67a4e80ec339d3a6a721ec8b83c85f8b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59
 Left Atrial Appendage Closure for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Ramon Quesada, MD, FACP, FACC, FSCAI, Medical Director, Interventional Cardiology Baptist Cardiac & Vascular Institute Miami, Florida
Left Atrial Appendage Closure for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Ramon Quesada, MD, FACP, FACC, FSCAI, Medical Director, Interventional Cardiology Baptist Cardiac & Vascular Institute Miami, Florida
 DISCLOSURES Ramon Quesada, MD I have no real or apparent conflicts of interest to report.
DISCLOSURES Ramon Quesada, MD I have no real or apparent conflicts of interest to report.
 Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest Within the past 12 months, I or my spouse/partner have had a financial interest/arrangement or affiliation with the organization(s) listed below. Affiliation/Financial Relationship Grant/Research Support Consulting Fees/Honoraria Company None Abbott, Cordis, St. Jude, W. L. Gore, NMT Medical, Terumo & Boston Scientific Corporation Major Stock Shareholder/Equity None Royalty Income None Ownership/Founder None Intellectual Property Rights None Other Financial Benefit None
Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest Within the past 12 months, I or my spouse/partner have had a financial interest/arrangement or affiliation with the organization(s) listed below. Affiliation/Financial Relationship Grant/Research Support Consulting Fees/Honoraria Company None Abbott, Cordis, St. Jude, W. L. Gore, NMT Medical, Terumo & Boston Scientific Corporation Major Stock Shareholder/Equity None Royalty Income None Ownership/Founder None Intellectual Property Rights None Other Financial Benefit None
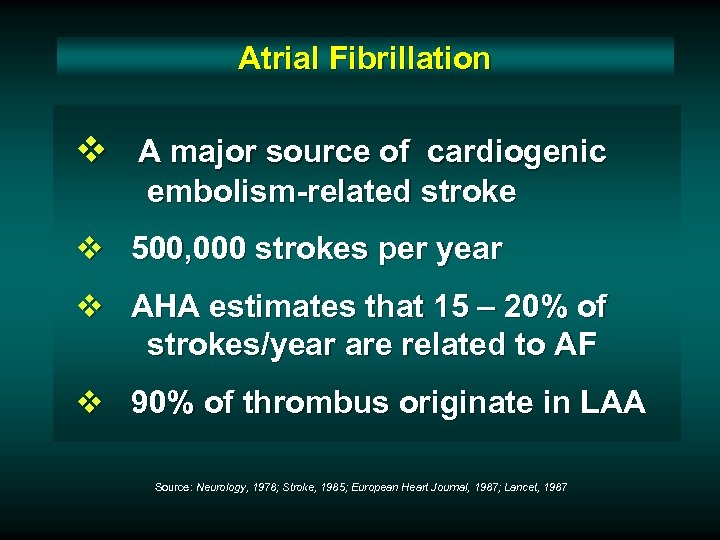 Atrial Fibrillation v A major source of cardiogenic embolism-related stroke v 500, 000 strokes per year v AHA estimates that 15 – 20% of strokes/year are related to AF v 90% of thrombus originate in LAA Source: Neurology, 1978; Stroke, 1985; European Heart Journal, 1987; Lancet, 1987
Atrial Fibrillation v A major source of cardiogenic embolism-related stroke v 500, 000 strokes per year v AHA estimates that 15 – 20% of strokes/year are related to AF v 90% of thrombus originate in LAA Source: Neurology, 1978; Stroke, 1985; European Heart Journal, 1987; Lancet, 1987
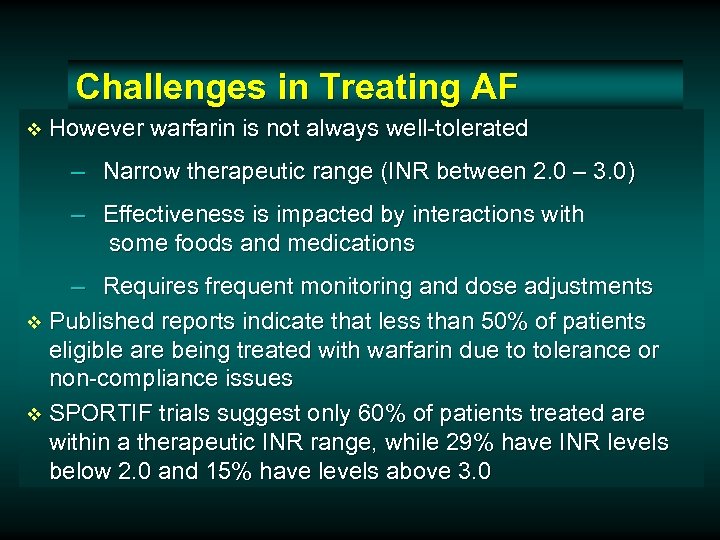 Challenges in Treating AF v However warfarin is not always well-tolerated – Narrow therapeutic range (INR between 2. 0 – 3. 0) – Effectiveness is impacted by interactions with some foods and medications – Requires frequent monitoring and dose adjustments v Published reports indicate that less than 50% of patients eligible are being treated with warfarin due to tolerance or non-compliance issues v SPORTIF trials suggest only 60% of patients treated are within a therapeutic INR range, while 29% have INR levels below 2. 0 and 15% have levels above 3. 0
Challenges in Treating AF v However warfarin is not always well-tolerated – Narrow therapeutic range (INR between 2. 0 – 3. 0) – Effectiveness is impacted by interactions with some foods and medications – Requires frequent monitoring and dose adjustments v Published reports indicate that less than 50% of patients eligible are being treated with warfarin due to tolerance or non-compliance issues v SPORTIF trials suggest only 60% of patients treated are within a therapeutic INR range, while 29% have INR levels below 2. 0 and 15% have levels above 3. 0
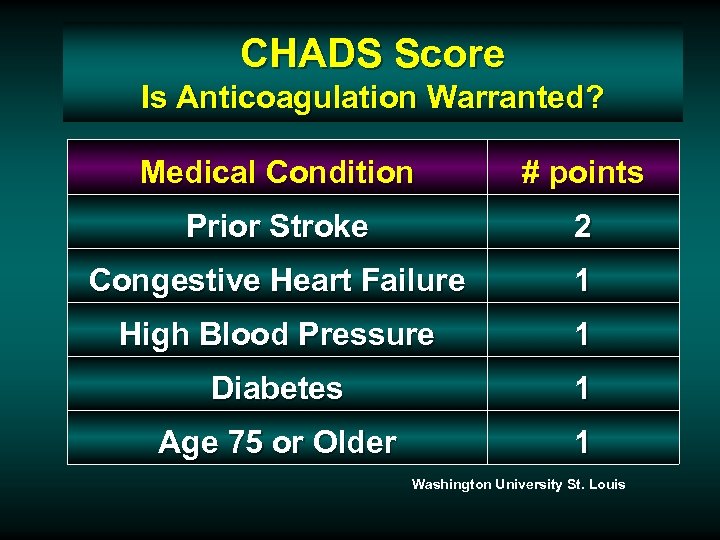 CHADS Score Is Anticoagulation Warranted? Medical Condition # points Prior Stroke 2 Congestive Heart Failure 1 High Blood Pressure 1 Diabetes 1 Age 75 or Older 1 Washington University St. Louis
CHADS Score Is Anticoagulation Warranted? Medical Condition # points Prior Stroke 2 Congestive Heart Failure 1 High Blood Pressure 1 Diabetes 1 Age 75 or Older 1 Washington University St. Louis
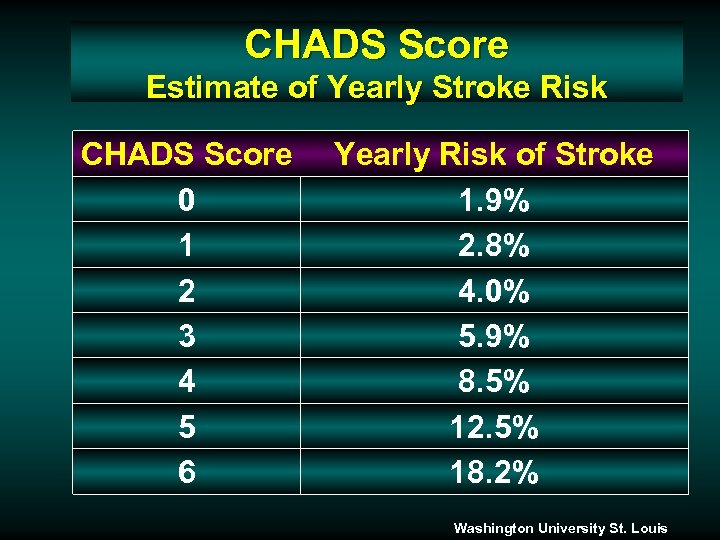 CHADS Score Estimate of Yearly Stroke Risk CHADS Score 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Yearly Risk of Stroke 1. 9% 2. 8% 4. 0% 5. 9% 8. 5% 12. 5% 18. 2% Washington University St. Louis
CHADS Score Estimate of Yearly Stroke Risk CHADS Score 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Yearly Risk of Stroke 1. 9% 2. 8% 4. 0% 5. 9% 8. 5% 12. 5% 18. 2% Washington University St. Louis
 An Alternative to Medical Therapy: Surgical Closure of Left Atrial Appendage as a Source of Emboli
An Alternative to Medical Therapy: Surgical Closure of Left Atrial Appendage as a Source of Emboli
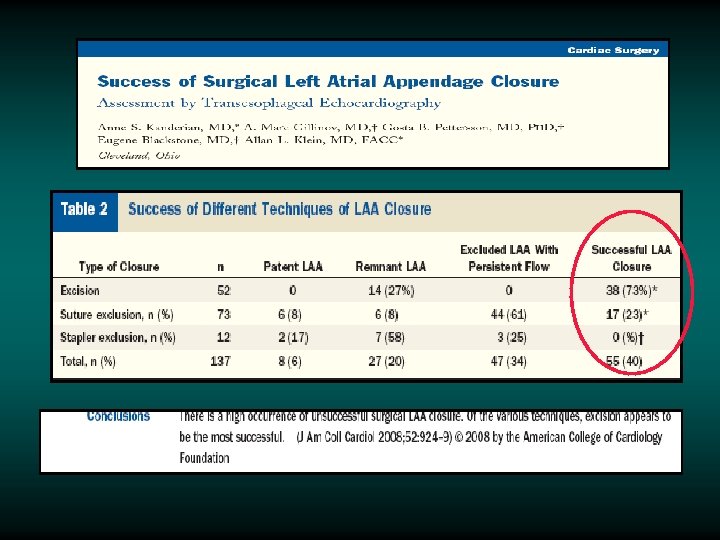
 An Alternative to Medical Therapy: Mechanical Closure of Left Atrial Appendage as a Source of Emboli
An Alternative to Medical Therapy: Mechanical Closure of Left Atrial Appendage as a Source of Emboli
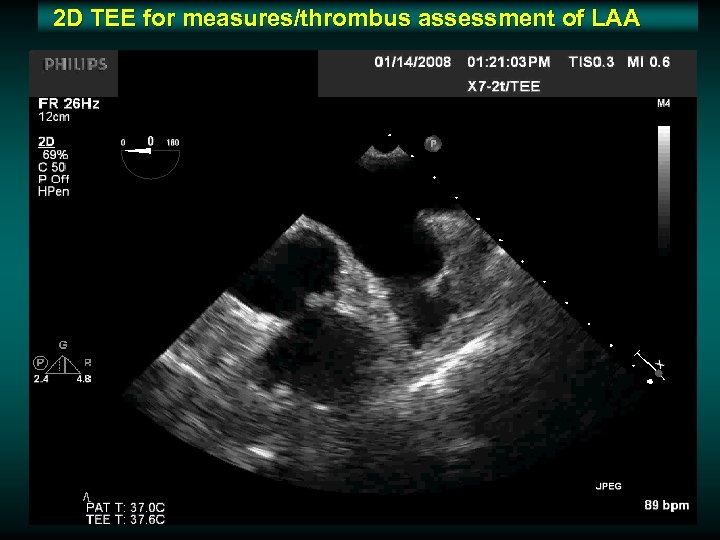 2 D TEE for measures/thrombus assessment of LAA
2 D TEE for measures/thrombus assessment of LAA
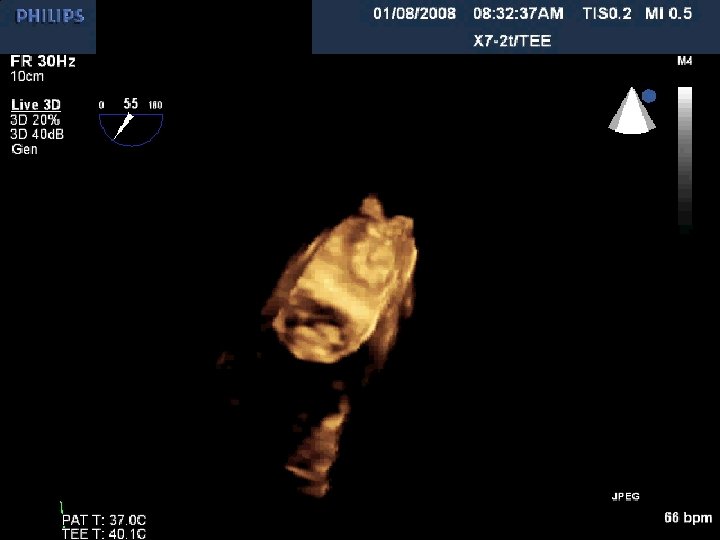
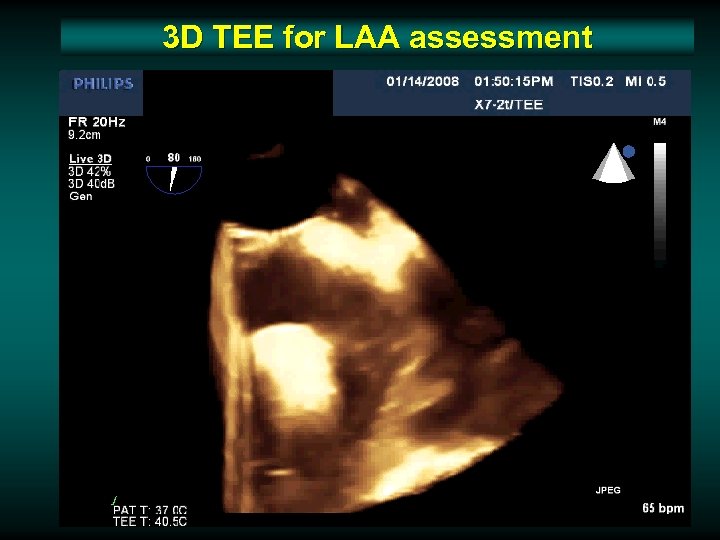 3 D TEE for LAA assessment
3 D TEE for LAA assessment
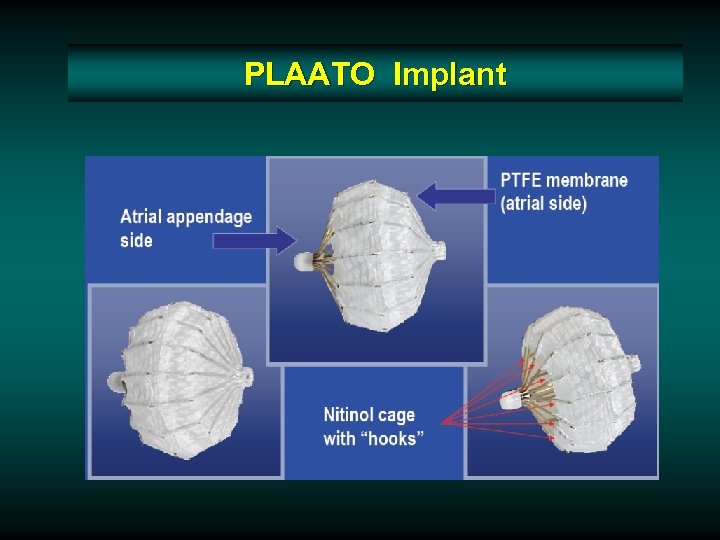 PLAATO Implant
PLAATO Implant
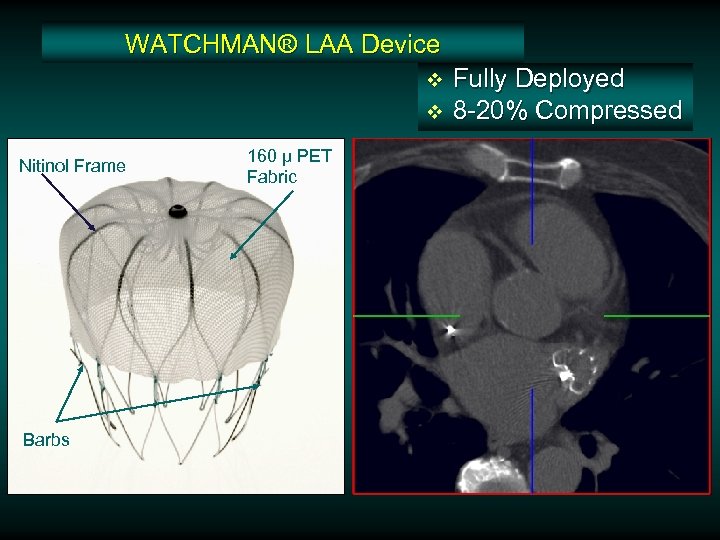 WATCHMAN® LAA Device v v Nitinol Frame Barbs 160 µ PET Fabric Fully Deployed 8 -20% Compressed
WATCHMAN® LAA Device v v Nitinol Frame Barbs 160 µ PET Fabric Fully Deployed 8 -20% Compressed
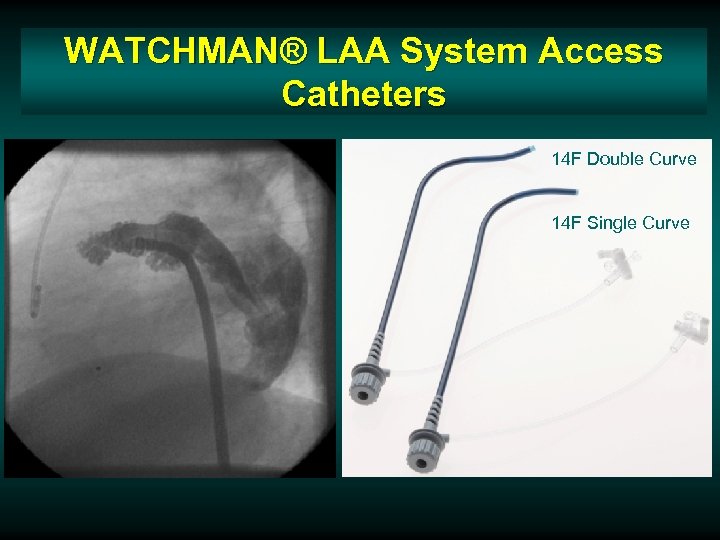 WATCHMAN® LAA System Access Catheters 14 F Double Curve 14 F Single Curve
WATCHMAN® LAA System Access Catheters 14 F Double Curve 14 F Single Curve
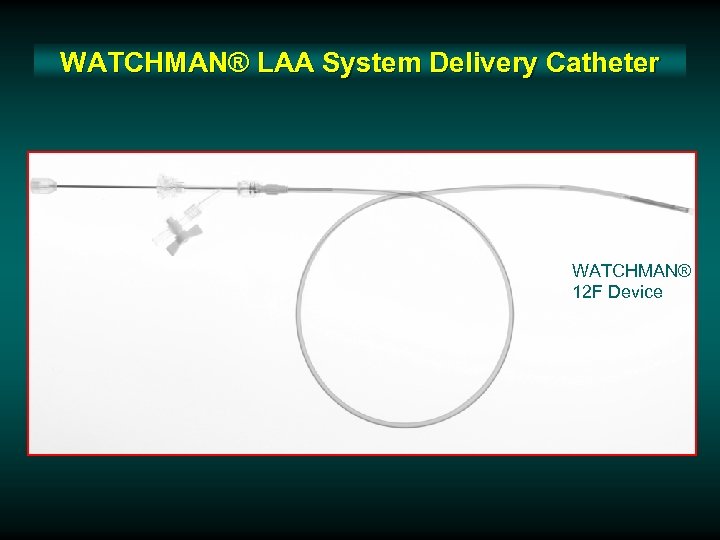 WATCHMAN® LAA System Delivery Catheter WATCHMAN® 12 F Device
WATCHMAN® LAA System Delivery Catheter WATCHMAN® 12 F Device
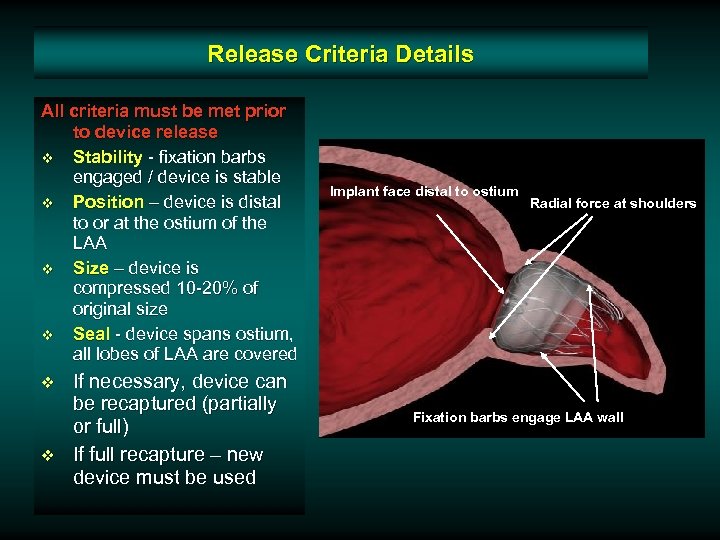 Release Criteria Details All criteria must be met prior to device release v Stability - fixation barbs engaged / device is stable v Position – device is distal to or at the ostium of the LAA v Size – device is compressed 10 -20% of original size v Seal - device spans ostium, all lobes of LAA are covered v v If necessary, device can be recaptured (partially or full) If full recapture – new device must be used Implant face distal to ostium Radial force at shoulders Fixation barbs engage LAA wall
Release Criteria Details All criteria must be met prior to device release v Stability - fixation barbs engaged / device is stable v Position – device is distal to or at the ostium of the LAA v Size – device is compressed 10 -20% of original size v Seal - device spans ostium, all lobes of LAA are covered v v If necessary, device can be recaptured (partially or full) If full recapture – new device must be used Implant face distal to ostium Radial force at shoulders Fixation barbs engage LAA wall
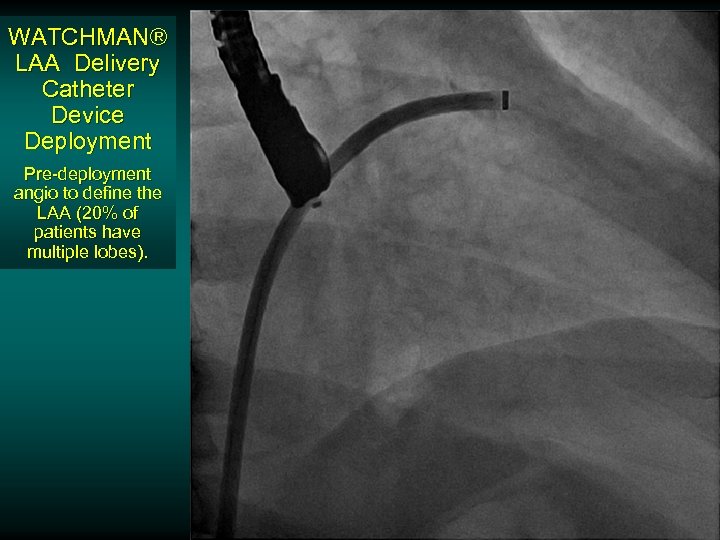 WATCHMAN® LAA Delivery Catheter Device Deployment Pre-deployment angio to define the LAA (20% of patients have multiple lobes).
WATCHMAN® LAA Delivery Catheter Device Deployment Pre-deployment angio to define the LAA (20% of patients have multiple lobes).
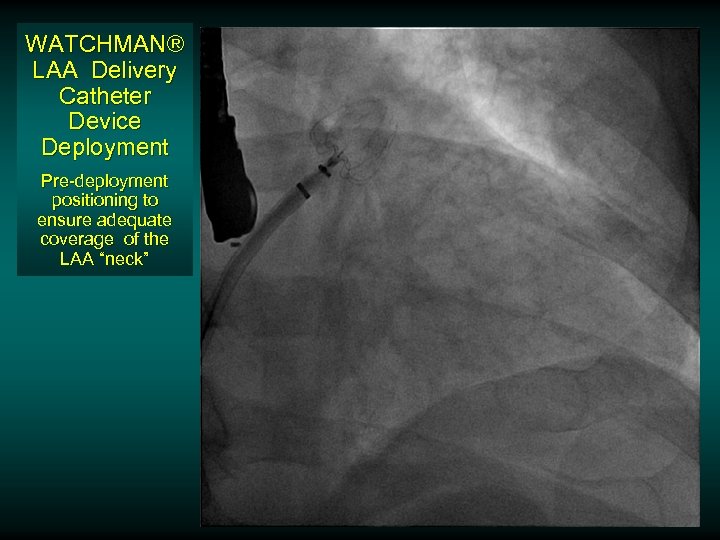 WATCHMAN® LAA Delivery Catheter Device Deployment Pre-deployment positioning to ensure adequate coverage of the LAA “neck”
WATCHMAN® LAA Delivery Catheter Device Deployment Pre-deployment positioning to ensure adequate coverage of the LAA “neck”
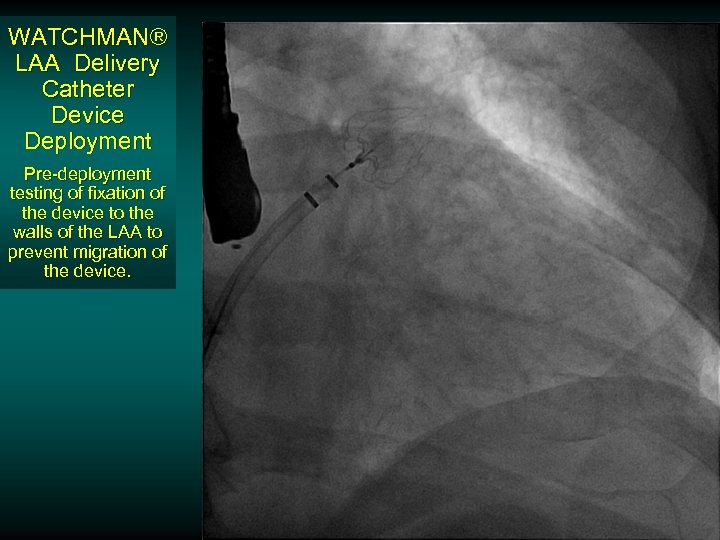 WATCHMAN® LAA Delivery Catheter Device Deployment Pre-deployment testing of fixation of the device to the walls of the LAA to prevent migration of the device.
WATCHMAN® LAA Delivery Catheter Device Deployment Pre-deployment testing of fixation of the device to the walls of the LAA to prevent migration of the device.
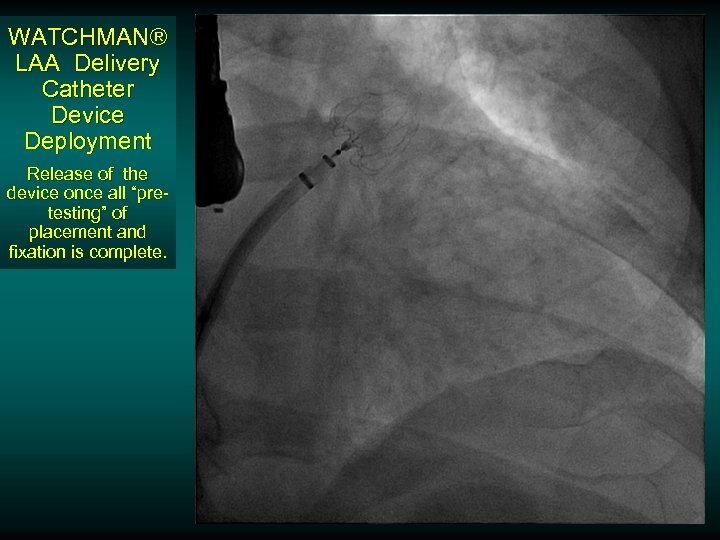 WATCHMAN® LAA Delivery Catheter Device Deployment Release of the device once all “pretesting” of placement and fixation is complete.
WATCHMAN® LAA Delivery Catheter Device Deployment Release of the device once all “pretesting” of placement and fixation is complete.
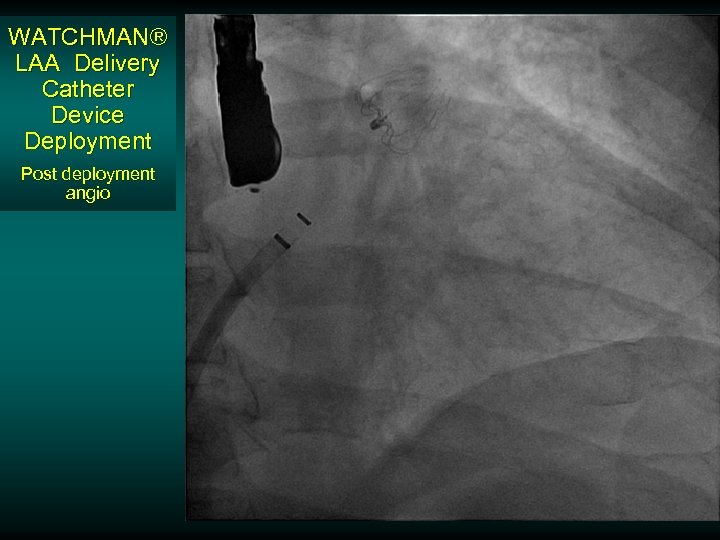 WATCHMAN® LAA Delivery Catheter Device Deployment Post deployment angio
WATCHMAN® LAA Delivery Catheter Device Deployment Post deployment angio
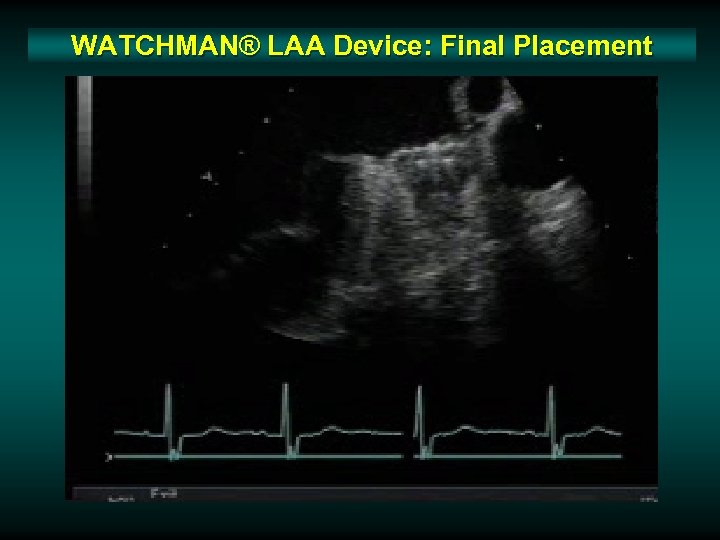 WATCHMAN® LAA Device: Final Placement
WATCHMAN® LAA Device: Final Placement
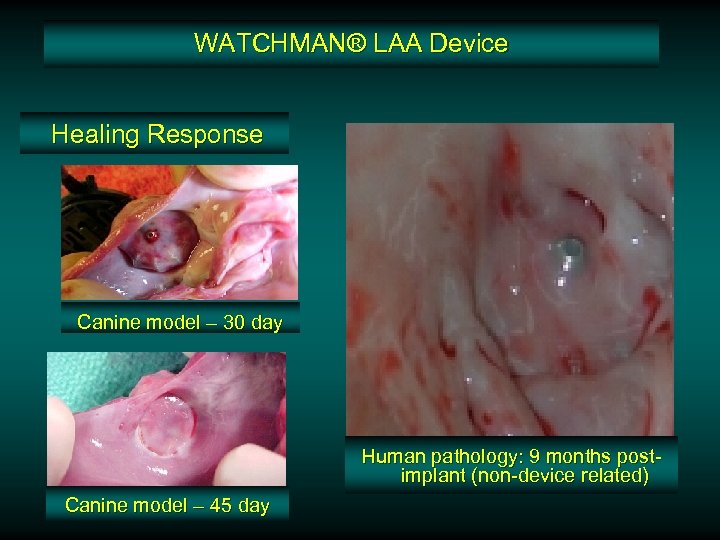 WATCHMAN® LAA Device Healing Response Canine model – 30 day Human pathology: 9 months postimplant (non-device related) Canine model – 45 day
WATCHMAN® LAA Device Healing Response Canine model – 30 day Human pathology: 9 months postimplant (non-device related) Canine model – 45 day
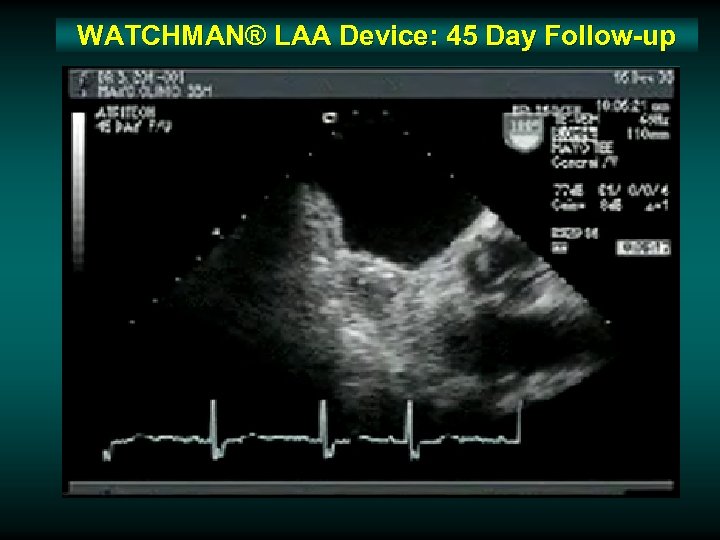 WATCHMAN® LAA Device: 45 Day Follow-up
WATCHMAN® LAA Device: 45 Day Follow-up
 v v v 66 pts. underwent device implantation. Mean follow-up was 740 ± 341 days. – ACC 2009: Duration of f/u now out to 5 years (mean >1300 days) At 45 days, 93% (54 of 58) devices showed successful sealing of LAA No strokes occurred during follow-up despite 90% of patients with discontinuation of anticoagulation. The expected annual risk of stroke based on the CHADS 2 score in this study cohort was calculated to be 1. 9/year. Sick, J Am Coll Cardiol 2007; 49: 1490– 5
v v v 66 pts. underwent device implantation. Mean follow-up was 740 ± 341 days. – ACC 2009: Duration of f/u now out to 5 years (mean >1300 days) At 45 days, 93% (54 of 58) devices showed successful sealing of LAA No strokes occurred during follow-up despite 90% of patients with discontinuation of anticoagulation. The expected annual risk of stroke based on the CHADS 2 score in this study cohort was calculated to be 1. 9/year. Sick, J Am Coll Cardiol 2007; 49: 1490– 5
 What We’ve Learned From This Pilot Series Appreciation of the variability of the anatomy of the LAA v Use of additional imaging tools v Variability and the fragility of the LAA required modifications to the device v
What We’ve Learned From This Pilot Series Appreciation of the variability of the anatomy of the LAA v Use of additional imaging tools v Variability and the fragility of the LAA required modifications to the device v
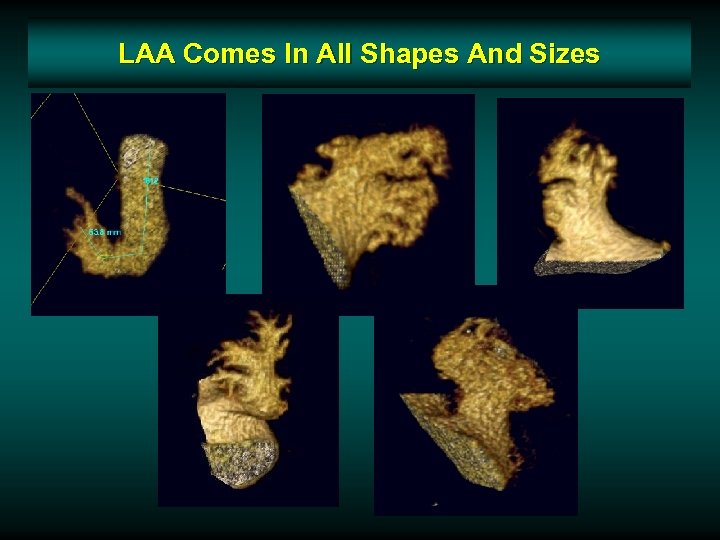 LAA Comes In All Shapes And Sizes
LAA Comes In All Shapes And Sizes
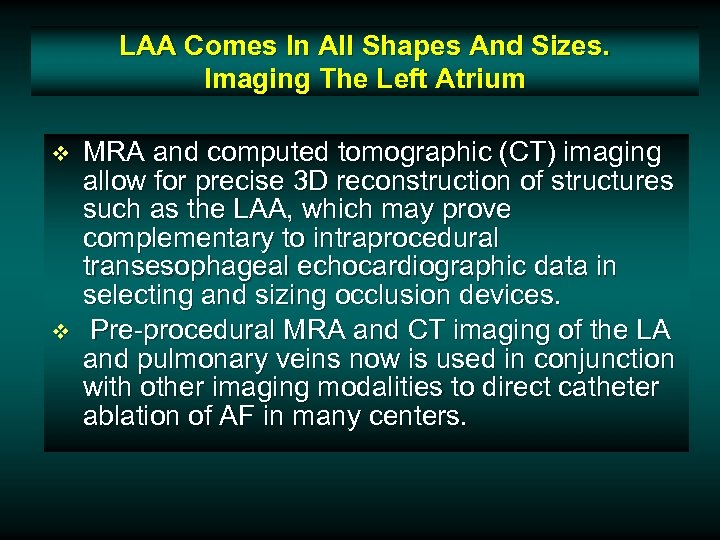 LAA Comes In All Shapes And Sizes. Imaging The Left Atrium v v MRA and computed tomographic (CT) imaging allow for precise 3 D reconstruction of structures such as the LAA, which may prove complementary to intraprocedural transesophageal echocardiographic data in selecting and sizing occlusion devices. Pre-procedural MRA and CT imaging of the LA and pulmonary veins now is used in conjunction with other imaging modalities to direct catheter ablation of AF in many centers.
LAA Comes In All Shapes And Sizes. Imaging The Left Atrium v v MRA and computed tomographic (CT) imaging allow for precise 3 D reconstruction of structures such as the LAA, which may prove complementary to intraprocedural transesophageal echocardiographic data in selecting and sizing occlusion devices. Pre-procedural MRA and CT imaging of the LA and pulmonary veins now is used in conjunction with other imaging modalities to direct catheter ablation of AF in many centers.
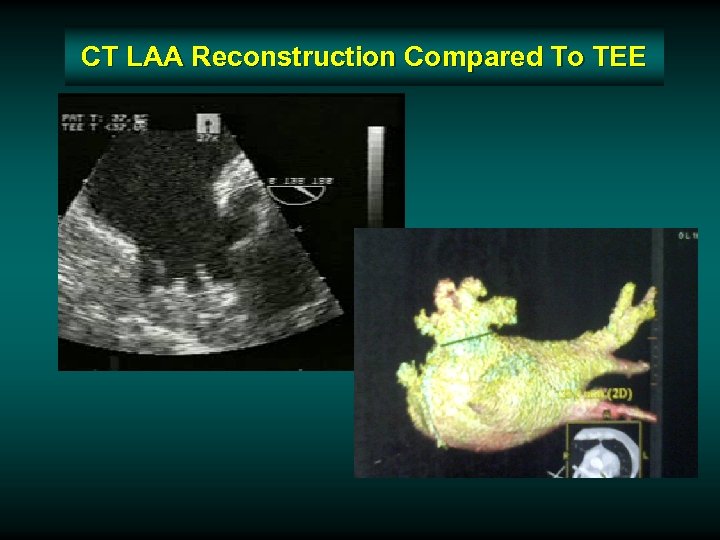 CT LAA Reconstruction Compared To TEE
CT LAA Reconstruction Compared To TEE
 Improvements in Device Technology Shorter length device v Modification in the delivery sheath with markers and a softer tip v
Improvements in Device Technology Shorter length device v Modification in the delivery sheath with markers and a softer tip v
 Improvements in Device Technology Shorter length device v Modification in the delivery sheath with markers and a softer tip v
Improvements in Device Technology Shorter length device v Modification in the delivery sheath with markers and a softer tip v
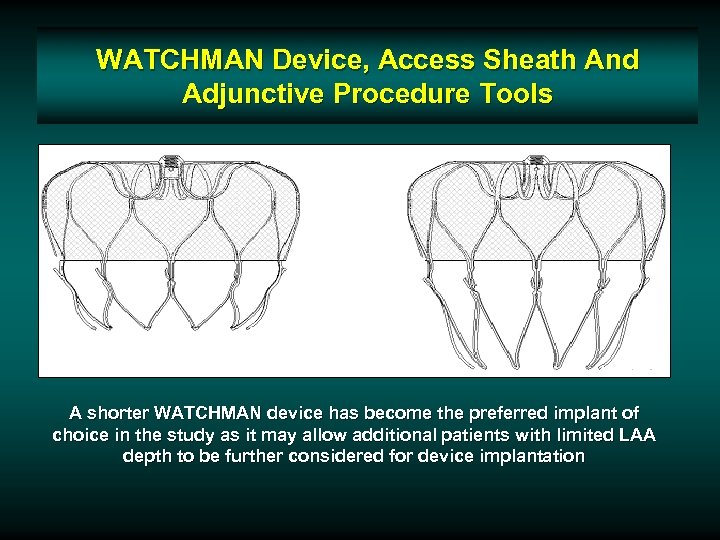 WATCHMAN Device, Access Sheath And Adjunctive Procedure Tools A shorter WATCHMAN device has become the preferred implant of choice in the study as it may allow additional patients with limited LAA depth to be further considered for device implantation
WATCHMAN Device, Access Sheath And Adjunctive Procedure Tools A shorter WATCHMAN device has become the preferred implant of choice in the study as it may allow additional patients with limited LAA depth to be further considered for device implantation
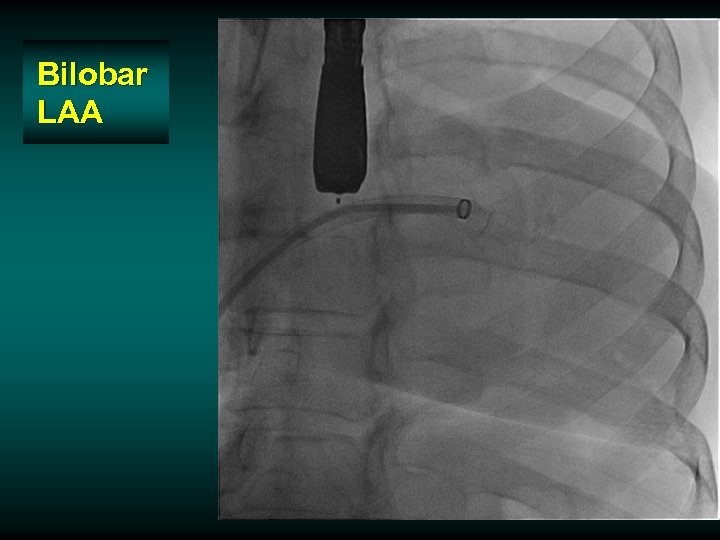 Bilobar LAA
Bilobar LAA
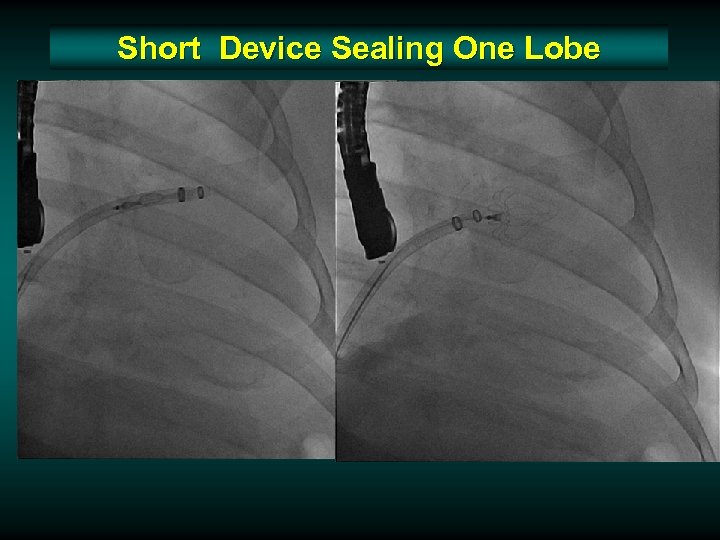 Short Device Sealing One Lobe
Short Device Sealing One Lobe
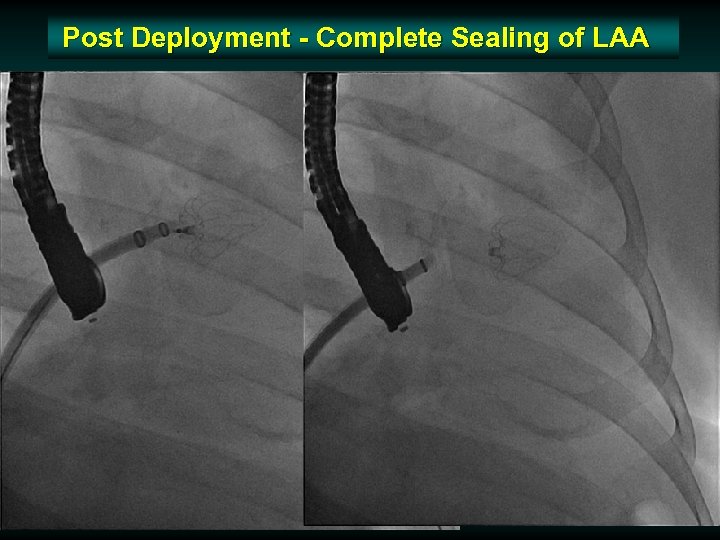 Post Deployment - Complete Sealing of LAA
Post Deployment - Complete Sealing of LAA
 Improvements in Device Technology Shorter length device v Modification in the delivery sheath with markers and a softer tip v
Improvements in Device Technology Shorter length device v Modification in the delivery sheath with markers and a softer tip v
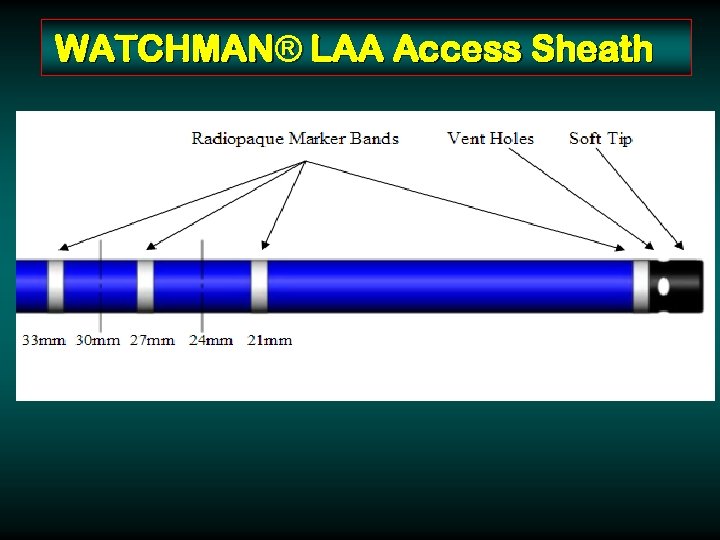 WATCHMAN® LAA Access Sheath 14 F Double Curve 14 F Single Curve
WATCHMAN® LAA Access Sheath 14 F Double Curve 14 F Single Curve
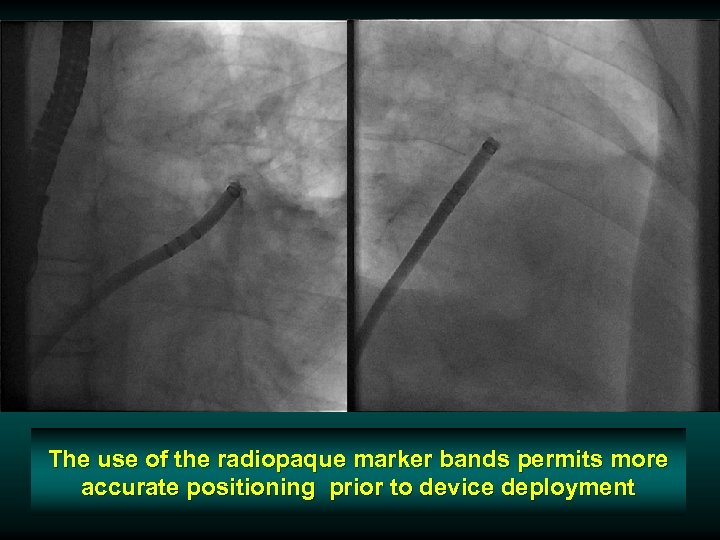 The use of the radiopaque marker bands permits more accurate positioning prior to device deployment
The use of the radiopaque marker bands permits more accurate positioning prior to device deployment
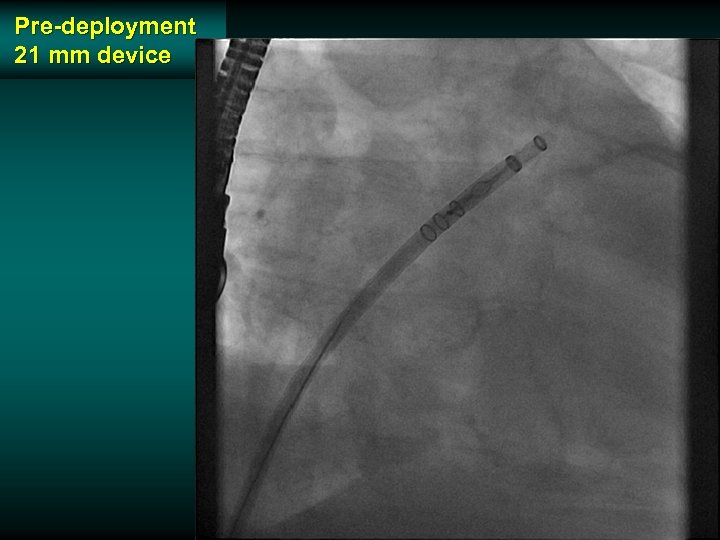 Pre-deployment 21 mm device
Pre-deployment 21 mm device
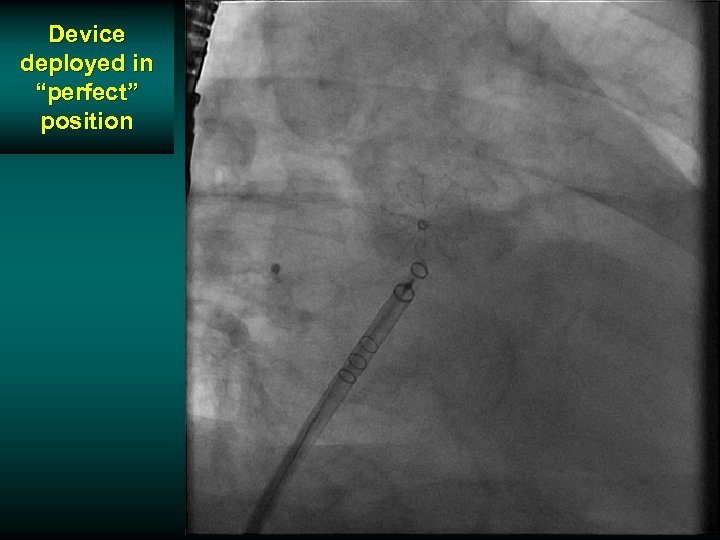 Device deployed in “perfect” position
Device deployed in “perfect” position
 PROTECT AF Clinical Trial Design v v v Prospective, randomized study of WATCHMAN LAA Device vs. Longterm Warfarin Therapy 2: 1 allocation ratio device to control 800 Patients enrolled from Feb 2005 to Jun 2008 – Device Group (463) – Control Group (244) v v – Roll-in Group (93) 59 Enrolling Centers (U. S. & Europe) Follow-up Requirements – TEE follow-up at 45 days, 6 months and 1 year – Clinical follow-up biannually up to 5 years v – Regular INR monitoring while taking warfarin Enrollment continues in Continued Access Registry
PROTECT AF Clinical Trial Design v v v Prospective, randomized study of WATCHMAN LAA Device vs. Longterm Warfarin Therapy 2: 1 allocation ratio device to control 800 Patients enrolled from Feb 2005 to Jun 2008 – Device Group (463) – Control Group (244) v v – Roll-in Group (93) 59 Enrolling Centers (U. S. & Europe) Follow-up Requirements – TEE follow-up at 45 days, 6 months and 1 year – Clinical follow-up biannually up to 5 years v – Regular INR monitoring while taking warfarin Enrollment continues in Continued Access Registry
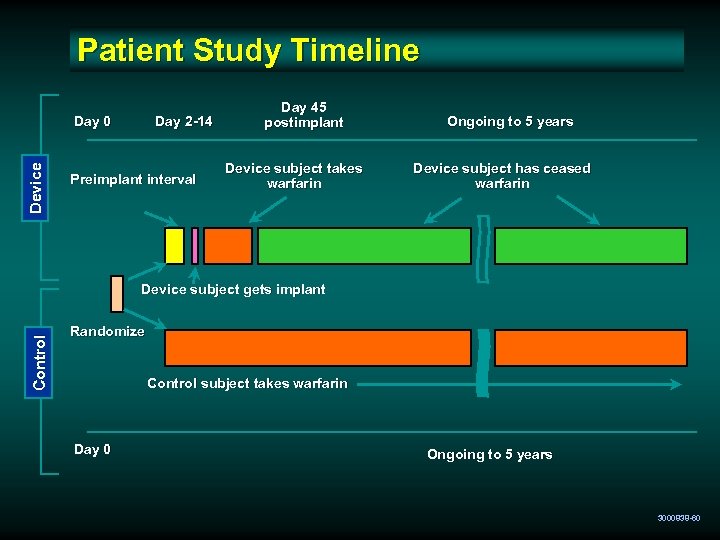 Patient Study Timeline Device Day 0 Day 2 -14 Preimplant interval Day 45 postimplant Device subject takes warfarin Ongoing to 5 years Device subject has ceased warfarin Control Device subject gets implant Randomize Control subject takes warfarin Day 0 Ongoing to 5 years 3000838 -60
Patient Study Timeline Device Day 0 Day 2 -14 Preimplant interval Day 45 postimplant Device subject takes warfarin Ongoing to 5 years Device subject has ceased warfarin Control Device subject gets implant Randomize Control subject takes warfarin Day 0 Ongoing to 5 years 3000838 -60
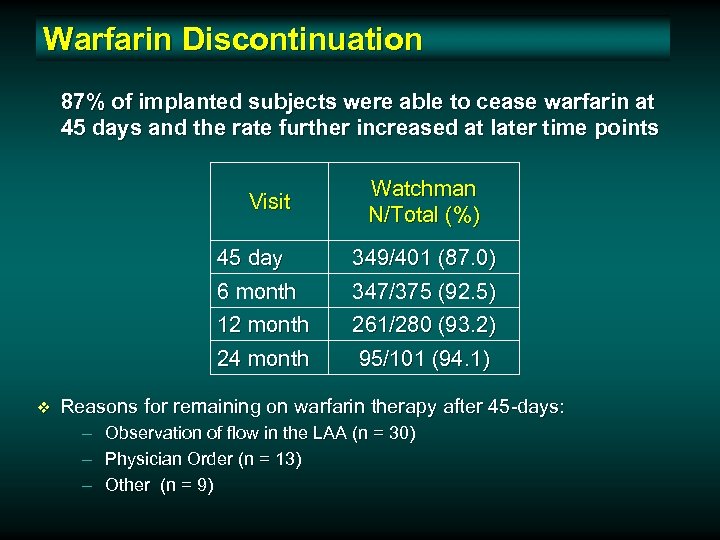 Warfarin Discontinuation 87% of implanted subjects were able to cease warfarin at 45 days and the rate further increased at later time points Visit Watchman N/Total (%) 45 day 6 month 12 month 24 month v 349/401 (87. 0) 347/375 (92. 5) 261/280 (93. 2) 95/101 (94. 1) Reasons for remaining on warfarin therapy after 45 -days: – – – Observation of flow in the LAA (n = 30) Physician Order (n = 13) Other (n = 9)
Warfarin Discontinuation 87% of implanted subjects were able to cease warfarin at 45 days and the rate further increased at later time points Visit Watchman N/Total (%) 45 day 6 month 12 month 24 month v 349/401 (87. 0) 347/375 (92. 5) 261/280 (93. 2) 95/101 (94. 1) Reasons for remaining on warfarin therapy after 45 -days: – – – Observation of flow in the LAA (n = 30) Physician Order (n = 13) Other (n = 9)
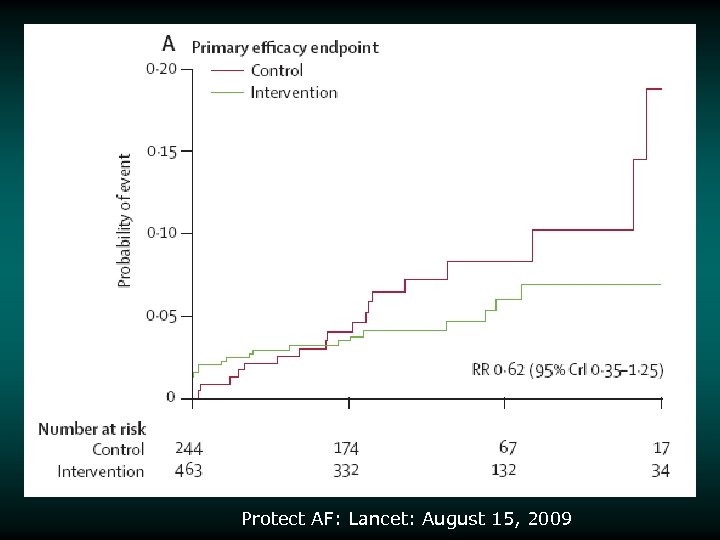
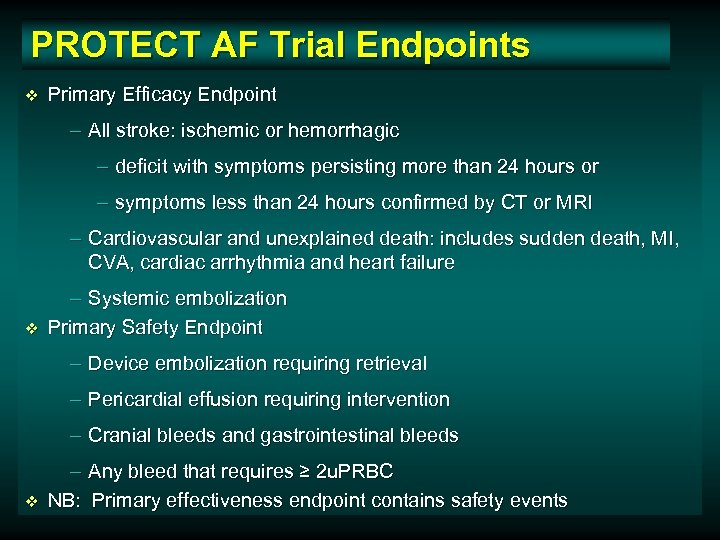 PROTECT AF Trial Endpoints v Primary Efficacy Endpoint – All stroke: ischemic or hemorrhagic – deficit with symptoms persisting more than 24 hours or – symptoms less than 24 hours confirmed by CT or MRI – Cardiovascular and unexplained death: includes sudden death, MI, CVA, cardiac arrhythmia and heart failure v – Systemic embolization Primary Safety Endpoint – Device embolization requiring retrieval – Pericardial effusion requiring intervention – Cranial bleeds and gastrointestinal bleeds v – Any bleed that requires ≥ 2 u. PRBC NB: Primary effectiveness endpoint contains safety events
PROTECT AF Trial Endpoints v Primary Efficacy Endpoint – All stroke: ischemic or hemorrhagic – deficit with symptoms persisting more than 24 hours or – symptoms less than 24 hours confirmed by CT or MRI – Cardiovascular and unexplained death: includes sudden death, MI, CVA, cardiac arrhythmia and heart failure v – Systemic embolization Primary Safety Endpoint – Device embolization requiring retrieval – Pericardial effusion requiring intervention – Cranial bleeds and gastrointestinal bleeds v – Any bleed that requires ≥ 2 u. PRBC NB: Primary effectiveness endpoint contains safety events
 Key Participation Criteria v v Key Inclusion Criteria – Age 18 years or older – Documented non-valvular AF – Eligible for long-term warfarin therapy, and no other conditions that would require long-term warfarin therapy – Calculated CHADS 2 score > 1 Key Exclusion Criteria – NYHA Class IV Congestive Heart Failure – ASD and/or atrial septal repair or closure device – Planned ablation procedure within 30 days of potential WATCHMAN Device implant – Symptomatic carotid disease – LVEF < 30% – TEE Criteria: Suspected or known intracardiac thrombus (dense spontaneous echo contract)
Key Participation Criteria v v Key Inclusion Criteria – Age 18 years or older – Documented non-valvular AF – Eligible for long-term warfarin therapy, and no other conditions that would require long-term warfarin therapy – Calculated CHADS 2 score > 1 Key Exclusion Criteria – NYHA Class IV Congestive Heart Failure – ASD and/or atrial septal repair or closure device – Planned ablation procedure within 30 days of potential WATCHMAN Device implant – Symptomatic carotid disease – LVEF < 30% – TEE Criteria: Suspected or known intracardiac thrombus (dense spontaneous echo contract)
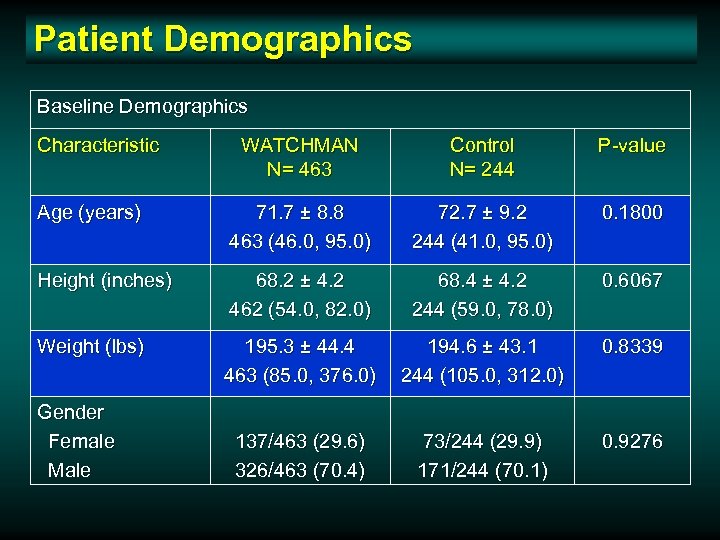 Patient Demographics Baseline Demographics Characteristic WATCHMAN N= 463 Control N= 244 P-value Age (years) 71. 7 ± 8. 8 463 (46. 0, 95. 0) 72. 7 ± 9. 2 244 (41. 0, 95. 0) 0. 1800 Height (inches) 68. 2 ± 4. 2 462 (54. 0, 82. 0) 68. 4 ± 4. 2 244 (59. 0, 78. 0) 0. 6067 Weight (lbs) 195. 3 ± 44. 4 463 (85. 0, 376. 0) 194. 6 ± 43. 1 244 (105. 0, 312. 0) 0. 8339 137/463 (29. 6) 326/463 (70. 4) 73/244 (29. 9) 171/244 (70. 1) 0. 9276 Gender Female Male
Patient Demographics Baseline Demographics Characteristic WATCHMAN N= 463 Control N= 244 P-value Age (years) 71. 7 ± 8. 8 463 (46. 0, 95. 0) 72. 7 ± 9. 2 244 (41. 0, 95. 0) 0. 1800 Height (inches) 68. 2 ± 4. 2 462 (54. 0, 82. 0) 68. 4 ± 4. 2 244 (59. 0, 78. 0) 0. 6067 Weight (lbs) 195. 3 ± 44. 4 463 (85. 0, 376. 0) 194. 6 ± 43. 1 244 (105. 0, 312. 0) 0. 8339 137/463 (29. 6) 326/463 (70. 4) 73/244 (29. 9) 171/244 (70. 1) 0. 9276 Gender Female Male
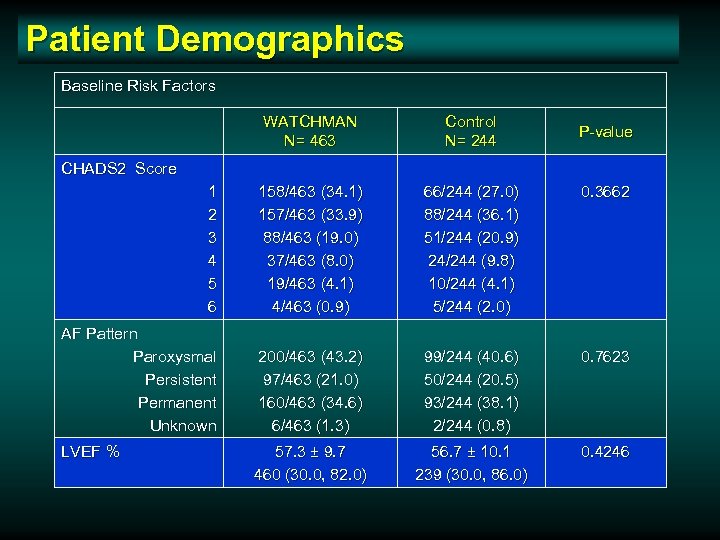 Patient Demographics Baseline Risk Factors WATCHMAN N= 463 Control N= 244 1 2 3 4 5 6 158/463 (34. 1) 157/463 (33. 9) 88/463 (19. 0) 37/463 (8. 0) 19/463 (4. 1) 4/463 (0. 9) 66/244 (27. 0) 88/244 (36. 1) 51/244 (20. 9) 24/244 (9. 8) 10/244 (4. 1) 5/244 (2. 0) 0. 3662 AF Pattern Paroxysmal Persistent Permanent Unknown 200/463 (43. 2) 97/463 (21. 0) 160/463 (34. 6) 6/463 (1. 3) 99/244 (40. 6) 50/244 (20. 5) 93/244 (38. 1) 2/244 (0. 8) 0. 7623 57. 3 ± 9. 7 460 (30. 0, 82. 0) 56. 7 ± 10. 1 239 (30. 0, 86. 0) 0. 4246 P-value CHADS 2 Score LVEF %
Patient Demographics Baseline Risk Factors WATCHMAN N= 463 Control N= 244 1 2 3 4 5 6 158/463 (34. 1) 157/463 (33. 9) 88/463 (19. 0) 37/463 (8. 0) 19/463 (4. 1) 4/463 (0. 9) 66/244 (27. 0) 88/244 (36. 1) 51/244 (20. 9) 24/244 (9. 8) 10/244 (4. 1) 5/244 (2. 0) 0. 3662 AF Pattern Paroxysmal Persistent Permanent Unknown 200/463 (43. 2) 97/463 (21. 0) 160/463 (34. 6) 6/463 (1. 3) 99/244 (40. 6) 50/244 (20. 5) 93/244 (38. 1) 2/244 (0. 8) 0. 7623 57. 3 ± 9. 7 460 (30. 0, 82. 0) 56. 7 ± 10. 1 239 (30. 0, 86. 0) 0. 4246 P-value CHADS 2 Score LVEF %
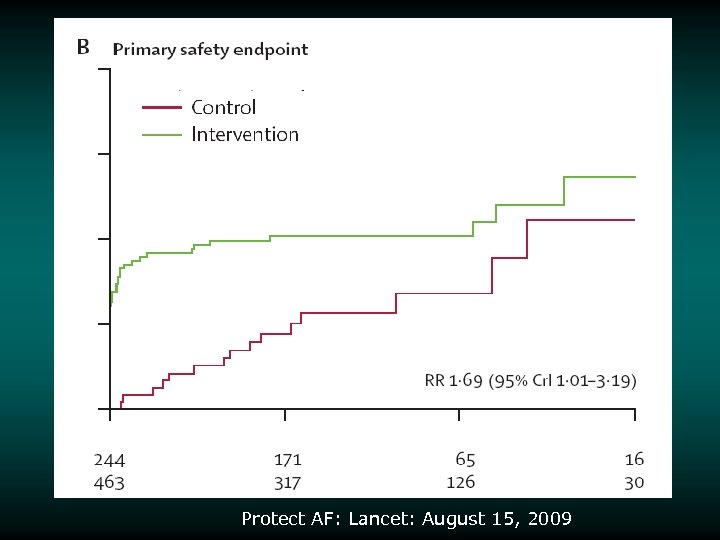
 Potential Safety Endpoints Device v Procedural complications – Pericardial effusion – Stroke – ischemic v Bleeding during 45 days of Warfarin
Potential Safety Endpoints Device v Procedural complications – Pericardial effusion – Stroke – ischemic v Bleeding during 45 days of Warfarin
 Protect AF: Lancet: August 15, 2009
Protect AF: Lancet: August 15, 2009
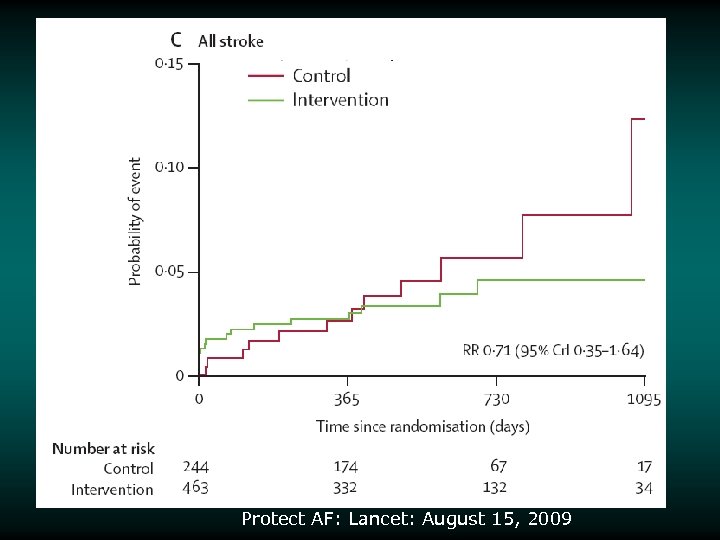
 Safety Events Stroke v Safety stroke events v Also counted as efficacy events in efficacy analyses v 5 events in device group classified as “ischemic stroke” – All periprocedural: extended hospitalization by 7 days – 3 were related to air embolism v 1 hemorrhagic stroke in device group vs 6 in control group – Device event occurred 15 days post implant while patient was on warfarin – 4/6 stroke events in control group patients resulted in death 3000838 -65
Safety Events Stroke v Safety stroke events v Also counted as efficacy events in efficacy analyses v 5 events in device group classified as “ischemic stroke” – All periprocedural: extended hospitalization by 7 days – 3 were related to air embolism v 1 hemorrhagic stroke in device group vs 6 in control group – Device event occurred 15 days post implant while patient was on warfarin – 4/6 stroke events in control group patients resulted in death 3000838 -65
 Protect AF: Lancet: August 15, 2009
Protect AF: Lancet: August 15, 2009
 Protect AF: Lancet: August 15, 2009
Protect AF: Lancet: August 15, 2009
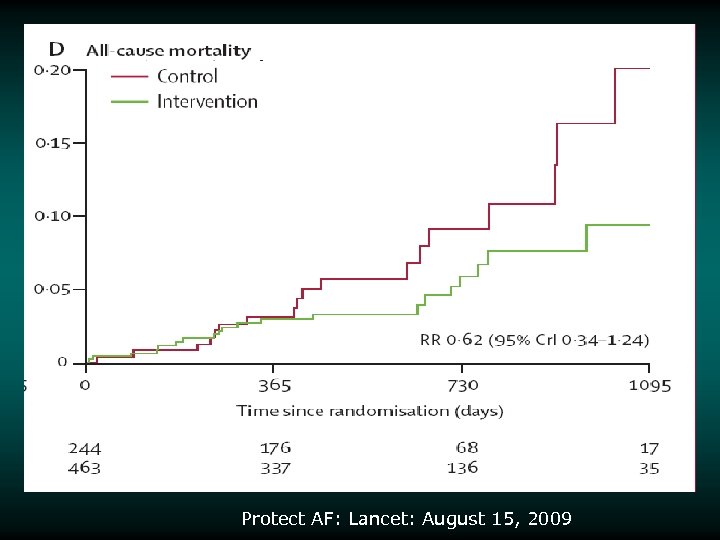 Protect AF: Lancet: August 15, 2009
Protect AF: Lancet: August 15, 2009
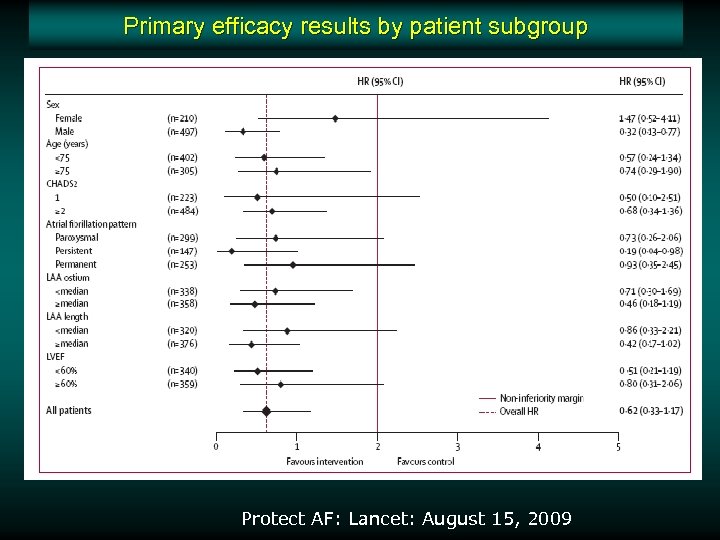 Primary efficacy results by patient subgroup Protect AF: Lancet: August 15, 2009
Primary efficacy results by patient subgroup Protect AF: Lancet: August 15, 2009
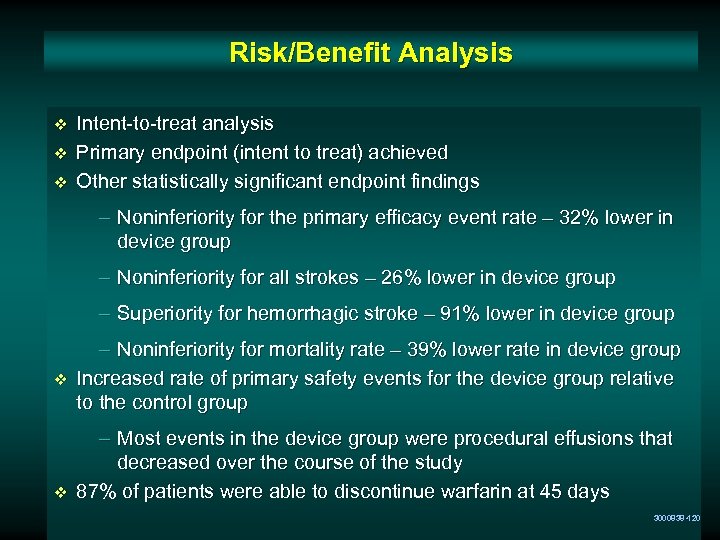 Risk/Benefit Analysis v v v Intent-to-treat analysis Primary endpoint (intent to treat) achieved Other statistically significant endpoint findings – Noninferiority for the primary efficacy event rate – 32% lower in device group – Noninferiority for all strokes – 26% lower in device group – Superiority for hemorrhagic stroke – 91% lower in device group v v – Noninferiority for mortality rate – 39% lower rate in device group Increased rate of primary safety events for the device group relative to the control group – Most events in the device group were procedural effusions that decreased over the course of the study 87% of patients were able to discontinue warfarin at 45 days 3000838 -120
Risk/Benefit Analysis v v v Intent-to-treat analysis Primary endpoint (intent to treat) achieved Other statistically significant endpoint findings – Noninferiority for the primary efficacy event rate – 32% lower in device group – Noninferiority for all strokes – 26% lower in device group – Superiority for hemorrhagic stroke – 91% lower in device group v v – Noninferiority for mortality rate – 39% lower rate in device group Increased rate of primary safety events for the device group relative to the control group – Most events in the device group were procedural effusions that decreased over the course of the study 87% of patients were able to discontinue warfarin at 45 days 3000838 -120
 Conclusion The WATCHMAN LAA Technology offers a safe and effective alternative to warfarin in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation at risk for stroke and who are eligible for warfarin therapy 3000838 -124
Conclusion The WATCHMAN LAA Technology offers a safe and effective alternative to warfarin in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation at risk for stroke and who are eligible for warfarin therapy 3000838 -124
 International Symposium on Endovascular Therapy Save the Date January, 2011 Thank You
International Symposium on Endovascular Therapy Save the Date January, 2011 Thank You


