d2c90673d1c8f190f6acc28ea16e3266.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 85
 Lecture Notes Artificial Intelligence: Definition Dae-Won Kim School of Computer Science & Engineering Chung-Ang University
Lecture Notes Artificial Intelligence: Definition Dae-Won Kim School of Computer Science & Engineering Chung-Ang University
 What are AI Systems?
What are AI Systems?
 Deep Blue defeated the world chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997
Deep Blue defeated the world chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997
 During the 1991 Gulf War, US forces deployed an AI logistics planning and scheduling program that involved up to 50, 000 vehicles, cargo, and people
During the 1991 Gulf War, US forces deployed an AI logistics planning and scheduling program that involved up to 50, 000 vehicles, cargo, and people
 Proverb solves crossword puzzles better than most humans
Proverb solves crossword puzzles better than most humans
 Sony’s AIBO and Honda’s ASIMO
Sony’s AIBO and Honda’s ASIMO
 Web Agents & Search engines: Google, Yahoo
Web Agents & Search engines: Google, Yahoo
 Recognition Systems: Speech, Character, Face, Iris, Fingerprint
Recognition Systems: Speech, Character, Face, Iris, Fingerprint
 Virtual Reality and Computer Vision
Virtual Reality and Computer Vision

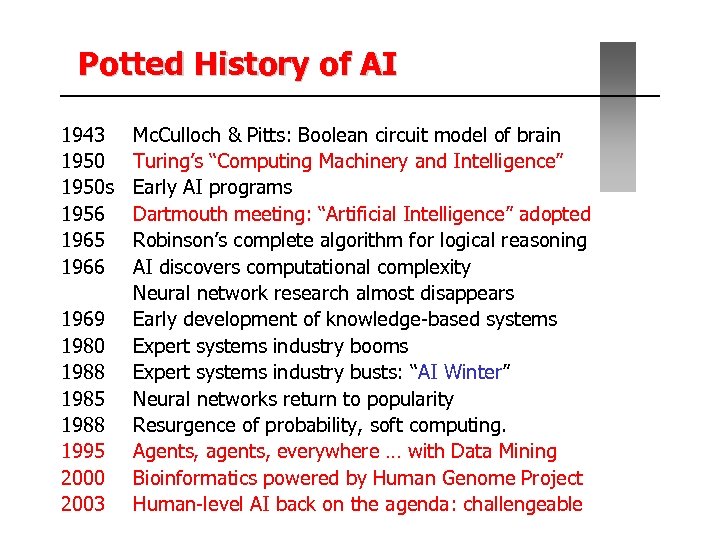 Potted History of AI 1943 1950 s 1956 1965 1966 1969 1980 1988 1985 1988 1995 2000 2003 Mc. Culloch & Pitts: Boolean circuit model of brain Turing’s “Computing Machinery and Intelligence” Early AI programs Dartmouth meeting: “Artificial Intelligence” adopted Robinson’s complete algorithm for logical reasoning AI discovers computational complexity Neural network research almost disappears Early development of knowledge-based systems Expert systems industry booms Expert systems industry busts: “AI Winter” Neural networks return to popularity Resurgence of probability, soft computing. Agents, agents, everywhere … with Data Mining Bioinformatics powered by Human Genome Project Human-level AI back on the agenda: challengeable
Potted History of AI 1943 1950 s 1956 1965 1966 1969 1980 1988 1985 1988 1995 2000 2003 Mc. Culloch & Pitts: Boolean circuit model of brain Turing’s “Computing Machinery and Intelligence” Early AI programs Dartmouth meeting: “Artificial Intelligence” adopted Robinson’s complete algorithm for logical reasoning AI discovers computational complexity Neural network research almost disappears Early development of knowledge-based systems Expert systems industry booms Expert systems industry busts: “AI Winter” Neural networks return to popularity Resurgence of probability, soft computing. Agents, agents, everywhere … with Data Mining Bioinformatics powered by Human Genome Project Human-level AI back on the agenda: challengeable
 Some researchers consider AI as one of the four concepts:
Some researchers consider AI as one of the four concepts:
 1. Systems that think like humans
1. Systems that think like humans
 2. Systems that think rationally
2. Systems that think rationally
 3. Systems that act like humans
3. Systems that act like humans
 4. Systems that act rationally
4. Systems that act rationally
 AI: Acting humanly
AI: Acting humanly
 Turing (1950): “The Turing Test”
Turing (1950): “The Turing Test”
 Can machines think?
Can machines think?
 Can machines behave intelligently?
Can machines behave intelligently?
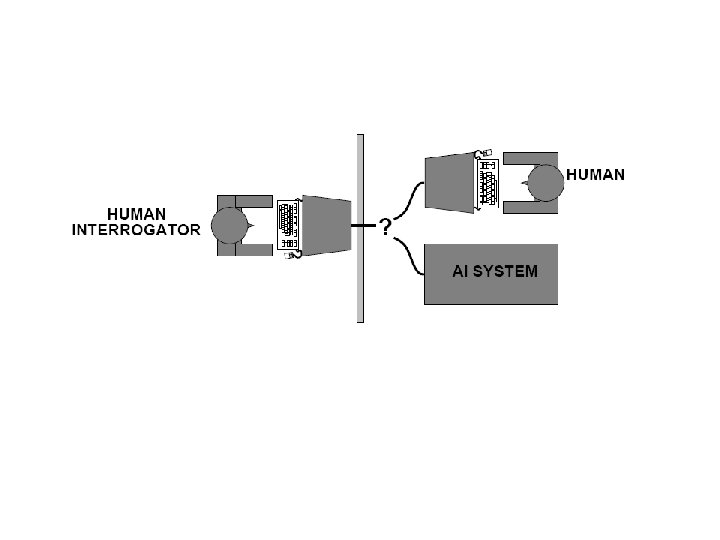
 Turing test is The ‘Imitation’ Game
Turing test is The ‘Imitation’ Game
 Predicted that by 2000, a machine might have 30% chance of fooling a lay person for 5 min. In 2014, something has happened. http: //www. bbc. com/news/technology-27762088
Predicted that by 2000, a machine might have 30% chance of fooling a lay person for 5 min. In 2014, something has happened. http: //www. bbc. com/news/technology-27762088
 Problem: Turing test is NOT …
Problem: Turing test is NOT …
 Turing test is NOT reproducible and amendable to mathematical analysis
Turing test is NOT reproducible and amendable to mathematical analysis
 AI: Thinking humanly
AI: Thinking humanly
 It requires scientific theories of internal activities of the brain
It requires scientific theories of internal activities of the brain
 What level of abstraction? “Knowledge” or “circuits”.
What level of abstraction? “Knowledge” or “circuits”.
 How to validate? Requires something
How to validate? Requires something
 Requires: Cognitive Science Predicting and testing behavior of human subjects (top-down)
Requires: Cognitive Science Predicting and testing behavior of human subjects (top-down)
 Requires: Cognitive Neuroscience Direct identification from neurological data (bottom up)
Requires: Cognitive Neuroscience Direct identification from neurological data (bottom up)
 Problem: Thinking humanly is NOT
Problem: Thinking humanly is NOT
 Both are distinct from AI in CS The available theories do not explain anything resembling human-level general intelligence.
Both are distinct from AI in CS The available theories do not explain anything resembling human-level general intelligence.
 AI: Thinking rationally
AI: Thinking rationally
 Laws of Thought: “What are correct arguments/thought processes? ” by Aristotle
Laws of Thought: “What are correct arguments/thought processes? ” by Aristotle
 Several Greek schools developed various forms of logic:
Several Greek schools developed various forms of logic:
 Logic: notation and rules of derivation of thoughts
Logic: notation and rules of derivation of thoughts
 Problem: Thinking rationally is NOT
Problem: Thinking rationally is NOT
 Not all intelligent behavior is mediated by logical deliberation
Not all intelligent behavior is mediated by logical deliberation
 AI: Acting rationally
AI: Acting rationally
 Rational behavior: doing the RIGHT thing
Rational behavior: doing the RIGHT thing
 The RIGHT thing: that which is expected to maximize goal achievement, given the available information
The RIGHT thing: that which is expected to maximize goal achievement, given the available information
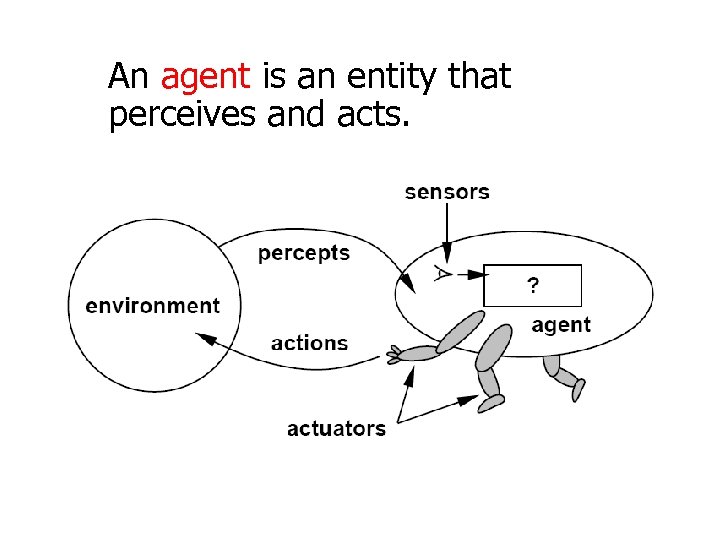 An agent is an entity that perceives and acts.
An agent is an entity that perceives and acts.
 Agents include humans, robots, programs, systems, etc.
Agents include humans, robots, programs, systems, etc.
 This course is about designing rational agents/SWs/programs/platforms.
This course is about designing rational agents/SWs/programs/platforms.
 Abstractly, an agent is a function from percept histories to actions f: P A
Abstractly, an agent is a function from percept histories to actions f: P A
 The agent program runs on the physical architecture to produce f
The agent program runs on the physical architecture to produce f
 For any given class of tasks and environments, we seek the agent with the best performance.
For any given class of tasks and environments, we seek the agent with the best performance.
 Problem: Acting rationally is NOT
Problem: Acting rationally is NOT
 Computational limitations make perfect rationality unachievable e. g. ) NP-hard problems
Computational limitations make perfect rationality unachievable e. g. ) NP-hard problems
 Design best program for given machine resources
Design best program for given machine resources
 Which of the following can be done at present? • • • Play a decent game of table tennis Drive safely along a curving mountain road Drive safely along Telegraph Avenue Buy a week’s worth of groceries on the web Discover and prove a new mathematical theorem Design and execute a research program in biology Write an intentionally funny story Give legal advice in a specialized area of law Translate spoken English into Swedish in real time Perform a complex surgical operation Converse successfully with another person for an hour
Which of the following can be done at present? • • • Play a decent game of table tennis Drive safely along a curving mountain road Drive safely along Telegraph Avenue Buy a week’s worth of groceries on the web Discover and prove a new mathematical theorem Design and execute a research program in biology Write an intentionally funny story Give legal advice in a specialized area of law Translate spoken English into Swedish in real time Perform a complex surgical operation Converse successfully with another person for an hour
 Artificial Intelligence Intelligent Agents Dae-Won Kim School of Computer Science & Engineering Chung-Ang University
Artificial Intelligence Intelligent Agents Dae-Won Kim School of Computer Science & Engineering Chung-Ang University
 The agent function maps from percept histories to actions: f: P A
The agent function maps from percept histories to actions: f: P A
 A Vacuum-cleaner Agent
A Vacuum-cleaner Agent
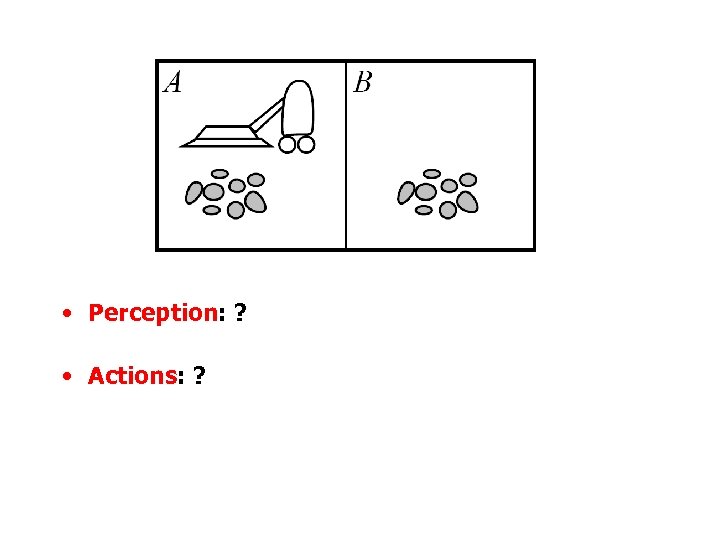 • Perception: ? • Actions: ?
• Perception: ? • Actions: ?
![• Perception: location and contents [A, Dirty]. • Actions: Left, Right, Suck, No. • Perception: location and contents [A, Dirty]. • Actions: Left, Right, Suck, No.](https://present5.com/presentation/d2c90673d1c8f190f6acc28ea16e3266/image-57.jpg) • Perception: location and contents [A, Dirty]. • Actions: Left, Right, Suck, No. Op
• Perception: location and contents [A, Dirty]. • Actions: Left, Right, Suck, No. Op
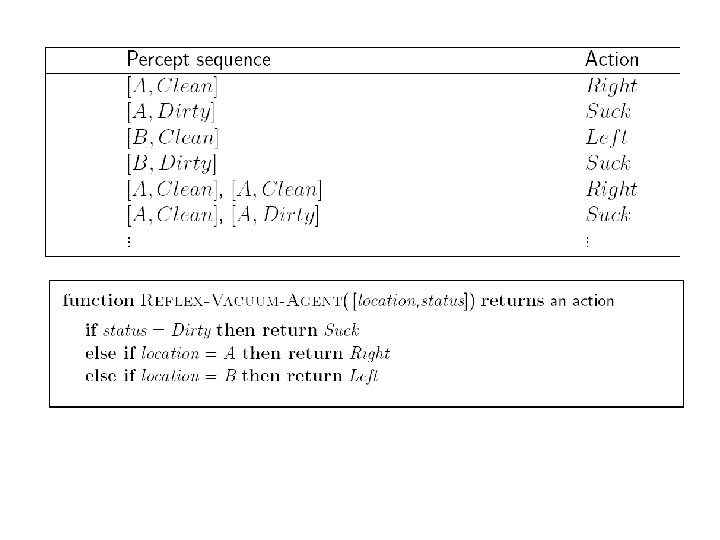
 Problem: A Vacuum-cleaner Agent
Problem: A Vacuum-cleaner Agent
 What is the right function?
What is the right function?
 Let’s talk about Rationality
Let’s talk about Rationality
 A rational agent chooses whichever action maximizes the expected value of the performance measure given the percept sequence to date
A rational agent chooses whichever action maximizes the expected value of the performance measure given the percept sequence to date
 What is performance measure?
What is performance measure?
 1 point per square cleaned up in time T?
1 point per square cleaned up in time T?
 Minus 1 point per move?
Minus 1 point per move?
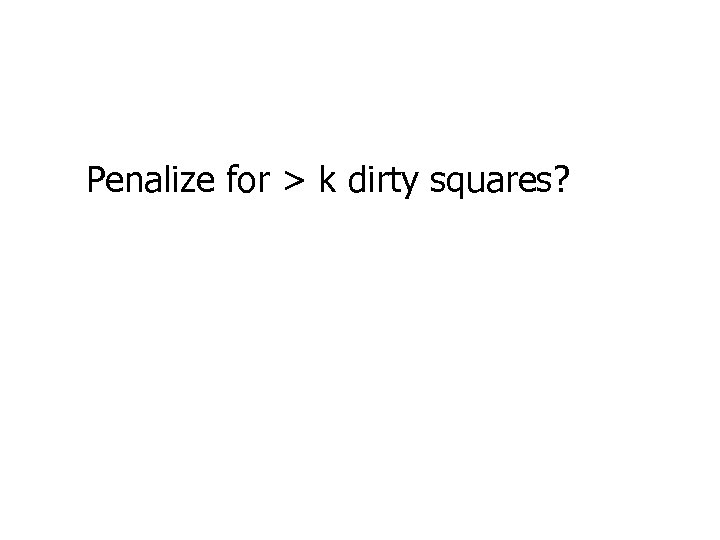 Penalize for > k dirty squares?
Penalize for > k dirty squares?
 Therefore, we can say
Therefore, we can say
 Rational omniscient
Rational omniscient
 Perception may not supply all information
Perception may not supply all information
 Rational clairvoyant
Rational clairvoyant
 Action outcomes may not be as expected
Action outcomes may not be as expected
 Hence, rational perfect
Hence, rational perfect
 To design a rational agent, we must specify the task environment (PEAS)
To design a rational agent, we must specify the task environment (PEAS)
 • Performance measure • Environment • Actuators • Sensors
• Performance measure • Environment • Actuators • Sensors
 Consider the task of designing the Google driverless car
Consider the task of designing the Google driverless car
 • P: safety, comfort, profits, legality • E: streets, freeways, traffic, weather • A: streering, accelerator, break • S: velocity, GPS, engine sensors
• P: safety, comfort, profits, legality • E: streets, freeways, traffic, weather • A: streering, accelerator, break • S: velocity, GPS, engine sensors
 Consider the task of designing an automated internet shopping agent: e. g. , Recommender system
Consider the task of designing an automated internet shopping agent: e. g. , Recommender system
 • P: price, quality, efficiency • E: WWW sites, vendors • A: display to user, follow URL • S: HTML, XML pages
• P: price, quality, efficiency • E: WWW sites, vendors • A: display to user, follow URL • S: HTML, XML pages
 Agent Types: four basic types in order of increasing generality
Agent Types: four basic types in order of increasing generality
 • Simple reflex agents • Reflex agents with state • Goal-based agents • Utility-based agents
• Simple reflex agents • Reflex agents with state • Goal-based agents • Utility-based agents
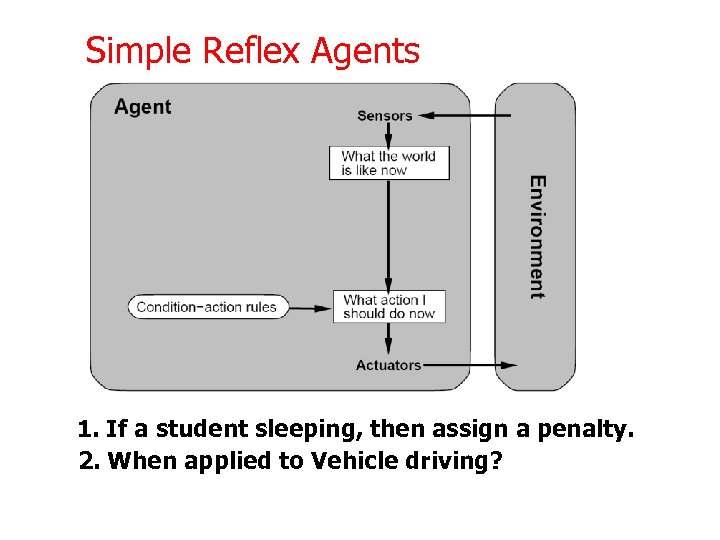 Simple Reflex Agents 1. If a student sleeping, then assign a penalty. 2. When applied to Vehicle driving?
Simple Reflex Agents 1. If a student sleeping, then assign a penalty. 2. When applied to Vehicle driving?
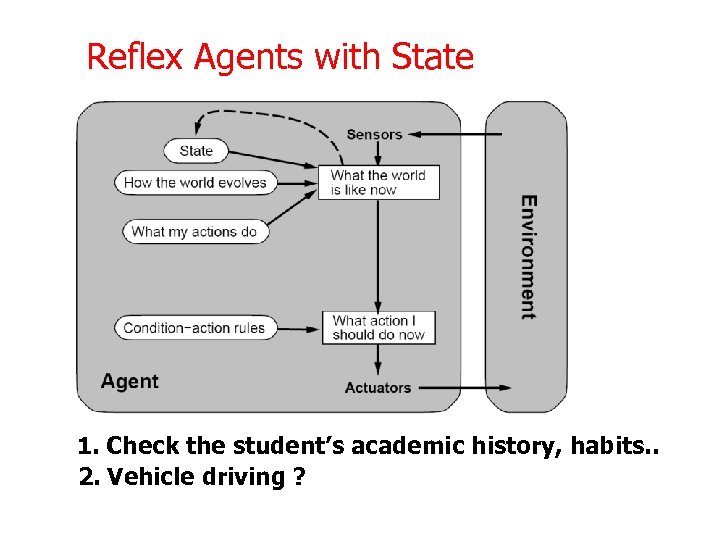 Reflex Agents with State 1. Check the student’s academic history, habits. . 2. Vehicle driving ?
Reflex Agents with State 1. Check the student’s academic history, habits. . 2. Vehicle driving ?
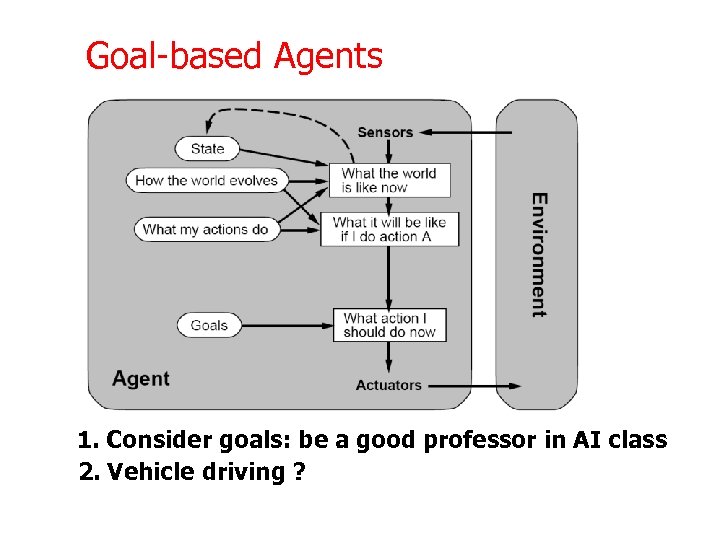 Goal-based Agents 1. Consider goals: be a good professor in AI class 2. Vehicle driving ?
Goal-based Agents 1. Consider goals: be a good professor in AI class 2. Vehicle driving ?
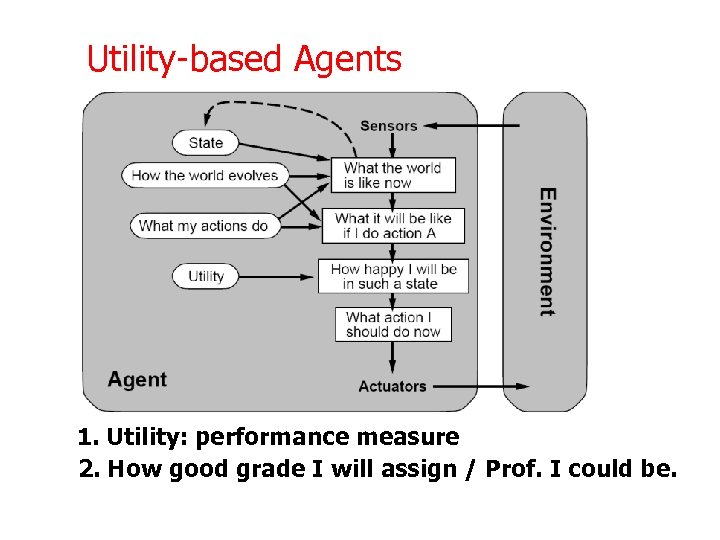 Utility-based Agents 1. Utility: performance measure 2. How good grade I will assign / Prof. I could be.
Utility-based Agents 1. Utility: performance measure 2. How good grade I will assign / Prof. I could be.
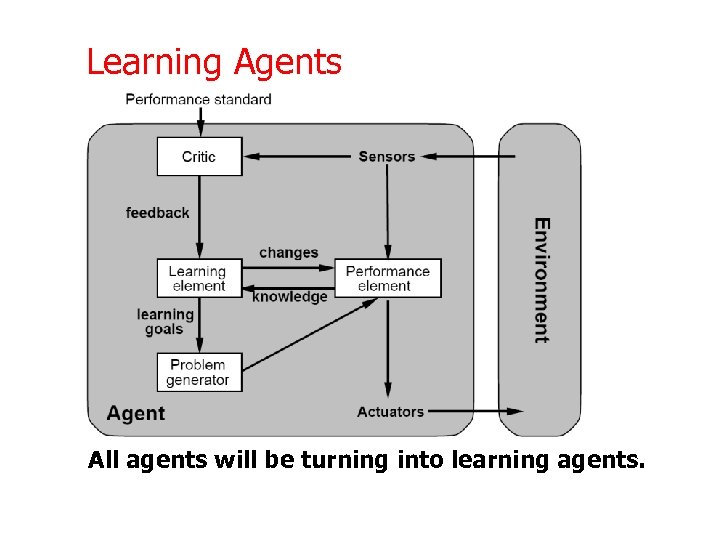 Learning Agents All agents will be turning into learning agents.
Learning Agents All agents will be turning into learning agents.


