4128254760e0779db6bed1c9fc939905.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56
 Lecture Power. Points Chapter 20 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Lecture Power. Points Chapter 20 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 20 Second Law of Thermodynamics Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Chapter 20 Second Law of Thermodynamics Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Units of Chapter 20 • The Second Law of Thermodynamics— Introduction • Heat Engines • Reversible and Irreversible Processes; the Carnot Engine • Refrigerators, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps • Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Units of Chapter 20 • The Second Law of Thermodynamics— Introduction • Heat Engines • Reversible and Irreversible Processes; the Carnot Engine • Refrigerators, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps • Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Units of Chapter 20 • Order to Disorder • Unavailability of Energy; Heat Death • Statistical Interpretation of Entropy and the Second Law • Thermodynamic Temperature; Third Law of Thermodynamics • Thermal Pollution, Global Warming, and Energy Resources Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Units of Chapter 20 • Order to Disorder • Unavailability of Energy; Heat Death • Statistical Interpretation of Entropy and the Second Law • Thermodynamic Temperature; Third Law of Thermodynamics • Thermal Pollution, Global Warming, and Energy Resources Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -1 The Second Law of Thermodynamics—Introduction The first law of thermodynamics tells us that energy is conserved. However, the absence of the process illustrated above indicates that conservation of energy is not the whole story. If it were, movies run backwards would look perfectly normal to us! Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -1 The Second Law of Thermodynamics—Introduction The first law of thermodynamics tells us that energy is conserved. However, the absence of the process illustrated above indicates that conservation of energy is not the whole story. If it were, movies run backwards would look perfectly normal to us! Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -1 The Second Law of Thermodynamics—Introduction The second law of thermodynamics is a statement about which processes occur and which do not. There are many ways to state the second law; here is one: Heat can flow spontaneously from a hot object to a cold object; it will not flow spontaneously from a cold object to a hot object. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -1 The Second Law of Thermodynamics—Introduction The second law of thermodynamics is a statement about which processes occur and which do not. There are many ways to state the second law; here is one: Heat can flow spontaneously from a hot object to a cold object; it will not flow spontaneously from a cold object to a hot object. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
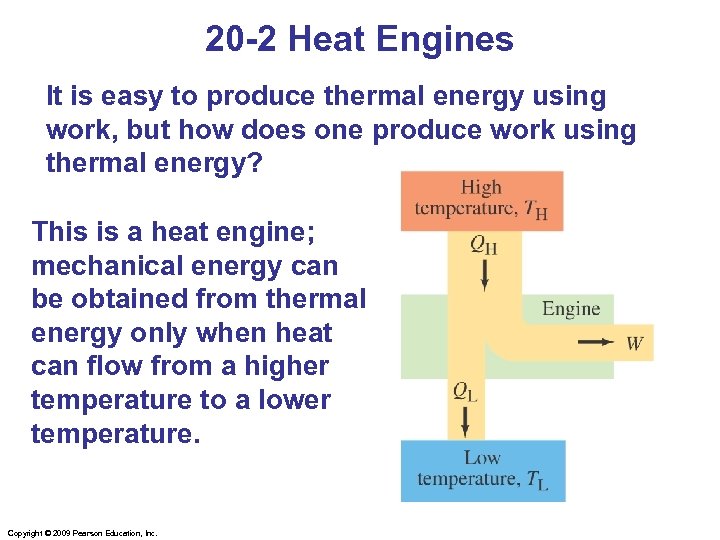 20 -2 Heat Engines It is easy to produce thermal energy using work, but how does one produce work using thermal energy? This is a heat engine; mechanical energy can be obtained from thermal energy only when heat can flow from a higher temperature to a lower temperature. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -2 Heat Engines It is easy to produce thermal energy using work, but how does one produce work using thermal energy? This is a heat engine; mechanical energy can be obtained from thermal energy only when heat can flow from a higher temperature to a lower temperature. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -2 Heat Engines We will discuss only engines that run in a repeating cycle; the change in internal energy over a cycle is zero, as the system returns to its initial state. The high-temperature reservoir transfers an amount of heat QH to the engine, where part of it is transformed into work W and the rest, QL, is exhausted to the lower temperature reservoir. Note that all three of these quantities are positive. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -2 Heat Engines We will discuss only engines that run in a repeating cycle; the change in internal energy over a cycle is zero, as the system returns to its initial state. The high-temperature reservoir transfers an amount of heat QH to the engine, where part of it is transformed into work W and the rest, QL, is exhausted to the lower temperature reservoir. Note that all three of these quantities are positive. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
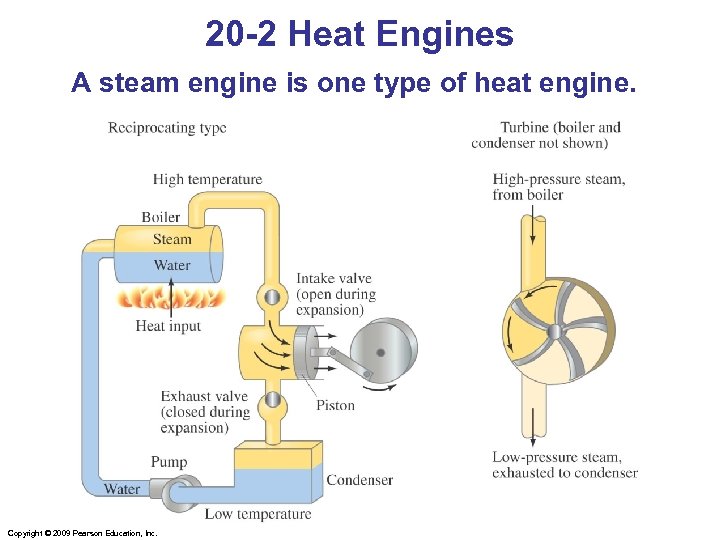 20 -2 Heat Engines A steam engine is one type of heat engine. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -2 Heat Engines A steam engine is one type of heat engine. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
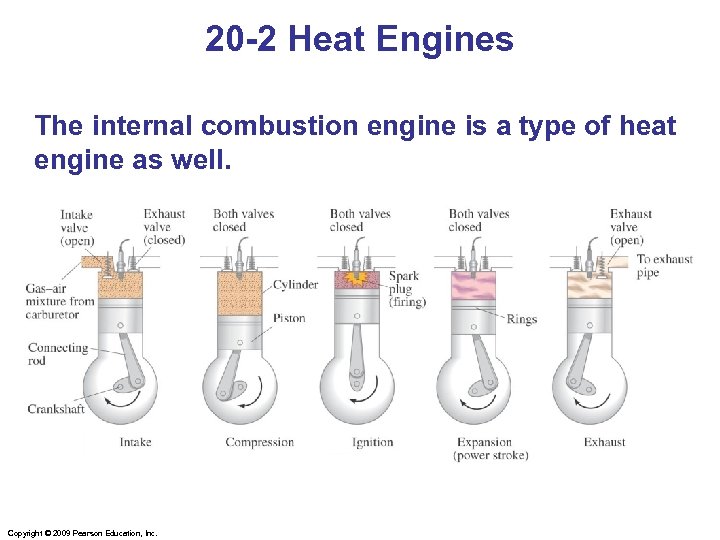 20 -2 Heat Engines The internal combustion engine is a type of heat engine as well. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -2 Heat Engines The internal combustion engine is a type of heat engine as well. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -2 Heat Engines Why does a heat engine need a temperature difference? Otherwise the work done on the system in one part of the cycle would be equal to the work done by the system in another part, and the net work would be zero. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -2 Heat Engines Why does a heat engine need a temperature difference? Otherwise the work done on the system in one part of the cycle would be equal to the work done by the system in another part, and the net work would be zero. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -2 Heat Engines The efficiency of the heat engine is the ratio of the work done to the heat input: Using conservation of energy to eliminate W, we find: Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -2 Heat Engines The efficiency of the heat engine is the ratio of the work done to the heat input: Using conservation of energy to eliminate W, we find: Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -2 Heat Engines Example 20 -1: Car efficiency. An automobile engine has an efficiency of 20% and produces an average of 23, 000 J of mechanical work per second during operation. (a) How much heat input is required, and (b)(b) How much heat is discharged as waste heat from this engine, per second? Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -2 Heat Engines Example 20 -1: Car efficiency. An automobile engine has an efficiency of 20% and produces an average of 23, 000 J of mechanical work per second during operation. (a) How much heat input is required, and (b)(b) How much heat is discharged as waste heat from this engine, per second? Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
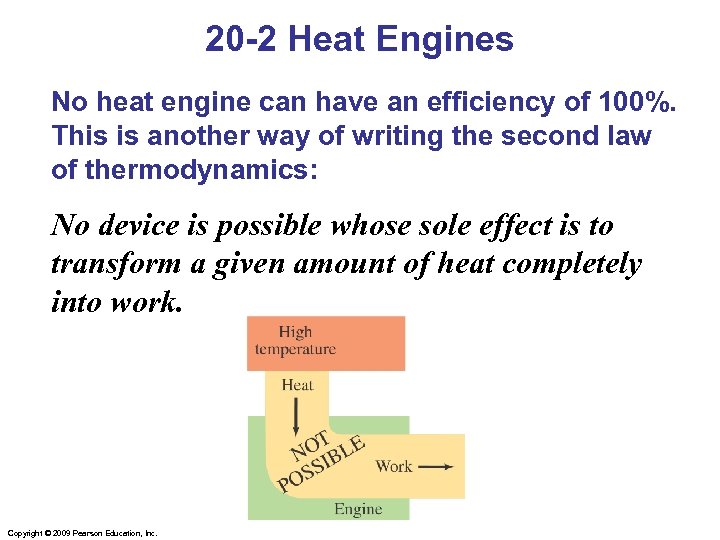 20 -2 Heat Engines No heat engine can have an efficiency of 100%. This is another way of writing the second law of thermodynamics: No device is possible whose sole effect is to transform a given amount of heat completely into work. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -2 Heat Engines No heat engine can have an efficiency of 100%. This is another way of writing the second law of thermodynamics: No device is possible whose sole effect is to transform a given amount of heat completely into work. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
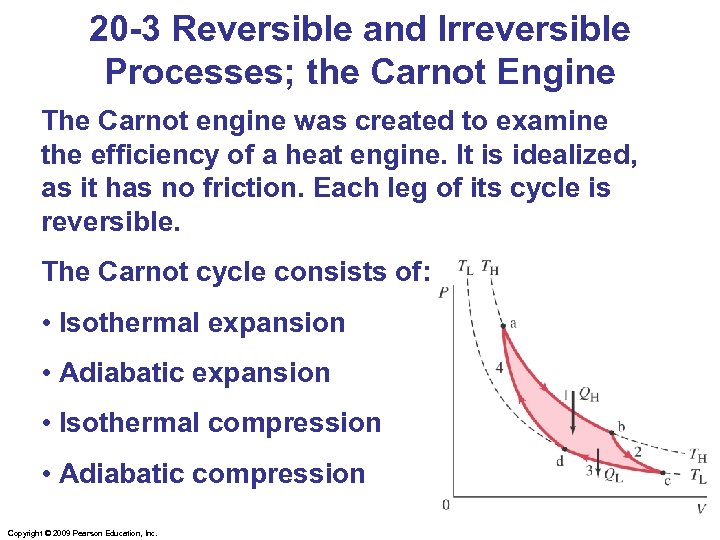 20 -3 Reversible and Irreversible Processes; the Carnot Engine The Carnot engine was created to examine the efficiency of a heat engine. It is idealized, as it has no friction. Each leg of its cycle is reversible. The Carnot cycle consists of: • Isothermal expansion • Adiabatic expansion • Isothermal compression • Adiabatic compression Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -3 Reversible and Irreversible Processes; the Carnot Engine The Carnot engine was created to examine the efficiency of a heat engine. It is idealized, as it has no friction. Each leg of its cycle is reversible. The Carnot cycle consists of: • Isothermal expansion • Adiabatic expansion • Isothermal compression • Adiabatic compression Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -3 Reversible and Irreversible Processes; the Carnot Engine For an ideal reversible engine, the efficiency can be written in terms of the temperature: From this we see that 100% efficiency can be achieved only if the cold reservoir is at absolute zero, which is impossible. Real engines have some frictional losses; the best achieve 60– 80% of the Carnot value of efficiency. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -3 Reversible and Irreversible Processes; the Carnot Engine For an ideal reversible engine, the efficiency can be written in terms of the temperature: From this we see that 100% efficiency can be achieved only if the cold reservoir is at absolute zero, which is impossible. Real engines have some frictional losses; the best achieve 60– 80% of the Carnot value of efficiency. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -3 Reversible and Irreversible Processes; the Carnot Engine Example 20 -2: A phony claim? An engine manufacturer makes the following claims: An engine’s heat input per second is 9. 0 k. J at 435 K. The heat output per second is 4. 0 k. J at 285 K. Do you believe these claims? Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -3 Reversible and Irreversible Processes; the Carnot Engine Example 20 -2: A phony claim? An engine manufacturer makes the following claims: An engine’s heat input per second is 9. 0 k. J at 435 K. The heat output per second is 4. 0 k. J at 285 K. Do you believe these claims? Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -3 Reversible and Irreversible Processes; the Carnot Engine Automobiles run on the Otto cycle, shown here, which is two adiabatic paths alternating with two constant-volume paths. The gas enters the engine at point a and is ignited at point b. Curve cd is the power stroke, and da is the exhaust. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -3 Reversible and Irreversible Processes; the Carnot Engine Automobiles run on the Otto cycle, shown here, which is two adiabatic paths alternating with two constant-volume paths. The gas enters the engine at point a and is ignited at point b. Curve cd is the power stroke, and da is the exhaust. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -3 Reversible and Irreversible Processes; the Carnot Engine Example 20 -3: The Otto cycle. (a) Show that for an ideal gas as working substance, the efficiency of an Otto cycle engine is e = 1 – (Va/Vb)1 -γ where γ is the ratio of specific heats (γ = CP/CV) and Va/Vb is the compression ratio. (a)(b) Calculate the efficiency for a compression ratio Va/Vb = 8. 0 assuming a diatomic gas like O 2 and N 2. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -3 Reversible and Irreversible Processes; the Carnot Engine Example 20 -3: The Otto cycle. (a) Show that for an ideal gas as working substance, the efficiency of an Otto cycle engine is e = 1 – (Va/Vb)1 -γ where γ is the ratio of specific heats (γ = CP/CV) and Va/Vb is the compression ratio. (a)(b) Calculate the efficiency for a compression ratio Va/Vb = 8. 0 assuming a diatomic gas like O 2 and N 2. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
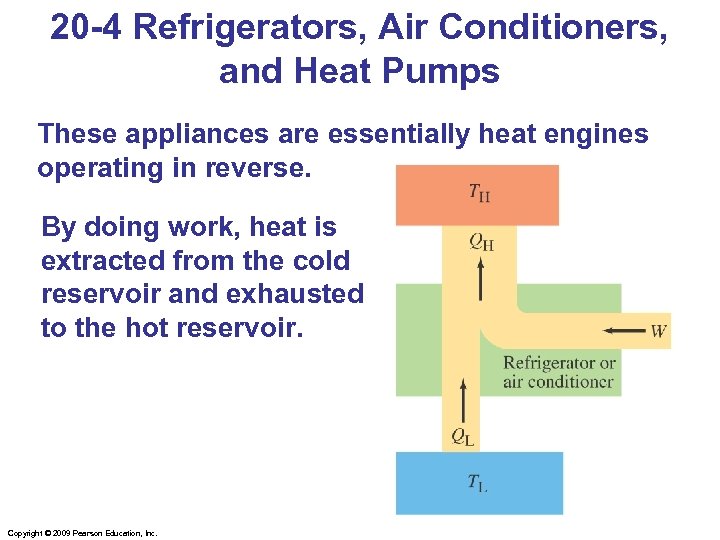 20 -4 Refrigerators, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps These appliances are essentially heat engines operating in reverse. By doing work, heat is extracted from the cold reservoir and exhausted to the hot reservoir. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -4 Refrigerators, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps These appliances are essentially heat engines operating in reverse. By doing work, heat is extracted from the cold reservoir and exhausted to the hot reservoir. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
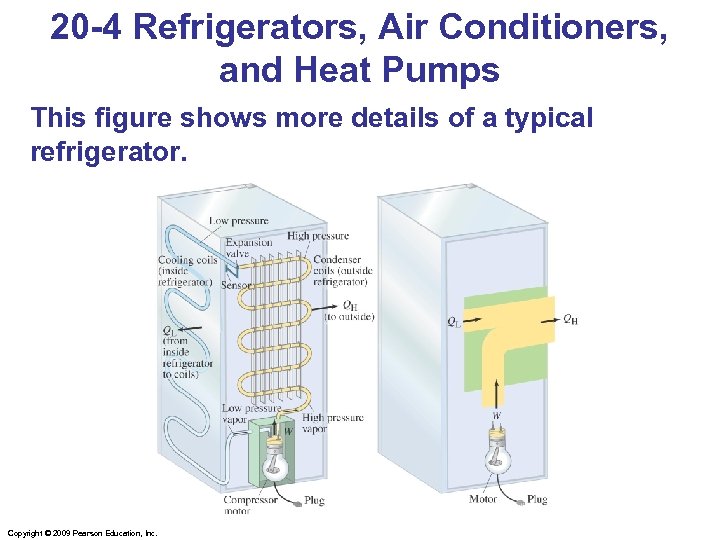 20 -4 Refrigerators, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps This figure shows more details of a typical refrigerator. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -4 Refrigerators, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps This figure shows more details of a typical refrigerator. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
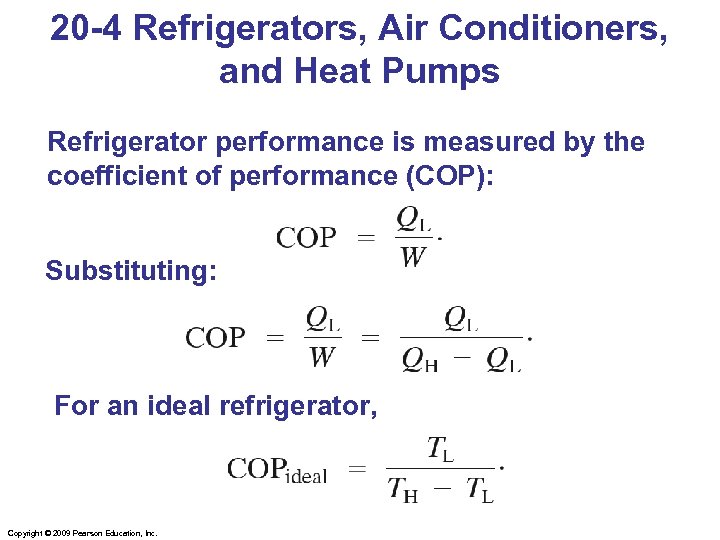 20 -4 Refrigerators, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps Refrigerator performance is measured by the coefficient of performance (COP): Substituting: For an ideal refrigerator, Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -4 Refrigerators, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps Refrigerator performance is measured by the coefficient of performance (COP): Substituting: For an ideal refrigerator, Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -4 Refrigerators, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps Example 20 -4: Making ice. A freezer has a COP of 3. 8 and uses 200 W of power. How long would it take this otherwise empty freezer to freeze an ice-cube tray that contains 600 g of water at 0°C? Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -4 Refrigerators, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps Example 20 -4: Making ice. A freezer has a COP of 3. 8 and uses 200 W of power. How long would it take this otherwise empty freezer to freeze an ice-cube tray that contains 600 g of water at 0°C? Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
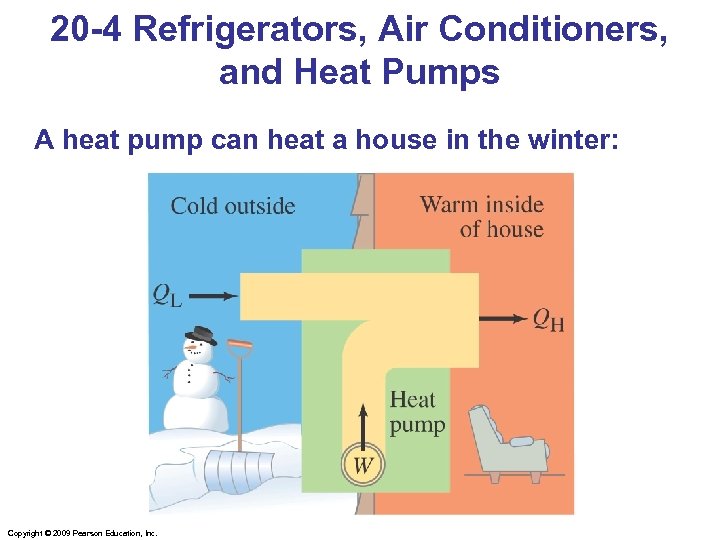 20 -4 Refrigerators, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps A heat pump can heat a house in the winter: Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -4 Refrigerators, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps A heat pump can heat a house in the winter: Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
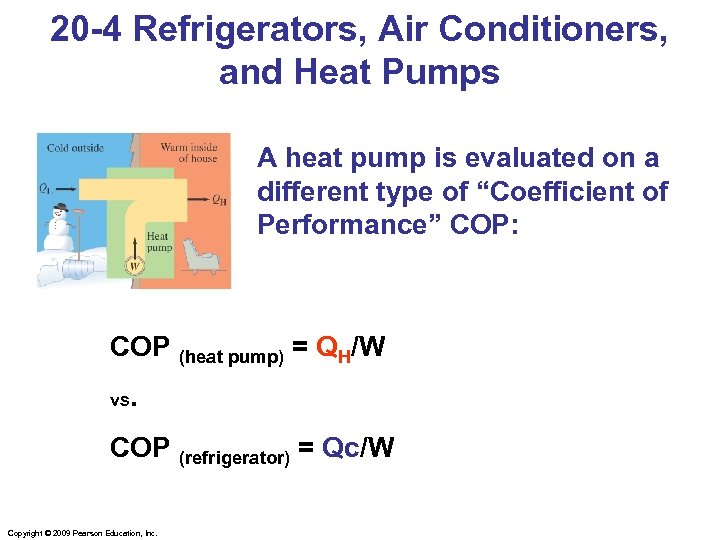 20 -4 Refrigerators, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps A heat pump is evaluated on a different type of “Coefficient of Performance” COP: COP (heat pump) = QH/W vs. COP (refrigerator) = Qc/W Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -4 Refrigerators, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps A heat pump is evaluated on a different type of “Coefficient of Performance” COP: COP (heat pump) = QH/W vs. COP (refrigerator) = Qc/W Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
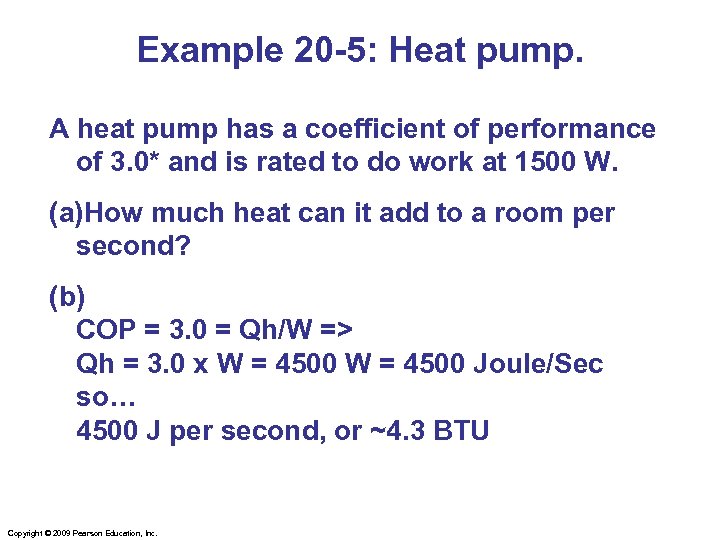 Example 20 -5: Heat pump. A heat pump has a coefficient of performance of 3. 0* and is rated to do work at 1500 W. (a)How much heat can it add to a room per second? (b) COP = 3. 0 = Qh/W => Qh = 3. 0 x W = 4500 Joule/Sec so… 4500 J per second, or ~4. 3 BTU Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Example 20 -5: Heat pump. A heat pump has a coefficient of performance of 3. 0* and is rated to do work at 1500 W. (a)How much heat can it add to a room per second? (b) COP = 3. 0 = Qh/W => Qh = 3. 0 x W = 4500 Joule/Sec so… 4500 J per second, or ~4. 3 BTU Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Example 20 -5: Heat pump. A heat pump has a coefficient of performance of 3. 0* and is rated to do work at 1500 W. (b) If the heat pump were turned around to act as an air conditioner in the summer, what would you expect its coefficient of performance to be, assuming all else stays the same? Qc = Qh – W = 4500 J – 1500 J = 3000 J And COP (refrigerator) = Qc/W = 3000/1500 = 2 Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Example 20 -5: Heat pump. A heat pump has a coefficient of performance of 3. 0* and is rated to do work at 1500 W. (b) If the heat pump were turned around to act as an air conditioner in the summer, what would you expect its coefficient of performance to be, assuming all else stays the same? Qc = Qh – W = 4500 J – 1500 J = 3000 J And COP (refrigerator) = Qc/W = 3000/1500 = 2 Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
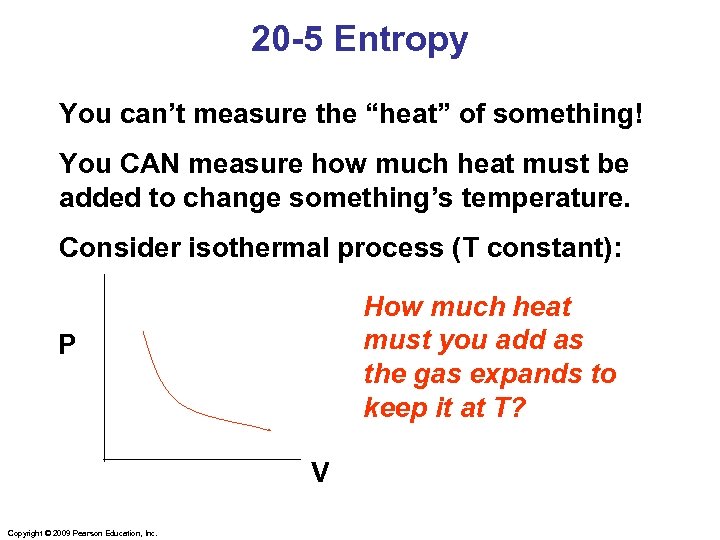 20 -5 Entropy You can’t measure the “heat” of something! You CAN measure how much heat must be added to change something’s temperature. Consider isothermal process (T constant): How much heat must you add as the gas expands to keep it at T? P V Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -5 Entropy You can’t measure the “heat” of something! You CAN measure how much heat must be added to change something’s temperature. Consider isothermal process (T constant): How much heat must you add as the gas expands to keep it at T? P V Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
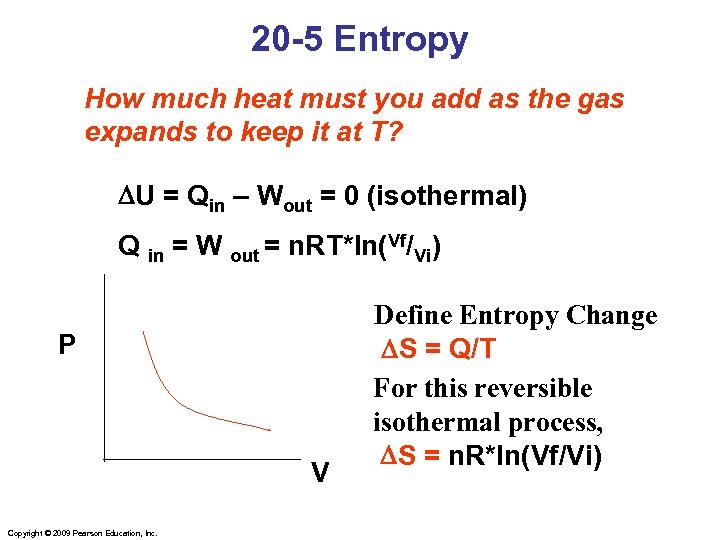 20 -5 Entropy How much heat must you add as the gas expands to keep it at T? DU = Qin – Wout = 0 (isothermal) Q in = W out = n. RT*ln(Vf/Vi) P V Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Define Entropy Change DS = Q/T For this reversible isothermal process, DS = n. R*ln(Vf/Vi)
20 -5 Entropy How much heat must you add as the gas expands to keep it at T? DU = Qin – Wout = 0 (isothermal) Q in = W out = n. RT*ln(Vf/Vi) P V Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Define Entropy Change DS = Q/T For this reversible isothermal process, DS = n. R*ln(Vf/Vi)
 20 -5 Entropy = “S” A *state* variable for a gas (P, V, T) A measure of “disorder” of a system An indicator of the likelihood (probability) of reaction directions (towards higher S) Measured only when it *changes* Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -5 Entropy = “S” A *state* variable for a gas (P, V, T) A measure of “disorder” of a system An indicator of the likelihood (probability) of reaction directions (towards higher S) Measured only when it *changes* Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
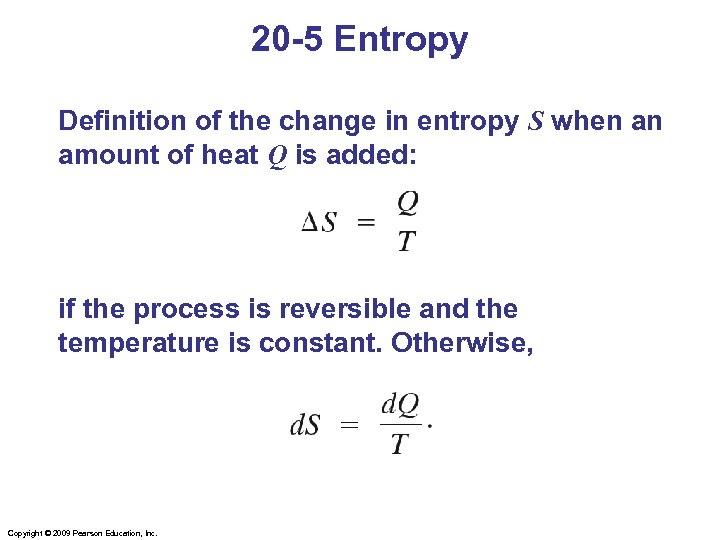 20 -5 Entropy Definition of the change in entropy S when an amount of heat Q is added: if the process is reversible and the temperature is constant. Otherwise, Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -5 Entropy Definition of the change in entropy S when an amount of heat Q is added: if the process is reversible and the temperature is constant. Otherwise, Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -5 Entropy IF the temperature is NOT constant: Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -5 Entropy IF the temperature is NOT constant: Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
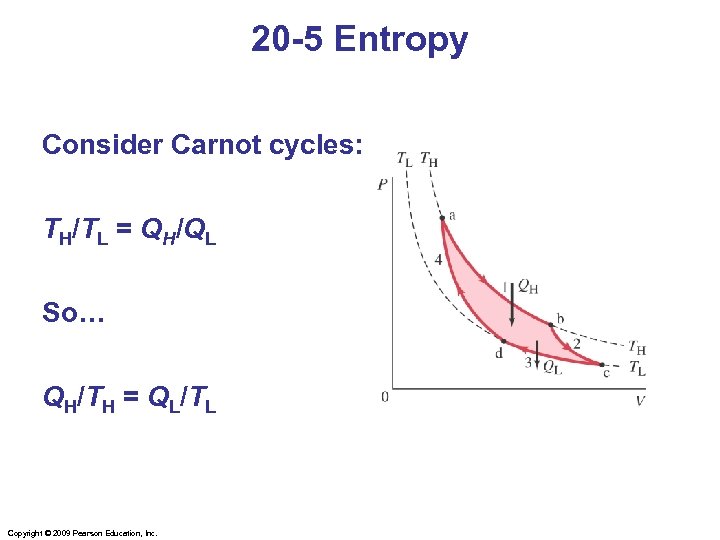 20 -5 Entropy Consider Carnot cycles: TH/TL = QH/QL So… QH/TH = QL/TL Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -5 Entropy Consider Carnot cycles: TH/TL = QH/QL So… QH/TH = QL/TL Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
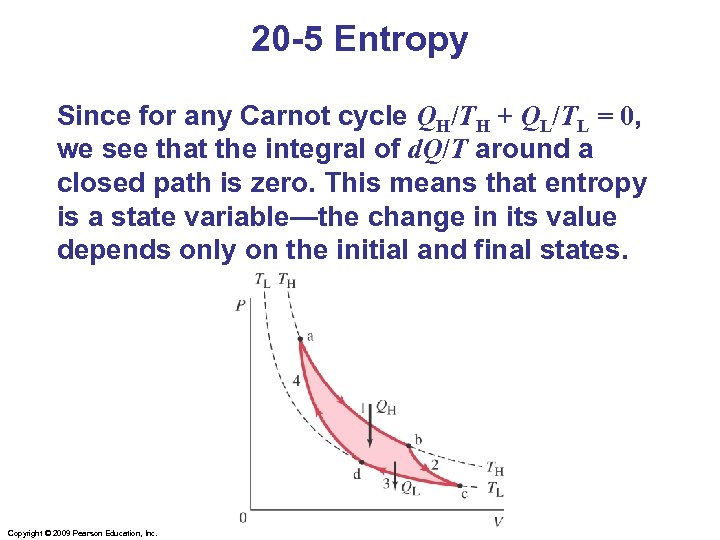 20 -5 Entropy Since for any Carnot cycle QH/TH + QL/TL = 0, we see that the integral of d. Q/T around a closed path is zero. This means that entropy is a state variable—the change in its value depends only on the initial and final states. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -5 Entropy Since for any Carnot cycle QH/TH + QL/TL = 0, we see that the integral of d. Q/T around a closed path is zero. This means that entropy is a state variable—the change in its value depends only on the initial and final states. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
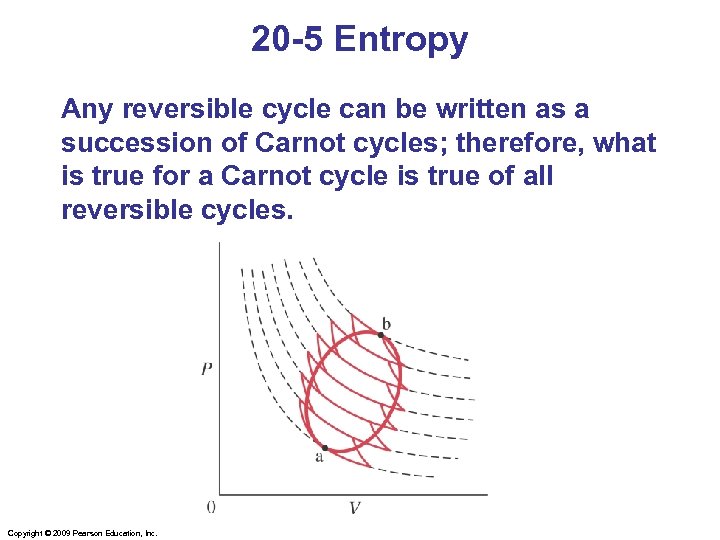 20 -5 Entropy Any reversible cycle can be written as a succession of Carnot cycles; therefore, what is true for a Carnot cycle is true of all reversible cycles. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -5 Entropy Any reversible cycle can be written as a succession of Carnot cycles; therefore, what is true for a Carnot cycle is true of all reversible cycles. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
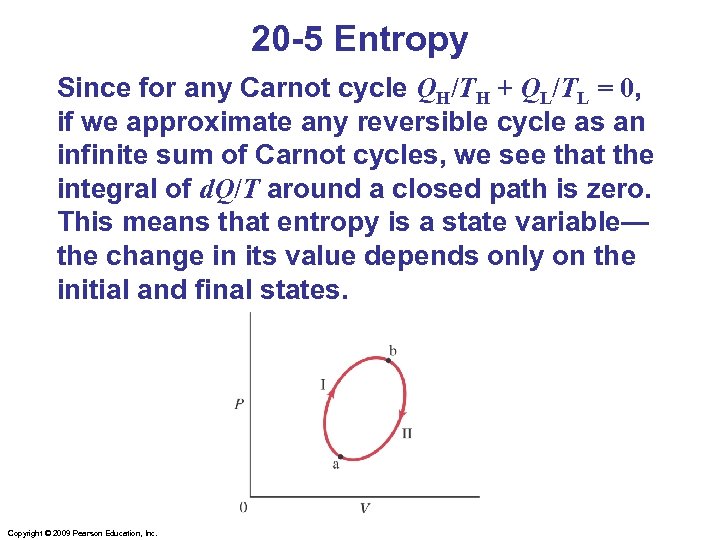 20 -5 Entropy Since for any Carnot cycle QH/TH + QL/TL = 0, if we approximate any reversible cycle as an infinite sum of Carnot cycles, we see that the integral of d. Q/T around a closed path is zero. This means that entropy is a state variable— the change in its value depends only on the initial and final states. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -5 Entropy Since for any Carnot cycle QH/TH + QL/TL = 0, if we approximate any reversible cycle as an infinite sum of Carnot cycles, we see that the integral of d. Q/T around a closed path is zero. This means that entropy is a state variable— the change in its value depends only on the initial and final states. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -6 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Example 20 -6: Entropy change when mixing water. A sample of 50. 0 kg of water at 20. 00°C is mixed with 50. 0 kg of water at 24. 00°C. Estimate the change in entropy. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -6 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Example 20 -6: Entropy change when mixing water. A sample of 50. 0 kg of water at 20. 00°C is mixed with 50. 0 kg of water at 24. 00°C. Estimate the change in entropy. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -6 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics The total entropy always increases when heat flows from a warmer object to a colder one in an isolated two-body system. The heat transferred is the same, and the cooler object is at a lower average temperature than the warmer one, so the entropy gained by the cooler one is always more than the entropy lost by the warmer one. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -6 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics The total entropy always increases when heat flows from a warmer object to a colder one in an isolated two-body system. The heat transferred is the same, and the cooler object is at a lower average temperature than the warmer one, so the entropy gained by the cooler one is always more than the entropy lost by the warmer one. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -6 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Example 20 -7: Entropy changes in a free expansion. Consider the adiabatic free expansion of n moles of an ideal gas from volume V 1 to volume V 2, where V 2 > V 1. Calculate the change in entropy (a) of the gas and (b) of the surrounding environment. (c) Evaluate ΔS for 1. 00 mole, with V 2 = 2. 00 V 1. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -6 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Example 20 -7: Entropy changes in a free expansion. Consider the adiabatic free expansion of n moles of an ideal gas from volume V 1 to volume V 2, where V 2 > V 1. Calculate the change in entropy (a) of the gas and (b) of the surrounding environment. (c) Evaluate ΔS for 1. 00 mole, with V 2 = 2. 00 V 1. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -6 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Example 20 -8: Heat transfer. A red-hot 2. 00 -kg piece of iron at temperature T 1 = 880 K is thrown into a huge lake whose temperature is T 2 = 280 K. Assume the lake is so large that its temperature rise is insignificant. Determine the change in entropy (a) of the iron and (b) of the surrounding environment (the lake). Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -6 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Example 20 -8: Heat transfer. A red-hot 2. 00 -kg piece of iron at temperature T 1 = 880 K is thrown into a huge lake whose temperature is T 2 = 280 K. Assume the lake is so large that its temperature rise is insignificant. Determine the change in entropy (a) of the iron and (b) of the surrounding environment (the lake). Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -6 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics The fact that after every interaction the entropy of the system plus the environment increases is another way of putting the second law of thermodynamics: The entropy of an isolated system never decreases. It either stays constant (reversible processes) or increases (irreversible processes). Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -6 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics The fact that after every interaction the entropy of the system plus the environment increases is another way of putting the second law of thermodynamics: The entropy of an isolated system never decreases. It either stays constant (reversible processes) or increases (irreversible processes). Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -7 Order to Disorder Entropy is a measure of the disorder of a system. This gives us yet another statement of the second law: Natural processes tend to move toward a state of greater disorder. Example: If you put milk and sugar in your coffee and stir it, you wind up with coffee that is uniformly milky and sweet. No amount of stirring will get the milk and sugar to come back out of solution. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -7 Order to Disorder Entropy is a measure of the disorder of a system. This gives us yet another statement of the second law: Natural processes tend to move toward a state of greater disorder. Example: If you put milk and sugar in your coffee and stir it, you wind up with coffee that is uniformly milky and sweet. No amount of stirring will get the milk and sugar to come back out of solution. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -7 Order to Disorder Another example: When a tornado hits a building, there is major damage. You never see a tornado approach a pile of rubble and leave a building behind when it passes. Thermal equilibrium is a similar process—the uniform final state has more disorder than the separate temperatures in the initial state. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -7 Order to Disorder Another example: When a tornado hits a building, there is major damage. You never see a tornado approach a pile of rubble and leave a building behind when it passes. Thermal equilibrium is a similar process—the uniform final state has more disorder than the separate temperatures in the initial state. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -8 Unavailability of Energy; Heat Death Another consequence of the second law: In any natural process, some energy becomes unavailable to do useful work. If we look at the universe as a whole, it seems inevitable that, as more and more energy is converted to unavailable forms, the ability to do work anywhere will gradually vanish. This is called the heat death of the universe. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -8 Unavailability of Energy; Heat Death Another consequence of the second law: In any natural process, some energy becomes unavailable to do useful work. If we look at the universe as a whole, it seems inevitable that, as more and more energy is converted to unavailable forms, the ability to do work anywhere will gradually vanish. This is called the heat death of the universe. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
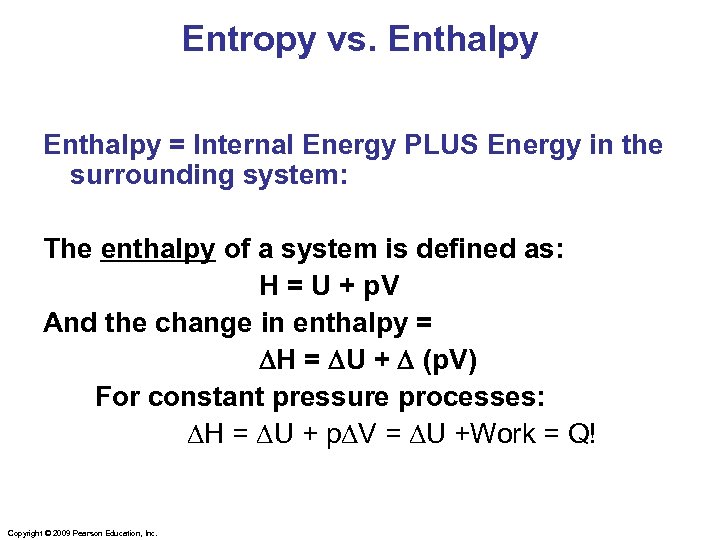 Entropy vs. Enthalpy = Internal Energy PLUS Energy in the surrounding system: The enthalpy of a system is defined as: H = U + p. V And the change in enthalpy = DH = DU + D (p. V) For constant pressure processes: DH = DU + p. DV = DU +Work = Q! Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Entropy vs. Enthalpy = Internal Energy PLUS Energy in the surrounding system: The enthalpy of a system is defined as: H = U + p. V And the change in enthalpy = DH = DU + D (p. V) For constant pressure processes: DH = DU + p. DV = DU +Work = Q! Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Entropy vs. Enthalpy is sometimes described as the heat content of a system under a given pressure, Such a visualization assumes no energy exchange with the environment other than heat or expansion work. Given such restrictions, it can be shown that: The enthalpy is the total amount of energy which the system can emit through heat, Adding or removing energy through heat is the only way to change the enthalpy, and The amount of change in enthalpy is equal to the amount of energy added through heat. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Entropy vs. Enthalpy is sometimes described as the heat content of a system under a given pressure, Such a visualization assumes no energy exchange with the environment other than heat or expansion work. Given such restrictions, it can be shown that: The enthalpy is the total amount of energy which the system can emit through heat, Adding or removing energy through heat is the only way to change the enthalpy, and The amount of change in enthalpy is equal to the amount of energy added through heat. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Entropy vs. Enthalpy ENTHALPHY: Is the energy content of a process (chemical, thermodynamic, mechanical, etc) that can be recovered. It is also described as useful energy. ENTROPY: Is the energy content of a process (chemical, thermodynamic, mechanical, etc) that CANNOT be recovered. It is also described as chaos. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Entropy vs. Enthalpy ENTHALPHY: Is the energy content of a process (chemical, thermodynamic, mechanical, etc) that can be recovered. It is also described as useful energy. ENTROPY: Is the energy content of a process (chemical, thermodynamic, mechanical, etc) that CANNOT be recovered. It is also described as chaos. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
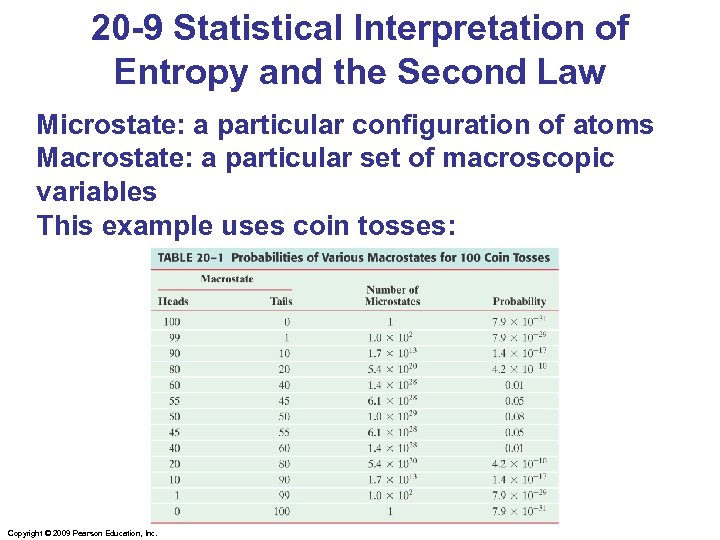 20 -9 Statistical Interpretation of Entropy and the Second Law Microstate: a particular configuration of atoms Macrostate: a particular set of macroscopic variables This example uses coin tosses: Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -9 Statistical Interpretation of Entropy and the Second Law Microstate: a particular configuration of atoms Macrostate: a particular set of macroscopic variables This example uses coin tosses: Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
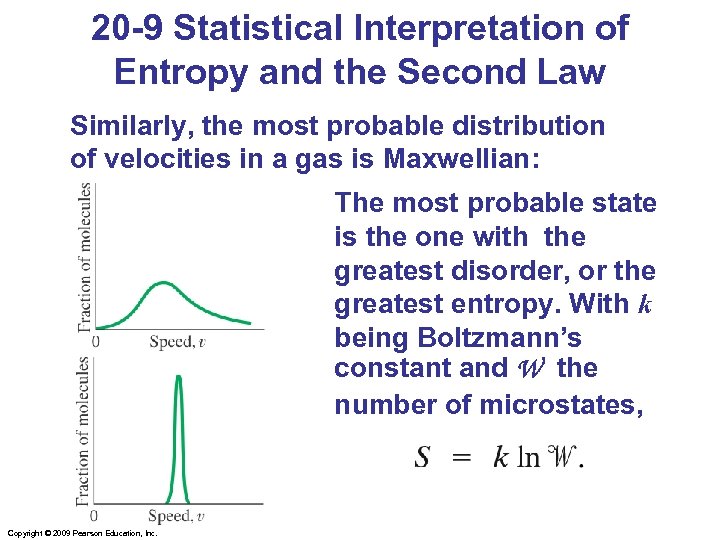 20 -9 Statistical Interpretation of Entropy and the Second Law Similarly, the most probable distribution of velocities in a gas is Maxwellian: The most probable state is the one with the greatest disorder, or the greatest entropy. With k being Boltzmann’s constant and W the number of microstates, Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -9 Statistical Interpretation of Entropy and the Second Law Similarly, the most probable distribution of velocities in a gas is Maxwellian: The most probable state is the one with the greatest disorder, or the greatest entropy. With k being Boltzmann’s constant and W the number of microstates, Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -9 Statistical Interpretation of Entropy and the Second Law Example 20 -9: Free expansion—statistical determination of entropy. Determine the change in entropy for the adiabatic free expansion of one mole of a gas as its volume doubles. Assume W, the number of microstates for each macrostate, is the number of possible positions. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -9 Statistical Interpretation of Entropy and the Second Law Example 20 -9: Free expansion—statistical determination of entropy. Determine the change in entropy for the adiabatic free expansion of one mole of a gas as its volume doubles. Assume W, the number of microstates for each macrostate, is the number of possible positions. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -9 Statistical Interpretation of Entropy and the Second Law In this form, the second law of thermodynamics does not forbid processes in which the total entropy decreases; it just makes them exceedingly unlikely. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -9 Statistical Interpretation of Entropy and the Second Law In this form, the second law of thermodynamics does not forbid processes in which the total entropy decreases; it just makes them exceedingly unlikely. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -10 Thermodynamic Temperature; Third Law of Thermodynamics Since the ratio of heats exchanged between the hot and cold reservoirs in a Carnot engine is equal to the ratio of temperatures, we can define a temperature scale using the triple point of water: T = (273. 16 K)(Q/Qtp). Here, Q and Qtp are the heats exchanged by a Carnot engine with reservoirs at temperatures T and Ttp. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -10 Thermodynamic Temperature; Third Law of Thermodynamics Since the ratio of heats exchanged between the hot and cold reservoirs in a Carnot engine is equal to the ratio of temperatures, we can define a temperature scale using the triple point of water: T = (273. 16 K)(Q/Qtp). Here, Q and Qtp are the heats exchanged by a Carnot engine with reservoirs at temperatures T and Ttp. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -10 Thermodynamic Temperature; Third Law of Thermodynamics Also, since the maximum efficiency of a heat engine is there is no way to achieve a temperature of absolute zero. This is the third law of thermodynamics: It is not possible to reach absolute zero in any finite number of processes. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -10 Thermodynamic Temperature; Third Law of Thermodynamics Also, since the maximum efficiency of a heat engine is there is no way to achieve a temperature of absolute zero. This is the third law of thermodynamics: It is not possible to reach absolute zero in any finite number of processes. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 20 -11 Thermal Pollution, Global Warming, and Energy Resources Over 90% of the energy used in the U. S. is generated using heat engines to drive turbines and generators—even nuclear power plants use the energy generated from fission heat water for a steam engine. The thermal output QL of all these heat engines contributes to warming of the atmosphere and water. This is an inevitable consequence of the second law of thermodynamics. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
20 -11 Thermal Pollution, Global Warming, and Energy Resources Over 90% of the energy used in the U. S. is generated using heat engines to drive turbines and generators—even nuclear power plants use the energy generated from fission heat water for a steam engine. The thermal output QL of all these heat engines contributes to warming of the atmosphere and water. This is an inevitable consequence of the second law of thermodynamics. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Summary of Chapter 20 • Heat engine changes heat into useful work • Efficiency: work/heat input • Maximum efficiency: 1 – TL/TH • Refrigerators and air conditioners are heat engines, reversed; COP = heat removed/work • Heat pump: COP = heat delivered/work • Second law of thermodynamics: Natural processes always tend to increase entropy Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Summary of Chapter 20 • Heat engine changes heat into useful work • Efficiency: work/heat input • Maximum efficiency: 1 – TL/TH • Refrigerators and air conditioners are heat engines, reversed; COP = heat removed/work • Heat pump: COP = heat delivered/work • Second law of thermodynamics: Natural processes always tend to increase entropy Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Summary of Chapter 20 • Entropy change in reversible process: • Change in entropy gives direction to “arrow of time” • As time goes on, energy becomes degraded. • Heat engines cause thermal pollution. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
Summary of Chapter 20 • Entropy change in reversible process: • Change in entropy gives direction to “arrow of time” • As time goes on, energy becomes degraded. • Heat engines cause thermal pollution. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.


