87ec0309197fbc86709cde35a0c93f47.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

Legislative Branch

Congressional Structure

Congress HOUSE 435 %Pop 2 Yrs Total people # of Reps for state Length of terms SENATE 100 (2*50) 2 Per state 6 Yrs Qualifications 25 Yrs Age 30 Yrs 7 Yrs Citizen of US 9 Yrs Must reside in the State that they represent

Terms and Sessions • • Congressional Term - 2 years 2 Sessions per term (each 1 year long) Work day: Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday. Working time: Noon to 5 – 6 o’clock. Recess = temporary break Special Session= Outside of regular hours Joint Session= Both House and Senate “State of the Union” Called by president

Determining Representatives • Census=Every 10 years to determine population Census • Reapportion= Divide number of representatives Reapportion between states • Redistrict=when apportionment changes Redistrict • Gerrymander= drawing district lines based on Gerrymander some characteristic other than just population a) Cracking b) Packing

As of 2012 Prior to 2012
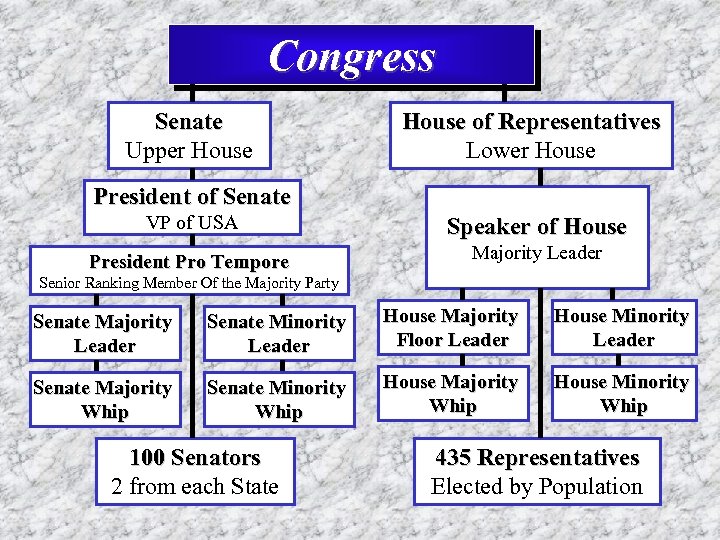
Congress Senate Upper House of Representatives Lower House President of Senate VP of USA Speaker of House President Pro Tempore Majority Leader Senior Ranking Member Of the Majority Party Senate Majority Leader Senate Minority Leader House Majority Floor Leader House Minority Leader Senate Majority Whip Senate Minority Whip House Majority Whip House Minority Whip 100 Senators 2 from each State 435 Representatives Elected by Population

Congressional Leadership

Leadership in the House of Representatives SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE Selected by the majority party Job: Presiding Officer of the House Power: Decides which committee a bill goes to. Paul Ryan (R-WI) Assumed role 2015

Leadership in the House of Representatives SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE Selected by the majority party Majority Leader Leads the majority party Job: Shepherds legislation Kevin Mc. Carthy R- CA Minority Leader Leads the minority party Job: Leads Opposition Nancy Pelosi (D-Ca)

Leadership in the House of Representatives SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE Selected by the majority party Majority Leader Minority Leader Majority Whip Job: Assists the leader, rounds up votes, heads large group of deputy and assistant whips. Minority Whip Job: Assists the leader, rounds up votes, heads large group of deputy and assistant whips. Steve Scalise Steny Hoyer R-LA D-MD

Georgia’s Representation • Georgia currently has 14 congressional districts. • Wheeler’s current congressional district is the 6 th represented by: • Republican • Serves on: Committees and Caucuses Congressman Tom Price


Leadership in the United States Senate PRESIDENT OF THE SENATE The Vice President of the United States Vice President Joe Biden Elected in 2008 Job: Presiding Officer of the Senate Power: Breaks tie in legislation. Otherwise does not vote.

Leadership in the United States Senate PRESIDENT OF THE SENATE The Vice President of the United States PRESIDENT PRO TEMPORE Selected by majority party. Usually most senior member of the Senate majority party Job: Presides over the Senate when the Vice President is absent. Vice President-Elect Mike Pence Orrin Hatch (R-UT)

Leadership in the United States Senate

Leadership in the United States Senate Majority Leader Minority Leader Leads the majority party Job: Shepherds legislation Leads the minority party Job: Leads Opposition Also plans the senate work schedule, assigns bills and senators to committees Harry Reid (D-NV) Mitch Mc. Connell (R-KY)

Leadership in the United States Senate Minority Whip Assist the Minority Leader Job: Makes sure legislators are present for key votes Majority Whip Assist the Majority Leader Job: Makes sure legislators are present for key votes Richard Durbin D-IL John Cornyn R-TX

Georgia’s Representation Senator Johnny Isakson Senator David Perdue AND

Congressional Rules and Benefits

Congressional Characteristics • Seniority – the most senior members get more choice of assignments (exists only in the senate) • Specialization – committees consist of members who are experts in specific area of policy (ie. Docter on Health Com. ) • Reciprocity/logrolling - support for each others bill. (You vote in my bill, I’ll vote in your bill)

Privileges and Penalties • Congressional Immunity : ______ • Expel Members with 2/3 rd vote. • Censure Members • Codes of Ethic

Compensation and Benefits • Salaries ($174, 000 -2014). – 27 th Amendment allows the current Congress to increase the salary of those serving in the next Congressional Term • Outside Income allowed • Offices – In DC and at home • Expense Accounts • “Franking Privilege” Free Stationary and Postage

Compensation and Benefits Cont. • Computer service • TV and radio broadcast • Travel expenses • Pension Plan and Retirement Income. • Incumbent = helped to get reelected.

Congressional Powers

Congressional Powers I. Legislative Powers A. Sovereign Powers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Provide for common defense Make rules on citizenship Run Armed Services Declare War Govern Washington D. C.

Congressional Powers B. Financial power 1. Lay and collect taxes, borrow money, establish bankruptcy laws, Coin and print money, Punish counterfeiters Ø Revenue Bills – tax bills must originate in the House (Ways and Means Committee) Ø Appropriations bills – any law that authorizes congress to spend money Ø National debt – total dollar amount owed by the goverment at any given time

Congressional Powers Cont. 2. Regulate Trade a. Duties – taxes on imports b. Excises – taxes on particular goods

Congressional Powers Cont. C. Regulate Commerce 1. Interstate commerce 2. Foreign commerce 3. Meaning of commerce – now it far exceeds just the buying and selling of products. – Has allowed congress to control working conditions including minimum wage

Congressional Powers II. Non-Legislative Powers - SENATE A. Advise and Consent 1. Presidential Appointments (V. P. , Justices, and Cabinet) 2. Treaties with Foreign Nations 3. Convict and Remove Federal Officials (2/3 rds in Senate) III. Non-Legislative Powers - HOUSE A. Impeachment (Majority in House) » Formal charge of wrongdoing

Congressional Powers IV. Non-Legislative Powers A. Providing for the Nations Growth – Naturalization – the process by which immigrants to the U. S. may become citizens. – Authorize admission of new states – Pass laws to govern territories – Pass laws to govern federal property (military bases, govt. buildings)

Congressional Powers B. Amend the Constitution C. Count Electoral Votes • If no majority: – the House will elect the President – the Senate will elect the Vice President D. Gov. “Watchdog” – Hold the executive branch accountable for enforcing laws passed by Congress

Other Legislative Powers • Grant copyrights – exclusive right to publish and sell a literary, musical, or artistic work for a specified period of time Grant patents - exclusive right of an inventor to manufacture, use and sell his or her invention for a specific period, currently 7 years

Congress & The Other Branches

Congress and The Judiciary 1. Establish Federal Courts 2. Set number of Supreme Court Justices 3. Set the Jurisdiction of the Federal Judiciary

Government Watchdog • Power to investigate – Done by standing or select committees – Lead to new legislation, changes in government programs, or removal of officials from office – Have the power to subpoena witnesses, prosecute witnesses for perjury, or hold them in contempt if they refuse to testify – Witnesses can be granted immunity

Government Watchdog • Legislative Oversight – A continuing review of how effectively the executive branch carries out the laws that Congress passes – Legislative Reorganization Act of 1946 and 1970 “Each standing committee shall review and study, on a continuing basis, the application, administration and execution” of law in area of its responsibility

Government Watchdog • Limitations on Legislative Oversight – First, lawmakers do not have enough staff, time, or money to effectively monitor the executive branch – Second, lawmakers know that there are not many votes to be gained from most oversight activities – Third, the language of some laws are too vague making it difficult to judge – Finally, committees might, sometimes favor the federal agencies they oversee

Congress in Your Life… Make the Laws Oversight Inform us of the laws Constituent services

Congress is Important! For Georgia! And for you!
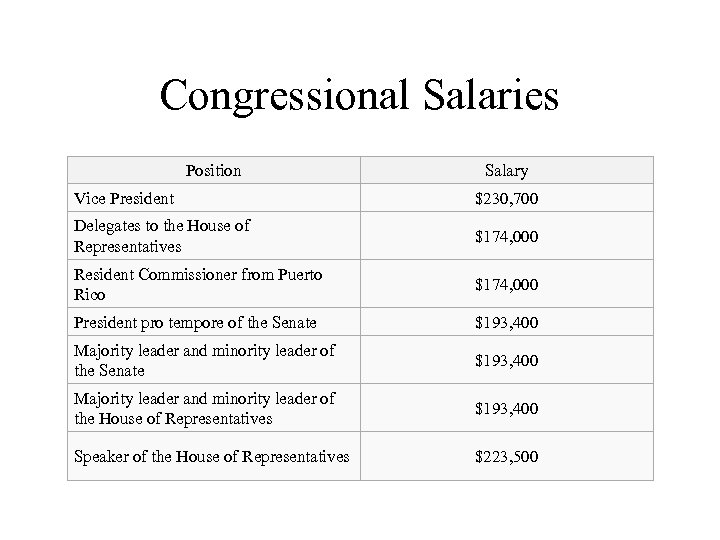
Congressional Salaries Position Salary Vice President $230, 700 Delegates to the House of Representatives $174, 000 Resident Commissioner from Puerto Rico $174, 000 President pro tempore of the Senate $193, 400 Majority leader and minority leader of the House of Representatives $193, 400 Speaker of the House of Representatives $223, 500

87ec0309197fbc86709cde35a0c93f47.ppt