L_1_Contrastive Typology_Presentation.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Lecture One Contrastive vs Comparative Typology of Languages
Lecture One Contrastive vs Comparative Typology of Languages
 Overview The lecture focuses on two principal ways of classifying languages within the notion of comparative vs contrastive typology: genetic system of classification; typological system of classification.
Overview The lecture focuses on two principal ways of classifying languages within the notion of comparative vs contrastive typology: genetic system of classification; typological system of classification.
 Genetic System of Classification groups languages into family trees and traces their historical development through the process of linguistic reconstruction thus providing a temporal view of how languages change over time
Genetic System of Classification groups languages into family trees and traces their historical development through the process of linguistic reconstruction thus providing a temporal view of how languages change over time
 Typological System of Classification focuses more on language similarities than differences and classifies languages in a manner that is aligned with the notion of language universals
Typological System of Classification focuses more on language similarities than differences and classifies languages in a manner that is aligned with the notion of language universals
 Comparative Linguistics independent linguistic discipline with the goal of reconstructing the origins, developmental history, and relationships of and between individual languages on the basis of comparative studies (reconstruction)
Comparative Linguistics independent linguistic discipline with the goal of reconstructing the origins, developmental history, and relationships of and between individual languages on the basis of comparative studies (reconstruction)
 Distinguished Scholars Friedrich von Schlegel Franz Bopp Rasmus Rask Jcob Grimm Alexander Schleicher
Distinguished Scholars Friedrich von Schlegel Franz Bopp Rasmus Rask Jcob Grimm Alexander Schleicher
 Contrastive Linguistics Linguistic subdiscipline concerned with the synchronic, comparative study of two or more languages or language varieties (e. g. dialects)
Contrastive Linguistics Linguistic subdiscipline concerned with the synchronic, comparative study of two or more languages or language varieties (e. g. dialects)
 Distinguished Scholars: Mark Hellinger. (1977). Kontrastive Linguistik Deutsch/Englisch: Theorie und Anwendung. Hueber Hochschulreihe 23. München: Hueber. Claire James. (1980). Contrastive analysis. London: Longman. John Hawkins. (1986). A Comparative Typology of English and German. Unifying the Contrasts. London & Sydney: Croom Helm. more on: http: //www. tuchemnitz. de/phil/english/chairs/linguist/independent/kursmaterialien/contrli/index. html
Distinguished Scholars: Mark Hellinger. (1977). Kontrastive Linguistik Deutsch/Englisch: Theorie und Anwendung. Hueber Hochschulreihe 23. München: Hueber. Claire James. (1980). Contrastive analysis. London: Longman. John Hawkins. (1986). A Comparative Typology of English and German. Unifying the Contrasts. London & Sydney: Croom Helm. more on: http: //www. tuchemnitz. de/phil/english/chairs/linguist/independent/kursmaterialien/contrli/index. html
 Ferdinand de Saussure Synchronic and Diachronic View of Language
Ferdinand de Saussure Synchronic and Diachronic View of Language
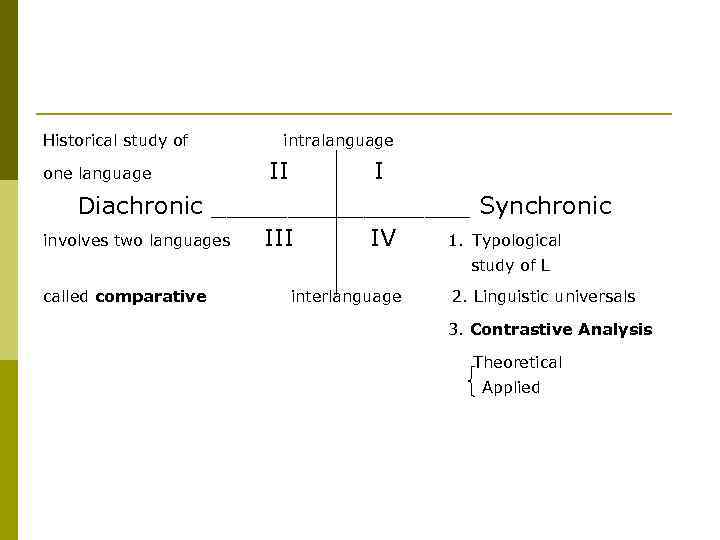 Historical study of intralanguage II I Diachronic _________ Synchronic involves two languages III IV 1. Typological one language study of L called comparative interlanguage 2. Linguistic universals 3. Contrastive Analysis Theoretical Applied
Historical study of intralanguage II I Diachronic _________ Synchronic involves two languages III IV 1. Typological one language study of L called comparative interlanguage 2. Linguistic universals 3. Contrastive Analysis Theoretical Applied
 Everything that relates to the static side of our science is synchronic; everything that has to do with evolution is diachronic (F. de Saussure). Thus generally speaking, in the field of linguistics, comparative linguistics is intended to 1) make a diachronic study of some related languages so as to 2) create a parent language or ancestor language.
Everything that relates to the static side of our science is synchronic; everything that has to do with evolution is diachronic (F. de Saussure). Thus generally speaking, in the field of linguistics, comparative linguistics is intended to 1) make a diachronic study of some related languages so as to 2) create a parent language or ancestor language.
 Conversely, contrastive linguistics involves a synchronic study of two unrelated languages so as to find out the dissimilarities in phonological, morphological and syntactic aspects. The former aims mainly at the homogeneity while the latter mainly at the heterogeneity.
Conversely, contrastive linguistics involves a synchronic study of two unrelated languages so as to find out the dissimilarities in phonological, morphological and syntactic aspects. The former aims mainly at the homogeneity while the latter mainly at the heterogeneity.
 Comparative vs Contrastive Linguistics Comparative study 1. make a diachronic study; 2. the subjects comparison are limited to its parent language; 3. the study aims at the homogeneity of the languages compared; Contrastive study 1. make a synchronic study; 2. the subjects of comparison be its parent or not parent 3. the study aims at the heterogeneity of the languages compared; 4. the languages compared are limited to two, generally 4. the languages compared are not limited; speaking; 5. it is intended to penetrate and 5. provide a practical use in make clear the laws of the historical language teaching; dictionary development; compiling; translation; international communication.
Comparative vs Contrastive Linguistics Comparative study 1. make a diachronic study; 2. the subjects comparison are limited to its parent language; 3. the study aims at the homogeneity of the languages compared; Contrastive study 1. make a synchronic study; 2. the subjects of comparison be its parent or not parent 3. the study aims at the heterogeneity of the languages compared; 4. the languages compared are limited to two, generally 4. the languages compared are not limited; speaking; 5. it is intended to penetrate and 5. provide a practical use in make clear the laws of the historical language teaching; dictionary development; compiling; translation; international communication.
 Methodological Steps in Contrastive Linguistics 1. Description: 1) Selection of items to be compared; 2) Characterisation of items in terms of some language independent theoretical model. 2. Juxtaposition - search for and identification of cross-linguistic equivalents. 3. Comparison - specification of degree and type of correspondence between compared items.
Methodological Steps in Contrastive Linguistics 1. Description: 1) Selection of items to be compared; 2) Characterisation of items in terms of some language independent theoretical model. 2. Juxtaposition - search for and identification of cross-linguistic equivalents. 3. Comparison - specification of degree and type of correspondence between compared items.
 Levels of Description in Contrastive Linguistics Phonology Morpho-Syntax / Grammar Lexis Pragmatics Text/Discourse Note: Although languages are classified typologically on the basis of phonological, morphological and syntactical characteristics that they share or do not share, much of the research in this area has been centered on morphology and syntacs.
Levels of Description in Contrastive Linguistics Phonology Morpho-Syntax / Grammar Lexis Pragmatics Text/Discourse Note: Although languages are classified typologically on the basis of phonological, morphological and syntactical characteristics that they share or do not share, much of the research in this area has been centered on morphology and syntacs.
 Summing Up Contrastive Linguistics is a branch of linguistics. Contrastive Linguistics makes a synchronic study. Contrastive Linguistics makes a comparison of two languages (generally speaking) whose subjects can be its parent or not parent language. Contrastive Linguistics is a study aiming at the heterogeneity of the languages compared. Contrastive Linguistics provides a practical use in language teaching; dictionary compiling; translation; and international communication.
Summing Up Contrastive Linguistics is a branch of linguistics. Contrastive Linguistics makes a synchronic study. Contrastive Linguistics makes a comparison of two languages (generally speaking) whose subjects can be its parent or not parent language. Contrastive Linguistics is a study aiming at the heterogeneity of the languages compared. Contrastive Linguistics provides a practical use in language teaching; dictionary compiling; translation; and international communication.


