Lectures 1-2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Lectures 1 -2. Psychological Factors Contributing to Second Language Acquisition

Personality factors: • • self-esteem inhibition risk-taking anxiety and competitiveness empathy introversion and extraversion personality type motivation

Self-esteem Characteristics: - most important aspect of any human behavior - personal judgment of worthiness - derived from the accumulation of experiences with oneself and others

3 levels of self-esteem General relatively stable Situational one’s appraisals of oneself in work/education/home Task one’s self-evaluation of speaking, writing , or particular exercises

? a. What is the relationship between success and self-esteem? b. Should teachers improve general selfesteem or simply improve a learner’s proficiency in the language? c. Can teachers let self-esteem take care of itself?

Self-esteem improvement Strategic techniques for self-esteem improvement 1. Let your students hear or guess that you do believe in them. 2. Let them know and make lists of their strengths. 3. Let them exploit their strengths practically in class. 4. Let them feel certain progress (at least ‘a little’) but at every single lesson.

Inhibition. Characteristics: - Closely connected with selfesteem - The process of building defenses to protect the ego.

? What is the relationship between human ego and language ego? b. Who is able to withstand threats to their ego, those with higher self-esteem or lower self-esteem? c. When can mistakes be viewed as threats to one’s ego? a.

Strategic techniques to reduce inhibition: Teaching approach: meaningful classroom communication to lower interpersonal ego-barriers. Lower your students inhibition through 1. Singing songs 2. Playing guessing and communication games 3. Doing role-plays 4. Laughing with them 5. Plenty of group work 6. Sharing fears in small group

Risk-taking Characteristics: - Affects creativity and success both in oral and written language - Closely connected with self-esteem Types: high risk-takers moderate risk-takers low risk-takers

? a. Are language achievers high/moderate/low risk takers and why? b. What should a teacher do if a student is blurting out meaningless verbal garbage? c. How can a teacher train students to be accurate language guessers?

Risk-taking encouragement: 1. 2. 3. Praise your students for making sincere efforts to try out language. Use more fluency exercises where errors are not corrected. Give home tasks where students may have a chance to experiment with language.

Anxiety. Characteristic: -Arises when facing a complex task and we start doubt our own abilities. -Interrelated with self-esteem, inhibition and risk taking.

Levels of anxiety. Trait generally anxious about many things State in relation to some particular event or act Foreign language : communication anxiety –apprehension, fear of negative social evaluation, test anxiety over academic evaluation.

Promoting facilitating anxiety strategic techniques: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Promote supportive and cooperative learning Direct students to share their knowledge Play dow competition among students Get the class to think of themselves as a team Do considerable amount of small group work.

Empathy Characteristics: - Projection of one’s personality into the personality of another to understand his feeling better (putting yourself into smb else’s shoes) - Gained when you’re got knowledge of your own feelings - Not only must learner-speaker correctly identify cognitive and affective sets in the nearer but must do so in a language in which he is insecure.

? a. b. What kind of drills and exercises could be devised that require a person to predict or guess another person’s response? How worthwhile would it be to try to organize FL classes that operate on a high-empathy basis?

Exercising empathy strategic techniques: a. Asking questions for clarification or verification or correction b. Cooperating more with other learners and proficient users of language. c. Developing cultural understanding and becoming aware of other’s thoughts and feelings.

Extraversion and introversion. Characteristics: - Extraverted people receive ego enhancement self-esteem, and a sense of wholeness from other people. - Introverted people derive a sense of wholeness from the reflection of their selves (they have an inner strength of character)

? a. What is a misleading tendency among teachers to treat extraversion and introversion in FL class? b. How effective are methods that involve drama, pantomime, humor, role plays and other personality exposure?

Learning fair attitude strategic techniques. 1. 2. 3. Be sensitive to a student’s willingness to speak out in class. Remember that introverts tend to learn analytically in planned and organized way, they are analytical thinkers Remember that extraverts are people oriented and learn though intuition and interaction with others, they are global thinkers.

Personality types. 1) p 2) p 3) p 4) p introversion versus extraversion sensing versus intuition thinking versus feeling judging versus perceiving
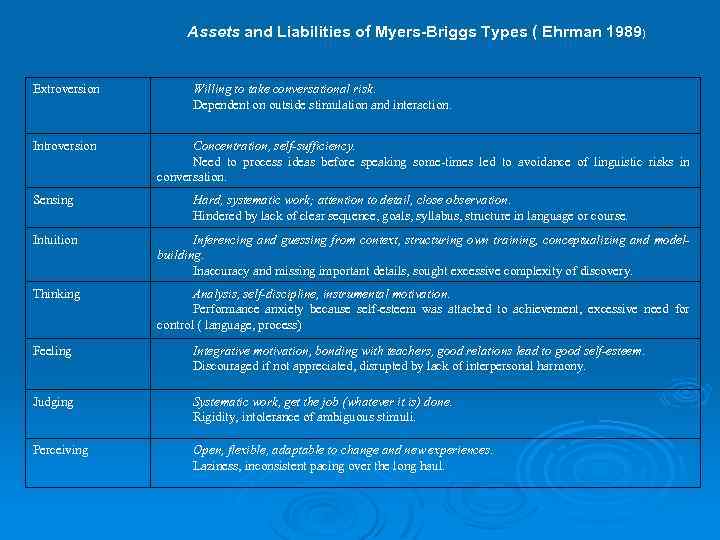
Assets and Liabilities of Myers-Briggs Types ( Ehrman 1989) Extroversion Introversion Sensing Willing to take conversational risk. Dependent on outside stimulation and interaction. Concentration, self-sufficiency. Need to process ideas before speaking some-times led to avoidance of linguistic risks in conversation. Hard, systematic work; attention to detail, close observation. Hindered by lack of clear sequence, goals, syllabus, structure in language or course. Intuition Inferencing and guessing from context, structuring own training, conceptualizing and modelbuilding. Inaccuracy and missing important details, sought excessive complexity of discovery. Thinking Analysis, self-discipline, instrumental motivation. Performance anxiety because self-esteem was attached to achievement, excessive need for control ( language, process) Feeling Integrative motivation, bonding with teachers, good relations lead to good self-esteem. Discouraged if not appreciated, disrupted by lack of interpersonal harmony. Judging Systematic work, get the job (whatever it is) done. Rigidity, intolerance of ambiguous stimuli. Perceiving Open, flexible, adaptable to change and new experiences. Laziness, inconsistent pacing over the long haul.

Motivation Characteristics - inner drive, impulse, emotion, desire to do smth. Types: 1) general, situational, task-oriented 2) intrinsic/ extrinsic 3) integrative/ instrumental

? 1. 2. What kind of motivation is more powerful to succeed in learning a SL? How can teachers create foster and maintain motivation in students?

Improving motivation strategic techniques: Develop intrinsic motivation with the help of the ways proposed below. Short-term measures ( within lessons) 1. Challenge students to think 2. Set up a need to communicate 3. Show interest on the student’s opinions/exercise and relate the content of lessons to this. 4. Make the learning experience ‘enjoyable’ 5. Ensure that there is sufficient variety of activity, focus (of interaction) and pace. Long-term measures ( over a term or course) 1. Make the aims and goals of the course clear well in advance and draw the attention of the students to the achievement of these. 2. Bring in and use materials such as maps, books and brochures and be prepared to provide background information to the materials. 3. Involve students in discussions about your approach and respond flexibly to their expectations. 4. Identify needs and take these into account. 5. Devote time and attention to group dynamics ( e. g. choose activities not only for reasons of language learning but also because they may foster positive communal feeling) 6. Regularly demonstrate progress through repeating activities exercisestests or showing them what they did some time before.

Seminar 1. Personality factors contributing to SLA. I Prepare to answer and discuss the questions: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) 16) 17) What is the role of psychology in SLA? What are general and personal psychological factors contributing to SLA? What is the relationship between success and self-esteem? Should teachers improve general self-esteem or simply improve a learner’s proficiency in the language? Can teachers let self-esteem take care of itself? What is the relationship between human ego and language ego? Who is able to withstand threats to their ego, those with higher self-esteem or lower self-esteem? When can mistakes be viewed as threats to one’s ego? Are language achievers high/moderate/low risk takers and why? What should a teacher do if a student is blurting out meaningless verbal garbage? How can a teacher train students to be accurate language guessers? What kind of drills and exercises could be devised that require a person to predict or guess another person’s response? How worthwhile would it be to try to organize FL classes that operate on a high-empathy basis? What is a misleading tendency among teachers to treat extraversion and introversion in FL class? How effective are methods that involve drama, pantomime, humor, role plays and other personality exposure? What kind of motivation is more powerful to succeed in learning a SL? How can teachers create foster and maintain motivation in students?

II Do Myers-Briggs Personality test ( 70 questions) to identify your personality indicator III Analyze the influence of your personality indicator on your learning preferences, strengths and weaknesses in SLA in a onepage essay with examples.
Lectures 1-2.ppt