6714ead7d42d62aab30bafda526cf6c9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Legislation Screening audiometry Dr Jan Lapere SANS 10083: 2013 edition 5. 2 Updated 03 -09 -2014
Legislation Screening audiometry Dr Jan Lapere SANS 10083: 2013 edition 5. 2 Updated 03 -09 -2014
 Noise exposure & OHSA Legal compliance OHSA: Noise-induced Hearing Loss Regulations are applicable at any workplace where persons are exposed to noise at or above the noise-rating limit of 85 d. B(A) . 2
Noise exposure & OHSA Legal compliance OHSA: Noise-induced Hearing Loss Regulations are applicable at any workplace where persons are exposed to noise at or above the noise-rating limit of 85 d. B(A) . 2
 Noise exposure & MHSA Legal compliance MHSA: • Regulation 11. 4: Occupational medicine: employer to establish and • • maintain medical surveillance where the equivalent, continuous A weighted sound pressure level, normalised to an eight hour working day or a forty hour working week, is equal to or exceeds 85 d. B(A) Regulation 9. 2: Occupational Hygiene : employer to establish and maintain a system of occupational hygiene measurements where noise is >= 82 d. B(A) Regulation 11. 8 of the Regulations Relating to Machinery and Equipment: the employer must report to the office of the Principal Inspector in the manner prescribed in this section any of the following occupational diseases that are as a result of working in the mining environment: Noise induced hearing loss that is reportable =PLH shift of 5% or more 3
Noise exposure & MHSA Legal compliance MHSA: • Regulation 11. 4: Occupational medicine: employer to establish and • • maintain medical surveillance where the equivalent, continuous A weighted sound pressure level, normalised to an eight hour working day or a forty hour working week, is equal to or exceeds 85 d. B(A) Regulation 9. 2: Occupational Hygiene : employer to establish and maintain a system of occupational hygiene measurements where noise is >= 82 d. B(A) Regulation 11. 8 of the Regulations Relating to Machinery and Equipment: the employer must report to the office of the Principal Inspector in the manner prescribed in this section any of the following occupational diseases that are as a result of working in the mining environment: Noise induced hearing loss that is reportable =PLH shift of 5% or more 3
 Standards • • • Act Regulation SANS codes Professional standards OMP Standard Operating Procedure 3/15/2018 4
Standards • • • Act Regulation SANS codes Professional standards OMP Standard Operating Procedure 3/15/2018 4
 Hearing Conservation program • • • Information and training of employees Duties of exposed persons Risk assessment Noise monitoring Medical surveillance Noise zone Control of noise exposure Records Hearing protective equipment Maintenance of control measures 5
Hearing Conservation program • • • Information and training of employees Duties of exposed persons Risk assessment Noise monitoring Medical surveillance Noise zone Control of noise exposure Records Hearing protective equipment Maintenance of control measures 5
 Medical Surveillance A planned programme of periodic examination (clinical, biological monitoring or medical tests) of exposed employees by an occupational health practitioner or, in prescribed cases, by an occupational medicine practitioner 6
Medical Surveillance A planned programme of periodic examination (clinical, biological monitoring or medical tests) of exposed employees by an occupational health practitioner or, in prescribed cases, by an occupational medicine practitioner 6
 OHSA = MHSA Noise Medical Surveillance Baseline audiogram • Before the employee commences employment or within 30 days of commencement • (if not possible: employee must be referred to an audiologist) • Standard = COIDA Instruction 171(? ) Periodic audiogram • First three years = annually • After three years = every two years if “no referral threshold” shift is evident: • If =>105 d. B(A) or gunshots: test at 6 -monthly intervals If no threshold shift: annual • Standard = SANS 10083 Exit audiogram • Audiogram within six months prior to termination is also OK • Standard = SANS 10083 Competent person Audiograms performed by competent person 7
OHSA = MHSA Noise Medical Surveillance Baseline audiogram • Before the employee commences employment or within 30 days of commencement • (if not possible: employee must be referred to an audiologist) • Standard = COIDA Instruction 171(? ) Periodic audiogram • First three years = annually • After three years = every two years if “no referral threshold” shift is evident: • If =>105 d. B(A) or gunshots: test at 6 -monthly intervals If no threshold shift: annual • Standard = SANS 10083 Exit audiogram • Audiogram within six months prior to termination is also OK • Standard = SANS 10083 Competent person Audiograms performed by competent person 7
 Competent person SANS 10083 -2013 a. b. c. d. e. f. Registered audiometrist or a hearing-aid acoustician Medical specialist in otorhinolaryngology Graduate in speech therapy and audiology Person holding certificate in audiometry issued by an institution recognized and approved by DOL or DME Occupational medical practitioner Person qualified in audiometric techniques from an institution registered with the relevant national authority in terms of the relevant national legislation and registered with the South African Society for Occupational Health Nursing (SASOHN) 8
Competent person SANS 10083 -2013 a. b. c. d. e. f. Registered audiometrist or a hearing-aid acoustician Medical specialist in otorhinolaryngology Graduate in speech therapy and audiology Person holding certificate in audiometry issued by an institution recognized and approved by DOL or DME Occupational medical practitioner Person qualified in audiometric techniques from an institution registered with the relevant national authority in terms of the relevant national legislation and registered with the South African Society for Occupational Health Nursing (SASOHN) 8
 Competent person OHSA • Health Professions Council of South Africa registered o ENT specialist o Speech therapist and audiologist o Occupational medicine practitioner • SAQA qualified audiometrist • Registered with SASOHN 9
Competent person OHSA • Health Professions Council of South Africa registered o ENT specialist o Speech therapist and audiologist o Occupational medicine practitioner • SAQA qualified audiometrist • Registered with SASOHN 9
 Competent person SANS 10083 -2013 • An otoscopic examination in accordance with 18. 3 and 20. 4 is required when audiometric testing is done • It is consequently strongly recommended that all prospective candidates to be trained as audiometrist from date of publication of this standard should successfully have completed anatomy and physiology at tertiary level 10
Competent person SANS 10083 -2013 • An otoscopic examination in accordance with 18. 3 and 20. 4 is required when audiometric testing is done • It is consequently strongly recommended that all prospective candidates to be trained as audiometrist from date of publication of this standard should successfully have completed anatomy and physiology at tertiary level 10
 Baseline audiogram 17. 1 Baseline audiometry should be conducted on: a) all prospective employees expected to enter a noise zone and for whom a valid baseline result has not been determined at a previous workplace b) all employees working in a newly identified noise zone These baselines should be established within 30 days of employment or identification of a noise zone Seasonal workers or workers performing work during intermittent periods should be subject to all prescribed audiometry 11
Baseline audiogram 17. 1 Baseline audiometry should be conducted on: a) all prospective employees expected to enter a noise zone and for whom a valid baseline result has not been determined at a previous workplace b) all employees working in a newly identified noise zone These baselines should be established within 30 days of employment or identification of a noise zone Seasonal workers or workers performing work during intermittent periods should be subject to all prescribed audiometry 11
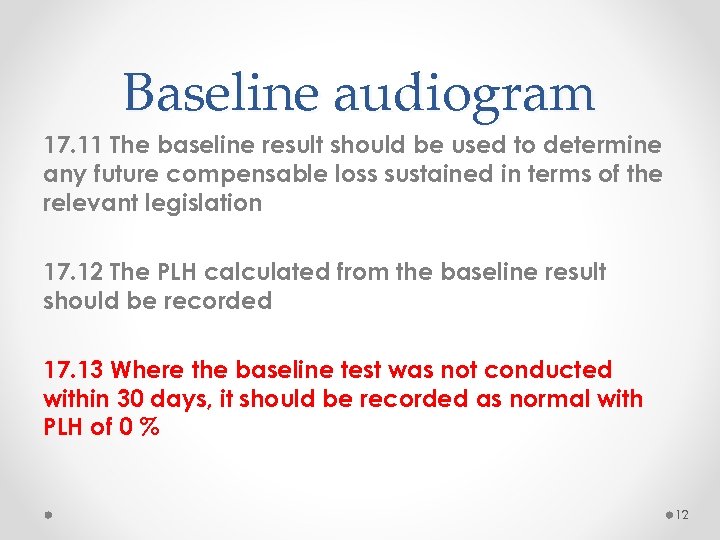 Baseline audiogram 17. 11 The baseline result should be used to determine any future compensable loss sustained in terms of the relevant legislation 17. 12 The PLH calculated from the baseline result should be recorded 17. 13 Where the baseline test was not conducted within 30 days, it should be recorded as normal with PLH of 0 % 12
Baseline audiogram 17. 11 The baseline result should be used to determine any future compensable loss sustained in terms of the relevant legislation 17. 12 The PLH calculated from the baseline result should be recorded 17. 13 Where the baseline test was not conducted within 30 days, it should be recorded as normal with PLH of 0 % 12
 Baseline audiogram 1. Otoscopic examination 2. Better of 2 screening tests on the same day o Test must not differ by more than 10 d. B at 0. 5, 1, 2, 3 and 4 k. Hz o Immediately preceded by at least 16 h of no exposure to rating limit o Wearing of hearing protectors does not satisfy this requirement 13
Baseline audiogram 1. Otoscopic examination 2. Better of 2 screening tests on the same day o Test must not differ by more than 10 d. B at 0. 5, 1, 2, 3 and 4 k. Hz o Immediately preceded by at least 16 h of no exposure to rating limit o Wearing of hearing protectors does not satisfy this requirement 13
 Baseline audiometric test • • • • Name, Identity number, Work identification Age Medical record, clinical info and recommendation Previous work noise exposure Name and type of business of the employer Nature of the work, including a description of the work procedure and area Date and place of the test Details of exit - and baseline audiometric record from previous employer Measured hearing levels of the initial and the repeat audiometry An indication which is the baseline audiogram Calculated PLH for the accepted baseline Deviation of measured hearing levels from exit audiometry from the previous employer (at least at 500 Hz, 1 k. Hz, 2 k. Hz, 3 k. Hz, 4 k. Hz, 6 k. Hz and 8 k. Hz) List of the test equipment &serial numbers & calibration dates & calibration organization Name of test officer 14
Baseline audiometric test • • • • Name, Identity number, Work identification Age Medical record, clinical info and recommendation Previous work noise exposure Name and type of business of the employer Nature of the work, including a description of the work procedure and area Date and place of the test Details of exit - and baseline audiometric record from previous employer Measured hearing levels of the initial and the repeat audiometry An indication which is the baseline audiogram Calculated PLH for the accepted baseline Deviation of measured hearing levels from exit audiometry from the previous employer (at least at 500 Hz, 1 k. Hz, 2 k. Hz, 3 k. Hz, 4 k. Hz, 6 k. Hz and 8 k. Hz) List of the test equipment &serial numbers & calibration dates & calibration organization Name of test officer 14
 Periodic Screening audiometry 1. Otoscopic examination 2. Pure tone air conduction audiogram o Immediately preceded by at least 16 h of no exposure to rating limit o Wearing of SANS 1451 -compliant hearing protection equipment satisfies this requirement o Repeated every 12 months, where the 8 h rating level < 105 d. BA and every six months if > 105 d. BA for the first 3 years 15
Periodic Screening audiometry 1. Otoscopic examination 2. Pure tone air conduction audiogram o Immediately preceded by at least 16 h of no exposure to rating limit o Wearing of SANS 1451 -compliant hearing protection equipment satisfies this requirement o Repeated every 12 months, where the 8 h rating level < 105 d. BA and every six months if > 105 d. BA for the first 3 years 15
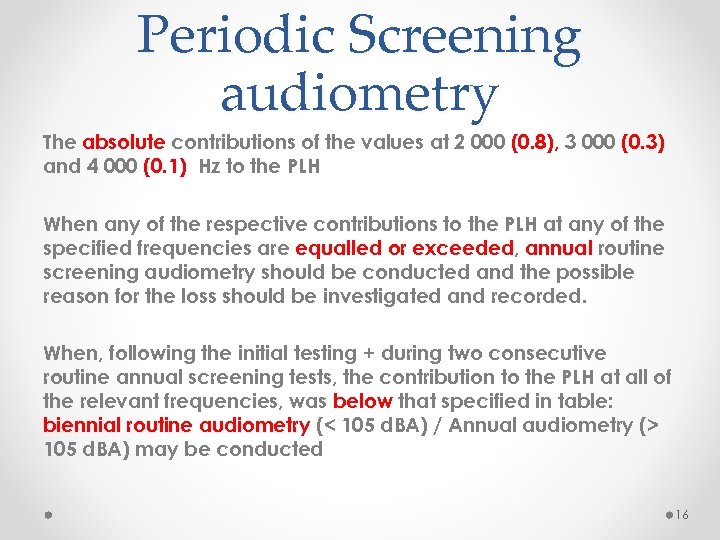 Periodic Screening audiometry The absolute contributions of the values at 2 000 (0. 8), 3 000 (0. 3) and 4 000 (0. 1) Hz to the PLH When any of the respective contributions to the PLH at any of the specified frequencies are equalled or exceeded, annual routine screening audiometry should be conducted and the possible reason for the loss should be investigated and recorded. When, following the initial testing + during two consecutive routine annual screening tests, the contribution to the PLH at all of the relevant frequencies, was below that specified in table: biennial routine audiometry (< 105 d. BA) / Annual audiometry (> 105 d. BA) may be conducted 16
Periodic Screening audiometry The absolute contributions of the values at 2 000 (0. 8), 3 000 (0. 3) and 4 000 (0. 1) Hz to the PLH When any of the respective contributions to the PLH at any of the specified frequencies are equalled or exceeded, annual routine screening audiometry should be conducted and the possible reason for the loss should be investigated and recorded. When, following the initial testing + during two consecutive routine annual screening tests, the contribution to the PLH at all of the relevant frequencies, was below that specified in table: biennial routine audiometry (< 105 d. BA) / Annual audiometry (> 105 d. BA) may be conducted 16
 Periodic audiometric test (SANS 10083) • • • • Name, identity number, work identification Age Trade name and type of business of the employer; Nature of the work (description of work procedure and area) Date and place of the test Details of baseline audiometry (@ commencement of employment) Measured hearing levels Calculated PLH (at each frequency) Increase in PLH from baseline audiogram @ 0. 5, 1, 2, 3 & 4 k. Hz PLH shift % Any repeat screening audiometric investigation Relevant clinical information & recommendations Referral documents to audiologist or medical practitioner List of the test equipment &serial numbers & calibration dates & calibration organization Name of test officer 17
Periodic audiometric test (SANS 10083) • • • • Name, identity number, work identification Age Trade name and type of business of the employer; Nature of the work (description of work procedure and area) Date and place of the test Details of baseline audiometry (@ commencement of employment) Measured hearing levels Calculated PLH (at each frequency) Increase in PLH from baseline audiogram @ 0. 5, 1, 2, 3 & 4 k. Hz PLH shift % Any repeat screening audiometric investigation Relevant clinical information & recommendations Referral documents to audiologist or medical practitioner List of the test equipment &serial numbers & calibration dates & calibration organization Name of test officer 17
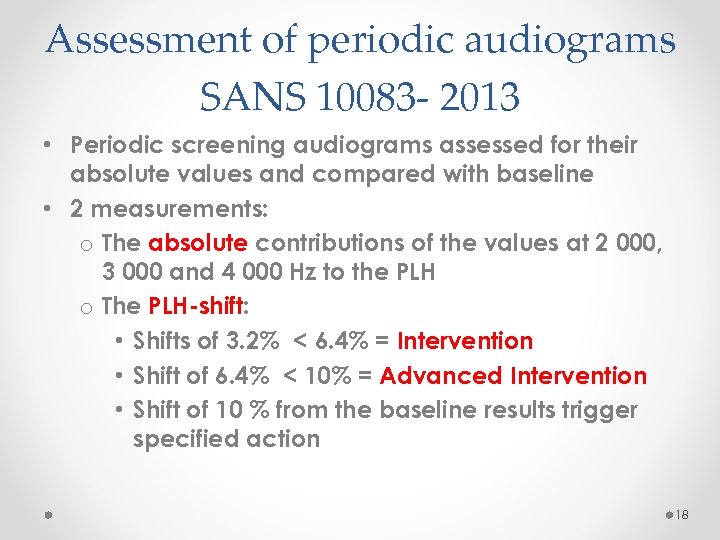 Assessment of periodic audiograms SANS 10083 - 2013 • Periodic screening audiograms assessed for their absolute values and compared with baseline • 2 measurements: o The absolute contributions of the values at 2 000, 3 000 and 4 000 Hz to the PLH o The PLH-shift: • Shifts of 3. 2% < 6. 4% = Intervention • Shift of 6. 4% < 10% = Advanced Intervention • Shift of 10 % from the baseline results trigger specified action 18
Assessment of periodic audiograms SANS 10083 - 2013 • Periodic screening audiograms assessed for their absolute values and compared with baseline • 2 measurements: o The absolute contributions of the values at 2 000, 3 000 and 4 000 Hz to the PLH o The PLH-shift: • Shifts of 3. 2% < 6. 4% = Intervention • Shift of 6. 4% < 10% = Advanced Intervention • Shift of 10 % from the baseline results trigger specified action 18
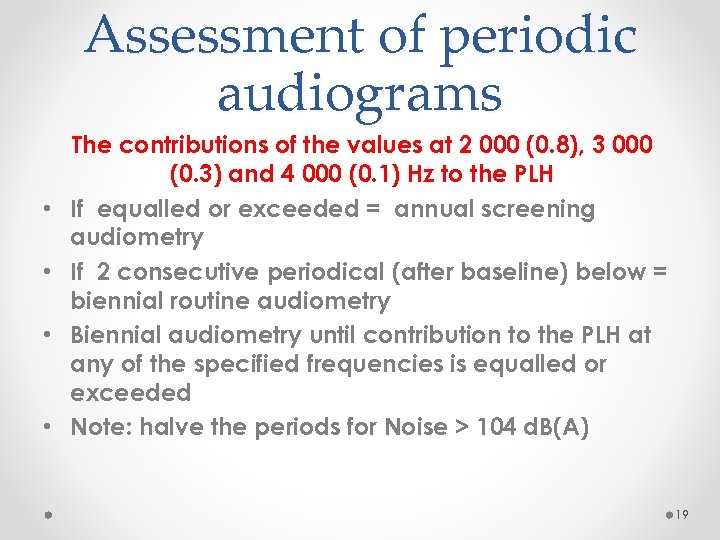 Assessment of periodic audiograms • • The contributions of the values at 2 000 (0. 8), 3 000 (0. 3) and 4 000 (0. 1) Hz to the PLH If equalled or exceeded = annual screening audiometry If 2 consecutive periodical (after baseline) below = biennial routine audiometry Biennial audiometry until contribution to the PLH at any of the specified frequencies is equalled or exceeded Note: halve the periods for Noise > 104 d. B(A) 19
Assessment of periodic audiograms • • The contributions of the values at 2 000 (0. 8), 3 000 (0. 3) and 4 000 (0. 1) Hz to the PLH If equalled or exceeded = annual screening audiometry If 2 consecutive periodical (after baseline) below = biennial routine audiometry Biennial audiometry until contribution to the PLH at any of the specified frequencies is equalled or exceeded Note: halve the periods for Noise > 104 d. B(A) 19
 Assessment of periodic audiograms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Intervention at PLH shifts of > 3. 2% < 6. 4% Employer to investigate & determine cause Inspect & check PPE for adequacy Inspect fit & use of PPE by employee Retrain employee in Regulation 3 Document intervention & archive for 40 years 20
Assessment of periodic audiograms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Intervention at PLH shifts of > 3. 2% < 6. 4% Employer to investigate & determine cause Inspect & check PPE for adequacy Inspect fit & use of PPE by employee Retrain employee in Regulation 3 Document intervention & archive for 40 years 20
 Assessment of periodic audiograms- MHSA only Intervention at PLH shifts of > = 5% 1. Same as Intervention SANS (as loss> 3. 2%) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Employer to investigate & determine cause Inspect & check PPE for adequacy Inspect fit & use of PPE by employee Retrain employee in Regulation 3 Document intervention & archive for 40 years 2. Reporting 1. Complete DMR 90 21
Assessment of periodic audiograms- MHSA only Intervention at PLH shifts of > = 5% 1. Same as Intervention SANS (as loss> 3. 2%) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Employer to investigate & determine cause Inspect & check PPE for adequacy Inspect fit & use of PPE by employee Retrain employee in Regulation 3 Document intervention & archive for 40 years 2. Reporting 1. Complete DMR 90 21
 Assessment of periodic audiograms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Intervention at PLH shifts of > 6. 4% < 10% Employer to investigate & determine cause- must include re-test and otoscopy Diagnostic test by audiologist to be considered Inspect & check PPE for adequacy Inspect fit & use of PPE by employee Retrain employee in Regulation 3 Document intervention & archive for 40 years 22
Assessment of periodic audiograms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Intervention at PLH shifts of > 6. 4% < 10% Employer to investigate & determine cause- must include re-test and otoscopy Diagnostic test by audiologist to be considered Inspect & check PPE for adequacy Inspect fit & use of PPE by employee Retrain employee in Regulation 3 Document intervention & archive for 40 years 22
 Assessment of periodic audiograms • • Intervention at PLH shifts of >10% Re-test employee If > 10 PLH shift: remove employee from noise Refer to audiologist for diagnostic audiometry If > 10 PLH confirmed: refer to ENT or OMP It is recommended that employee is removed from any noise zone Employer to investigate & determine cause Inspect & check PPE for adequacy Inspect fit & use of PPE by employee 23
Assessment of periodic audiograms • • Intervention at PLH shifts of >10% Re-test employee If > 10 PLH shift: remove employee from noise Refer to audiologist for diagnostic audiometry If > 10 PLH confirmed: refer to ENT or OMP It is recommended that employee is removed from any noise zone Employer to investigate & determine cause Inspect & check PPE for adequacy Inspect fit & use of PPE by employee 23
 Assessment of periodic audiograms • • • Intervention at PLH shifts of >10% If re-entry in noise zone: retrain Regulation 3 If continued loss: remove employee permanently from noise Report to COIDA Report to DME Document intervention & archive for 40 years 24
Assessment of periodic audiograms • • • Intervention at PLH shifts of >10% If re-entry in noise zone: retrain Regulation 3 If continued loss: remove employee permanently from noise Report to COIDA Report to DME Document intervention & archive for 40 years 24
 Audiometry (SANS 10083) • Otoscopic examination • Audiometer o At least type 4 specified in IEC 60645 -1 o Calibrated as per SANS 10154 -2012 o Test % 500 Hz, 1 k. Hz, 2 k. Hz, 3 k. Hz, 4 k. Hz, 6 k. Hz, 8 k. Hz • Test environment o Booth, room or mobile complies with SANS 10182 o Assessed annually by compliant organization o “mobile audiometric facility” = facility such as a caravan or a trailer that is specially designed to protect it from undue outside interference and that can be moved to different sites. The facility is used solely for audiometric purposes 25
Audiometry (SANS 10083) • Otoscopic examination • Audiometer o At least type 4 specified in IEC 60645 -1 o Calibrated as per SANS 10154 -2012 o Test % 500 Hz, 1 k. Hz, 2 k. Hz, 3 k. Hz, 4 k. Hz, 6 k. Hz, 8 k. Hz • Test environment o Booth, room or mobile complies with SANS 10182 o Assessed annually by compliant organization o “mobile audiometric facility” = facility such as a caravan or a trailer that is specially designed to protect it from undue outside interference and that can be moved to different sites. The facility is used solely for audiometric purposes 25
 Maintenance and calibration of audiometric equipment (SANS 10083) • All equipment o Calibrate before use as per SANS 10154 -2012 o Daily & weekly tests SANS 8253 -1: 2011 • Mobile audiometric facilities and audiometers calibrated and maintained in accordance with SANS 10154 -1: 2012 (new!) o Calibrating laboratory/organization to have traceability & to implement and maintain a quality management system in accordance with SANS 17025 o Calibration certificate compliant to SANS 10154 -1: 2012 26
Maintenance and calibration of audiometric equipment (SANS 10083) • All equipment o Calibrate before use as per SANS 10154 -2012 o Daily & weekly tests SANS 8253 -1: 2011 • Mobile audiometric facilities and audiometers calibrated and maintained in accordance with SANS 10154 -1: 2012 (new!) o Calibrating laboratory/organization to have traceability & to implement and maintain a quality management system in accordance with SANS 17025 o Calibration certificate compliant to SANS 10154 -1: 2012 26
 SANS 10154 -1: 2012 Mobile Audiometry 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. General requirements: deemed valid standard Audiometer mounted on anti-vibration platform whenever moved Audiometer to stay within specified calibration limits during calibration time interval Audiometer to stay within specified design limits (e. g. climatic conditions) Ambient noise levels at test site comply with limits specified in SANS 10182 Subjective tests carried out before the audiometer is used If any one of the requirements are not complied with, deem all the audiograms taken to be invalid 27
SANS 10154 -1: 2012 Mobile Audiometry 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. General requirements: deemed valid standard Audiometer mounted on anti-vibration platform whenever moved Audiometer to stay within specified calibration limits during calibration time interval Audiometer to stay within specified design limits (e. g. climatic conditions) Ambient noise levels at test site comply with limits specified in SANS 10182 Subjective tests carried out before the audiometer is used If any one of the requirements are not complied with, deem all the audiograms taken to be invalid 27
 SANS 10154 -1: 2012 Mobile Audiometry General requirements: deemed valid standard Calibration time interval = period between calibration of the audiometer at its original site before it is moved and recalibration of the audiometer upon its return, or after 3 months, whichever is shortest = In accordance with SANS 10154 28
SANS 10154 -1: 2012 Mobile Audiometry General requirements: deemed valid standard Calibration time interval = period between calibration of the audiometer at its original site before it is moved and recalibration of the audiometer upon its return, or after 3 months, whichever is shortest = In accordance with SANS 10154 28
 SANS 10154 -1: 2012 Mobile Audiometry 1. 2. 3. 4. General requirements: deemed valid standard Suitability of the test site Install mobile facility in position of use & measure the noise levels inside facility in accordance with SANS 10182. Repeat this process for each test site Install the audiometer in the position where it will be used at that specific site and measure the ambient noise levels in accordance with SANS 10182 Repeat this procedure for each test site 29
SANS 10154 -1: 2012 Mobile Audiometry 1. 2. 3. 4. General requirements: deemed valid standard Suitability of the test site Install mobile facility in position of use & measure the noise levels inside facility in accordance with SANS 10182. Repeat this process for each test site Install the audiometer in the position where it will be used at that specific site and measure the ambient noise levels in accordance with SANS 10182 Repeat this procedure for each test site 29
 SANS 10154 -1: 2012 Mobile Audiometry 10 Steps At the original site Step 1 a. Measure sound pressure levels of test environment (SANS 10182) b. Measure climatic conditions (see manufacturer standard) c. Calibrate the audiometer (see 10154) d. Record all the measurement results Step 2: Subjective tests before moving a. Experienced, qualified tester with normal hearing to listen carefully for distortions, attenuator and tone-switch transients and other unwanted sound from the audiometer at all the attenuator settings at all the test frequencies b. Take audiogram of person with known stable hearing and with hearing threshold level not exceeding 25 d. B, at each test frequency 30
SANS 10154 -1: 2012 Mobile Audiometry 10 Steps At the original site Step 1 a. Measure sound pressure levels of test environment (SANS 10182) b. Measure climatic conditions (see manufacturer standard) c. Calibrate the audiometer (see 10154) d. Record all the measurement results Step 2: Subjective tests before moving a. Experienced, qualified tester with normal hearing to listen carefully for distortions, attenuator and tone-switch transients and other unwanted sound from the audiometer at all the attenuator settings at all the test frequencies b. Take audiogram of person with known stable hearing and with hearing threshold level not exceeding 25 d. B, at each test frequency 30
 SANS 10154 -1: 2012 Mobile Audiometry 10 Steps Step 3: Move and arrival testing a. Move audiometer carefully on anti-vibration platform b. Monitor climatic conditions at the new test site c. Measure the sound pressure levels of the test environment at the new site d. Record the measurement results. e. Confirm compliance with requirements of SANS 10182 31
SANS 10154 -1: 2012 Mobile Audiometry 10 Steps Step 3: Move and arrival testing a. Move audiometer carefully on anti-vibration platform b. Monitor climatic conditions at the new test site c. Measure the sound pressure levels of the test environment at the new site d. Record the measurement results. e. Confirm compliance with requirements of SANS 10182 31
 SANS 10154 -1: 2012 Mobile Audiometry Step 4 & 5 Repeat subjective tests at new site Start audiometry 10 Steps Step 6 : repeat steps 2 to 5 with every move Step 7: Recalibrate audiometer at its original site upon return or within 3 months, whichever is the shortest (SANS 10154) Step 8: If audiometer does not comply with SANS 10154 deem all audiograms taken NULL AND VOID Step 9: Compare the measurement in 7 with those in 1 and record deviations for each move + distance covered + time interval. Reduce calibration interval to ensure deviations are not significant Step 10: Keep all records for 10 years and available to calibration laboratory 32
SANS 10154 -1: 2012 Mobile Audiometry Step 4 & 5 Repeat subjective tests at new site Start audiometry 10 Steps Step 6 : repeat steps 2 to 5 with every move Step 7: Recalibrate audiometer at its original site upon return or within 3 months, whichever is the shortest (SANS 10154) Step 8: If audiometer does not comply with SANS 10154 deem all audiograms taken NULL AND VOID Step 9: Compare the measurement in 7 with those in 1 and record deviations for each move + distance covered + time interval. Reduce calibration interval to ensure deviations are not significant Step 10: Keep all records for 10 years and available to calibration laboratory 32
 SANS 10154 -1: 2012 Calibration of pure-tone audiometers Part 1: Air conduction • Competence • Calibration of equipment • Procedure and documentation 33
SANS 10154 -1: 2012 Calibration of pure-tone audiometers Part 1: Air conduction • Competence • Calibration of equipment • Procedure and documentation 33
 SANS 10182: 2006 The measurement and assessment of acoustic environments for audiometric tests • Competence: SANS 17025/ISO/IEC 17025, General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. • Calibration of equipment: all equipment used annually calibrated: o Proven traceability as per Measuring Units and National Measuring Standards Act, 1973 (Act No. 76 of 1973) o In accordance with quality management system in accordance with SANS 17025 34
SANS 10182: 2006 The measurement and assessment of acoustic environments for audiometric tests • Competence: SANS 17025/ISO/IEC 17025, General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. • Calibration of equipment: all equipment used annually calibrated: o Proven traceability as per Measuring Units and National Measuring Standards Act, 1973 (Act No. 76 of 1973) o In accordance with quality management system in accordance with SANS 17025 34
 SANS 10182: 2006 Annex A • The determination of the sound insulation performance of an audiometric booth or a mobile audiometric facility in a non-laboratory environment 35
SANS 10182: 2006 Annex A • The determination of the sound insulation performance of an audiometric booth or a mobile audiometric facility in a non-laboratory environment 35
 SANS 10083 - 2013 Time to re-assess standard practices!! 3/15/2018 36
SANS 10083 - 2013 Time to re-assess standard practices!! 3/15/2018 36


