Lecture 9 Curriculum.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Lecture 9 Speech materials development
Lecture 9 Speech materials development
 Teaching Listening
Teaching Listening
 Definition: • Listening is a communicative skill with the purpose of receiving, comprehending and interpreting an oral message.
Definition: • Listening is a communicative skill with the purpose of receiving, comprehending and interpreting an oral message.
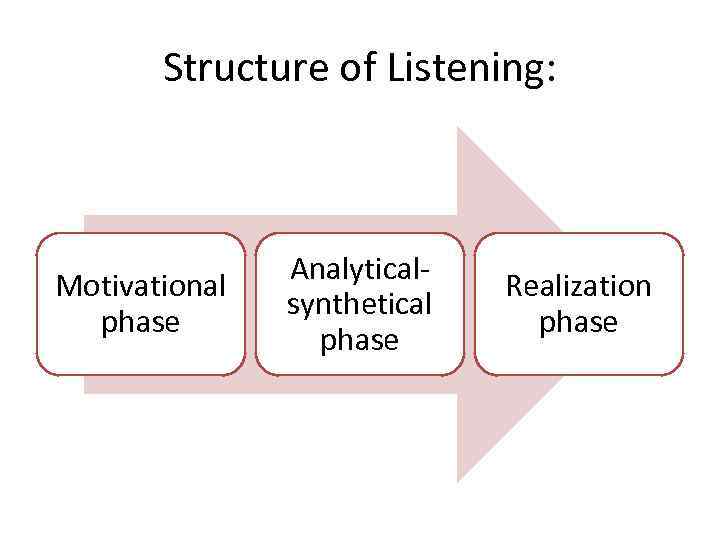 Structure of Listening: Motivational phase Analyticalsynthetical phase Realization phase
Structure of Listening: Motivational phase Analyticalsynthetical phase Realization phase
 Factors of effecting listening: Interest Tempo of presentation Language peculiarities Peculiarities of memory Structure of composition Form of speaking (monologue, dialogue)
Factors of effecting listening: Interest Tempo of presentation Language peculiarities Peculiarities of memory Structure of composition Form of speaking (monologue, dialogue)
 Specific principles Principle 1. Teaching to listen is a communicative skills. It means that the learners are taught the ability to listen in real or close-to-real situations. Principle 2. Teaching to listen is based on authentic materials. It implies that the materials are either “authentic made” or “authentic like” for teaching purposes. Principle 3. Teaching to listen is an integrated skill. It should be taught in integration with other skills. Usually people listen and speak, listen and write listen and read. Listening is connected with speaking, writing and reading.
Specific principles Principle 1. Teaching to listen is a communicative skills. It means that the learners are taught the ability to listen in real or close-to-real situations. Principle 2. Teaching to listen is based on authentic materials. It implies that the materials are either “authentic made” or “authentic like” for teaching purposes. Principle 3. Teaching to listen is an integrated skill. It should be taught in integration with other skills. Usually people listen and speak, listen and write listen and read. Listening is connected with speaking, writing and reading.
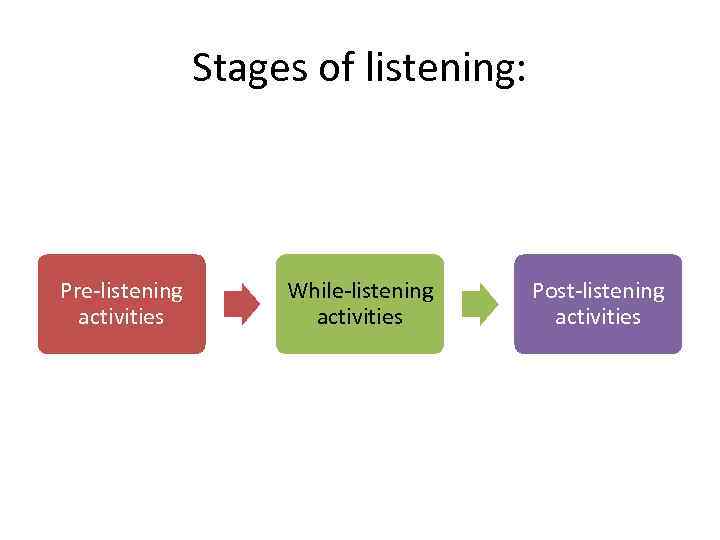 Stages of listening: Pre-listening activities While-listening activities Post-listening activities
Stages of listening: Pre-listening activities While-listening activities Post-listening activities

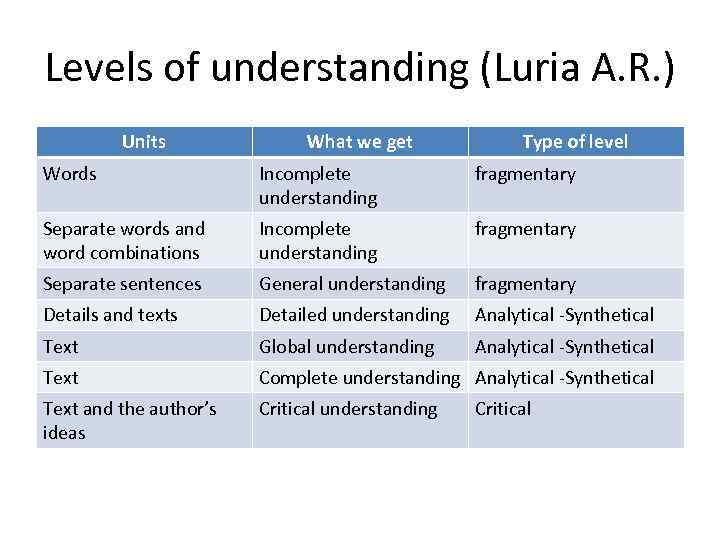 Levels of understanding (Luria A. R. ) Units What we get Type of level Words Incomplete understanding fragmentary Separate words and word combinations Incomplete understanding fragmentary Separate sentences General understanding fragmentary Details and texts Detailed understanding Analytical -Synthetical Text Global understanding Analytical -Synthetical Text Complete understanding Analytical -Synthetical Text and the author’s ideas Critical understanding Critical
Levels of understanding (Luria A. R. ) Units What we get Type of level Words Incomplete understanding fragmentary Separate words and word combinations Incomplete understanding fragmentary Separate sentences General understanding fragmentary Details and texts Detailed understanding Analytical -Synthetical Text Global understanding Analytical -Synthetical Text Complete understanding Analytical -Synthetical Text and the author’s ideas Critical understanding Critical
 Home task: Make a list of personal factors which make effective listening comprehension and give reasons why this might be so.
Home task: Make a list of personal factors which make effective listening comprehension and give reasons why this might be so.
 Teaching reading
Teaching reading
 Teaching Reading • Reading is a visual and cognitive process to extract meaning from writing by understanding the written text, processing information and relating it to existing experience.
Teaching Reading • Reading is a visual and cognitive process to extract meaning from writing by understanding the written text, processing information and relating it to existing experience.
 Aim – to form the technique of reading To master the technique of reading means: To be able to correctly associate letters and sounds To be able to read with correct word and sentence stress To read with correct melody and rhythm To improve reading speed
Aim – to form the technique of reading To master the technique of reading means: To be able to correctly associate letters and sounds To be able to read with correct word and sentence stress To read with correct melody and rhythm To improve reading speed
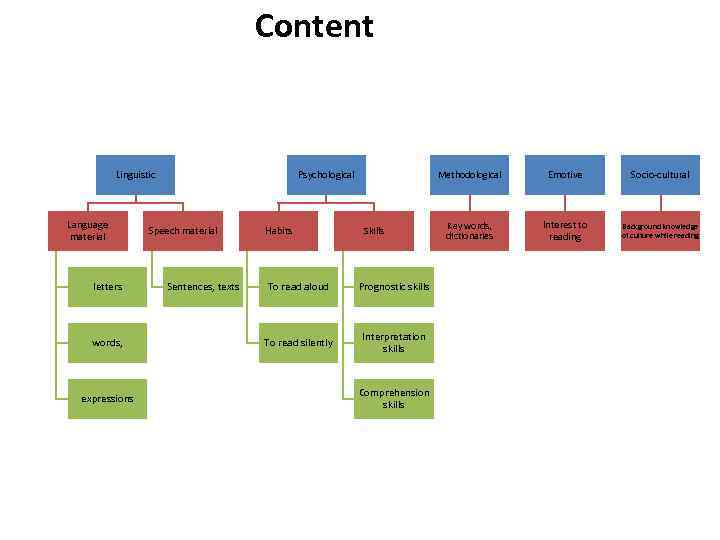 Content Linguistic Language material letters words, expressions Psychological Speech material Sentences, texts Habits Methodological Skills To read aloud Prognostic skills To read silently Interpretation skills Comprehension skills Emotive Socio-cultural Key words, dictionaries Interest to reading Background knowledge of culture while reading
Content Linguistic Language material letters words, expressions Psychological Speech material Sentences, texts Habits Methodological Skills To read aloud Prognostic skills To read silently Interpretation skills Comprehension skills Emotive Socio-cultural Key words, dictionaries Interest to reading Background knowledge of culture while reading
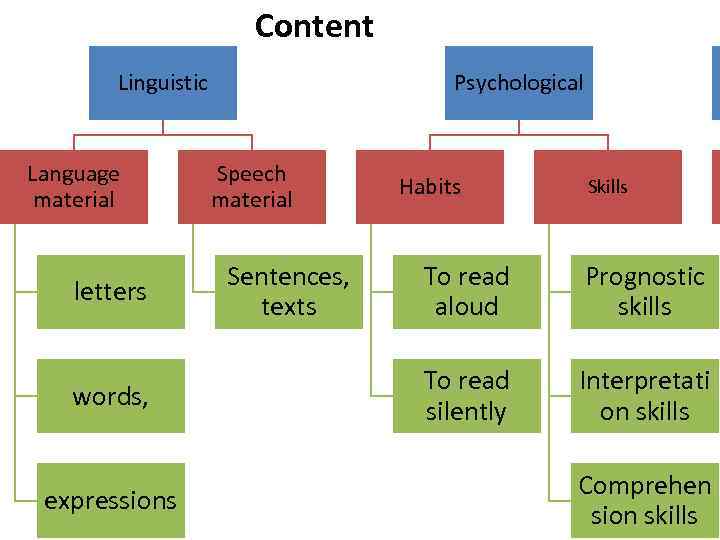 Content Linguistic Language material letters words, expressions Psychological Speech material Sentences, texts Habits Skills To read aloud Prognostic skills To read silently Interpretati on skills Comprehen sion skills
Content Linguistic Language material letters words, expressions Psychological Speech material Sentences, texts Habits Skills To read aloud Prognostic skills To read silently Interpretati on skills Comprehen sion skills
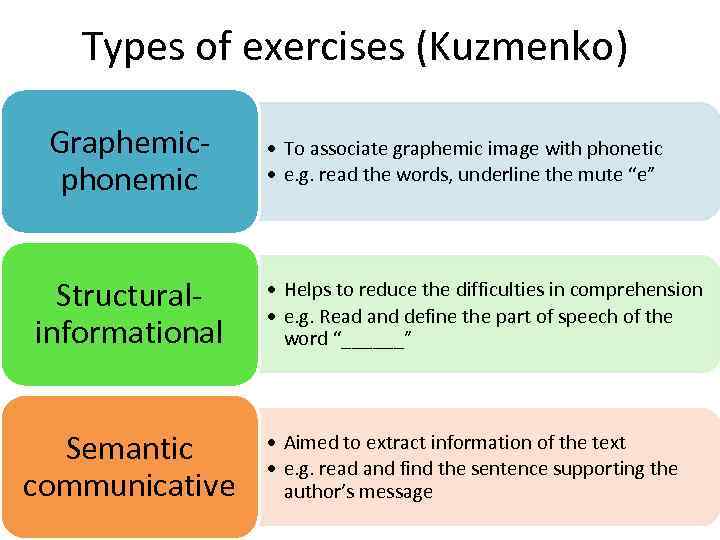 Types of exercises (Kuzmenko) Graphemicphonemic Structuralinformational Semantic communicative • To associate graphemic image with phonetic • e. g. read the words, underline the mute “e” • Helps to reduce the difficulties in comprehension • e. g. Read and define the part of speech of the word “______” • Aimed to extract information of the text • e. g. read and find the sentence supporting the author’s message
Types of exercises (Kuzmenko) Graphemicphonemic Structuralinformational Semantic communicative • To associate graphemic image with phonetic • e. g. read the words, underline the mute “e” • Helps to reduce the difficulties in comprehension • e. g. Read and define the part of speech of the word “______” • Aimed to extract information of the text • e. g. read and find the sentence supporting the author’s message
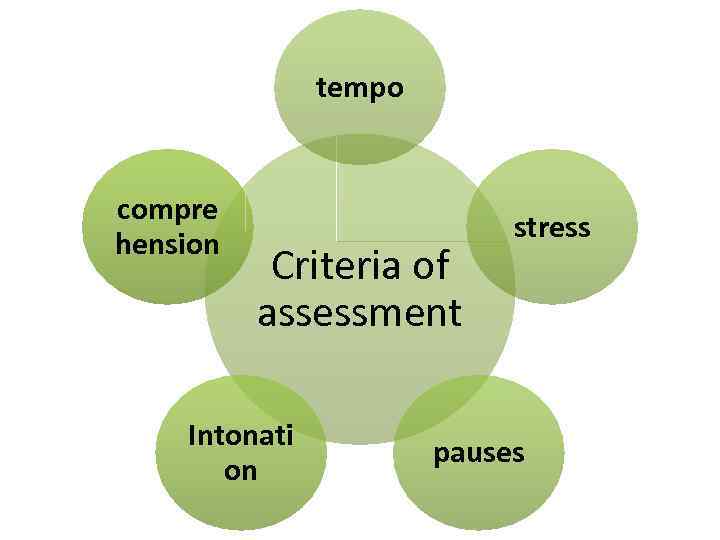 tempo compre hension Criteria of assessment Intonati on stress pauses
tempo compre hension Criteria of assessment Intonati on stress pauses
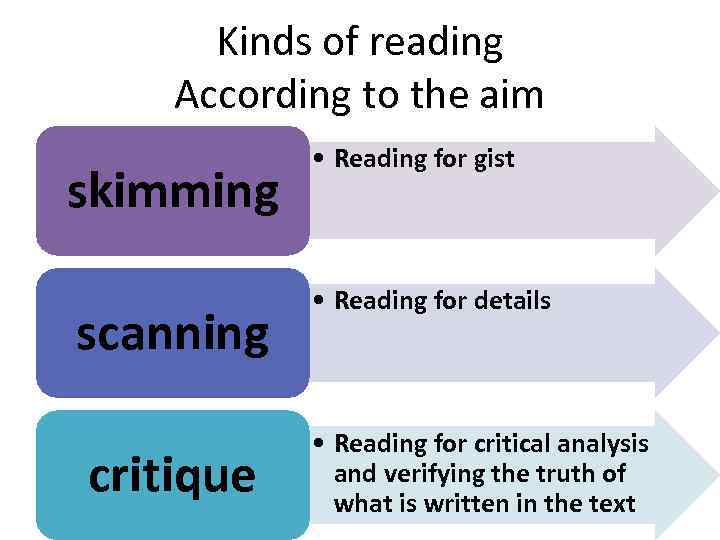 Kinds of reading According to the aim skimming scanning critique • Reading for gist • Reading for details • Reading for critical analysis and verifying the truth of what is written in the text
Kinds of reading According to the aim skimming scanning critique • Reading for gist • Reading for details • Reading for critical analysis and verifying the truth of what is written in the text
 Teaching Speaking
Teaching Speaking
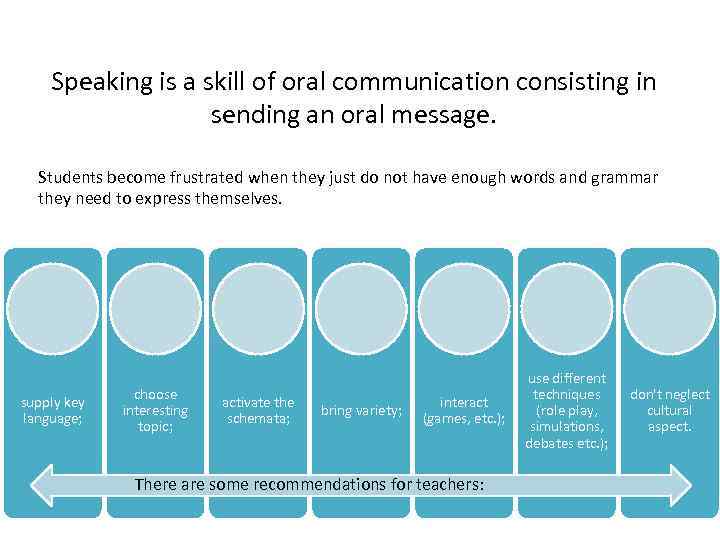 Speaking is a skill of oral communication consisting in sending an oral message. Students become frustrated when they just do not have enough words and grammar they need to express themselves. supply key language; choose interesting topic; activate the schemata; bring variety; interact (games, etc. ); There are some recommendations for teachers: use different techniques (role play, simulations, debates etc. ); don't neglect cultural aspect.
Speaking is a skill of oral communication consisting in sending an oral message. Students become frustrated when they just do not have enough words and grammar they need to express themselves. supply key language; choose interesting topic; activate the schemata; bring variety; interact (games, etc. ); There are some recommendations for teachers: use different techniques (role play, simulations, debates etc. ); don't neglect cultural aspect.
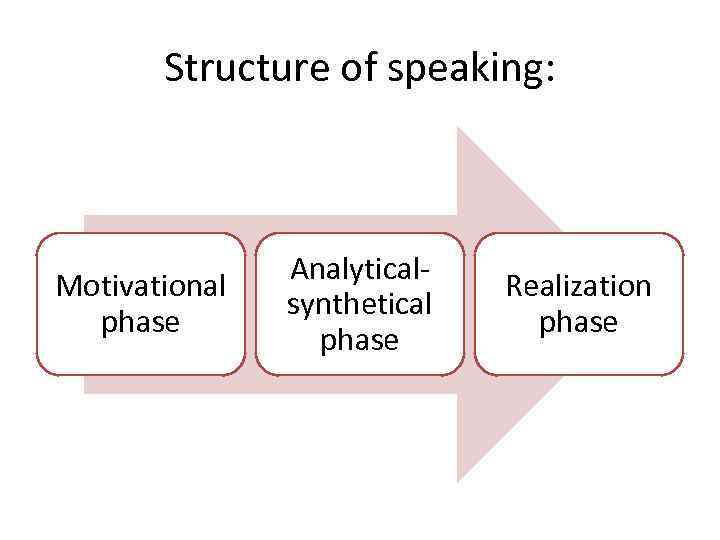 Structure of speaking: Motivational phase Analyticalsynthetical phase Realization phase
Structure of speaking: Motivational phase Analyticalsynthetical phase Realization phase
 Psychological characteristics of speaking: Motivated Addressed to sb Emotionally coloured Situational
Psychological characteristics of speaking: Motivated Addressed to sb Emotionally coloured Situational
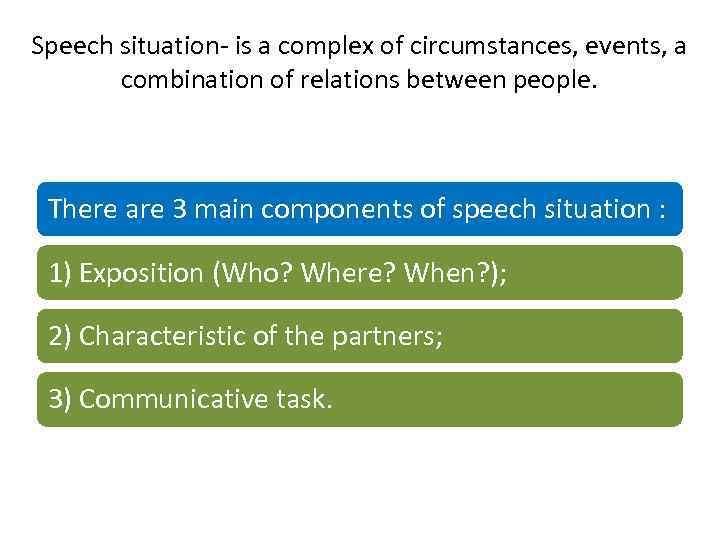 Speech situation- is a complex of circumstances, events, a combination of relations between people. There are 3 main components of speech situation : 1) Exposition (Who? Where? When? ); 2) Characteristic of the partners; 3) Communicative task.
Speech situation- is a complex of circumstances, events, a combination of relations between people. There are 3 main components of speech situation : 1) Exposition (Who? Where? When? ); 2) Characteristic of the partners; 3) Communicative task.
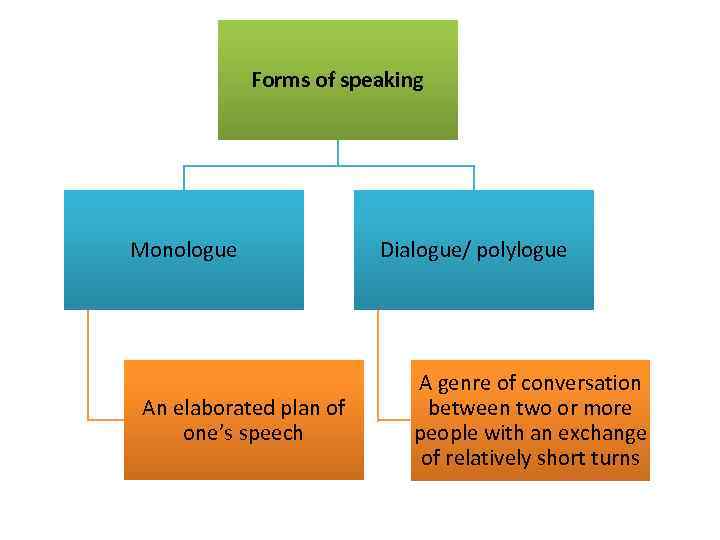 Forms of speaking Monologue An elaborated plan of one’s speech Dialogue/ polylogue A genre of conversation between two or more people with an exchange of relatively short turns
Forms of speaking Monologue An elaborated plan of one’s speech Dialogue/ polylogue A genre of conversation between two or more people with an exchange of relatively short turns
 Types of Monologues Praise Reproach Lecture Description • making positive statements about a person, object or idea • a expression of disapproval or disappointment • a talk or speech given to a group of people to teach them about a particular subject • telling the details to an active listener Narration • telling the development of events to an active listener Reasoning • Telling one’s thoughts to an active listener
Types of Monologues Praise Reproach Lecture Description • making positive statements about a person, object or idea • a expression of disapproval or disappointment • a talk or speech given to a group of people to teach them about a particular subject • telling the details to an active listener Narration • telling the development of events to an active listener Reasoning • Telling one’s thoughts to an active listener
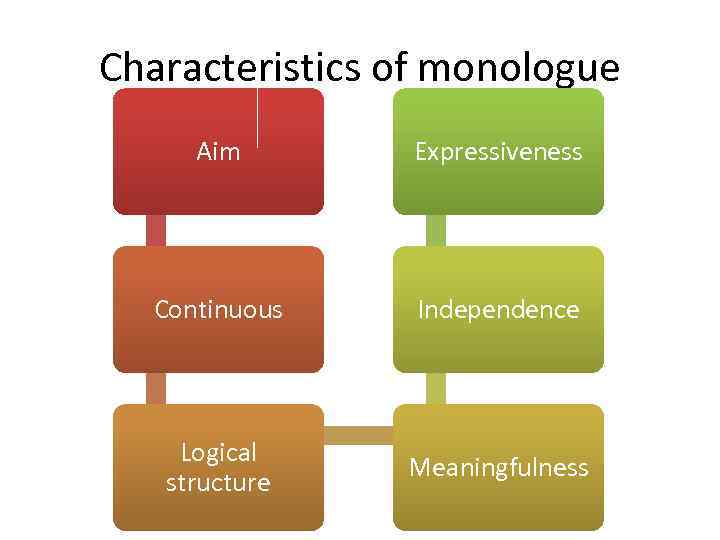 Characteristics of monologue Aim Expressiveness Continuous Independence Logical structure Meaningfulness
Characteristics of monologue Aim Expressiveness Continuous Independence Logical structure Meaningfulness
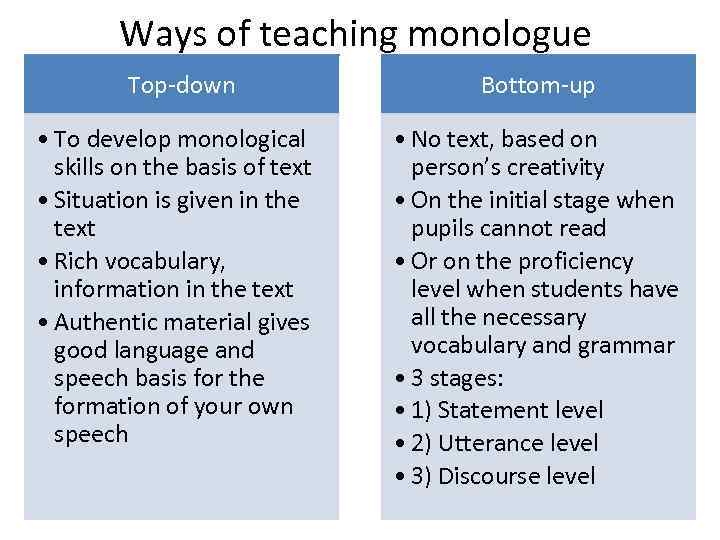 Ways of teaching monologue Top-down Bottom-up • To develop monological skills on the basis of text • Situation is given in the text • Rich vocabulary, information in the text • Authentic material gives good language and speech basis for the formation of your own speech • No text, based on person’s creativity • On the initial stage when pupils cannot read • Or on the proficiency level when students have all the necessary vocabulary and grammar • 3 stages: • 1) Statement level • 2) Utterance level • 3) Discourse level
Ways of teaching monologue Top-down Bottom-up • To develop monological skills on the basis of text • Situation is given in the text • Rich vocabulary, information in the text • Authentic material gives good language and speech basis for the formation of your own speech • No text, based on person’s creativity • On the initial stage when pupils cannot read • Or on the proficiency level when students have all the necessary vocabulary and grammar • 3 stages: • 1) Statement level • 2) Utterance level • 3) Discourse level
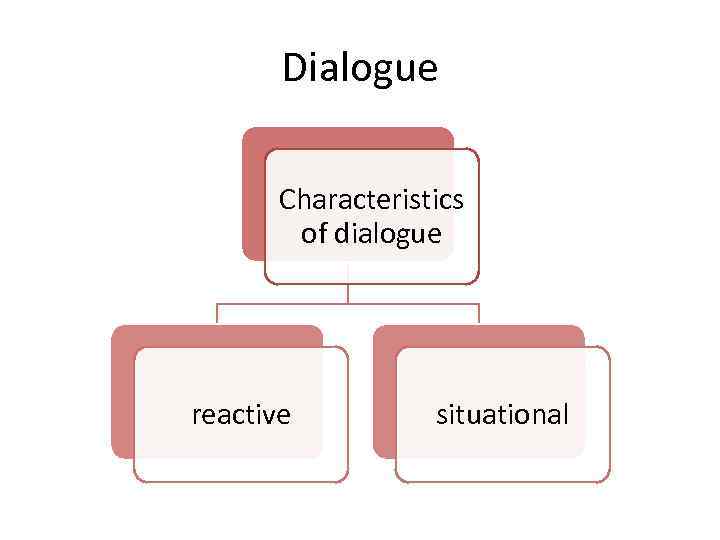 Dialogue Characteristics of dialogue reactive situational
Dialogue Characteristics of dialogue reactive situational
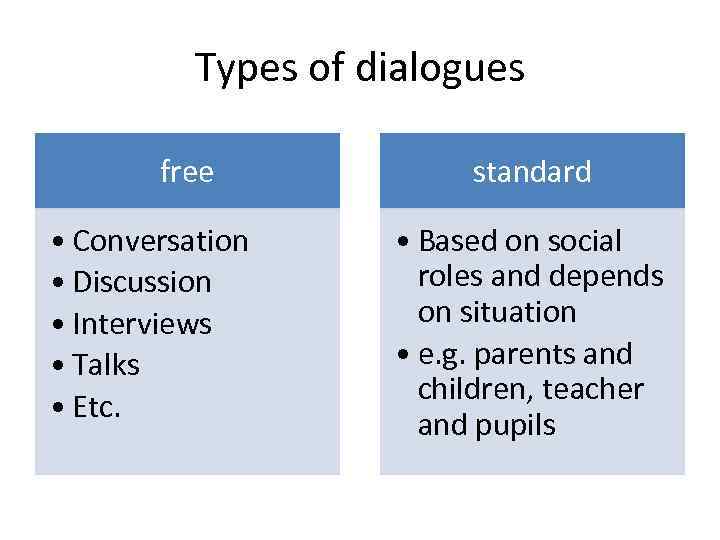 Types of dialogues free • Conversation • Discussion • Interviews • Talks • Etc. standard • Based on social roles and depends on situation • e. g. parents and children, teacher and pupils
Types of dialogues free • Conversation • Discussion • Interviews • Talks • Etc. standard • Based on social roles and depends on situation • e. g. parents and children, teacher and pupils
 Thanks for your attention!
Thanks for your attention!


