation and involve general matters EX. taxation, civil rights or terrorism
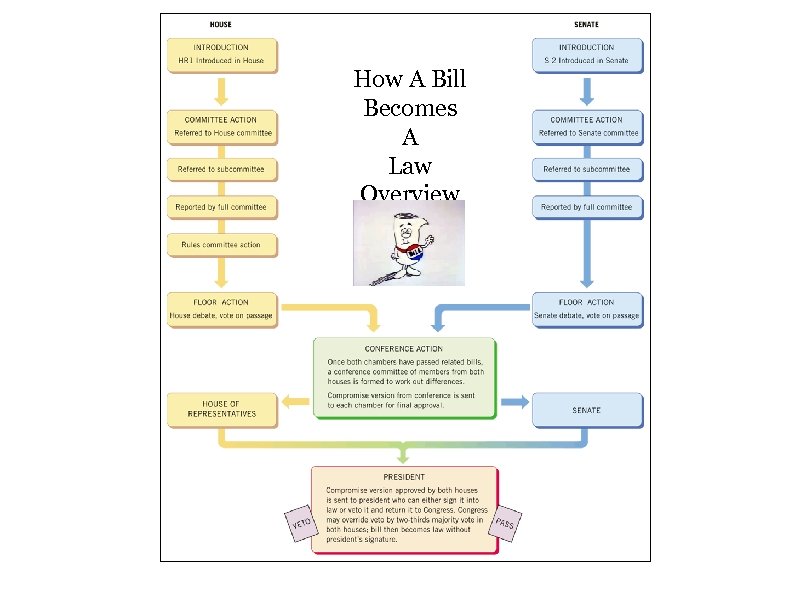
How A Bill Becomes A Law Overview

HOW A BILL BECOMES A LAW • HOR- representative drops bill in the hopper • Senate- senator introduces bill on the floor • The House Rules Committee (controls the schedule of bill debates for the House) gives priority to the bills that are most important • The Senate usually debates bills in chronological order

HOW A BILL BECOMES A LAW COMMITTEE ACTION • Standing committees have life and death power over bills! • The committee can: o Pass the bill without changes to floor debate o Mark up a bill with changes & suggest that it be passed o Replace the original bill with a new alternative o Ignore the bill & let it die (which is known as pigeon-hole veto) o Kill the bill outright by majority vote
HOW A BILL BECOMES A LAW • FLOOR ACTION • Debates pros & cons of bill • HOR allows only relevant amendments to bill to be added • Senate allows addition of bill riders (amendments completely unrelated to bill!)

HOW A BILL BECOMES A LAW • Christmas Tree bills. Senate allows multiple unrelated amendments to be tacked onto bills

HOW A BILL BECOMES A LAW • HOR- the Rules Committee sets the terms for debate (Traffic officer) o time limits on the discussion (pro/con) • Senators can speak as long as they wish, and they are not even required to address the topic at hand o o o Filibuster-talk a bill to death no one Senator may speak for more than one hour at a time Longest filibuster was in 1964 & lasted 74 days! • The Senate can end a filibuster if 3/5 ths (60%) of the members vote for a cloture

HOW A BILL BECOMES A LAW Simple majority vote in both HOR and Senate sends the bill to the Presidential Action 1. Sign and declare the bill a new law 2. Veto (refuse to sign) the bill 3. Do nothing for 10 days, and if Congress is in session the bill becomes a law without the President’s signature! 4. If Congress is not in session or is getting ready to adjourn, and the President does not sign it, after 10 days it will have been pocket vetoed

HOW A BILL BECOMES A LAW • Congressional Override-Congress can overturn a presidential veto with 2/3 majority vote by both HOR & Senate • Very few bills ever make it back through the process to be overturned!

Checks and Balances What are the Checks on other Branches by Congress? • The things Congress can do to prevent the other branches from having to much power

Checks and Balances What are the Checks on other Branches by Congress? • Executive Branch • Impeach and remove president • Override veto • Controls spending • Approves or rejects presidential nominations • Senate ratifies all US treaties
Checks and Balances What are the Checks on other Branches by Congress? • Judicial Branch • Impeach and remove federal judges • Establishes lower federal courts
78af6f3d9dd2b996a02a451be279e129.ppt