03e27bd3aa0f2193b2ef0267d41b1923.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Lectures on respiratory physiology Control of Ventilation
Lectures on respiratory physiology Control of Ventilation
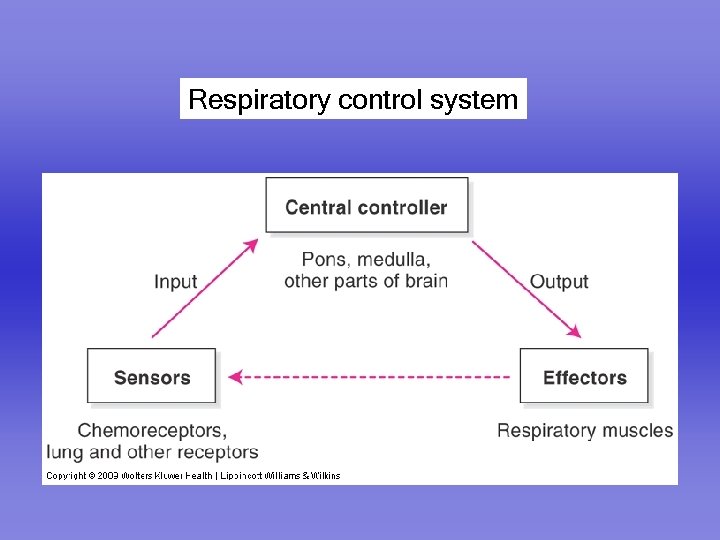 Respiratory control system
Respiratory control system
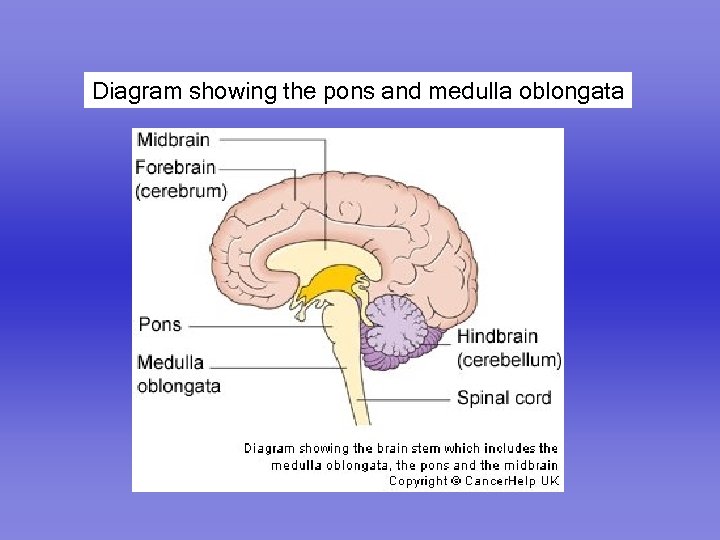 Diagram showing the pons and medulla oblongata
Diagram showing the pons and medulla oblongata
 Rhythm controllers in the brainstem 1) Medulla Dorsal respiratory group – associated with inspiration Ventral respiratory group – associated with expiration. Pre-Botzinger Complex - pattern generator, also ventral 2) Pons Apneustic center – has an excitatory function Pneumotaxic center – can inhibit inspiration
Rhythm controllers in the brainstem 1) Medulla Dorsal respiratory group – associated with inspiration Ventral respiratory group – associated with expiration. Pre-Botzinger Complex - pattern generator, also ventral 2) Pons Apneustic center – has an excitatory function Pneumotaxic center – can inhibit inspiration
 Other regions of the brain that can affect respiration 1) Cortex Can exercise voluntary control 2) Limbic system and hypothalamus Emotional states
Other regions of the brain that can affect respiration 1) Cortex Can exercise voluntary control 2) Limbic system and hypothalamus Emotional states
 Effectors 1) Diaphragm 2) Intercostal muscles 3) Abdominal muscles 4) Accessory muscles
Effectors 1) Diaphragm 2) Intercostal muscles 3) Abdominal muscles 4) Accessory muscles
 Sensors 1) Central chemoreceptor 2) Peripheral chemoreceptors 3) Lung receptors 4) Other receptors
Sensors 1) Central chemoreceptor 2) Peripheral chemoreceptors 3) Lung receptors 4) Other receptors
 Chemoreceptors Specialized tissues that responds to a change in the chemical composition of the blood or other fluid Central chemoreceptor Peripheral chemoreceptors
Chemoreceptors Specialized tissues that responds to a change in the chemical composition of the blood or other fluid Central chemoreceptor Peripheral chemoreceptors
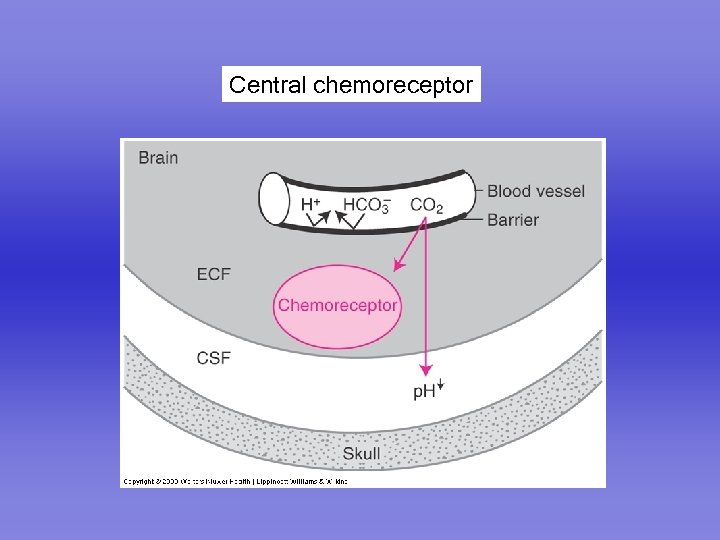 Central chemoreceptor
Central chemoreceptor
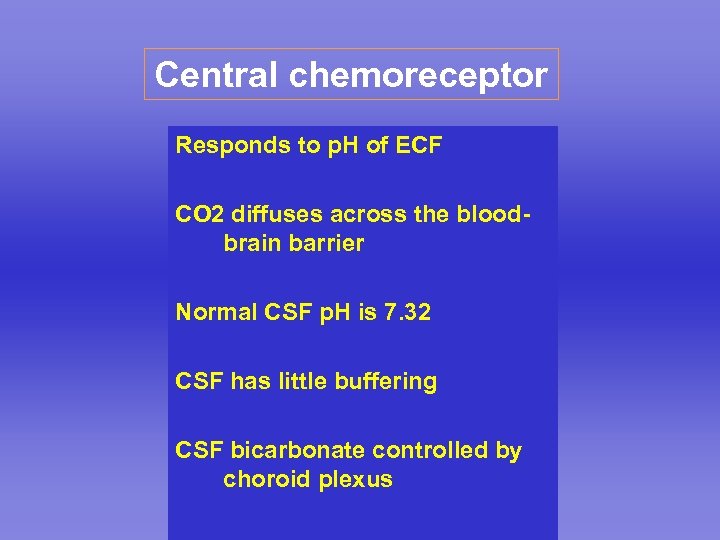 Central chemoreceptor Responds to p. H of ECF CO 2 diffuses across the bloodbrain barrier Normal CSF p. H is 7. 32 CSF has little buffering CSF bicarbonate controlled by choroid plexus
Central chemoreceptor Responds to p. H of ECF CO 2 diffuses across the bloodbrain barrier Normal CSF p. H is 7. 32 CSF has little buffering CSF bicarbonate controlled by choroid plexus
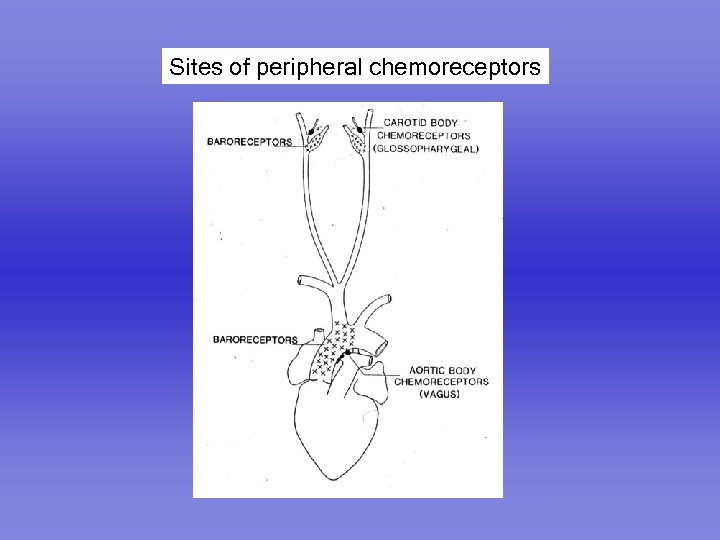 Sites of peripheral chemoreceptors
Sites of peripheral chemoreceptors
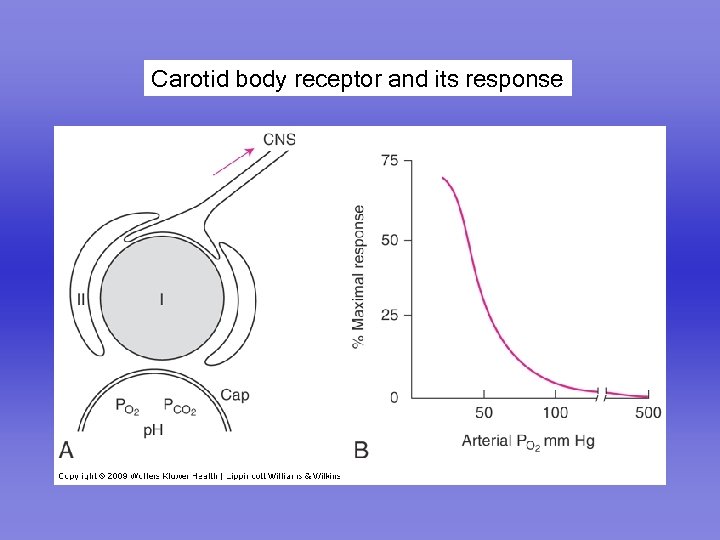 Carotid body receptor and its response
Carotid body receptor and its response
 Carotid bodies Respond to PO 2, PCO 2 and p. H Little response in normoxia Very high blood flow Respond to arterial, not venous PO 2 Fast response
Carotid bodies Respond to PO 2, PCO 2 and p. H Little response in normoxia Very high blood flow Respond to arterial, not venous PO 2 Fast response
 Lung receptors 1) Pulmonary stretch receptors (also called slowly-adapting pulmonary stretch receptors) Responsible for the Hering-Breuer reflex 2) Irritant receptors (also called rapidly-adapting pulmonary stretch receptors) 3) J receptors (juxta-capillary receptors) 4) Bronchial C fibers
Lung receptors 1) Pulmonary stretch receptors (also called slowly-adapting pulmonary stretch receptors) Responsible for the Hering-Breuer reflex 2) Irritant receptors (also called rapidly-adapting pulmonary stretch receptors) 3) J receptors (juxta-capillary receptors) 4) Bronchial C fibers
 Other receptors 1) Nose and upper airway 2) Joint and muscle 3) Gamma system 4) Arterial baroreceptors 5) Pain and temperature
Other receptors 1) Nose and upper airway 2) Joint and muscle 3) Gamma system 4) Arterial baroreceptors 5) Pain and temperature
 Integrated responses 1) Response to increased PCO 2 2) Response to reduced PO 2 3) Response to changes in p. H 4) Response to exercise
Integrated responses 1) Response to increased PCO 2 2) Response to reduced PO 2 3) Response to changes in p. H 4) Response to exercise
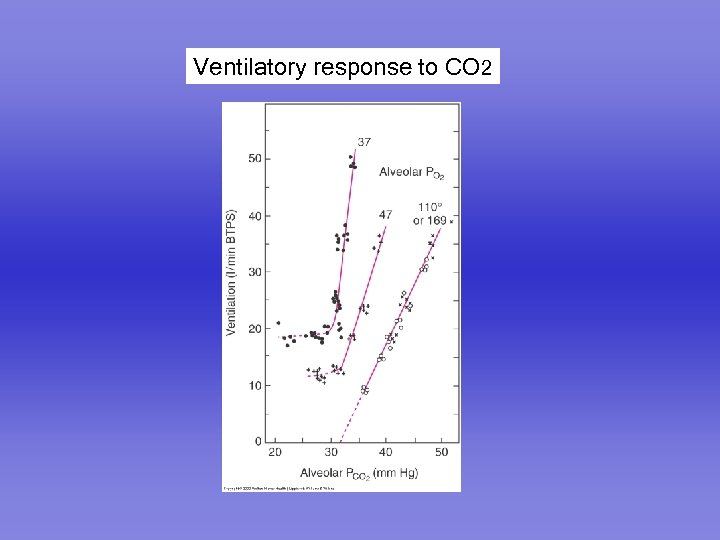 Ventilatory response to CO 2
Ventilatory response to CO 2
 Response to CO 2 Primary factor in the control of ventilation Measured by rebreathing from a bag Inspiratory pressure following brief occlusion Response is altered by sleep, age, genetic factors Reduced by increasing the work of breathing
Response to CO 2 Primary factor in the control of ventilation Measured by rebreathing from a bag Inspiratory pressure following brief occlusion Response is altered by sleep, age, genetic factors Reduced by increasing the work of breathing
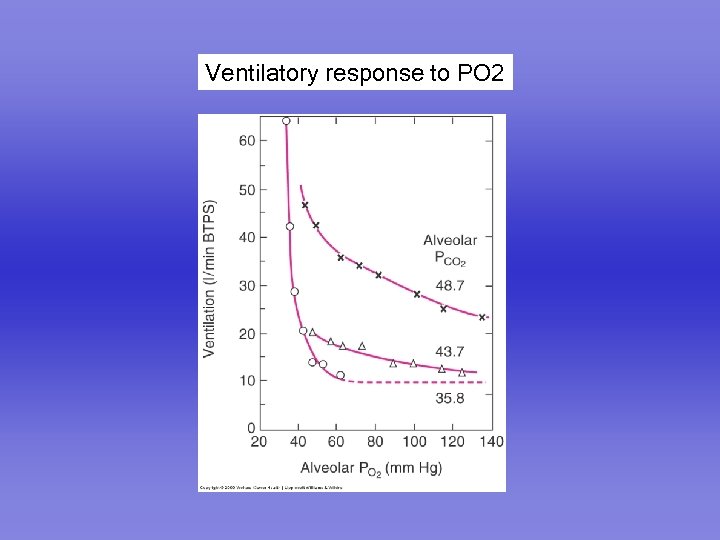 Ventilatory response to PO 2
Ventilatory response to PO 2
 Response to reduced PO 2 No role under normoxic conditions Measured by rebreathing from a bag Increased response if the PCO 2 is raised Important at high altitude Important in some patients with chronic lung disease
Response to reduced PO 2 No role under normoxic conditions Measured by rebreathing from a bag Increased response if the PCO 2 is raised Important at high altitude Important in some patients with chronic lung disease
 Response to reduced p. H Sensed by the peripheral chemoreceptors Important in metabolic acidosis If the reduction is severe, central chemoreceptors may be stimulated
Response to reduced p. H Sensed by the peripheral chemoreceptors Important in metabolic acidosis If the reduction is severe, central chemoreceptors may be stimulated
 Response to exercise Blood gases are normal p. H is normal except at heavy exercise ? Cortex, impulses from limbs, increased temperature, resetting of CO 2 reference level
Response to exercise Blood gases are normal p. H is normal except at heavy exercise ? Cortex, impulses from limbs, increased temperature, resetting of CO 2 reference level
 Sleep apnea 1) Obstructive: very common; often associated with obesity; sleep deprivation may cause daytime somnolence and impaired cognitive function 2) Central: respiratory depression during sleep; recognized by the absence of respiratory efforts
Sleep apnea 1) Obstructive: very common; often associated with obesity; sleep deprivation may cause daytime somnolence and impaired cognitive function 2) Central: respiratory depression during sleep; recognized by the absence of respiratory efforts
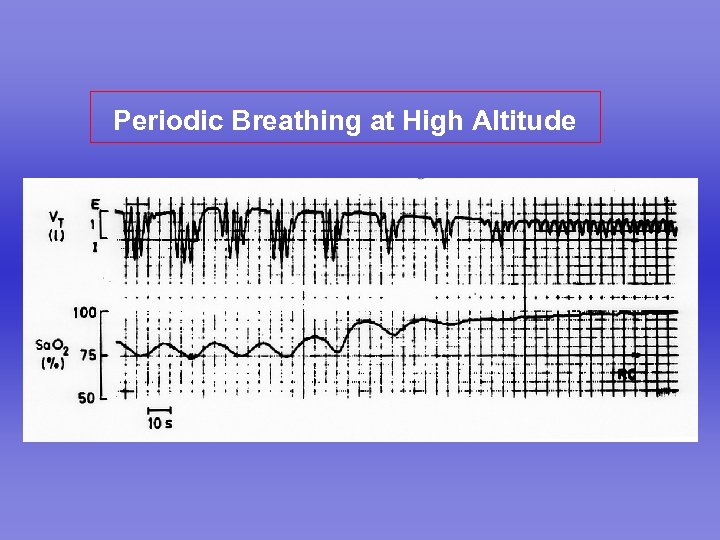 Periodic Breathing at High Altitude
Periodic Breathing at High Altitude


