Lecture 3-4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Lectures 3 -4. PFLT. Intelligence and Cognitive Styles and their Contribution to SLA.
Lectures 3 -4. PFLT. Intelligence and Cognitive Styles and their Contribution to SLA.
 Intelligence Traditional view (2) linguistic and logical – mathematical abilities (Alfred Binet research). Modern view (7) : Linguistic Logical-math Spatial Musical Bodily- kinesthetic Interpersonal Intrapersonal
Intelligence Traditional view (2) linguistic and logical – mathematical abilities (Alfred Binet research). Modern view (7) : Linguistic Logical-math Spatial Musical Bodily- kinesthetic Interpersonal Intrapersonal
 Strategic technique: - Differentiate methods in accordance to multiple intelligence of your students. - Use different activities according to intelligence type preferences.
Strategic technique: - Differentiate methods in accordance to multiple intelligence of your students. - Use different activities according to intelligence type preferences.
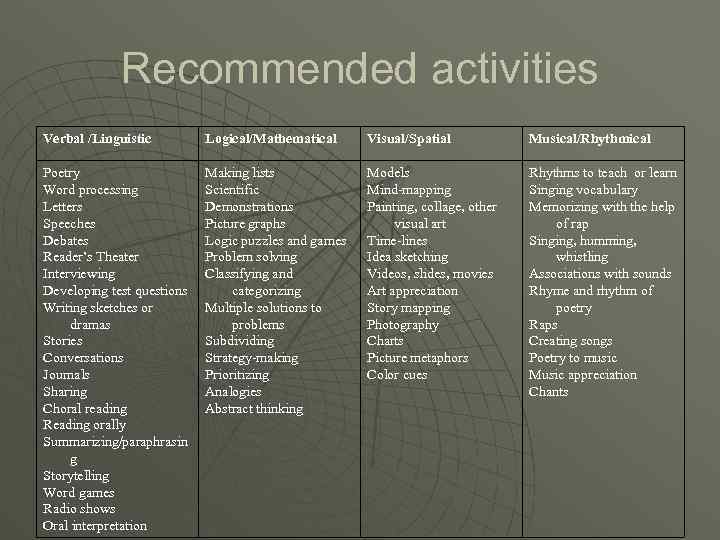 Recommended activities Verbal /Linguistic Logical/Mathematical Visual/Spatial Musical/Rhythmical Poetry Word processing Letters Speeches Debates Reader’s Theater Interviewing Developing test questions Writing sketches or dramas Stories Conversations Journals Sharing Choral reading Reading orally Summarizing/paraphrasin g Storytelling Word games Radio shows Oral interpretation Making lists Scientific Demonstrations Picture graphs Logic puzzles and games Problem solving Classifying and categorizing Multiple solutions to problems Subdividing Strategy-making Prioritizing Analogies Abstract thinking Models Mind-mapping Painting, collage, other visual art Time-lines Idea sketching Videos, slides, movies Art appreciation Story mapping Photography Charts Picture metaphors Color cues Rhythms to teach or learn Singing vocabulary Memorizing with the help of rap Singing, humming, whistling Associations with sounds Rhyme and rhythm of poetry Raps Creating songs Poetry to music Music appreciation Chants
Recommended activities Verbal /Linguistic Logical/Mathematical Visual/Spatial Musical/Rhythmical Poetry Word processing Letters Speeches Debates Reader’s Theater Interviewing Developing test questions Writing sketches or dramas Stories Conversations Journals Sharing Choral reading Reading orally Summarizing/paraphrasin g Storytelling Word games Radio shows Oral interpretation Making lists Scientific Demonstrations Picture graphs Logic puzzles and games Problem solving Classifying and categorizing Multiple solutions to problems Subdividing Strategy-making Prioritizing Analogies Abstract thinking Models Mind-mapping Painting, collage, other visual art Time-lines Idea sketching Videos, slides, movies Art appreciation Story mapping Photography Charts Picture metaphors Color cues Rhythms to teach or learn Singing vocabulary Memorizing with the help of rap Singing, humming, whistling Associations with sounds Rhyme and rhythm of poetry Raps Creating songs Poetry to music Music appreciation Chants
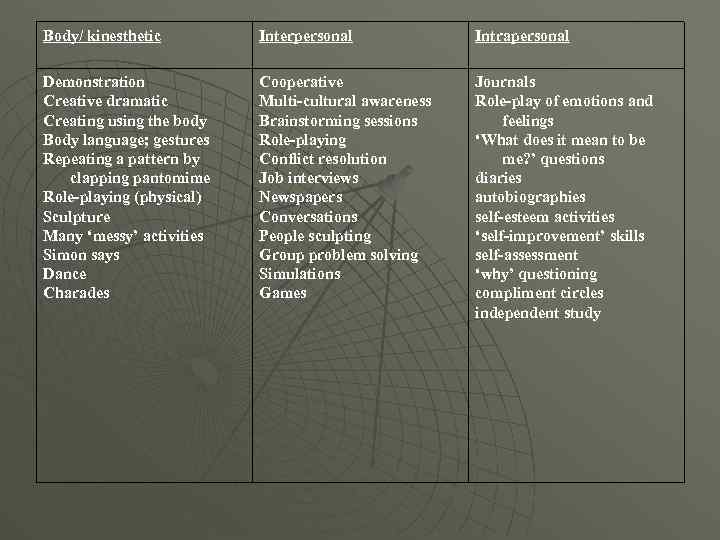 Body/ kinesthetic Interpersonal Intrapersonal Demonstration Creative dramatic Creating using the body Body language; gestures Repeating a pattern by clapping pantomime Role-playing (physical) Sculpture Many ‘messy’ activities Simon says Dance Charades Cooperative Multi-cultural awareness Brainstorming sessions Role-playing Conflict resolution Job interviews Newspapers Conversations People sculpting Group problem solving Simulations Games Journals Role-play of emotions and feelings ‘What does it mean to be me? ’ questions diaries autobiographies self-esteem activities ‘self-improvement’ skills self-assessment ‘why’ questioning compliment circles independent study
Body/ kinesthetic Interpersonal Intrapersonal Demonstration Creative dramatic Creating using the body Body language; gestures Repeating a pattern by clapping pantomime Role-playing (physical) Sculpture Many ‘messy’ activities Simon says Dance Charades Cooperative Multi-cultural awareness Brainstorming sessions Role-playing Conflict resolution Job interviews Newspapers Conversations People sculpting Group problem solving Simulations Games Journals Role-play of emotions and feelings ‘What does it mean to be me? ’ questions diaries autobiographies self-esteem activities ‘self-improvement’ skills self-assessment ‘why’ questioning compliment circles independent study
 Learning styles Cognitive, affective, and physiological traits of how learners perceive, interact with, and respond to the learning environment. -field independence/ dependence - Left and right brain functioning - Ambiguity tolerance/ intolerance - Reflectivity and impulsivity - Visual and auditory
Learning styles Cognitive, affective, and physiological traits of how learners perceive, interact with, and respond to the learning environment. -field independence/ dependence - Left and right brain functioning - Ambiguity tolerance/ intolerance - Reflectivity and impulsivity - Visual and auditory
 Field-independent style Strength: - Enables to distinguish parts from a whole; - To concentrate on smth; Weakness: - Cognitive ‘tunnel – vision’ forces you to see only the parts and fail to see their relationship to the whole. (You can’t see the forest for the trees)
Field-independent style Strength: - Enables to distinguish parts from a whole; - To concentrate on smth; Weakness: - Cognitive ‘tunnel – vision’ forces you to see only the parts and fail to see their relationship to the whole. (You can’t see the forest for the trees)
 Field-dependent style Strength perceive the whole picture, have a larger view of a problem or idea or event. Weakness fail to see a tree in the forest.
Field-dependent style Strength perceive the whole picture, have a larger view of a problem or idea or event. Weakness fail to see a tree in the forest.
 Affectively Field independent persons are generally more independent, competitive, and self-confident. They are products of democratic and industrialized society. 2) Field dependent are more socialized; derive self-esteem from persons around , and more emphatic. They are products of authoritarian and agrarian societies. 1)
Affectively Field independent persons are generally more independent, competitive, and self-confident. They are products of democratic and industrialized society. 2) Field dependent are more socialized; derive self-esteem from persons around , and more emphatic. They are products of authoritarian and agrarian societies. 1)
 Strategic techniques -understand the preferred style of each learner and sow the seeds for flexibility. - Encourage and get the learn to invoke the appropriate style for the context; where he can exercise a sufficient degree of an appropriate style.
Strategic techniques -understand the preferred style of each learner and sow the seeds for flexibility. - Encourage and get the learn to invoke the appropriate style for the context; where he can exercise a sufficient degree of an appropriate style.
 Left and right brain functioning. ! Both hemispheres operate together as a ‘team’. Left hemisphere logical, analytical thought. So, left –brain-dominant SL learner are better at producing separate words, specifics of language, abstraction, classification and reorganization. Right hemisphere visual, tactile, auditory images, holistic, integrative, emotion info. So, right-brain dominant SL learner are better at intuitive problem -solving and interpret the general frame of language.
Left and right brain functioning. ! Both hemispheres operate together as a ‘team’. Left hemisphere logical, analytical thought. So, left –brain-dominant SL learner are better at producing separate words, specifics of language, abstraction, classification and reorganization. Right hemisphere visual, tactile, auditory images, holistic, integrative, emotion info. So, right-brain dominant SL learner are better at intuitive problem -solving and interpret the general frame of language.
 Strategic technique: - To understand the brain dominance of each learner and provide them with activities in which each hemisphere has participated optimally. Left –Brain Dominance Right-Brain Dominance Intellectual Remembers names Responds to verbal instructions and explanations Experiments systematically and with control Makes objective judgments Planned and structures Prefers established, certain information Analytic reader Reliance on language in thinking and remembering Prefers talking and writing Prefers multiple choice tests Control feelings Not good at interpreting body language Rarely uses metaphors Favors logical problem solving Intuitive Remembering faces Responds to demonstrated, illustrated or symbolic instructions Experiments randomly and with less restraint Makes subjective judgments Fluid and spontaneous Prefers elusive, uncertain information Synthesizing reader Reliance on images in thinking and remembering Prefers drawing and manipulating objects Prefers open-ended questions More free with feelings Good at interpreting body language Frequently uses metaphors Favors intuitive problem solving
Strategic technique: - To understand the brain dominance of each learner and provide them with activities in which each hemisphere has participated optimally. Left –Brain Dominance Right-Brain Dominance Intellectual Remembers names Responds to verbal instructions and explanations Experiments systematically and with control Makes objective judgments Planned and structures Prefers established, certain information Analytic reader Reliance on language in thinking and remembering Prefers talking and writing Prefers multiple choice tests Control feelings Not good at interpreting body language Rarely uses metaphors Favors logical problem solving Intuitive Remembering faces Responds to demonstrated, illustrated or symbolic instructions Experiments randomly and with less restraint Makes subjective judgments Fluid and spontaneous Prefers elusive, uncertain information Synthesizing reader Reliance on images in thinking and remembering Prefers drawing and manipulating objects Prefers open-ended questions More free with feelings Good at interpreting body language Frequently uses metaphors Favors intuitive problem solving
 Ambiguity tolerance/ intolerance Strength -Ambiguity tolerant person is free to entertain a number of innovations and affectively not disturbed by uncertainty and ambiguity. Weakness- linguistic rules may not be effectively integrated into a whole system and become meaningless chunks. Ambiguity intolerant person Strength – guards against the wishy-washiness Weakness – close the mind and become too narrow to be creative
Ambiguity tolerance/ intolerance Strength -Ambiguity tolerant person is free to entertain a number of innovations and affectively not disturbed by uncertainty and ambiguity. Weakness- linguistic rules may not be effectively integrated into a whole system and become meaningless chunks. Ambiguity intolerant person Strength – guards against the wishy-washiness Weakness – close the mind and become too narrow to be creative
 Strategic techniques: - Recognize the style of each learner, and exercise certain tolerance of ambiguity, not too much for it may be perceived as a threat and become harmful in SLA.
Strategic techniques: - Recognize the style of each learner, and exercise certain tolerance of ambiguity, not too much for it may be perceived as a threat and become harmful in SLA.
 Reflectivity and impulsivity Reflective person systematic style, weighing all the considerations in a problem, extensive reflection Impulsive person intuitive style making a number of different gambles on the basis of ‘hunches’ immediate reflection.
Reflectivity and impulsivity Reflective person systematic style, weighing all the considerations in a problem, extensive reflection Impulsive person intuitive style making a number of different gambles on the basis of ‘hunches’ immediate reflection.
 Strategic techniques: - - don’t judge mistakes too harshly, especially with impulsive style learners; Allow more time for a reflective style learner to struggle with responses Remember, impulsive styles go through a number of rapid transitions of semi grammatical stages Reflective persons require larger leaps from stage to stage.
Strategic techniques: - - don’t judge mistakes too harshly, especially with impulsive style learners; Allow more time for a reflective style learner to struggle with responses Remember, impulsive styles go through a number of rapid transitions of semi grammatical stages Reflective persons require larger leaps from stage to stage.
 Visual and auditory styles Visual learner visual input Visual Learners Auditory learner auditory input Writing down key facts or Their preferences: a Mind Map Visualizing what they are learning Creating pictures and diagrams from what they are learning Using time lines, for remembering dates Creating their own strong visual links Using pictures, diagrams, charts, film, video, graphics, etc Auditory Learners Hearing a seminar, presentation or explanation Reading aloud to themselves Reading with emotion or accent Making a tape of key points to listen to in the car, whilst ironing, etc. Verbally summarize in their own words Explain the subject to someone else Use their own internal voice to verbalize what they are learning.
Visual and auditory styles Visual learner visual input Visual Learners Auditory learner auditory input Writing down key facts or Their preferences: a Mind Map Visualizing what they are learning Creating pictures and diagrams from what they are learning Using time lines, for remembering dates Creating their own strong visual links Using pictures, diagrams, charts, film, video, graphics, etc Auditory Learners Hearing a seminar, presentation or explanation Reading aloud to themselves Reading with emotion or accent Making a tape of key points to listen to in the car, whilst ironing, etc. Verbally summarize in their own words Explain the subject to someone else Use their own internal voice to verbalize what they are learning.
 Strategic technique - remember, successful learners utilize both visual and auditory input, with slight preference one way, so provide your learner with variety and train them to use both inputs.
Strategic technique - remember, successful learners utilize both visual and auditory input, with slight preference one way, so provide your learner with variety and train them to use both inputs.
 Seminar questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What is the relationship between intelligence and SLA? Describe unique abilities of each intelligence type and offer activities to meet the needs of this type. Identify advantages and disadvantages of field dependence and independence and their affect on success in SLA. Describe different talents of left and right hemisphere functioning relating to SLA. What can be the affect on SLA of too tolerance or too much intolerance of ambiguity of stimuli? Describe the strengths and weaknesses of reflective and impulsive style learners. Which activities would be more friendly for visual learners and which for auditory? How can a SL teacher help their students be more successful (concerning intelligence and learning styles)
Seminar questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What is the relationship between intelligence and SLA? Describe unique abilities of each intelligence type and offer activities to meet the needs of this type. Identify advantages and disadvantages of field dependence and independence and their affect on success in SLA. Describe different talents of left and right hemisphere functioning relating to SLA. What can be the affect on SLA of too tolerance or too much intolerance of ambiguity of stimuli? Describe the strengths and weaknesses of reflective and impulsive style learners. Which activities would be more friendly for visual learners and which for auditory? How can a SL teacher help their students be more successful (concerning intelligence and learning styles)
 II Do ‘Right and Left Brain Dominance test’ and intuitively identify your cognitive learning style. III Prepare a team presentation of a lesson with activities meeting the needs of different cognitive styles.
II Do ‘Right and Left Brain Dominance test’ and intuitively identify your cognitive learning style. III Prepare a team presentation of a lesson with activities meeting the needs of different cognitive styles.


