fe4a8786d30c669eb424e031f5727c10.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
 Lecture slides on: Computer Hardware Ports and Connectors Instructor Suleiman Mohammed, Institute of Computing & ICT, Ahmadu Bello University, , Zaria. citp(mcpn mncs)
Lecture slides on: Computer Hardware Ports and Connectors Instructor Suleiman Mohammed, Institute of Computing & ICT, Ahmadu Bello University, , Zaria. citp(mcpn mncs)
 Introduction n In the past connecting devices to your computer are at ease when we only use the keyboard, mouse, monitor and printers but now We have to deal with USB, Fire. Wire, network jacks and an assortment of audio and video connections. All those will be presented in this presentation Simple PC With only mouse keyboard and printer New types of Connectors USB are the for new devices as Technology grew most popular
Introduction n In the past connecting devices to your computer are at ease when we only use the keyboard, mouse, monitor and printers but now We have to deal with USB, Fire. Wire, network jacks and an assortment of audio and video connections. All those will be presented in this presentation Simple PC With only mouse keyboard and printer New types of Connectors USB are the for new devices as Technology grew most popular
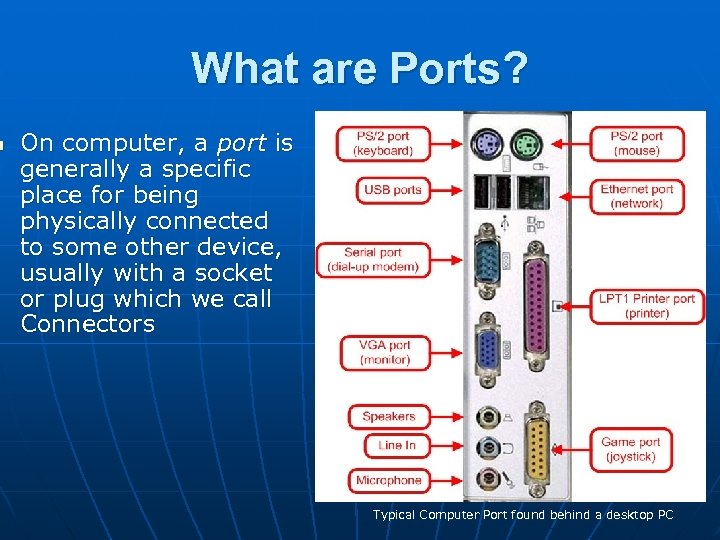 n What are Ports? On computer, a port is generally a specific place for being physically connected to some other device, usually with a socket or plug which we call Connectors n Typical Computer Port found behind a desktop PC
n What are Ports? On computer, a port is generally a specific place for being physically connected to some other device, usually with a socket or plug which we call Connectors n Typical Computer Port found behind a desktop PC
 What are Connectors? n A connector is any connector used within computers or to connect computers to networks, printers or other devices. Many types of computer connectors
What are Connectors? n A connector is any connector used within computers or to connect computers to networks, printers or other devices. Many types of computer connectors
 n The PS/2 Connector The PS/2 connector are use for connecting keyboard and mouse on the modern PCs. The PS 2 mouse connector and port is usually green in colour to distinguish it from the PS 2 keyboard, which is purple.
n The PS/2 Connector The PS/2 connector are use for connecting keyboard and mouse on the modern PCs. The PS 2 mouse connector and port is usually green in colour to distinguish it from the PS 2 keyboard, which is purple.
 The USB Port n Universal Serial Bus: a protocol for transferring data to and from digital devices. Many digital cameras and memory card readers connect to the USB port on a computer.
The USB Port n Universal Serial Bus: a protocol for transferring data to and from digital devices. Many digital cameras and memory card readers connect to the USB port on a computer.
 The Firewire IEEE 1394 Port n A type of cabling technology for transferring data to and from digital devices at high speed. Fire. Wire are typically faster than those that connect via USB.
The Firewire IEEE 1394 Port n A type of cabling technology for transferring data to and from digital devices at high speed. Fire. Wire are typically faster than those that connect via USB.
 The RJ 45 Ethernet Port n n LAN or (Local Area Network) uses a CAT 5 cable and a RJ 45 connection. The CAT 5 cable is also called the Ethernet Cable. Network connection generally uses a 10/100 Mbps speed. This means it has two different speeds 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps.
The RJ 45 Ethernet Port n n LAN or (Local Area Network) uses a CAT 5 cable and a RJ 45 connection. The CAT 5 cable is also called the Ethernet Cable. Network connection generally uses a 10/100 Mbps speed. This means it has two different speeds 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps.
 DB 25 Parallel Port n n The printer connects to your computer with a Parallel connector. This connector has 25 pins. Parallel means the device is capable of receiving more than one bit at a time (that is, it receives several bits in parallel).
DB 25 Parallel Port n n The printer connects to your computer with a Parallel connector. This connector has 25 pins. Parallel means the device is capable of receiving more than one bit at a time (that is, it receives several bits in parallel).
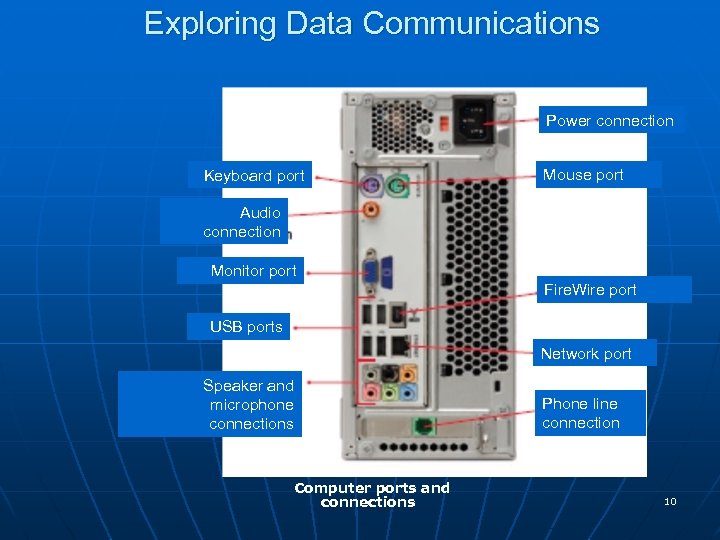 Exploring Data Communications Power connection Keyboard port Mouse port Audio connection Monitor port Fire. Wire port USB ports Network port Speaker and microphone connections Computer ports and connections Phone line connection 10
Exploring Data Communications Power connection Keyboard port Mouse port Audio connection Monitor port Fire. Wire port USB ports Network port Speaker and microphone connections Computer ports and connections Phone line connection 10
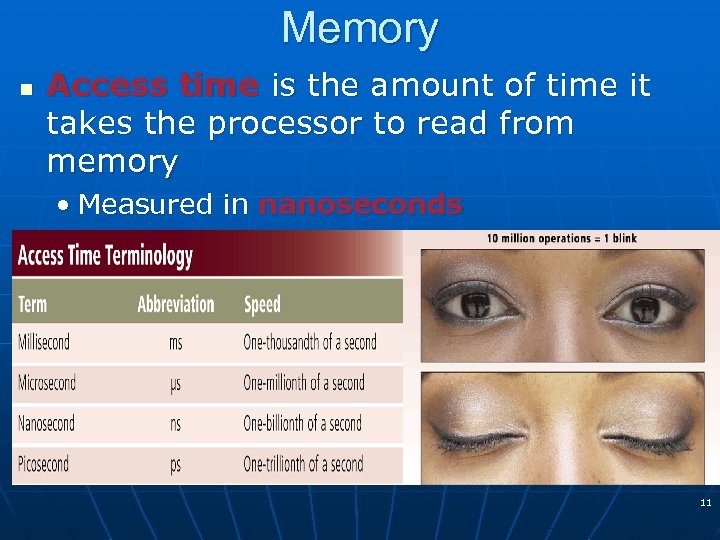 Memory n Access time is the amount of time it takes the processor to read from memory • Measured in nanoseconds 11
Memory n Access time is the amount of time it takes the processor to read from memory • Measured in nanoseconds 11
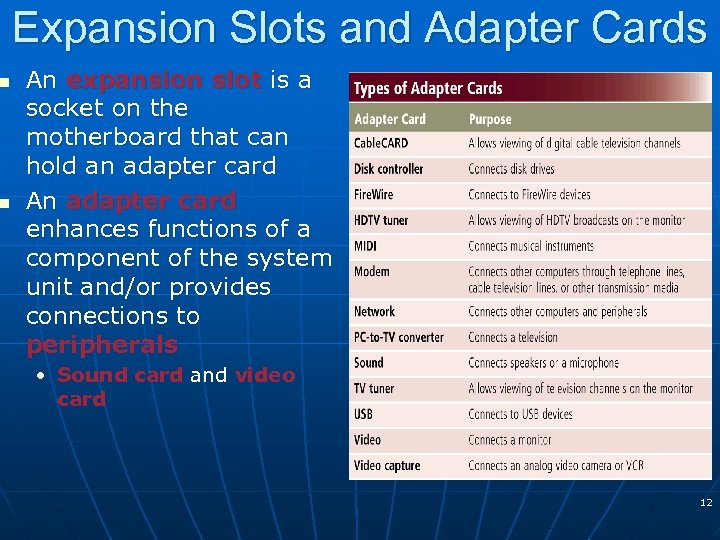 n n Expansion Slots and Adapter Cards An expansion slot is a socket on the motherboard that can hold an adapter card An adapter card enhances functions of a component of the system unit and/or provides connections to peripherals • Sound card and video card 12
n n Expansion Slots and Adapter Cards An expansion slot is a socket on the motherboard that can hold an adapter card An adapter card enhances functions of a component of the system unit and/or provides connections to peripherals • Sound card and video card 12
 Expansion Slots and Adapter Cards n With Plug and Play, the computer automatically can configure adapter cards and other peripherals as you install them 13
Expansion Slots and Adapter Cards n With Plug and Play, the computer automatically can configure adapter cards and other peripherals as you install them 13
 Expansion Slots and Adapter Cards n Removable flash memory includes: • Memory cards, USB flash drives, and PC Cards/Express. Card modules 14
Expansion Slots and Adapter Cards n Removable flash memory includes: • Memory cards, USB flash drives, and PC Cards/Express. Card modules 14
 Ports and Connectors A port is the point at which a peripheral attaches to or communicates with a system unit (sometimes referred to as a jack) A connector joins a cable to a port 15
Ports and Connectors A port is the point at which a peripheral attaches to or communicates with a system unit (sometimes referred to as a jack) A connector joins a cable to a port 15
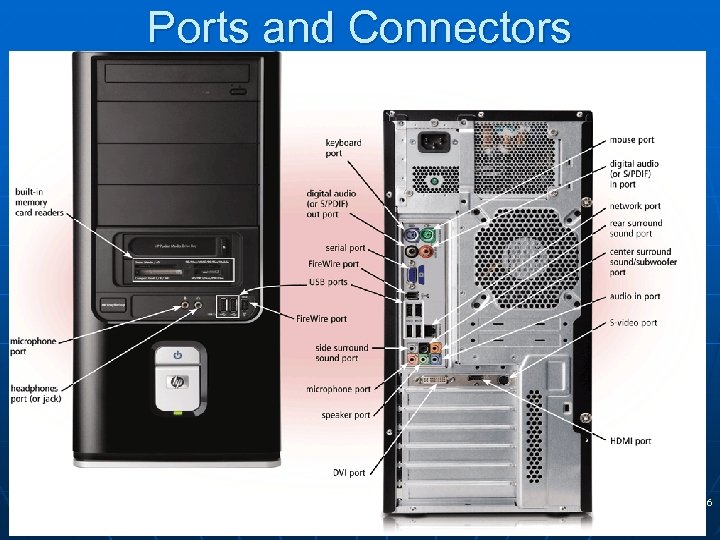 Ports and Connectors 16
Ports and Connectors 16
 Ports and Connectors n On a notebook computer, the ports are on the back, front, and/or sides 17
Ports and Connectors n On a notebook computer, the ports are on the back, front, and/or sides 17
 Ports and Connectors 18
Ports and Connectors 18
 Ports and Connectors n A USB port can connect up to 127 different peripherals together with a single connector • You can attach multiple peripherals using a single USB port with a USB hub 19
Ports and Connectors n A USB port can connect up to 127 different peripherals together with a single connector • You can attach multiple peripherals using a single USB port with a USB hub 19
 Ports and Connectors n Other types of ports include: Firewire port Bluetooth port SCSI port e. SATA port Ir. DA port Serial port MIDI port 20
Ports and Connectors n Other types of ports include: Firewire port Bluetooth port SCSI port e. SATA port Ir. DA port Serial port MIDI port 20
 Ports and Connectors A Bluetooth wireless port adapter converts a USB port into a Bluetooth port A smart phone might communicate with a notebook computer using an Ir. DA port 21
Ports and Connectors A Bluetooth wireless port adapter converts a USB port into a Bluetooth port A smart phone might communicate with a notebook computer using an Ir. DA port 21
 Ports and Connectors n n A port replicator is an external device that provides connections to peripherals through ports built into the device A docking station is an external device that attaches to a mobile computer or device 22
Ports and Connectors n n A port replicator is an external device that provides connections to peripherals through ports built into the device A docking station is an external device that attaches to a mobile computer or device 22
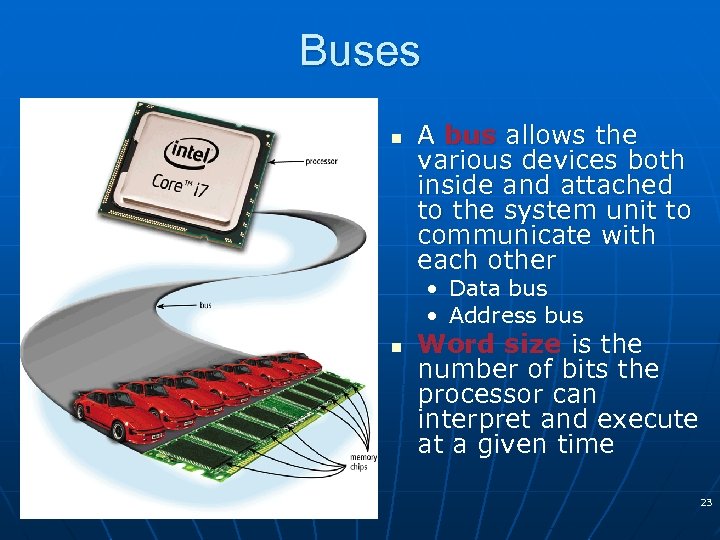 Buses n A bus allows the various devices both inside and attached to the system unit to communicate with each other • Data bus • Address bus n Word size is the number of bits the processor can interpret and execute at a given time 23
Buses n A bus allows the various devices both inside and attached to the system unit to communicate with each other • Data bus • Address bus n Word size is the number of bits the processor can interpret and execute at a given time 23
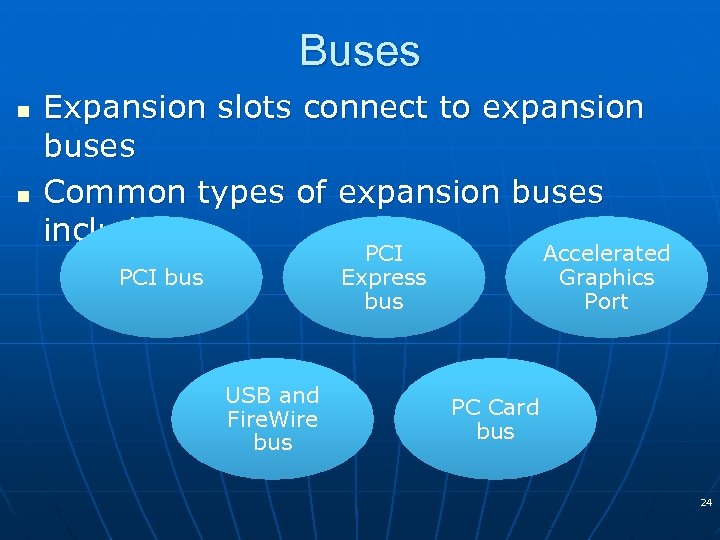 Buses n n Expansion slots connect to expansion buses Common types of expansion buses include: PCI Express bus PCI bus USB and Fire. Wire bus Accelerated Graphics Port PC Card bus 24
Buses n n Expansion slots connect to expansion buses Common types of expansion buses include: PCI Express bus PCI bus USB and Fire. Wire bus Accelerated Graphics Port PC Card bus 24
 Bays n A bay is an opening inside the system unit in which you can install additional equipment • A drive bay typically holds disk drives 25
Bays n A bay is an opening inside the system unit in which you can install additional equipment • A drive bay typically holds disk drives 25
 Cache Memory n n n Very fast memory used to improve the speed of a computer, doubling it in some cases Acts as an intermediate store between the CPU and main memory Stores the most frequently or recently used instructions and data for rapid retrieval n Generally between 1 Kb and 512 Kb n Much more expensive than normal RAM
Cache Memory n n n Very fast memory used to improve the speed of a computer, doubling it in some cases Acts as an intermediate store between the CPU and main memory Stores the most frequently or recently used instructions and data for rapid retrieval n Generally between 1 Kb and 512 Kb n Much more expensive than normal RAM
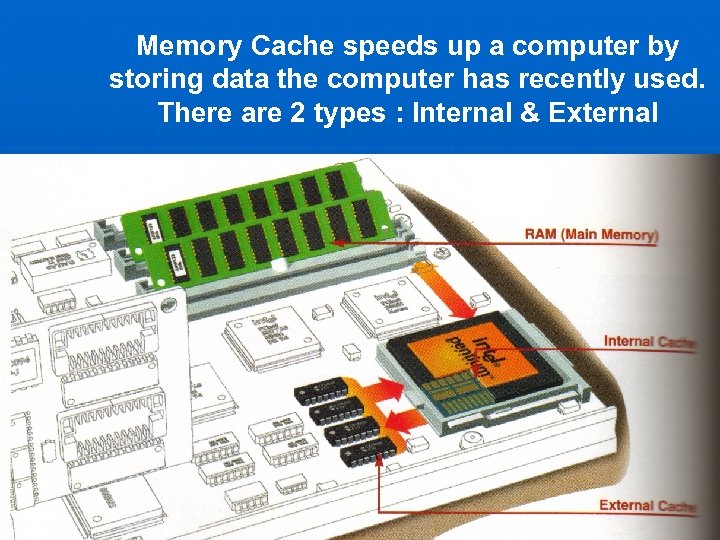 Memory Cache speeds up a computer by storing data the computer has recently used. There are 2 types : Internal & External
Memory Cache speeds up a computer by storing data the computer has recently used. There are 2 types : Internal & External
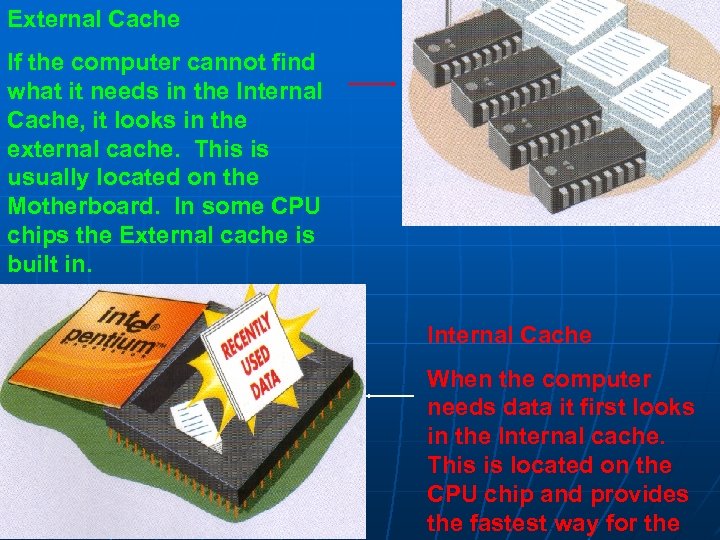 External Cache If the computer cannot find what it needs in the Internal Cache, it looks in the external cache. This is usually located on the Motherboard. In some CPU chips the External cache is built in. Internal Cache When the computer needs data it first looks in the Internal cache. This is located on the CPU chip and provides the fastest way for the
External Cache If the computer cannot find what it needs in the Internal Cache, it looks in the external cache. This is usually located on the Motherboard. In some CPU chips the External cache is built in. Internal Cache When the computer needs data it first looks in the Internal cache. This is located on the CPU chip and provides the fastest way for the
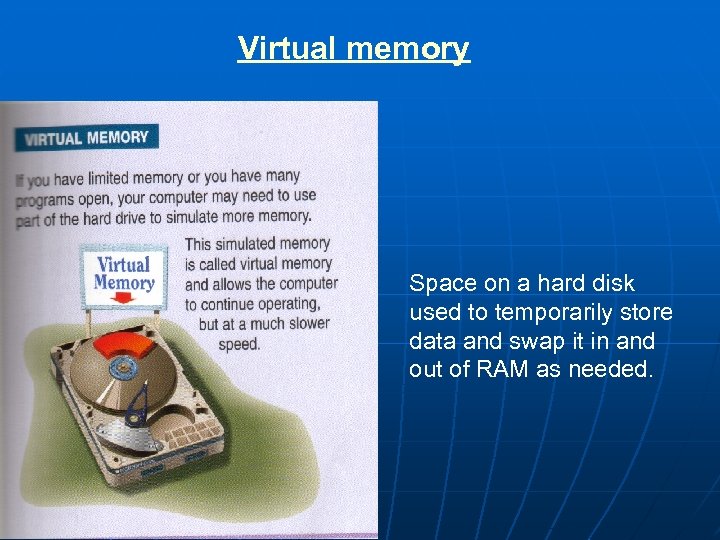 Virtual memory Space on a hard disk used to temporarily store data and swap it in and out of RAM as needed.
Virtual memory Space on a hard disk used to temporarily store data and swap it in and out of RAM as needed.
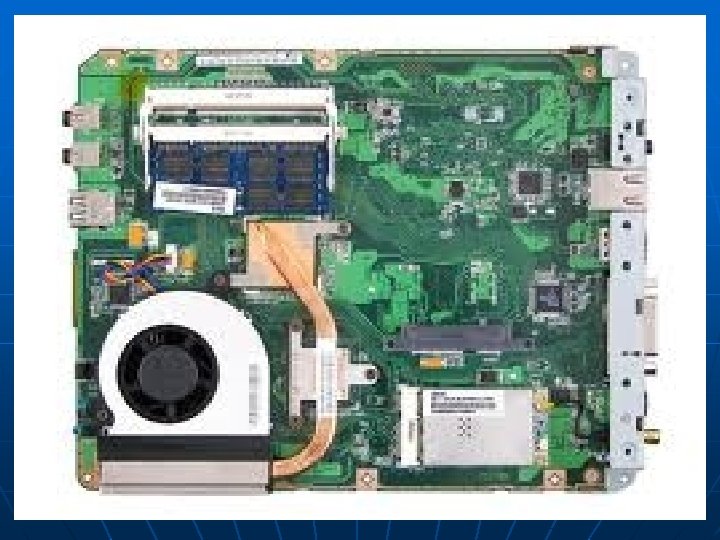
 Motherboard This is the main circuit board that all of the other internal components connect to. The CPU and memory are usually on the motherboard. Other systems may be found directly on the motherboard or connected to it through a secondary connection. For example, a sound card can be built into the motherboard or connected through PCI (Peripheral Component Interface).
Motherboard This is the main circuit board that all of the other internal components connect to. The CPU and memory are usually on the motherboard. Other systems may be found directly on the motherboard or connected to it through a secondary connection. For example, a sound card can be built into the motherboard or connected through PCI (Peripheral Component Interface).

 Auxiliary Storage Hard disks - all standalone PCs have in-built hard disk - typical capacity for Pentium PC is >= 40 Gb - used for storing software including the operating system, other systems software, application programs and data n Floppy disks - thin sheet of mylar plastic in hard 3½” casing - capacity 1. 44 Mb n CD-ROM - holds about 700 Mb n Zip disks - hold up to 250 Mb n
Auxiliary Storage Hard disks - all standalone PCs have in-built hard disk - typical capacity for Pentium PC is >= 40 Gb - used for storing software including the operating system, other systems software, application programs and data n Floppy disks - thin sheet of mylar plastic in hard 3½” casing - capacity 1. 44 Mb n CD-ROM - holds about 700 Mb n Zip disks - hold up to 250 Mb n
 Power supply An electrical transformer regulates the electricity used by the computer. Hard disk This is large-capacity permanent storage used to hold information such as programs and documents. Operating system This is the basic software that allows the user to interface with the computer.
Power supply An electrical transformer regulates the electricity used by the computer. Hard disk This is large-capacity permanent storage used to hold information such as programs and documents. Operating system This is the basic software that allows the user to interface with the computer.
 Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) Controller This is the primary interface for the hard drive, CDROM and floppy disk drive. Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Bus The most common way to connect additional components to the computer, PCI uses a series of slots on the motherboard that PCI cards plug into. SCSI Pronounced "scuzzy, " the small computer system interface is a method of adding additional devices, such as hard drives or scanners, to the computer.
Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) Controller This is the primary interface for the hard drive, CDROM and floppy disk drive. Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Bus The most common way to connect additional components to the computer, PCI uses a series of slots on the motherboard that PCI cards plug into. SCSI Pronounced "scuzzy, " the small computer system interface is a method of adding additional devices, such as hard drives or scanners, to the computer.
 AGP Accelerated Graphics Port is a very high-speed connection used by the graphics card to interface with the computer. Sound card This is used by the computer to record and play audio by converting analog sound into digital information and back again. Graphics card - This translates image data from the computer into a format that can be displayed by the monitor.
AGP Accelerated Graphics Port is a very high-speed connection used by the graphics card to interface with the computer. Sound card This is used by the computer to record and play audio by converting analog sound into digital information and back again. Graphics card - This translates image data from the computer into a format that can be displayed by the monitor.
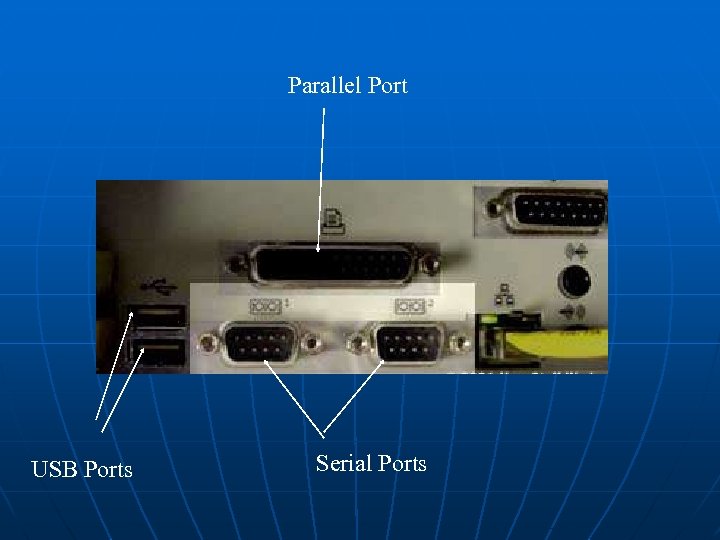 Parallel Port USB Ports Serial Ports
Parallel Port USB Ports Serial Ports
 SERIAL PORT Considered to be one of the most basic external connections to a computer, the serial port has been an integral part of most computers for more than 20 years. Although many of the newer systems have done away with the serial port completely in favor of USB connections, most modems still use the serial port, as do some printers, PDAs and digital cameras. Few computers have more than two serial ports.
SERIAL PORT Considered to be one of the most basic external connections to a computer, the serial port has been an integral part of most computers for more than 20 years. Although many of the newer systems have done away with the serial port completely in favor of USB connections, most modems still use the serial port, as do some printers, PDAs and digital cameras. Few computers have more than two serial ports.
 Parallel Ports If you have a printer connected to your computer, there is a good chance that it uses the parallel port. While USB is becoming increasingly popular, the parallel port is still a commonly used interface for printers. Parallel ports can be used to connect a host of popular computer peripherals: • Printers • Scanners • CD burners • External hard drives • Iomega Zip removable drives • Network adapters • Tape backup drives
Parallel Ports If you have a printer connected to your computer, there is a good chance that it uses the parallel port. While USB is becoming increasingly popular, the parallel port is still a commonly used interface for printers. Parallel ports can be used to connect a host of popular computer peripherals: • Printers • Scanners • CD burners • External hard drives • Iomega Zip removable drives • Network adapters • Tape backup drives
 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Ports The goal of USB is to end all of these headaches. The Universal Serial Bus gives you a single, standardized, easy-to-use way to connect up to 127 devices to a computer. Just about every peripheral made now comes in a USB version. A sample list of USB devices that you can buy today includes: Printers Scanners Mice Joysticks Flight yokes Digital cameras Webcams Scientific data acquisition devices Modems Speakers Telephones Storage devices such as Zip drives Video phones Network connections Connecting a USB device to a computer is simple -- you find the USB connector on the back of your machine and plug the USB connector into it.
Universal Serial Bus (USB) Ports The goal of USB is to end all of these headaches. The Universal Serial Bus gives you a single, standardized, easy-to-use way to connect up to 127 devices to a computer. Just about every peripheral made now comes in a USB version. A sample list of USB devices that you can buy today includes: Printers Scanners Mice Joysticks Flight yokes Digital cameras Webcams Scientific data acquisition devices Modems Speakers Telephones Storage devices such as Zip drives Video phones Network connections Connecting a USB device to a computer is simple -- you find the USB connector on the back of your machine and plug the USB connector into it.
 The rectangular socket is a typical USB socket on the back of a PC. A typical "B" connection A typical USB connector, called an "A" connection
The rectangular socket is a typical USB socket on the back of a PC. A typical "B" connection A typical USB connector, called an "A" connection
 Input and output devices n Input devices - Keyboard - mouse - barcode readers - Scanners Output devices - printer - plotter - VDU Can you name some others? n
Input and output devices n Input devices - Keyboard - mouse - barcode readers - Scanners Output devices - printer - plotter - VDU Can you name some others? n
 Power Supply The power supply converts the wall outlet AC power into DC power Some external peripherals have an AC adapter, which is an external power supply 42
Power Supply The power supply converts the wall outlet AC power into DC power Some external peripherals have an AC adapter, which is an external power supply 42
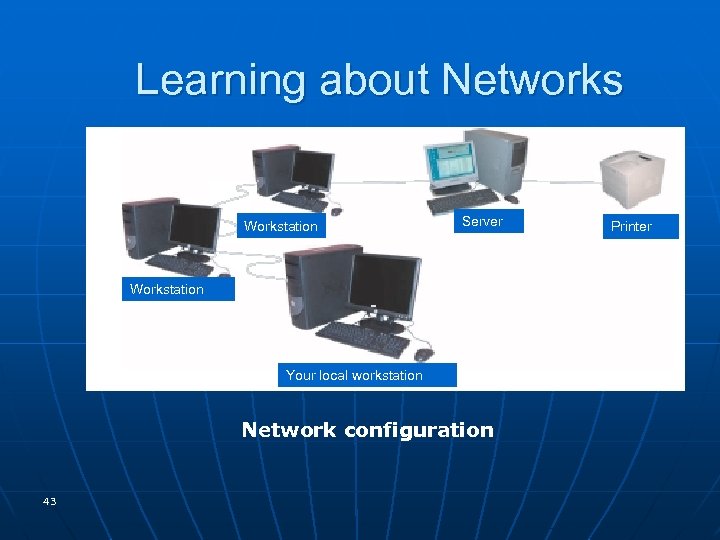 Learning about Networks Workstation Server Workstation Your local workstation Network configuration 43 Printer
Learning about Networks Workstation Server Workstation Your local workstation Network configuration 43 Printer
 Learning about Networks n LAN (local area network) • computers and peripherals located close to each other n WAN (wide area network) • more than one LAN connected together • the Internet is the largest example of a WAN n WLAN (wireless local area network) • computers and peripherals that use high-frequency radio waves instead of wires to communicate and connect in a network • Wi-Fi (wireless fidelity) describes WLANs connected using a standard radio frequency established by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 44
Learning about Networks n LAN (local area network) • computers and peripherals located close to each other n WAN (wide area network) • more than one LAN connected together • the Internet is the largest example of a WAN n WLAN (wireless local area network) • computers and peripherals that use high-frequency radio waves instead of wires to communicate and connect in a network • Wi-Fi (wireless fidelity) describes WLANs connected using a standard radio frequency established by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 44
 Learning about Networks n PAN (personal area network)—a network that )— allows two or more devices located close to each other to communicate or to connect a device to the Internet • infrared technology—uses infrared light waves to beam data from one device to another • Bluetooth—uses short range radio waves to connect a device wirelessly to another device or to the Internet n 45 Wi. MAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) • allows computers to connect over many miles to a LAN • a Wi. MAX tower sends signals to a Wi. MAX receiver built or plugged into a computer
Learning about Networks n PAN (personal area network)—a network that )— allows two or more devices located close to each other to communicate or to connect a device to the Internet • infrared technology—uses infrared light waves to beam data from one device to another • Bluetooth—uses short range radio waves to connect a device wirelessly to another device or to the Internet n 45 Wi. MAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) • allows computers to connect over many miles to a LAN • a Wi. MAX tower sends signals to a Wi. MAX receiver built or plugged into a computer
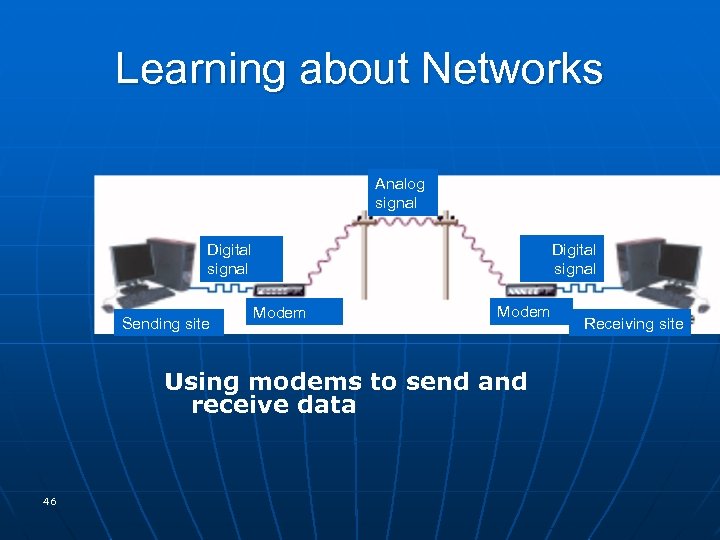 Learning about Networks Analog signal Digital signal Sending site Modem Using modems to send and receive data 46 Receiving site
Learning about Networks Analog signal Digital signal Sending site Modem Using modems to send and receive data 46 Receiving site
 Learning about Security Threats n 47 Security • refers to the steps a computer owner takes to prevent unauthorized use of or damage to the computer
Learning about Security Threats n 47 Security • refers to the steps a computer owner takes to prevent unauthorized use of or damage to the computer
 n n 48 Learning about Security Threats Malware • describes any program that is intended to cause harm or convey information to others without the owner’s permission Viruses • harmful programs that instruct your computer to perform destructive activities, such as erasing a disk drive • Antivirus software (virus protection software) searches executable files for the sequences of characters that may cause harm and disinfects the files by erasing or disabling those commands
n n 48 Learning about Security Threats Malware • describes any program that is intended to cause harm or convey information to others without the owner’s permission Viruses • harmful programs that instruct your computer to perform destructive activities, such as erasing a disk drive • Antivirus software (virus protection software) searches executable files for the sequences of characters that may cause harm and disinfects the files by erasing or disabling those commands
 Learning about Security Threats n n 49 Spyware • programs contained with other programs that track a computer user’s Internet usage and send this data back to the company or person that created it • usually installed without the computer user’s permission or knowledge • Anti-spyware software detects spyware and deletes them Adware • software installed with another program usually with the user’s permission • generates advertising revenue for the program’s creator by displaying targeted ads to the program’s user
Learning about Security Threats n n 49 Spyware • programs contained with other programs that track a computer user’s Internet usage and send this data back to the company or person that created it • usually installed without the computer user’s permission or knowledge • Anti-spyware software detects spyware and deletes them Adware • software installed with another program usually with the user’s permission • generates advertising revenue for the program’s creator by displaying targeted ads to the program’s user
 Learning about Security Threats n Firewall • prevents other computers on the Internet from accessing a computer and prevents programs on a computer from accessing the Internet without the computer user’s permission • can be either hardware or software • router n n 50 a device that controls traffic between network components usually has a built-in firewall. • software firewalls track all incoming and outgoing traffic
Learning about Security Threats n Firewall • prevents other computers on the Internet from accessing a computer and prevents programs on a computer from accessing the Internet without the computer user’s permission • can be either hardware or software • router n n 50 a device that controls traffic between network components usually has a built-in firewall. • software firewalls track all incoming and outgoing traffic
 Learning about Security Threats n n n 51 Spoofed site • a Web site set up to look like another Web site, but which does not belong to the organization portrayed in the site • the URL (address on the Web) looks similar to a URL from the legitimate site • usually set up to try to convince customers of the real site to enter personal information Phishing • the practice of sending e-mails to customers or potential customers of a legitimate Web site asking them to click a link in the e-mail • the link leads to a spoofed site Pharming • when a criminal breaks into a DNS server (a computer responsible for directing Internet traffic) and redirect any attempts to access a particular Web site to the criminal’s spoofed site
Learning about Security Threats n n n 51 Spoofed site • a Web site set up to look like another Web site, but which does not belong to the organization portrayed in the site • the URL (address on the Web) looks similar to a URL from the legitimate site • usually set up to try to convince customers of the real site to enter personal information Phishing • the practice of sending e-mails to customers or potential customers of a legitimate Web site asking them to click a link in the e-mail • the link leads to a spoofed site Pharming • when a criminal breaks into a DNS server (a computer responsible for directing Internet traffic) and redirect any attempts to access a particular Web site to the criminal’s spoofed site
 Protecting Information with Passwords n n 52 Logging in • signing in with a user name and password Strong password • at least eight characters • consists of upper- and lowercase letters and numbers • does not include common personal information
Protecting Information with Passwords n n 52 Logging in • signing in with a user name and password Strong password • at least eight characters • consists of upper- and lowercase letters and numbers • does not include common personal information
 End of Presentation Thank you
End of Presentation Thank you



