Лекция 15 ИБС, ЦВБ 2011.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52
Lecture subject: Coronary heart disease (CHD), cerebrovascular disease (CVD).

Coronary heart disease (CHD)

Coronary heart disease It is a group of diseases, caused by the relative or absolute deficiency of coronary blood flow «coronary heart disease» 1965

Coronary heart disease o Background diseases for CHD: atherosclerosis, essential hypertension, diabetes mellitus. o Course: acute, chronic.

Coronary heart disease Risk factors: - hyperlipidemia, - hypertension, - hypodynamia, - psychoemotional overstrain, - smoking, - compromised (burdened) heredity, - adiposity.
Acute CHD o Sudden cardiac death o Acute focal ischemic myocardosis o Myocardial infarction
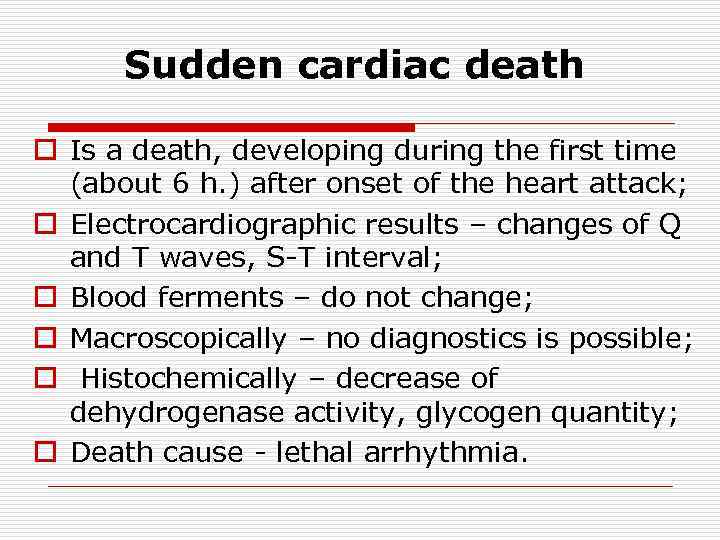
Sudden cardiac death o Is a death, developing during the first time (about 6 h. ) after onset of the heart attack; o Electrocardiographic results – changes of Q and T waves, S-T interval; o Blood ferments – do not change; o Macroscopically – no diagnostics is possible; o Histochemically – decrease of dehydrogenase activity, glycogen quantity; o Death cause - lethal arrhythmia.

Ischemic myocardosis o Is a death, developing during the first 6 -12 hours after onset of the heart attack; o Electrocardiographic results – changes of Q and T waves, S-T interval; o Blood ferments – creatine kinase, transaminase; o Macroscopically – salts of potassium tellurite, tetrazolium; o Histochemically – decrease of dehydrogenase activity, glycogen quantity; o Death cause - lethal arrhythmia.

Myocardial infarction Immediate causes: o Thrombosis; o Embolism; o Prolonged spasm; o Functional overstrain of an organ.
Myocardial infarction Development stages: o. Pre-necrotic; o. Necrotic; o. Organization; o. Postinfarction changes.
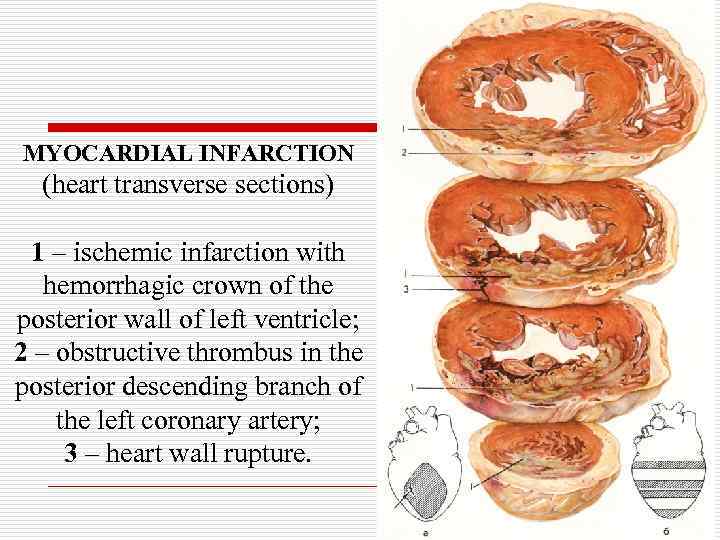
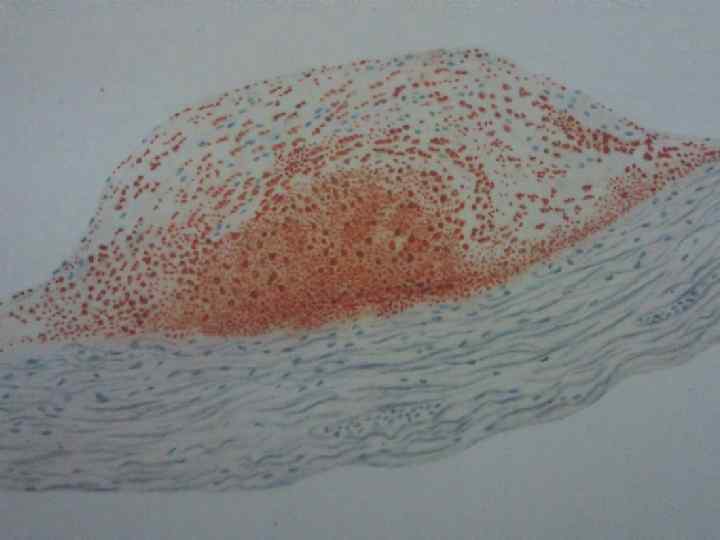
MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION (heart transverse sections) 1 – ischemic infarction with hemorrhagic crown of the posterior wall of left ventricle; 2 – obstructive thrombus in the posterior descending branch of the left coronary artery; 3 – heart wall rupture.

Myocardial infarction classification According to the onset time: o Primary; o Recurrent (3 -28 days); o Repeated (after 28 days).

Myocardial infarction classification According to localization: o o o Of the anterior wall of left ventricle; Of the posterior wall of left ventricle; Of the lateral wall of left ventricle; Of interventricular septum; Extensive infarction.

Myocardial infarction classification According to the prevalence: o Subendocardial; o Subepicardial; o Intramural; o Transmural.
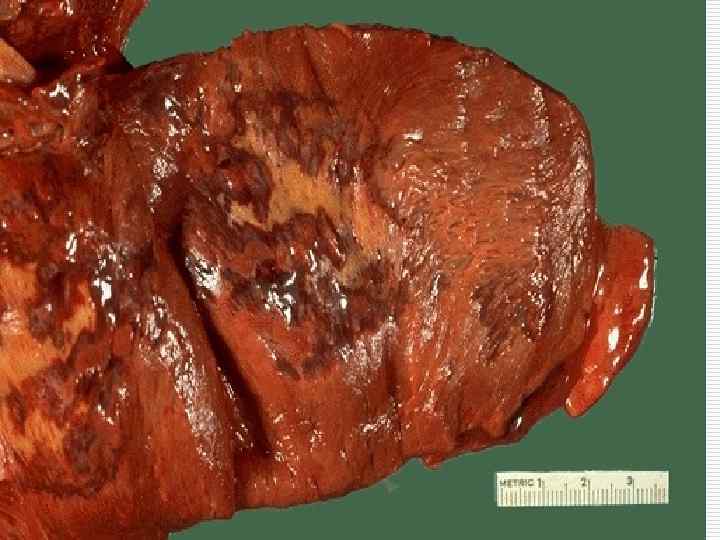
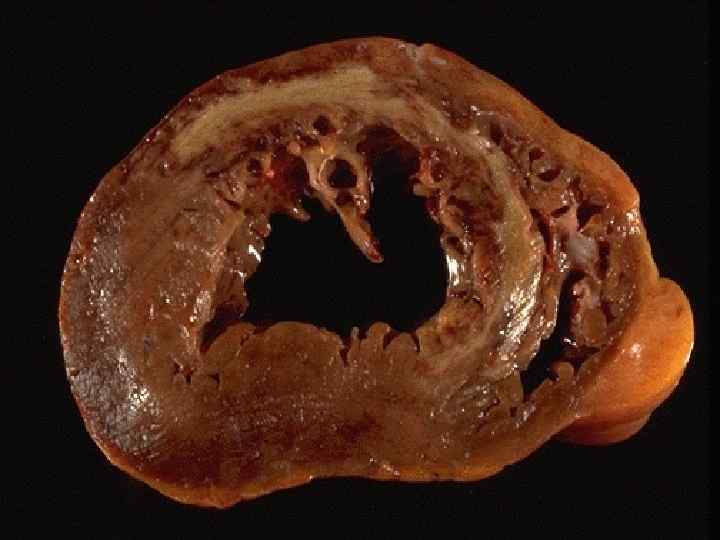
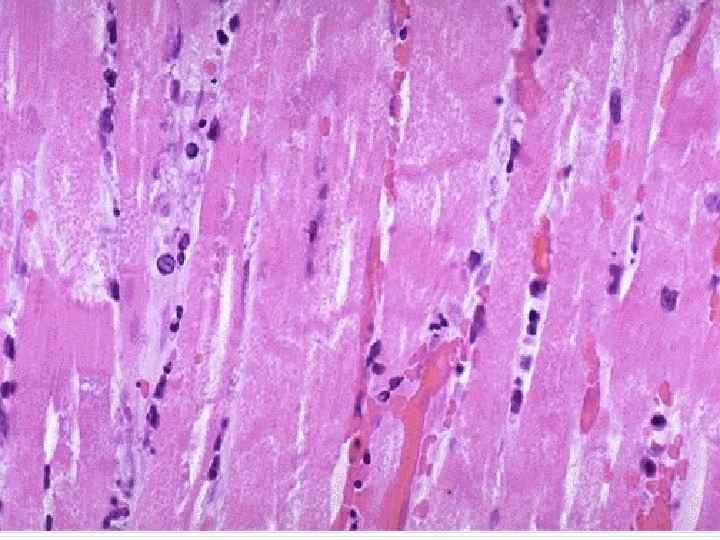
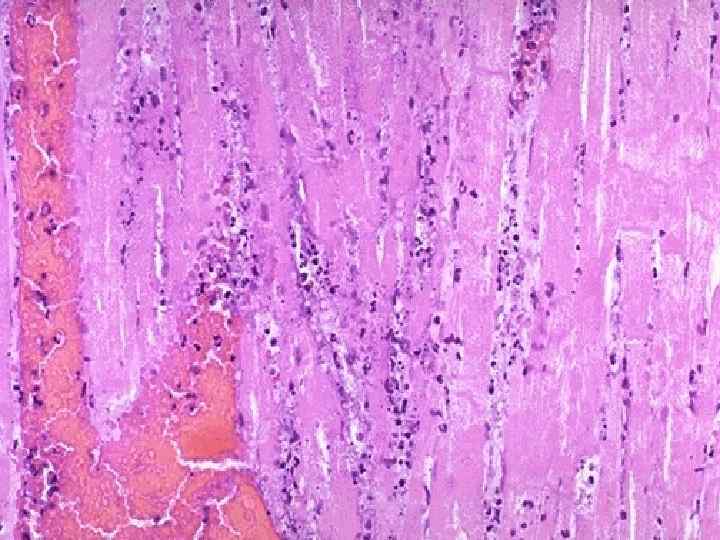
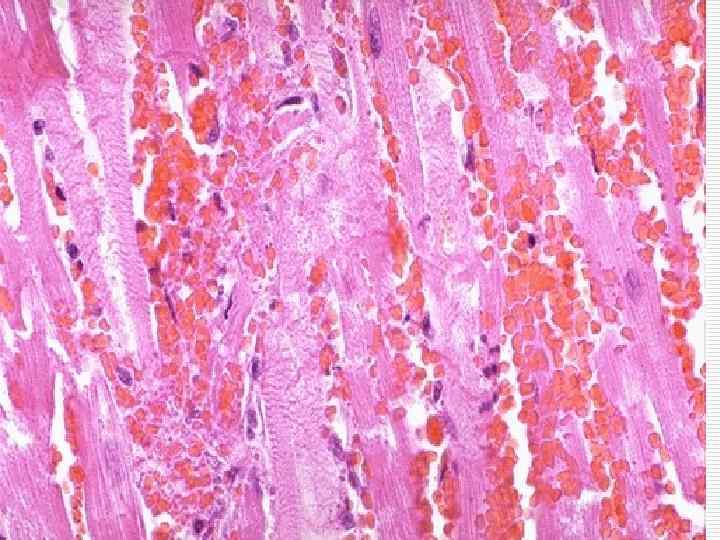
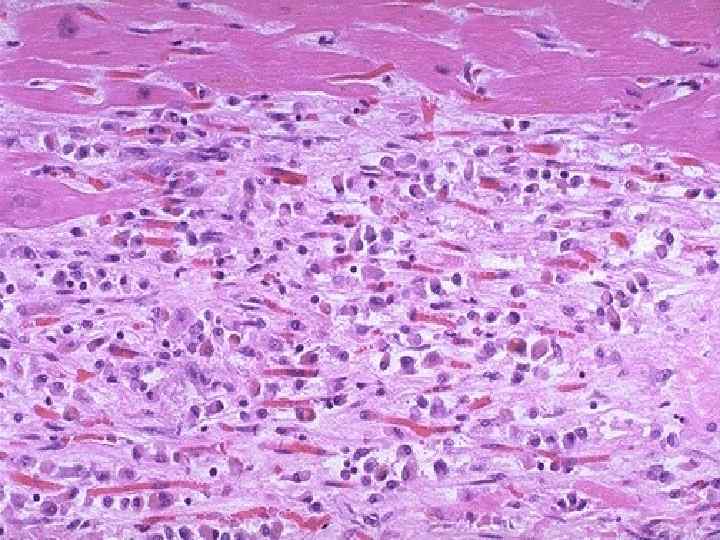
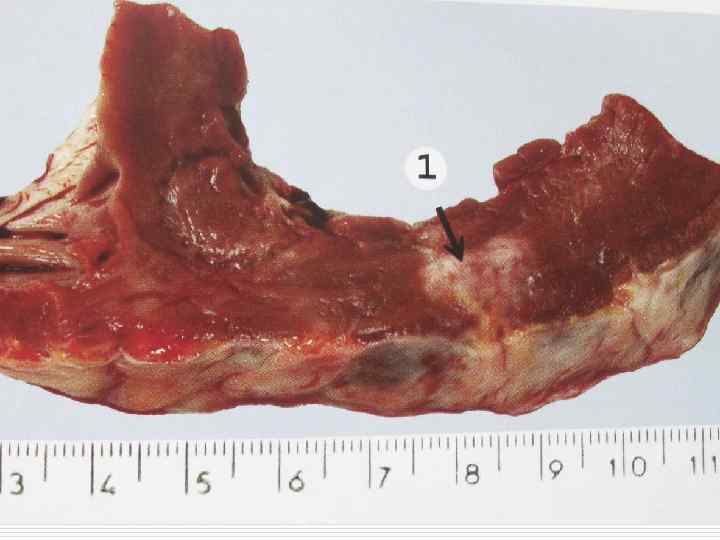
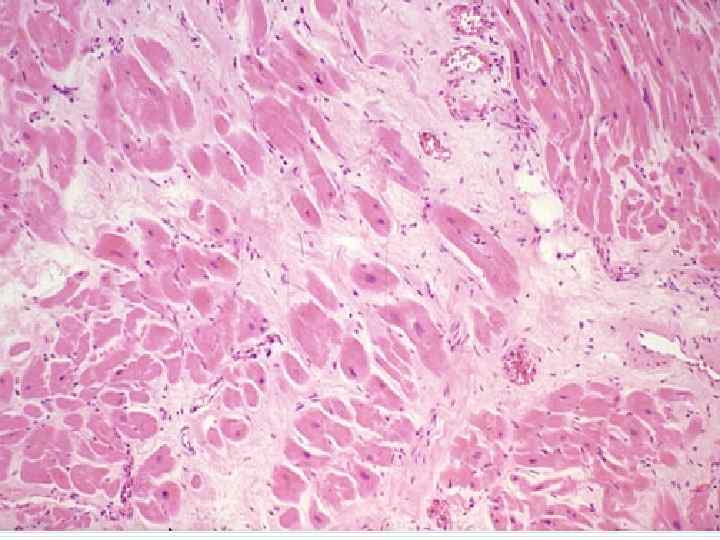

Myocardial infarction complications - Cardiogenic shock, asystolia; Acute cardiac aneurysm; Myocardium rupture; Hemotamponade; Thromboembolism; Pericarditis; Acute cardiac insufficiency; Pulmonary edema.
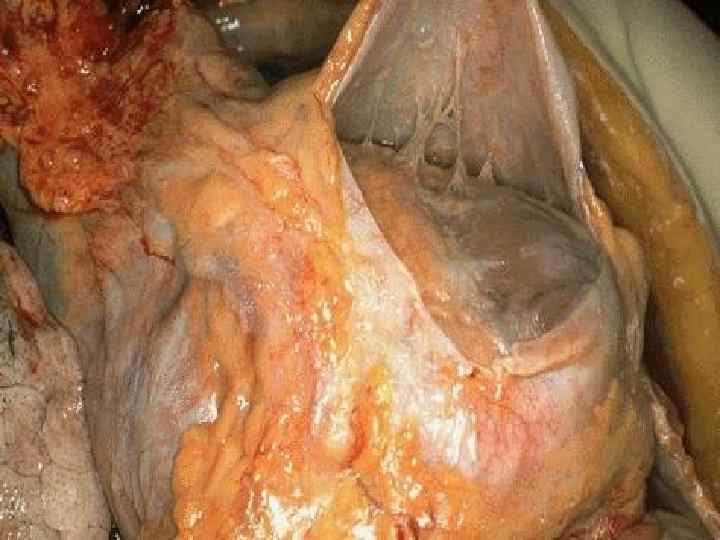
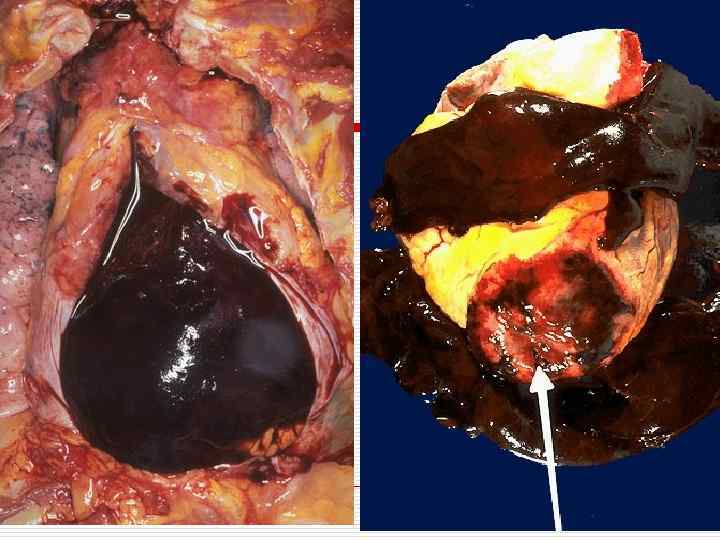
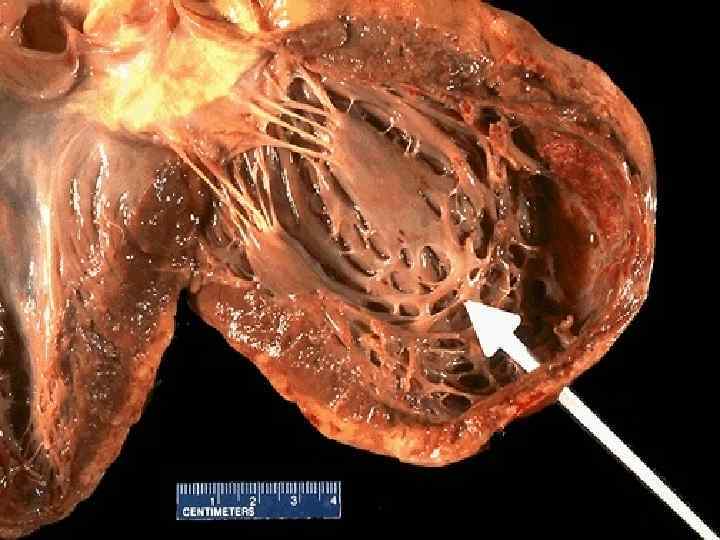
Chronic CHD o Atherosclerotic microfocal cardiosclerosis; o Postinfarction macrofocal cardiosclerosis; o Chronic cardiac aneurysm.
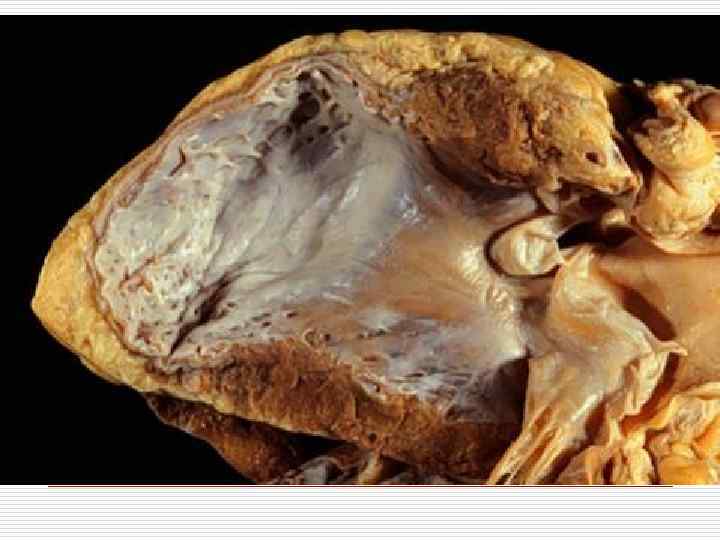
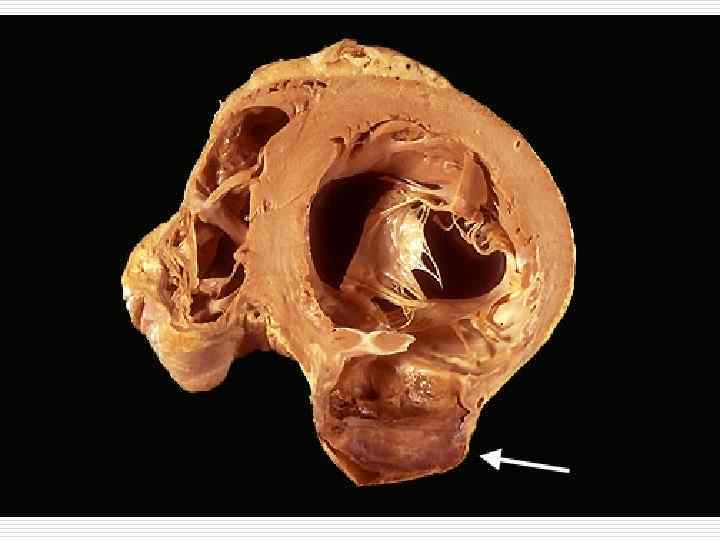
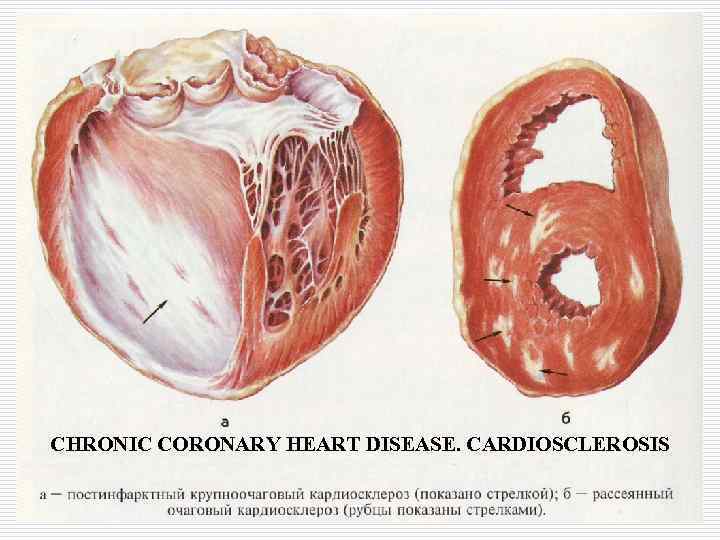
CHRONIC CORONARY HEART DISEASE. CARDIOSCLEROSIS
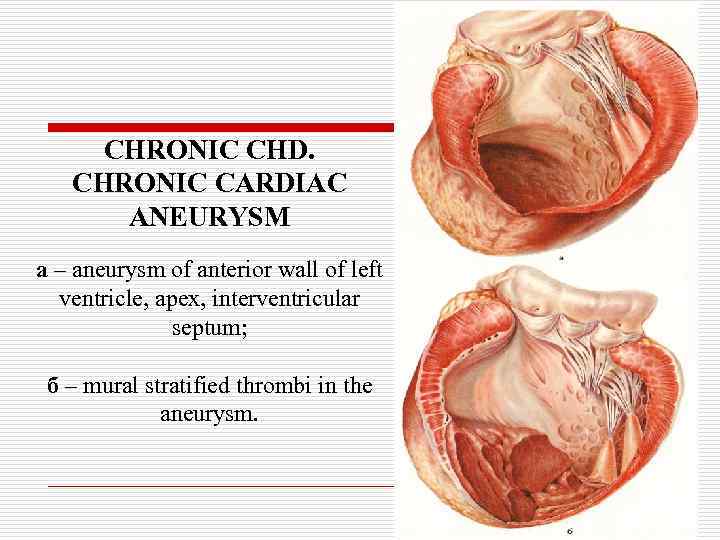
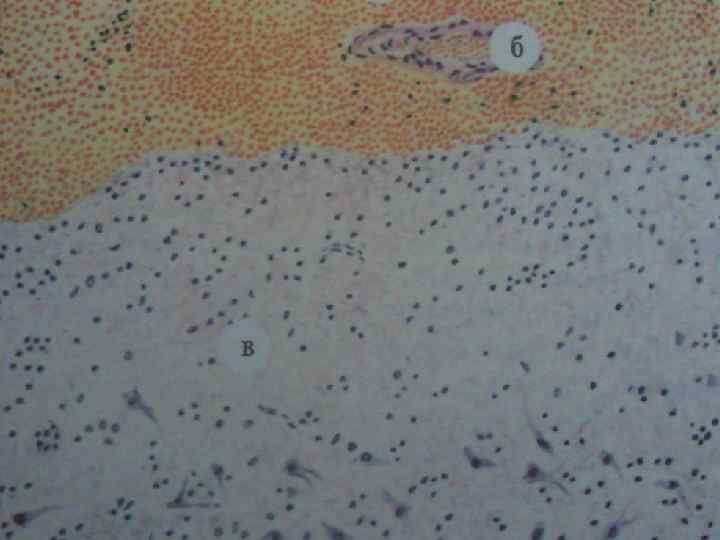
CHRONIC CHD. CHRONIC CARDIAC ANEURYSM а – aneurysm of anterior wall of left ventricle, apex, interventricular septum; б – mural stratified thrombi in the aneurysm.
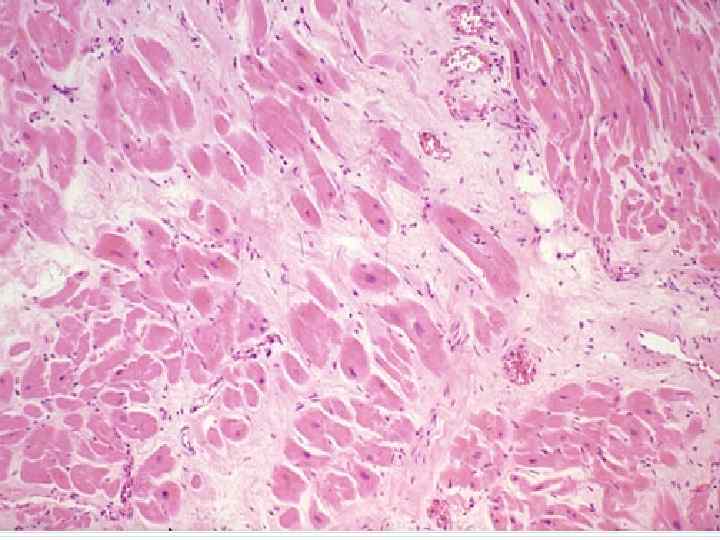
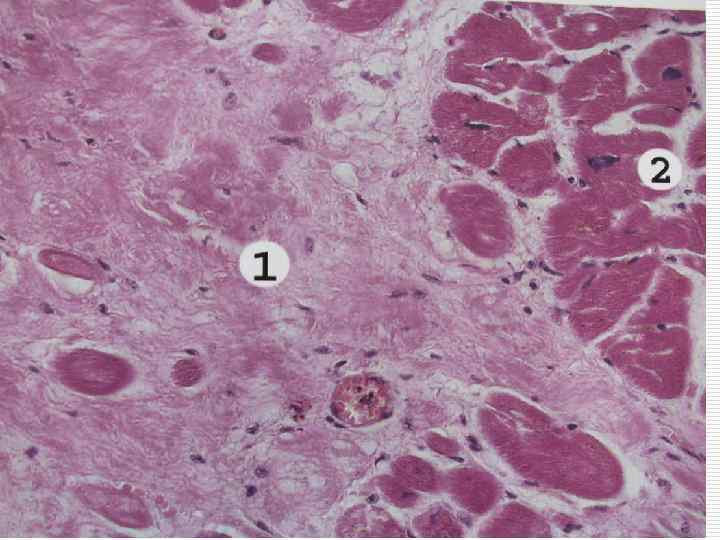

Cerebrovascular diseases o Essence: Acute derangements of cerebral circulation, background of which are atherosclerosis and essential hypertension o Background diseases: atherosclerosis, essential hypertension 1977

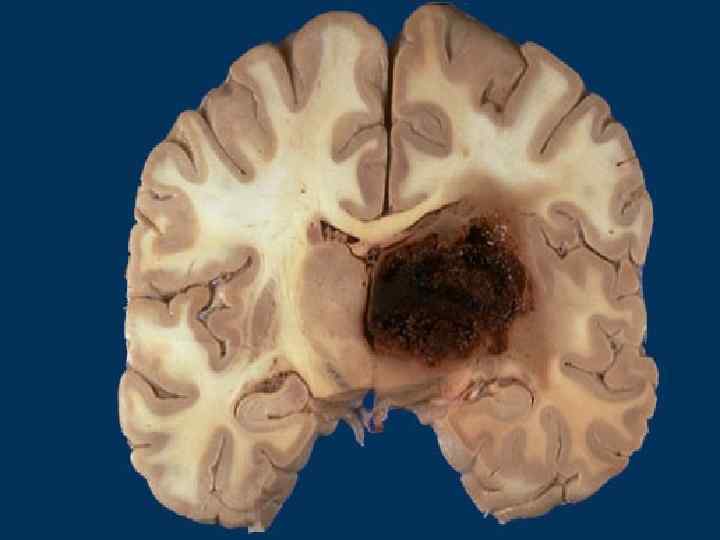
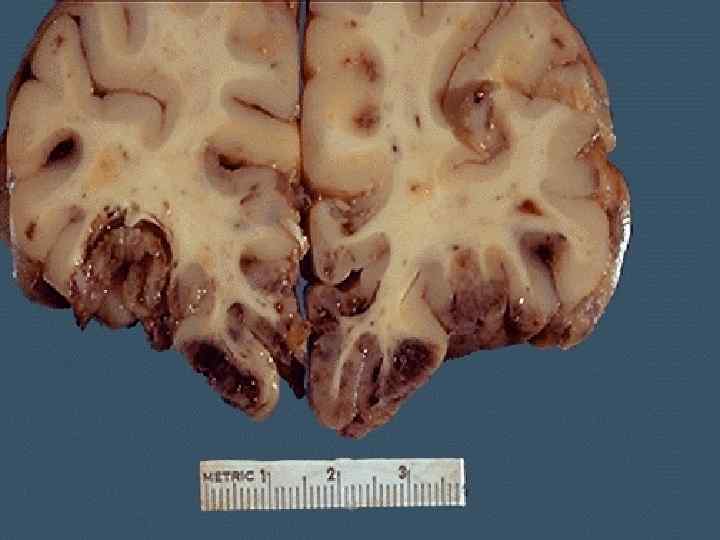
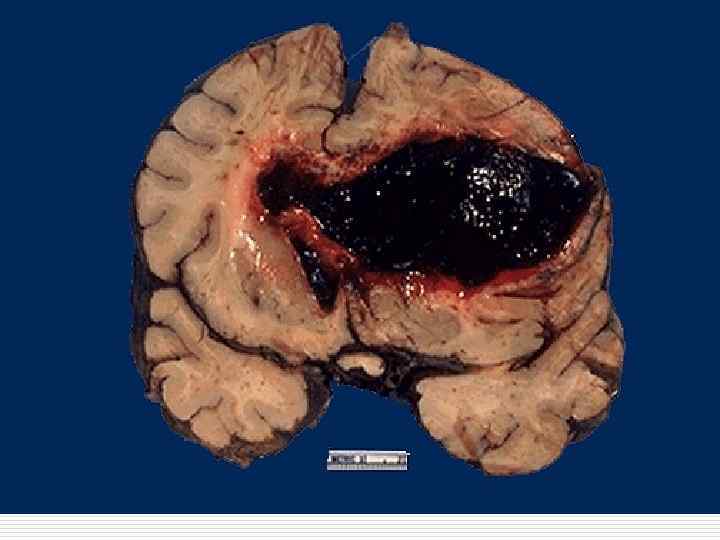
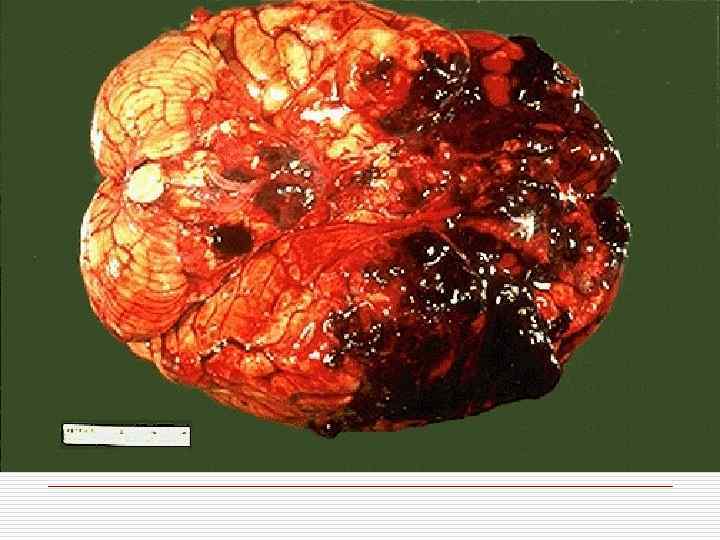
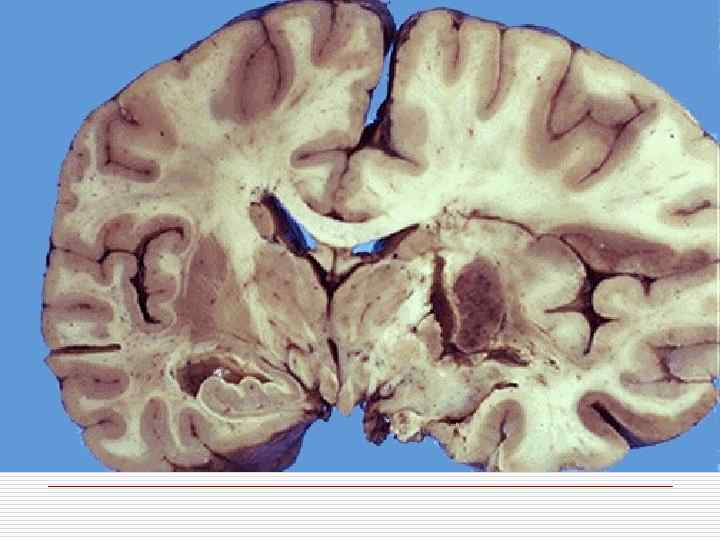
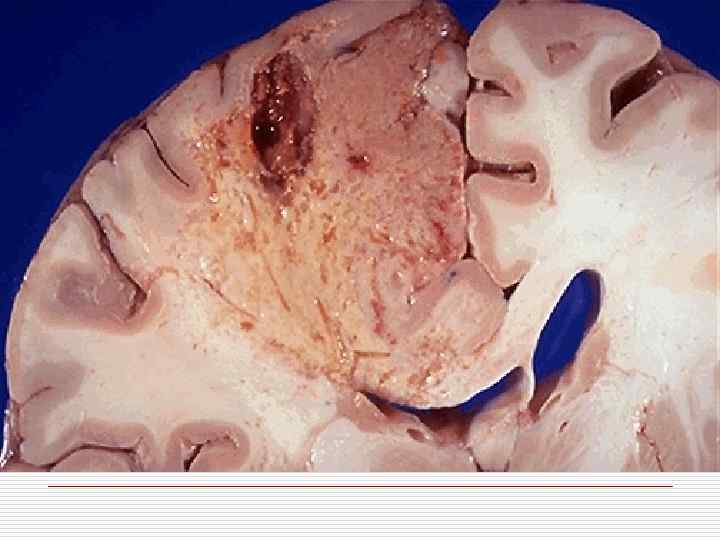
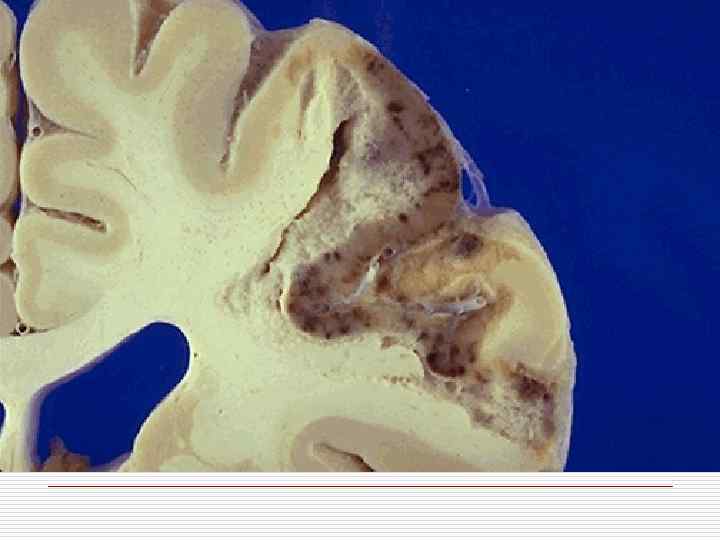
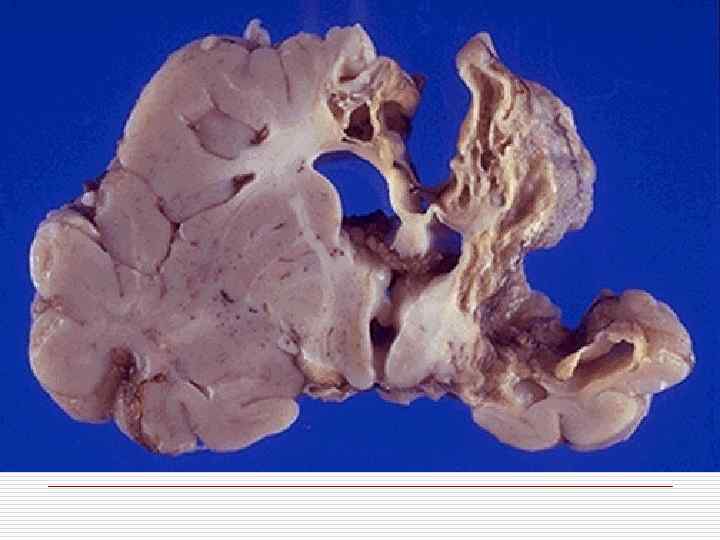
Classification of CVD With ischemic brain damage: o Ischemic encephalopathy; o Ischemic cerebral infarction; o Hemorrhagic cerebral infarction. Intracranial hemorrhages: o Intracerebral; o Subarachnoid; o Mixed.
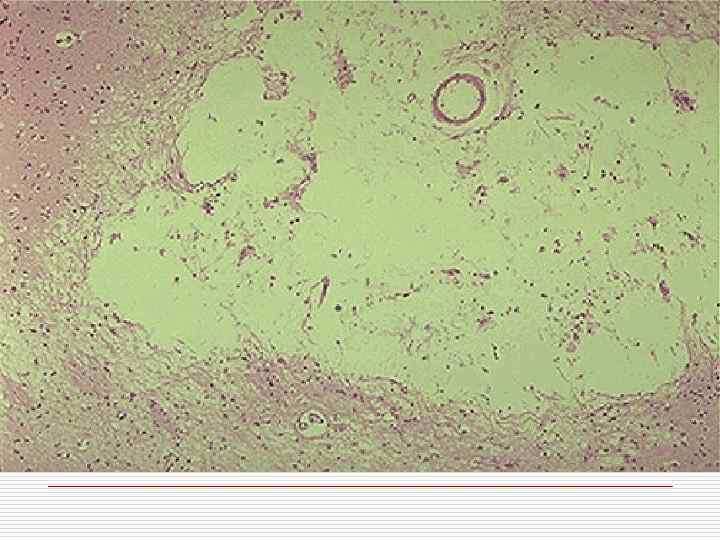
Ischemic brain damage mechanism o Stenosing atherosclerosis of cerebral arteries o Thrombosis, thromboembolism o Hemorrhagic component in ischemia zone is caused by erythrocytes diapedesis in demarcation zone
Intracranial hemorrhages mechanism o Rupture of pathologically transformed walls of cerebral arteries o Massive diapedesis of erythrocytes o Cerebral arteries aneurysms rupture
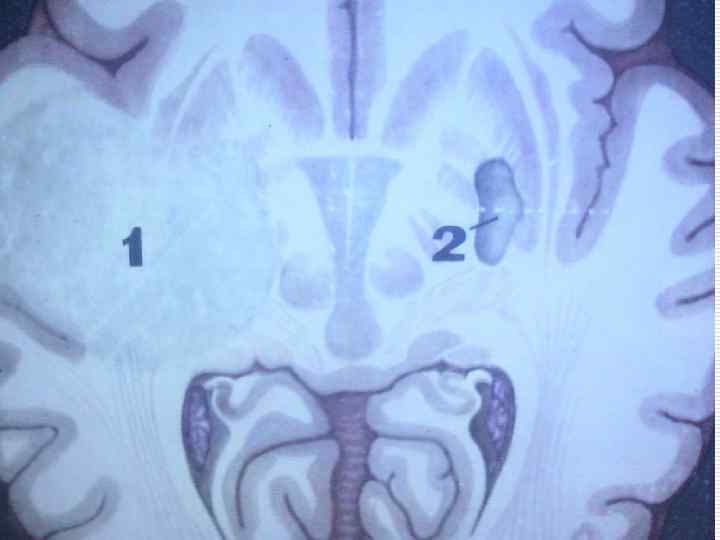
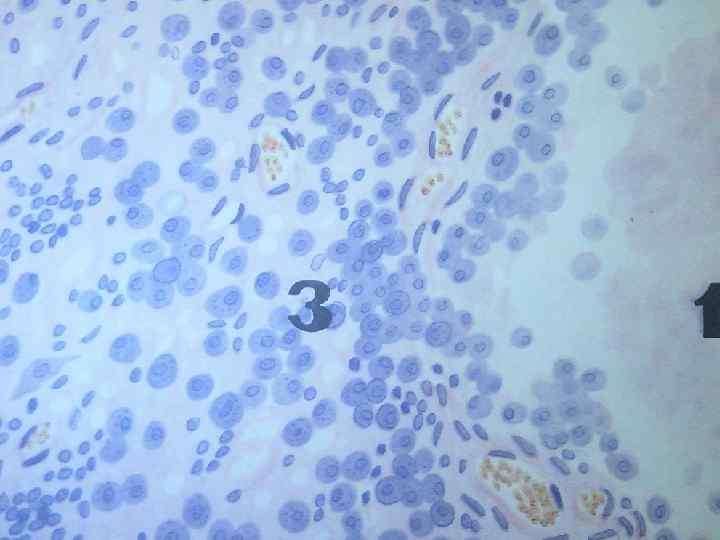

THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTION!!!
Лекция 15 ИБС, ЦВБ 2011.ppt