9b4ae1dae09364d2709188cd8318d6f1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

Lecture VII: Mashups CS 4593 Cloud-Oriented Big Data and Software Engineering

Outline • What are Mashups • Types of Mashups • How to build Mashups 2
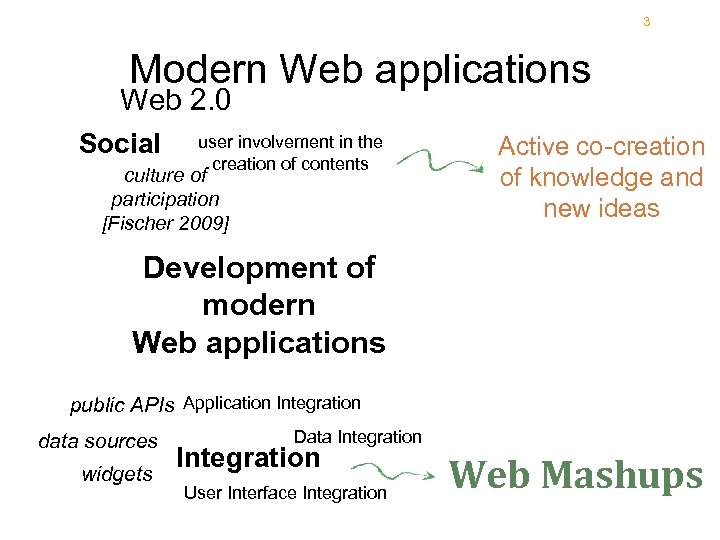
3 Modern Web applications Web 2. 0 Social user involvement in the creation of contents culture of participation [Fischer 2009] Active co-creation of knowledge and new ideas Development of modern Web applications public APIs Application Integration data sources widgets Data Integration User Interface Integration Web Mashups
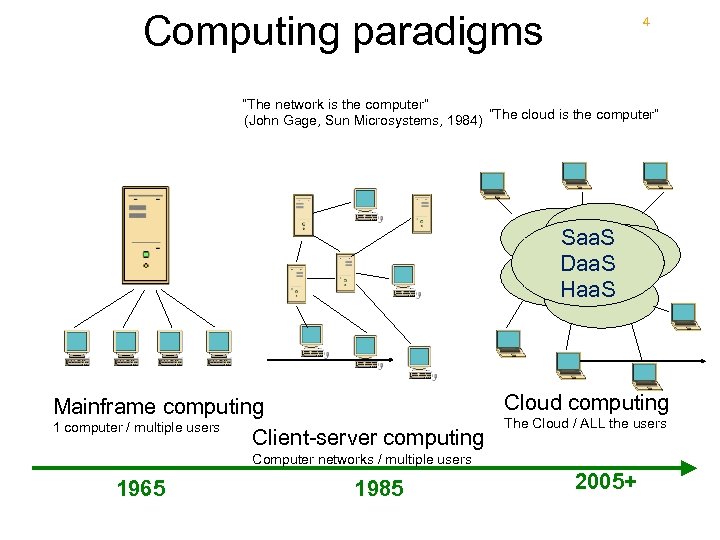
Computing paradigms 4 “The network is the computer” (John Gage, Sun Microsystems, 1984) “The cloud is the computer” Saa. S Daa. S Haa. S Cloud computing Mainframe computing The Cloud / ALL the users 1 computer / multiple users Client-server computing Computer networks / multiple users 1965 1985 2005+
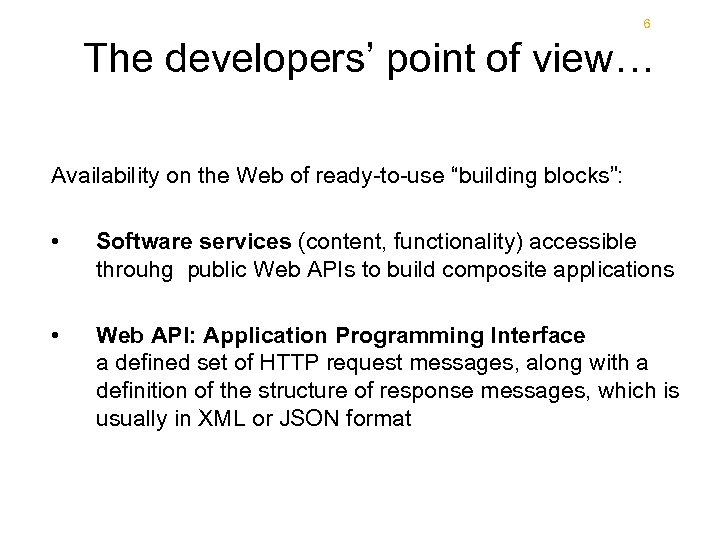
6 The developers’ point of view… Availability on the Web of ready-to-use “building blocks”: • Software services (content, functionality) accessible throuhg public Web APIs to build composite applications • Web API: Application Programming Interface a defined set of HTTP request messages, along with a definition of the structure of response messages, which is usually in XML or JSON format
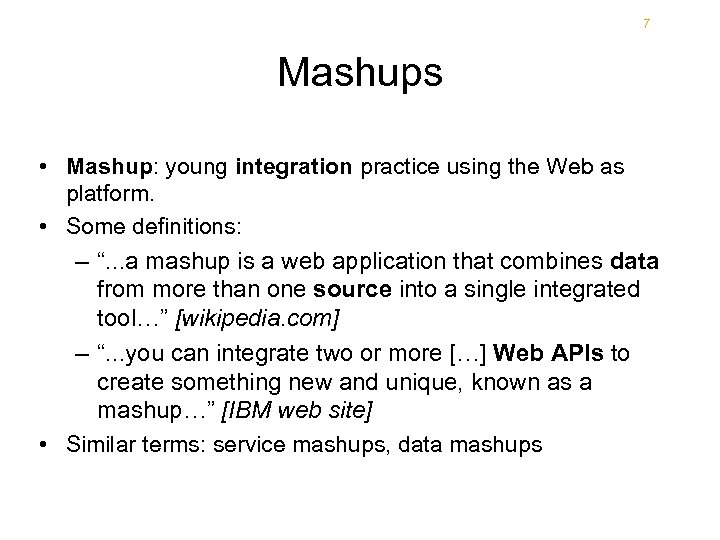
7 Mashups • Mashup: young integration practice using the Web as platform. • Some definitions: – “. . . a mashup is a web application that combines data from more than one source into a single integrated tool…” [wikipedia. com] – “. . . you can integrate two or more […] Web APIs to create something new and unique, known as a mashup…” [IBM web site] • Similar terms: service mashups, data mashups
Mashup = Integration in the Web 2. 0 way 8 • Highly user-driven: • • Oftentimes the actual providers of content/functionality are not even aware of being “wrapped” Google Maps example: initially skilled users «hacked» the code of the application • Strong evolution: from hacking to first systematic development approaches in a few years

9 Let’s see an example The Housing. Maps application (http: //www. housingmaps. com) A utility for finding a house for sale or for rent • Composed of: – Google Maps (http: //maps. google. com) – Craigslist (http: //www. craigslist. com)
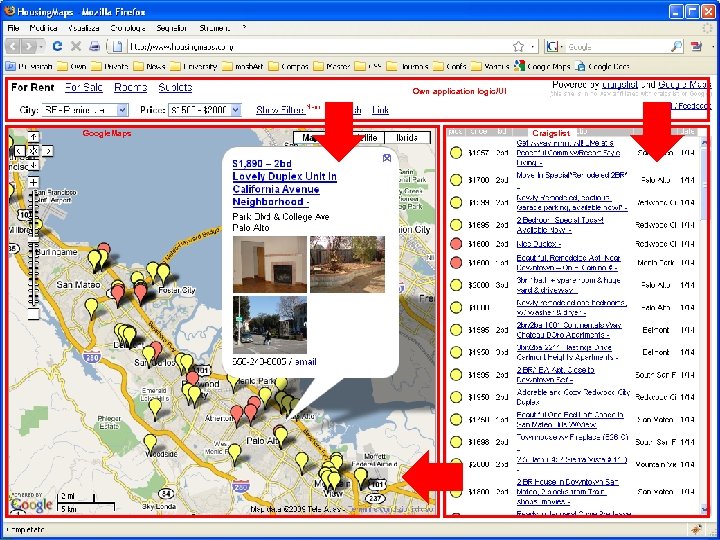
A mashup example Own application logic/UI Google. Maps • Housing. Maps (http: //www. housingmaps. com) – http: //maps. google. com – http: //www. craigslist. com Craigslist
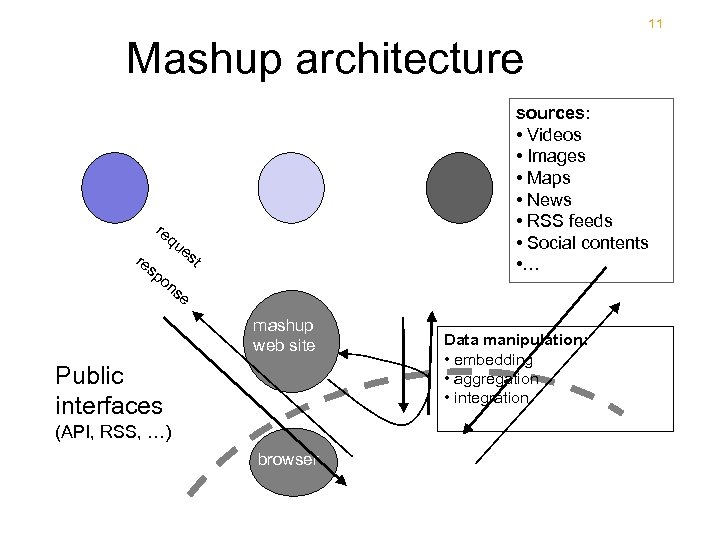
11 Mashup architecture re re qu sp sources: • Videos • Images • Maps • News • RSS feeds • Social contents • … es t on se mashup web site Public interfaces (API, RSS, …) browser Data manipulation: • embedding • aggregation • integration
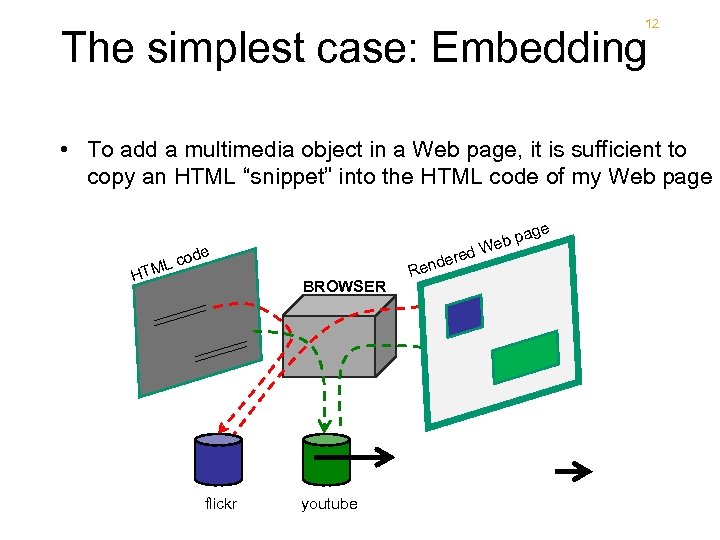
12 The simplest case: Embedding • To add a multimedia object in a Web page, it is sufficient to copy an HTML “snippet” into the HTML code of my Web page de co ML T H d BROWSER flickr youtube ere end R ge b pa We foto
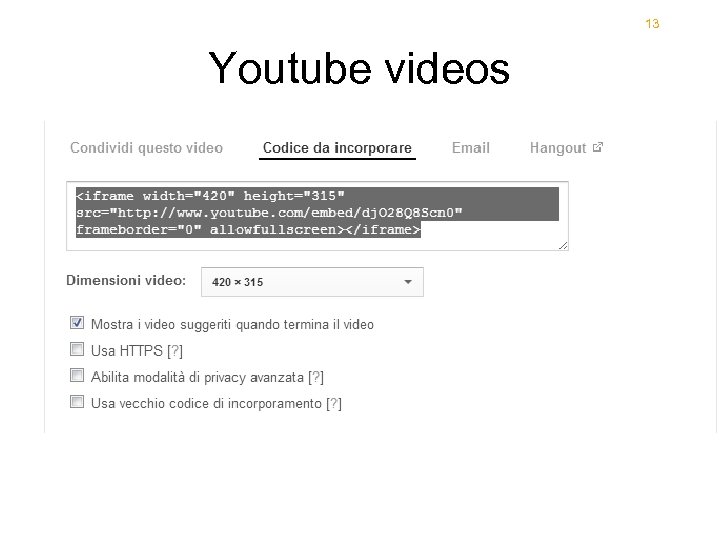
13 Youtube videos
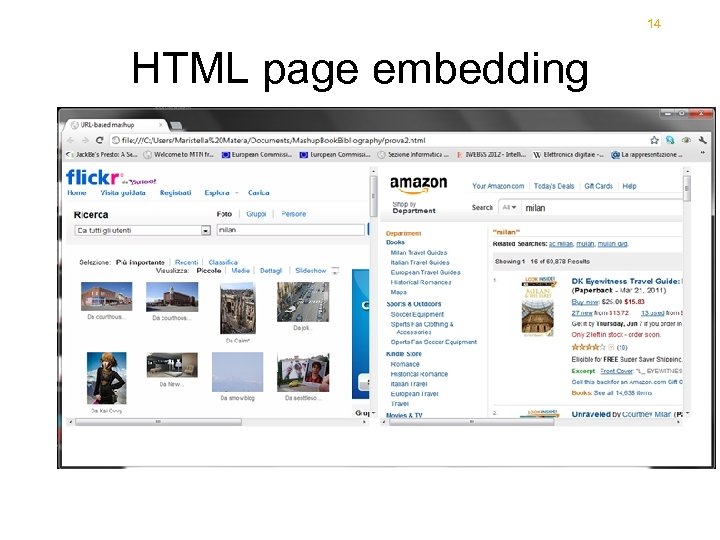
14 HTML page embedding

15 HTML embedding • • • <body> <iframe id="Flickr. Frame" src="http: //www. flickr. com/search/? q=milan" name="Flickr" style="width: 600 px; height: 500 px; border: 0 px"></iframe> <iframe id="Amazon. Frame" src="http: //amazon. com/s/? url=search-alias%3 Daps&field-keywords=milan" name="Amazon" style="width: 600 px; height: 500 px; border: 0 px"></iframe> </body> </html>
Content Aggregation Google News 16
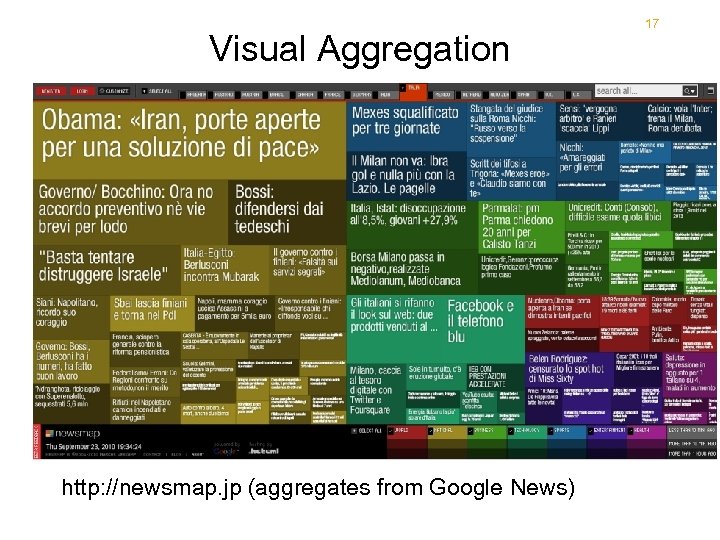
Visual Aggregation http: //newsmap. jp (aggregates from Google News) 17
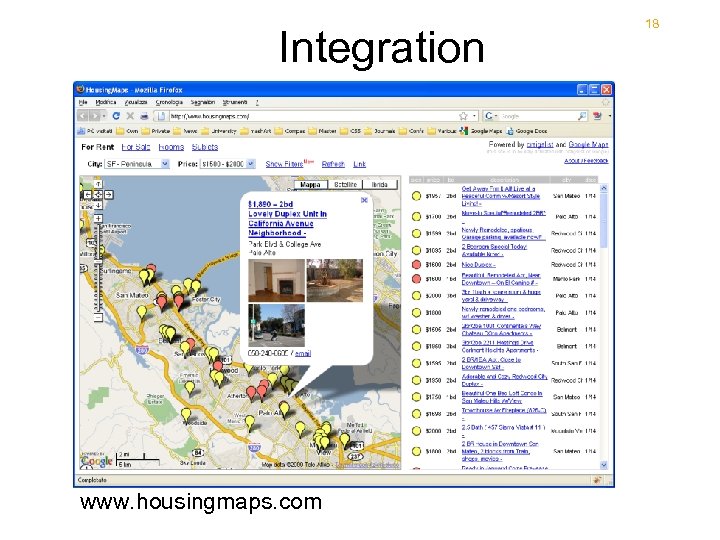
Integration www. housingmaps. com 18
Created with http: //maps. huge. info/zip. htm
Route Map for Deliveries http: //www. lcls. org/members/routemap. aspx
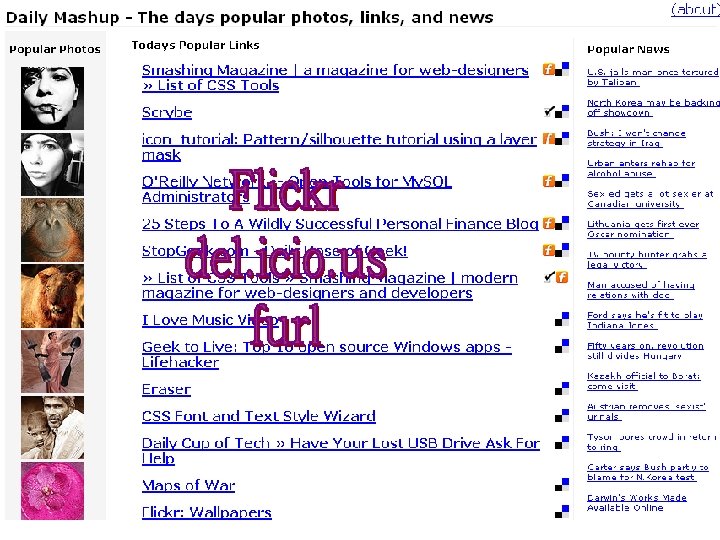

Newsmap USA Canada http: //www. marumushi. com/apps/newsmap. cfm

Newsmap • Reveals underlying patterns in news reporting across cultures • Uses Google News

Components • 24 Collections: • Programmable. Web (www. programmabel. Web. com) • Mashery (developer. mashery. com/apis) • Ecosystems: offer software components that are «compatible» and «integrable» to build composite applications • Word. Press (www. wordpress. org ) offer a large set of widgets and the possibility to include corresponding plugins into the development workspace • Netvibes. com: a portal with a huge number of widgets

Mashup Ecosystem • Open data • Open set of services • Small pieces loosely joined • You
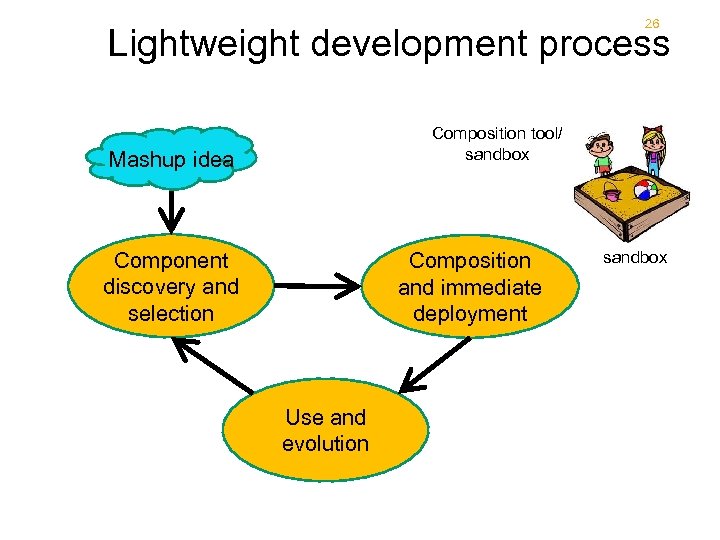
26 Lightweight development process Composition tool/ sandbox Mashup idea Component discovery and selection Composition and immediate deployment Use and evolution sandbox

29 Mashup: pros 29 • “Lightweight” applications • reduced amount of code to be written; just the code for integrating APIs • «Lightweight» development availability of tools who do not require many technical skills – e. g. , pipes • Low (o zero) costs for gathering data • Rapid development Reduced time-to-market, quick prototyping

30 Mashup: cons 30 • Dependency from the online data sources data quality, performances, service availbility and reliability, change in the service policy (licensing, acess restrictions, etc. ) • APIs: standards and versioning • Intellectual property and copyright “right to remix”: in which measure?
9b4ae1dae09364d2709188cd8318d6f1.ppt